Survey Work and Design
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
overall survey design and preliminary planning
questionnaire design and pre-testing
final survey design and planning
sample selection and data collection
data coding, data file construction, analysis, and final report
What are the 5 stages of survey work?
sampling and non-sampling
What are the two types of error in survey work?
sampling error
directly attributable to the fact that not all the population units are observed
extent depends on sample size and variability of the population
sampling error
only asking selected college students re: online learning readiness
non-sampling error
All error sources unrelated to the sampling of the respondents.
non-sampling error
coverage bias, selection bias, nonresponse bias, interviewer error, response error, coding error
sampling error + non-sampling error
What is the formula for the total survey error?
Determine appropriate sample size
define target population
attempt to maximize population coverage
select sample that fairly represents entire population
obtain data from as much of the selected sample as possible
properly train and supervise interviewers
use good questionnaire design
exercise decent control over coding and data entry
How do you minimize errors?
target population
Population from which information is ideally acquired from.
survey population (sampled population)
Population from which a sample is actually taken.
List of elements covering target population
e.g. list of all registered voters in the province
each unit must be counted only once, and must be distinguishable from other units
provides up-to-date information
A sampling frame must posses the following characteristics, these are?
Sampling Unit
Unit which is part of the sampling process.
Observation unit
Object on which the measurement is actually taken (element)
list of HEIs, 25 HEIs in Western Visayas, and deans/chancellors
It is argued by some that the overall quality of graduates in higher education institutions or HEIs (colleges, universities, and the like) in the Philippines, particularly in Western Visayas, is declining. A survey of these HEIs will be undertaken to investigate this claim. A random sample of 25 higher education institutions is taken from the list of all HEIs in the region. Then, the chancellor/deans of each selected university is interviewed.
What is the sampling frame, sampling unit, and observation unit in this situation?
more confidence can be placed in the conclusions drawn
In a sampling plan, the larger sample means that?
less reliability
In a sampling plan, greater diversity means?
True
TRUE or FALSE: In a sampling plan, bias must be avoided when selecting a sample.
False
TRUE or FALSE: In a sampling plan, there must be a selective factor.
True
TRUE or FALSE: In a sampling plan, the researcher must consider the efficiency of the scheme (reliability in relation to unit cost.)
False
TRUE or FALSE: In a sampling plan, mere size assure representativeness in a sample.
Sampling methods
process of selecting a sample
done to estimate and test a claim about an unknown parameter from a well-defined population
no need to conduct a full census to obtain information
less cost
timeliness
accuracy
detailed information
destructive testing
What are the reasons for conducting a sampling method?
Destructive sampling
Carried out to the specimen's failure in order to understand its performance or material behavior under different loads (e.g. light bulbsarried out to the specimen's failure in order to understand its performance or material behavior under different loads (e.g. light bulbs)
procedure should be easily implemented and practical
for statistical analysis, a sample must represent the population and reliability must be measurable
What are the 2 criteria for acceptability of a sampling method?
Probability of selection (P1)
Chance, ranging from 0 to 1, that each unit in the population is included in the sample, usually determined from the elements of the sampling frame, where N - populations size and n - sample size.
Non-probability sampling
Not all the elements in the population have the chance to be included in the sample
Pi not specified
Researcher cannot assert that the sample is representative of the larger population; statistics must be descriptive only
extreme difficulties in locating or identifying subjects
only few are willing to be interviewed
probability sampling is more expensive to implement
What are the useful cases to apply non-probability sampling?
purposive, convenience, quota, snowball
What are the 4 types of non-probability sampling?
Purposive
judgment sampling
sets out to make sample agree with the population with regards to certain characteristics
Purposive
Which type of non-probability sampling is this?
Conducting pilot testing to gather feedback from the market before launching a new product; researcher chooses expert wine tasters to do this.
Convenience
Haphazard/accidental sampling
Choosing units which are at hand or are convenient to interview
Convenience
Which type of non-probability sampling is this?
Standing at a grocery store and asking customers if they are willing to answer questions re: satisfaction
Quota
Sample has the same proportions of individuals as the entire population with respect to known characteristics.
Quota
Which type of non-probability sampling is this?
10% of the population is made up of indigenous peoples → 10% of sample are IPs
Quota
Sample has the same proportions of individuals as the entire population with respect to known characteristics
Snowball
Which type of non-probability sampling is this?
Investigating lifestyle of those engaged in illegal prostitution → asking prostitutes to refer other people
Probability Sampling
Every element of the population is given a known nonzero chance of being selected in the sample
Used if main objective is to make inferences about a population
specifies rules for both sample selection and estimation
simple random sampling (SRS)
stratified random sampling
systematic sampling
cluster sampling
multi-stage samp[ling
What are the 5 types of probability sampling?
simple random sampling
Selecting a sample size of n, giving each unit an equal chance of being included in the sample
Can be one with replacement (SRSWR) or without replacement (SRSWOR)
Selection of units uses some random process,
theory involved is easy to understand
estimation methods are simple and easy
What are the 2 advantages of simple random sampling?
sampling frame is necessary
sample chosen may be widely spread → higher transportation costs
sample chosen may not be truly typical of the population if it is heterogeneous
What are the 3 disadvantages of simple random sampling?
Stratified Sampling
Population is stratified/divided into more or less homogeneous subpopulations (strata) before sampling is performed
SRS is performed in each of the stratum
equally and proportionally
Allocating n among the strata can be done in 2 way, thee are?
equally
This is the formula for stratified sampling in which way?
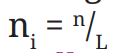
proportionally
This is the formula for stratified sampling in which way?
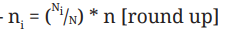
may increase precision of the estimates of the characteristics of the population
more comprehensive data analysis
administratively convenient to implement
What are the 3 advantages in stratified sampling?
listing of the population for each stratum is needed
stratification of the population may require additional prior information about the population and its strata
What are the 2 disadvantages in stratified sampling?
Systematic Sampling
Selection of samples involves taking every kth unit from an ordered population.
First unit (r) is selected at random
1 and k
In systematic sampling, if k is an integer, r is between…
1 and N (circular systematic selection)
In systematic sampling, if k is not an integer, r is between…
drawing sample is administratively easy to implement
possible to select a sample from the field without a frame
What are the 2 advantages in stratified sampling?
If periodic irregularities are found in the list, a systematic sample may consist of similar unit,
What is one disadvantage of systematic sampling?
clusters
Mutually exclusive subpopulations which together comprise the entire population
Cluster Sampling
Involves selecting a sample of distinct groups • sample clusters may be chosen by SRS or systematic sampling
Difference: clusters are preferably formed with heterogeneous units.
Cluster Sampling
What type of probability sampling is this?
From a hospital's 12 departments, six were randomly selected; every intern in these six sampled departments was given a questionnaire (+followed-up) until all of them successfully completed the questionnaires.
No need for the population list of elements
Administratively convenient to implement
What are the 2 advantages of cluster sampling?
Difficulty of estimation procedures
What is one disadvantage of cluster sampling?
Multi—stage sampling
Selection of sample is accomplished in two or more steps
1. population is divided into a number of primary/first-stage units from which a sample is drawn
2. within the sampled first-stage units. a sample of secondary/second-stage units is drawn
3. further stages may be added if desired
Multi-stage sampling
What type of probability sampling is this?
From the 12 departments in the hospital, 4 were randomly selected; from each sampled departments, 10 interns were given questionnaire
Simple two-stage sampling
Units are grouped into N primary sampling units (PSUs) and a simple random sample of n PSUs are selected
Each of the n PSUs selected with Mi elements, a simple random sample of mi units called secondary sampling units (SSUs) will be obtained.
reduced listing and transportation costs
What is one advantage of multi-stage sampling?
difficulty of estimation procedures
sampling procedure entails more planning before actual selection is done
What are the two disadvantages of multi-stage sampling?
True
TRUE or FALSE: A stratified sample yields more reliable results than a SRS of same size.
False
TRUE or FALSE: Cluster sampling may be expected to yield a more reliable result over a SRS of the same size
True
TRUE or FALSE: A small random or stratified sample is much superior to a larger but badly selected sample