Chapter 14 - Genomes
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Term genome was coined in 1920, to refer to
a complete set of chromosomes and its genes
- Now it refers to all the DNA in a haploid set of chromosomes
Term genomics was coined in 1986, to indicate
the study of genomes
Positional Cloning
- Gene-by-gene approach that matches single genes to specific diseases
- Begins with a phenotype, and gradually identifies a causative gene, localizing it to a part of a chromosome
- Yielded discoveries of genes that cause diseases as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington disease.
Linkage Studies
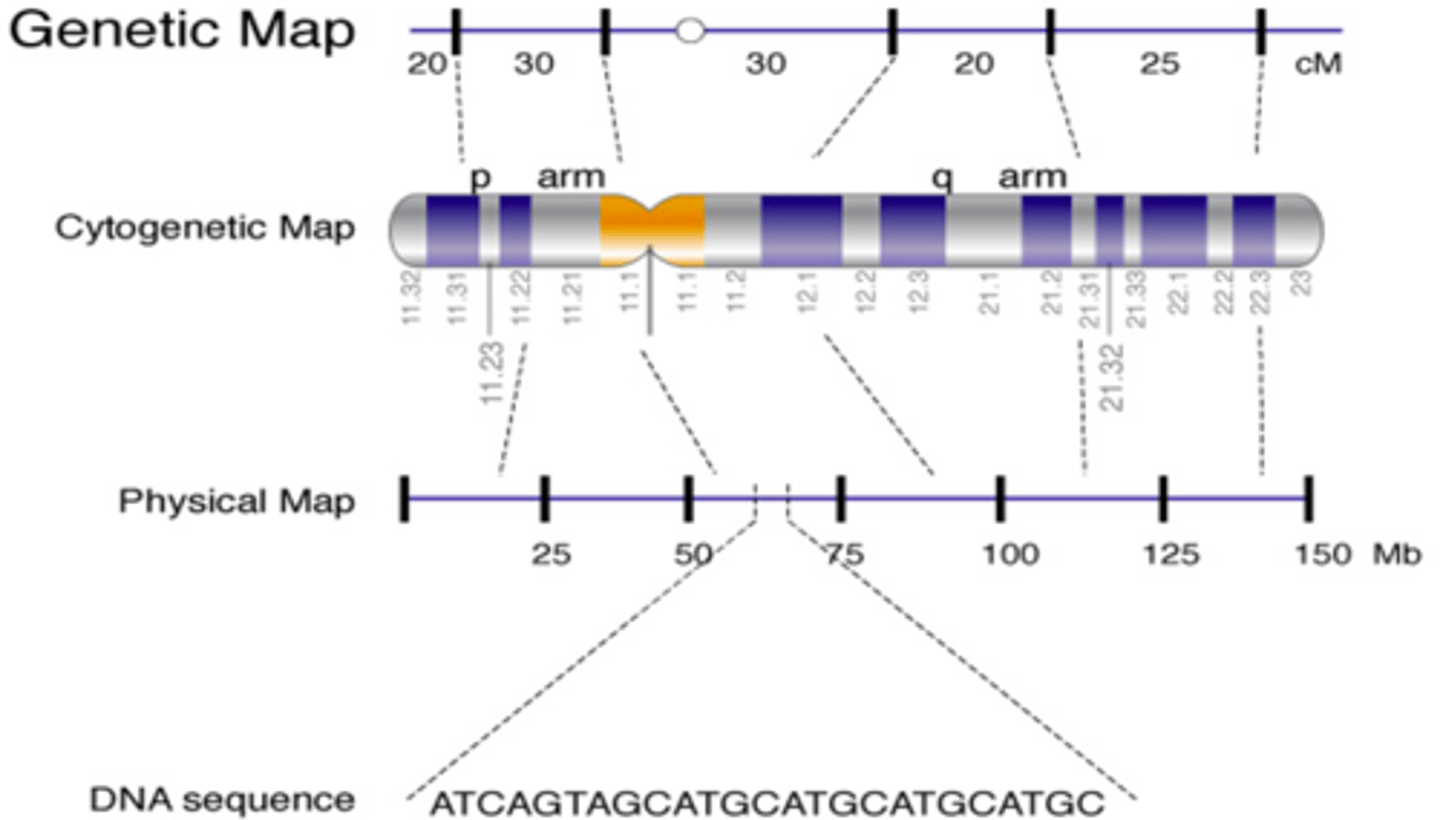
Genetic maps have increases in detail and resolution
- Cytogenetic map
- linkage map
- physical map
- sequence map
- PIC IN NOTES
Cytogenetic Map
Distinguishes DNA sequences that are at least 5K kilobases apart
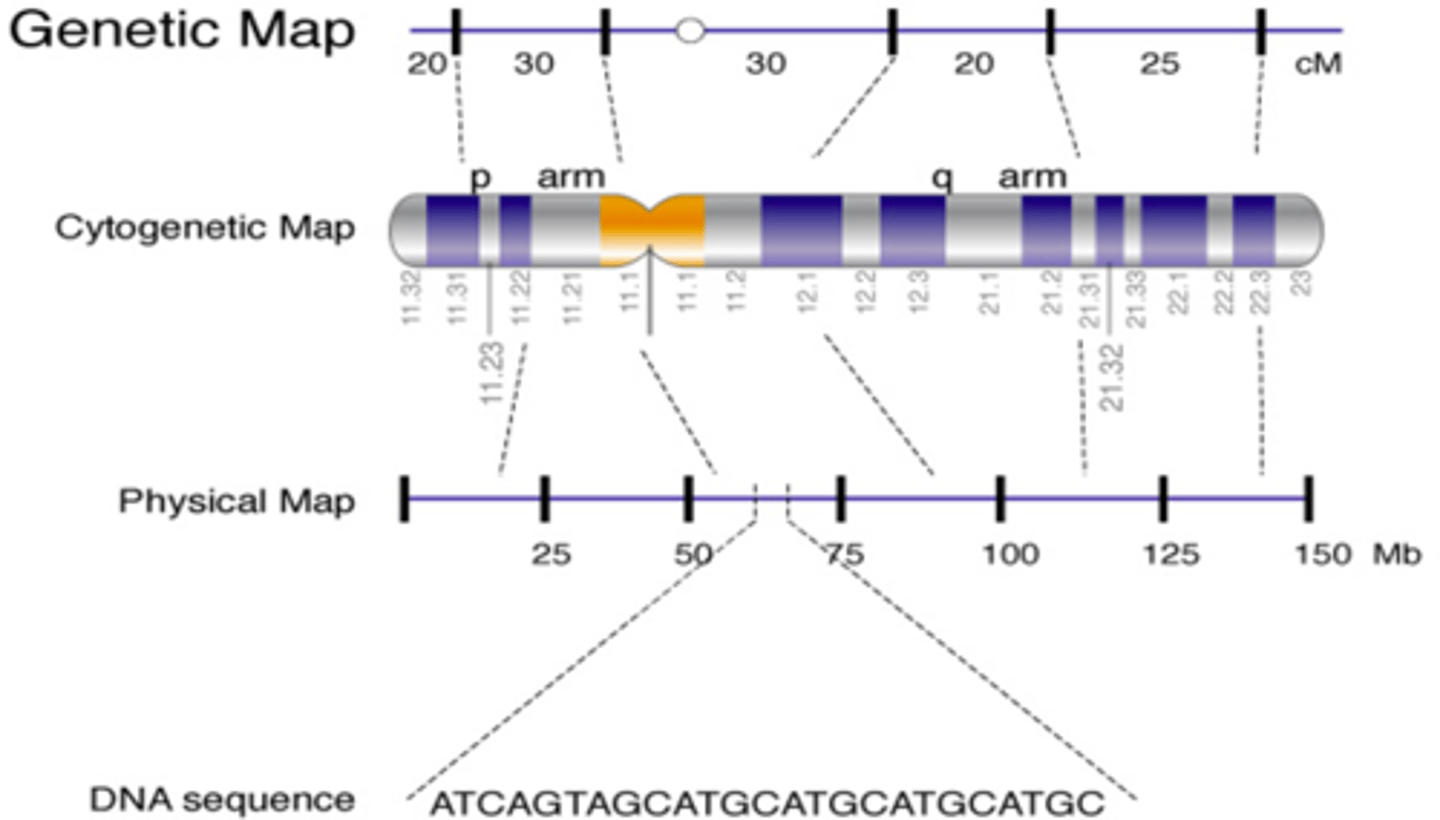
Linkage Map
genes hundreds of kilobases apart
Physical Map
genes tens of kilobases apart
Sequence Map
Depicts the order of bases
The Human Genome Project
- Idea to sequence the human genome emerged in the 198-s with several goals (Exposure to radiation & origin of cancer)
- Officially started in 1990
o $3 billion, 15-year project
- Draft of the human genome in 2001
- Finished sequence in 2003
- Represents the work of thousands of researchers in an international collaboration.
Key Inventions
- Expressed Sequence Tag (EST) technology
- DNA microarrays
Expressed Sequence Tag (EST) technology
- Enables researchers to find protein-encoding genes
- cDNAs (complementary DNA) that are expressed in a particular cell type
DNA microarrays
- Display short DNA molecules
- Important in sequencing and assessing gene expression
Sequencing the Human Genome (Steps)
- 1) Researchers cut several genomes-worth of DNA into overlapping pieces of about 40 kilobases
- 2) Cutting into small fragments and sequencing
- 3) Computer algorithms were used to search for overlaps
- 4) By overlapping the pieces, the software derives the overall DNA sequence.
Sequencing the Human Genome: Route-1
- The U.S. government-funded international consortium used a clone-by-clone approach
o Approach pieces one chromosome at a time
o 1) STS "sequence tagged site: known parts of chromosomes
o 2) Overlapped large pieces, called contigs
o 3) BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) a cloning vector
- PIC IN NOTES!
Sequencing the Human Genome: Route-2
- Whole genome shotgun approach
- PIC IN NOTES
Sequencing Genomes
1) Short-gunned DNA sequencing
2) Assembly by overlapping
3) Annotate function by other species
4) DNA microarrays display genome pieces
The following fragments of DNA correspond to a section of the genome.
ACTGT, GTGTT, GACTC, TTCAAC, ACTGA, TGAC
- What is the derived sequence?
ACTGTGTTCAACTGACTC
Types of Information in Human Genome - from genetic pioneers J. Craig Venter and James Watson
The first two human genomes sequenced were from these two scientists
- Copy number variants (CNV) contribute to genetic variation
Types of Information in Human Genome - The third person to have genome sequenced was called, simply, "YH"
He is Han Chinese, an East Asian population that accounts for 30% of modern humanity
Each of the three men has about ...
- 1.2 million SNPs, but a unique collection. (SNP = >1% of population)
o About 0.07% of our SNPs may affect our phenotypes
Limitations of Genome Sequencing
- Genome sequencing does not provide a complete picture of health.
- Technically, it will not detect
o Copy number variants
o Mitochondrial DNA
o Uniparental disomy
o Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions
- In a conceptual sense, genome information must be interpreted to be useful.
Practical Medical Matters
- Genetic and genomic testing as part of health care must meet certain practical criteria (clinical utility)
- A DNA test result alone is not sufficient to diagnose a disease, but may support a clinical diagnosis based on symptoms and other tests
Incomplete penetrance
Genotype does not always foretell phenotype, e.g. Polydactyly
Variable expressivity
different severities in different individuals, e.g. Polydactyly
Epistasis
gene-gene interactions, e.g. H gene
Genetic Heterogeneity
mutation in more than one gene causing a phenotype, e.g. Marfan
Environmental influences
epigenetics
A genomic view expands knowledge
Exome sequencing
Genomic sequencing
Whole genome sequencing
Genome-wide association studies
Exome sequencing
the exons (The protein-encoding parts)
Genomic sequencing
more information than an exome
Whole genome sequencing
to entire genomes derived from many overlapped copies
Genome-wide association studies
SNPs
- Icelandic genomes- human genetic diversity
o Sites of 4.5 million crossover events that recombined parental chromosomes
o More than 200,000 de novo mutations
- Crossing over and de novo mutations are not as random as had been thought
o At least 35 genes affect crossover frequency and location.
Crossing over and de novo mutations are connected
- New point mutations are more likely to arise within 1 kb of sites of crossing over in males and females
- Another mutational "hot spot" is 40 kb away from the crossover, but only in the genomes of females.
- PIC IN NOTES