PathFit 2: Physical Fitness Testing and Exercise Overview
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Body Mass Index (BMI)
A measure of body fat based on weight in relation to height, calculated using the formula: BMI = Weight (Kg) / [Height (m)]^2.
![<p>A measure of body fat based on weight in relation to height, calculated using the formula: BMI = Weight (Kg) / [Height (m)]^2.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0e2a279f-9345-48bc-9b86-23cbf3e3930f.jpg)
Waist-Hip Ratio (WHR)
A measurement that compares the circumference of the waist to that of the hips, calculated using the formula: WHR = Midpoint / Hips.

Flexibility
The ability to move joints through their full range of motion, often measured by the Sit and Reach test.
Sit and Reach Test
A flexibility test where the subject sits with legs straight and reaches forward to measure how far they can reach.
High Performance (Flexibility)
For males: 7 inches and above; for females: 8 inches and above.
Good Fitness (Flexibility)
For males: 3 to 6 inches; for females: 5 to 7 inches.
Marginal Fitness (Flexibility)
For males: 0 to 2 inches; for females: 0 to 4 inches.
Low Fitness (Flexibility)
For both males and females: -1 inches and below.
Muscular Strength
The maximum amount of force that a muscle or group of muscles can exert.
Push-Up Test
A test of muscular strength where the subject performs as many push-ups as possible.

High Performance (Push-Ups)
For males: 36 reps and above; for females: 16 reps and above.
Good Fitness (Push-Ups)
For males: 26-35 reps; for females: 10-15 reps.
Marginal Fitness (Push-Ups)
For males: 16-25 reps; for females: 6-10 reps.
Low Fitness (Push-Ups)
For males: 15 reps and below; for females: 5 reps and below.
Squats
A test of muscular strength where the subject performs squats until they can no longer continue.
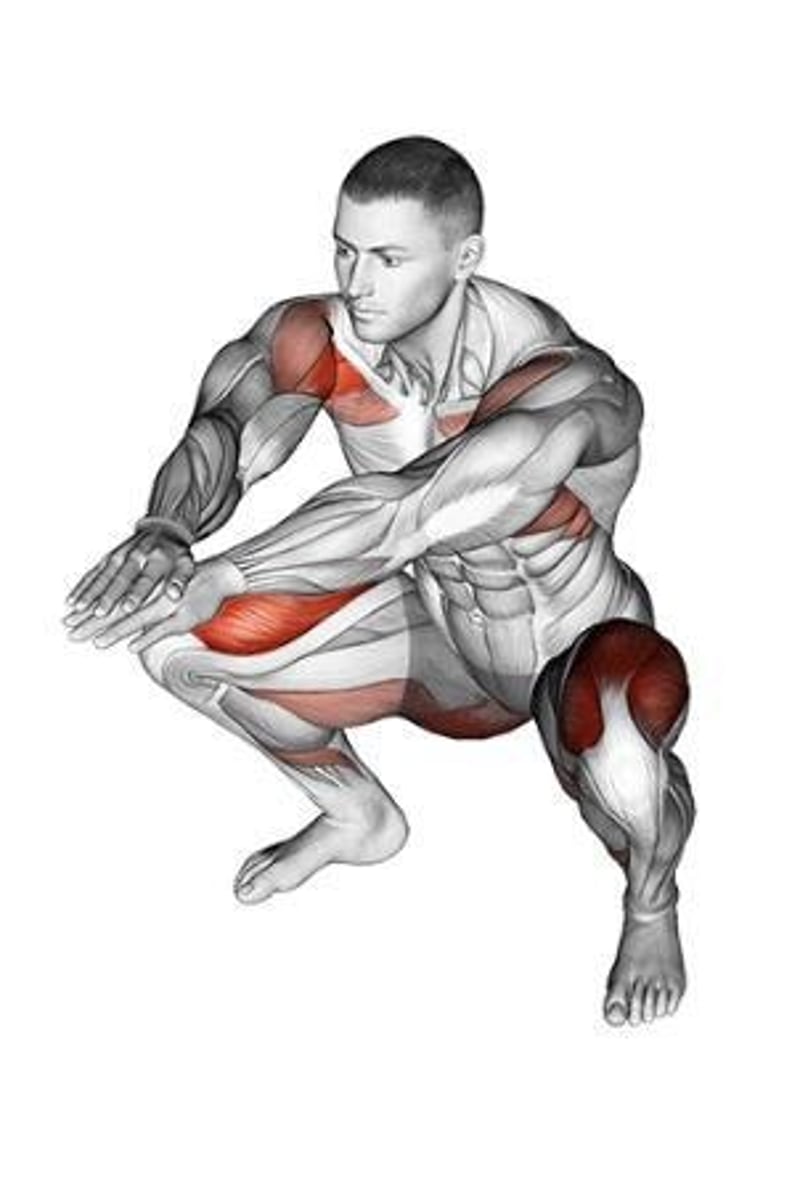
High Performance (Squats)
For males: 36 reps and above; for females: 26 reps and above.
Good Fitness (Squats)
For males: 26-35 reps; for females: 21-25 reps.
Marginal Fitness (Squats)
For males: 21-25 reps; for females: 16-20 reps.
Low Fitness (Squats)
For males: 20 reps and below; for females: 15 reps and below.
Muscular Endurance
The ability of a muscle to sustain repeated contractions against resistance for an extended period.
Forearm Plank Test
A test of muscular endurance where the subject holds a plank position for as long as possible.
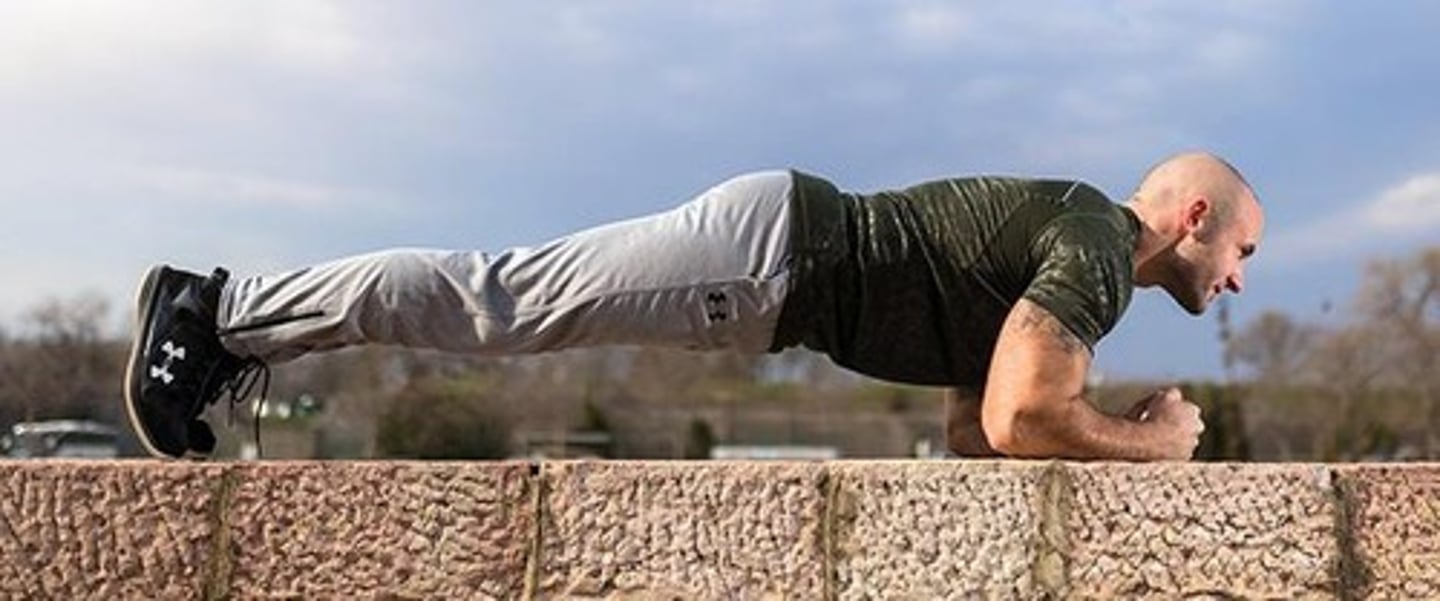

High Performance (Forearm Plank)
For males: 2:00 minutes and above; for females: 1:46 minutes and above.
Good Fitness (Forearm Plank)
For males: 1:00-1:59 minutes; for females: 1:00-1:35 minutes.
Marginal Fitness (Forearm Plank)
For males: 31-59 seconds; for females: 16-59 seconds.
Low Fitness (Forearm Plank)
For males: 30 seconds and below; for females: 15 seconds and below.
Cardio Respiratory Endurance
The ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen to the muscles during sustained physical activity.
3 Minutes Step-Up Test
A test of cardio respiratory endurance where the subject steps up and down on a platform for 3 minutes.

High Performance (Step-Up Test)
For males: 80 bpm and below; for females: 90 bpm and below.
Good Fitness (Step-Up Test)
For males: 81-90 bpm; for females: 91-100 bpm.
Marginal Fitness (Step-Up Test)
For males: 91-110 bpm; for females: 101-120 bpm.
Low Fitness (Step-Up Test)
For males: 111 bpm and above; for females: 121 bpm and above.
Take-off Line
The line behind which a performer must stand before starting a jump.
Crouch Position
A position assumed by the performer at the signal 'Ready', with tips of shoes behind the take-off line.
Un-crouch Position
Position with buttocks up and both hands on the starting line at the signal 'Get Set'.
Stopwatch
A device used by the partner to time the performer from the signal 'GO' until they cross the finish line.
Record Time
The time recorded in the nearest 0.00.01 seconds after the performer crosses the finish line.
Scoring
The method of recording time in nearest seconds.
Excellent Classification (Male)
3 seconds and below.
Excellent Classification (Female)
4.4 seconds and below.
Above Average Classification (Male)
4.2-4.0 seconds.
Above Average Classification (Female)
4.6-4.5 seconds.
Average Classification (Male)
4.4-4.3 seconds.
Average Classification (Female)
4.8-4.7 seconds.
Below Average Classification (Male)
4.6-4.5 seconds.
Below Average Classification (Female)
5-4.9 seconds.
Poor Classification (Male)
4.7 seconds and above.
Poor Classification (Female)
6 seconds and above.
Hexagon Agility Test
A test where the performer jumps clockwise and counterclockwise inside a hexagon.
Average Time Calculation
Add the time of two revolutions and divide by 2 to get the average.
Standing Long Jump
A test where the performer jumps as far as possible from a standing position.
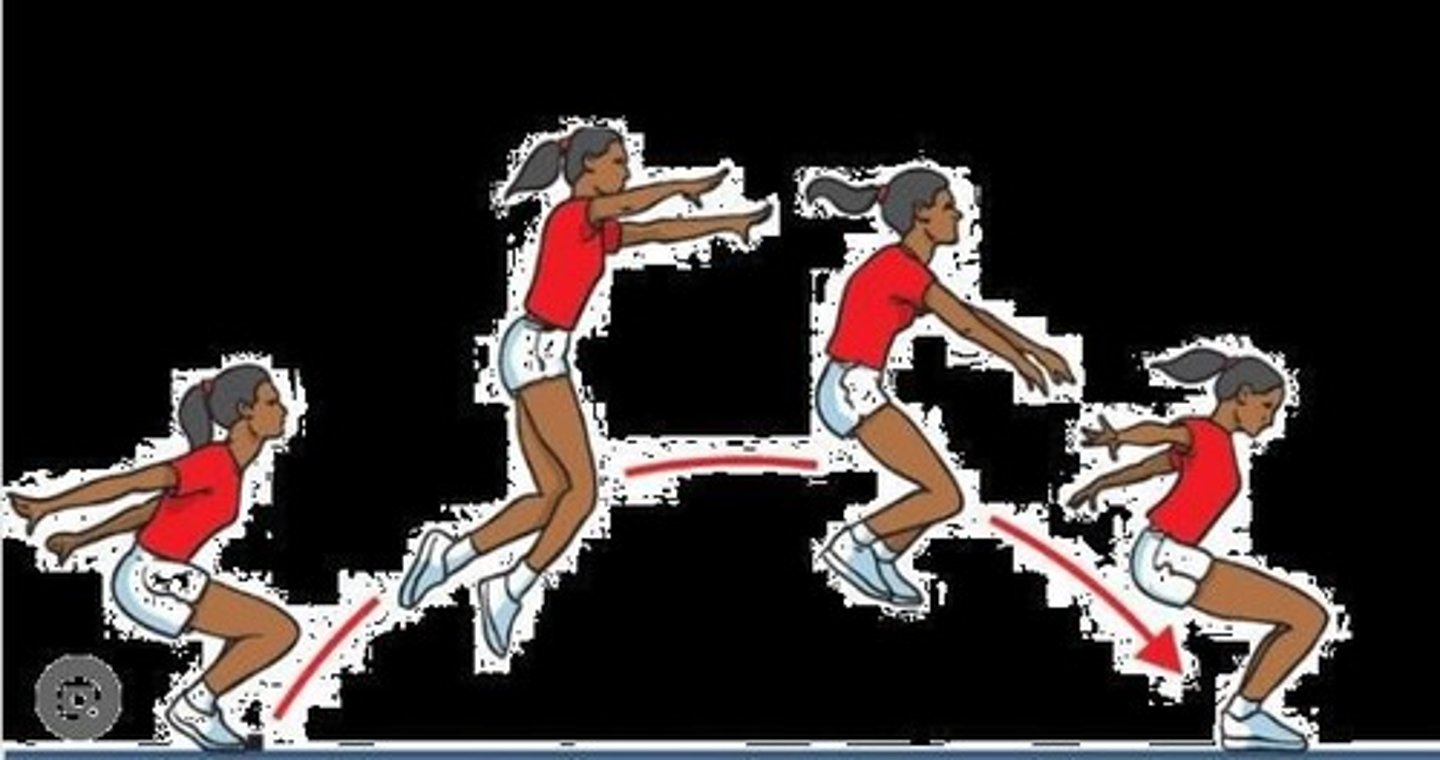

Best Distance Recording
The distance recorded in meters to the nearest 0.1 centimeters after a jump.
Stick Drop Test
A test measuring reaction time by catching a ruler or stick dropped by a partner.
Middle Score Calculation
The middle of three scores recorded in the Stick Drop Test.
Excellent Classification (Reaction Time)
0-5 cm.
Very Good Classification (Reaction Time)
6-11 cm.
Good Classification (Reaction Time)
12-18 cm.
Fair Classification (Reaction Time)
19-25 cm.
Needs Improvement Classification (Reaction Time)
26-30 cm.
Poor Classification (Reaction Time)
Did not catch.
Centimeters
Measurement used to classify performance levels.
Excellent
0-5cm classification for performance.
Very Good
6-11cm classification for performance.
Good
12-18cm classification for performance.
Fair
19-25cm classification for performance.
Needs Improvement
26-30cm classification for performance.
Poor
Did not catch classification for performance.
Hand Wall Toss Test
A test to assess coordination through catching a ball thrown against a wall.
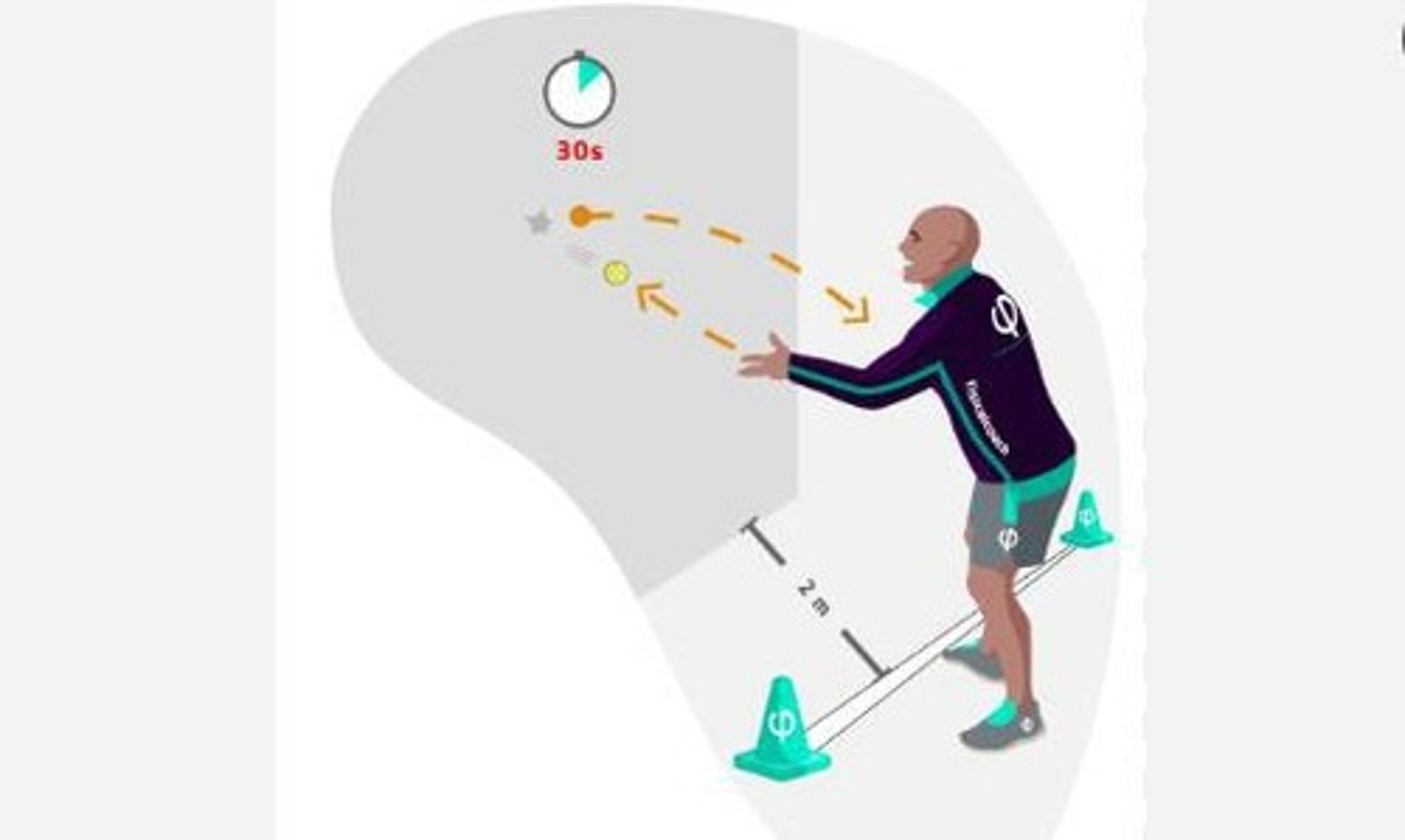
Successful Catches
Number of successful catches made in the Hand Wall Toss Test.
Excellent (Successful Catches)
36 and above successful catches.
Good (Successful Catches)
30-35 successful catches.
Average (Successful Catches)
20-29 successful catches.
Fair (Successful Catches)
15-19 successful catches.
Poor (Successful Catches)
Below 15 successful catches.
Stork Balance Test
A test to assess balance by standing on one foot.
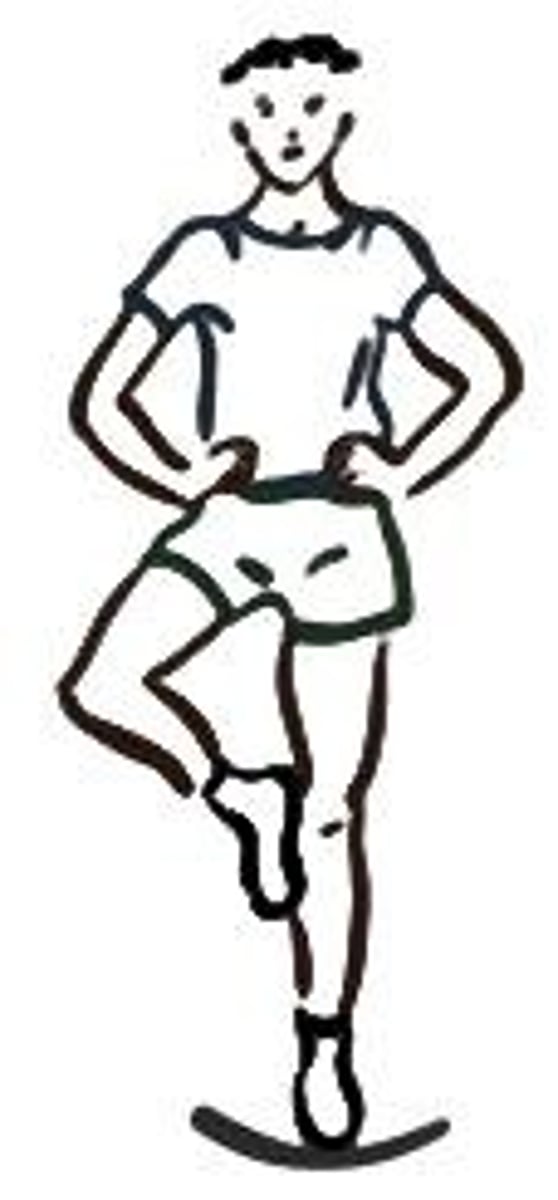

Mechanics of Stork Balance Test
Procedure for performing the Stork Balance Test.
Scoring of Stork Balance Test
Record the time taken on both feet in nearest seconds and divide by two for average percentage score.
Excellent (Stork Balance)
3:01 seconds and above.
Very Good (Stork Balance)
2:41 - 3:00 minutes.
Good (Stork Balance)
1:21 - 2:40 seconds.
Fair (Stork Balance)
41 seconds - 1:20 seconds.
Needs Improvement (Stork Balance)
1-40 seconds.
Somatotype
A system of classifying an individual according to body shape.
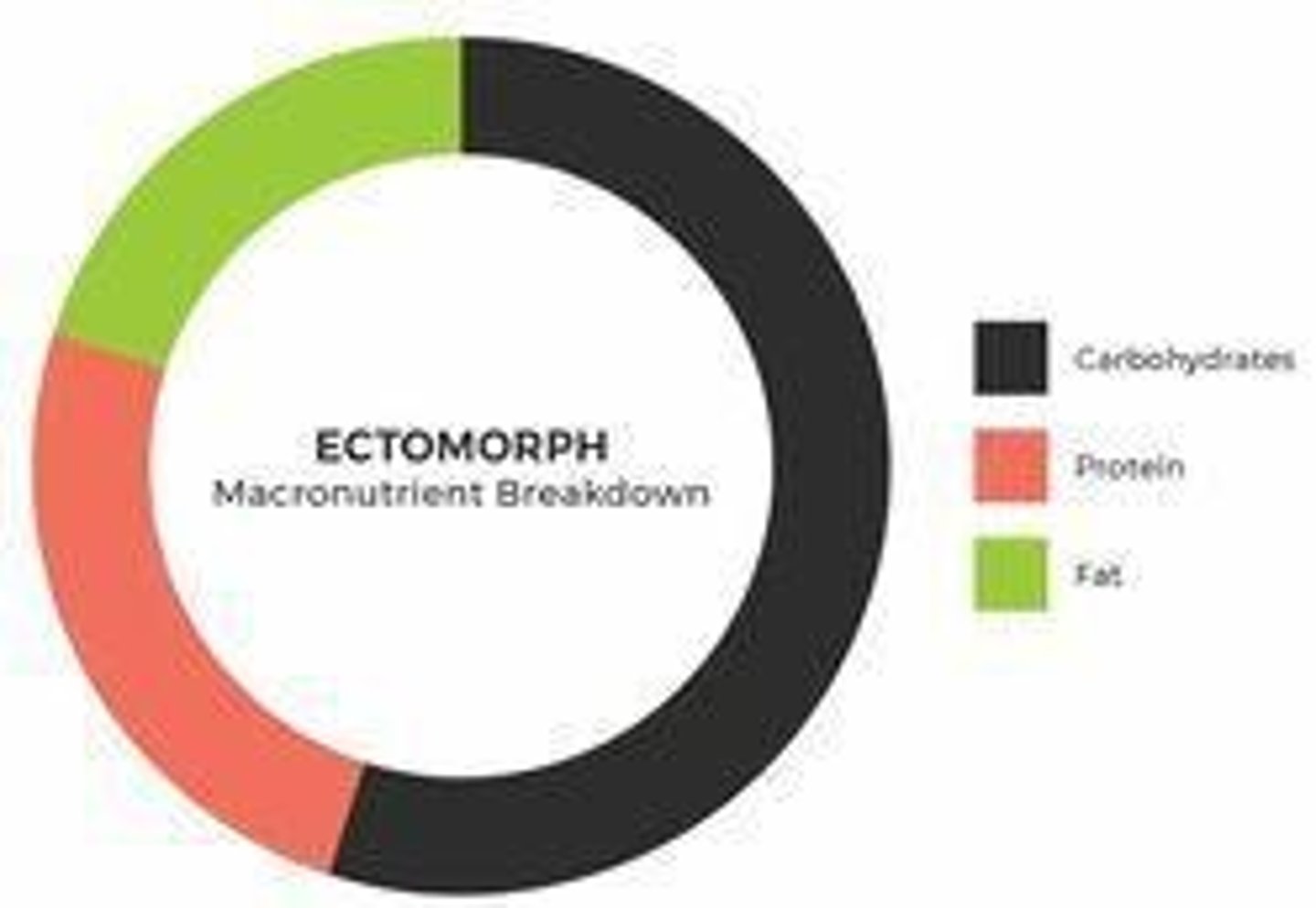
Ectomorph
Body type characterized as lean and small with low muscle mass.
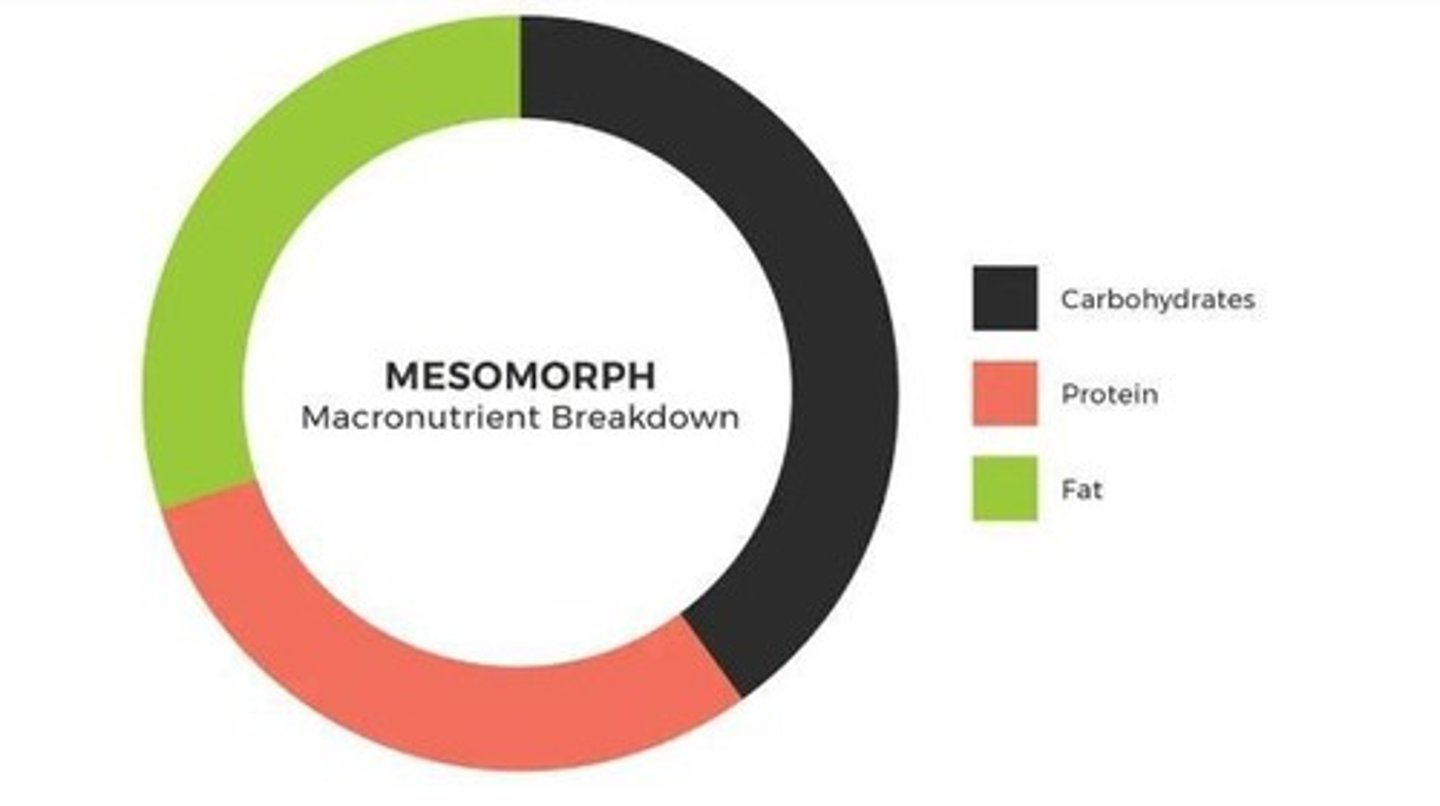
Mesomorph
Body type with a predominance of muscles and larger bone structure.
Endomorph
Body type characterized by roundness and a higher percentage of body fat.
Nutrition
The need to consume more than 40 different nutrients for good health.
Nutrition
Refers to the food intake, which is the key to any level of physical conditioning.
Nutrient
The substance in food that provides structural or functional components or energy to the body.
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts, including carbohydrates, fats, and protein.
Carbohydrates
A type of macronutrient that provides energy to the body.
Fats
A type of macronutrient that provides energy and supports cell growth.
Protein
A type of macronutrient essential for body growth, repair, and maintenance.
Micronutrients
Nutrients required in smaller amounts, including vitamins and minerals.
Vitamins
Organic compounds that are essential for normal growth and nutrition.
Minerals
Inorganic elements that are essential for various bodily functions.
Essential nutrient
The substance that must be obtained from the diet because the body cannot make it in sufficient quantity.
Go Foods
Foods that assist the body in functioning efficiently and actively, primarily focusing on carbohydrates, sugar, and fats.
Carbohydrate requirement for adults
Adults require 255 to 325 grams of carbs per day.
Grow Foods
Protein-rich diets that aid in the body's growth, strength, and health.
Protein functions
Proteins serve as the basis for making hormones, enzymes, and antibodies, and for repairing cells and tissues.