Infectious Diseases II: Bacterial Infections
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Timing of perioperative antibiotics:
Beta Lactams (eg. cefazolin)
infusion time + why
short infusion -> 60 min before
short half life -> peak [ ] would have been eliminated before 1st incision
Timing of perioperative antibiotics:
Vancomycin, FQs
infusion time + why
Longer infusion time -> 120 min
if start earlier, most of ABX would still be hanging in bag
Intraoperative redosing of antibiotics:
when? how dosed?
Surgeries > 4 hours
Major blood loss (lost blood contains infused ABX)
re-dosed based on half life. eg cefazolin half life is 4 hours so should be re-dosed q4h
Duration of antibiotics for surgery prophylaxis:
DOT + why?
<24h (most need single pre-op dose)
increases risk for ade, antimicrobial resistance, C.diff infections
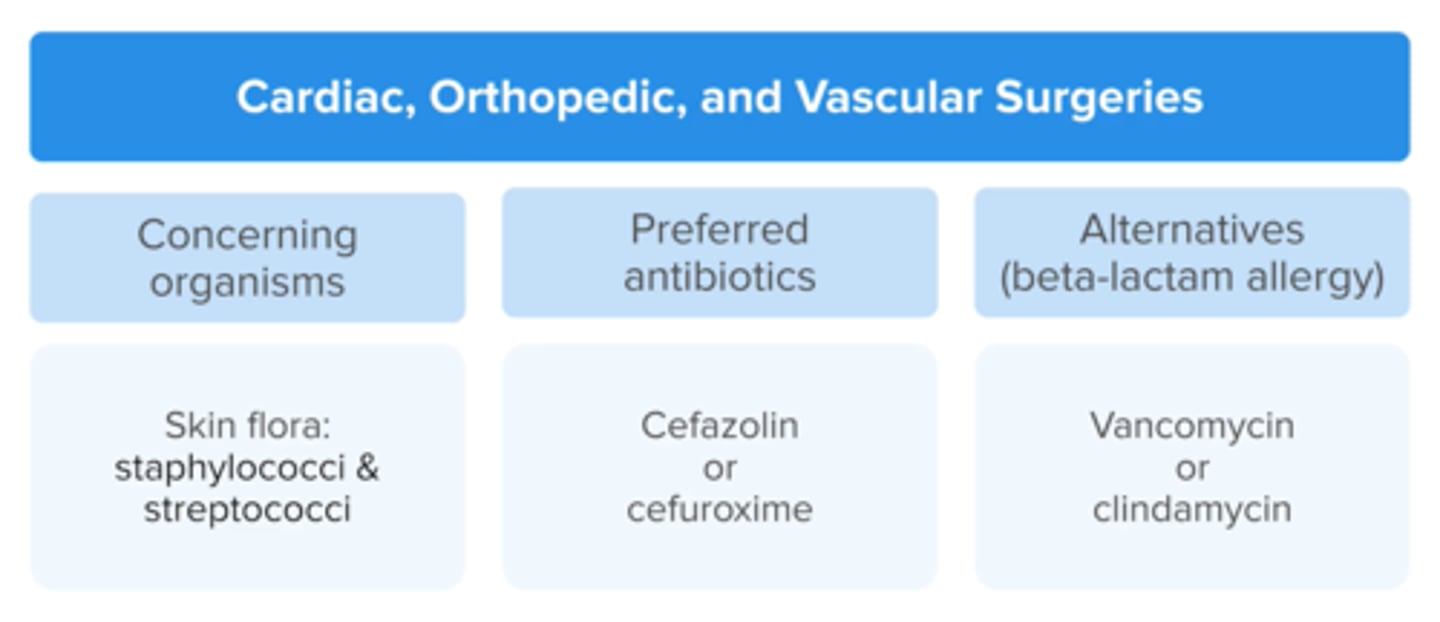
Perioperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Cardiac, vascular, or orthopedic
concerning organism(s) 2
Preferred ABX 2
ALTS (beta lactam) 2
MRSA risk
staph, strep
Cefazolin or cefuroxime (3rd gen cephs) -> great coverage
if Beta lactam allergy: vanc or clindamycin
add vancomycin if MRSA is colonized
Perioperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis
Colon/colorectal (GI) surgery:
concerning organism(s) 2
Preferred ABX 2
ALTS (beta lactam) 2
MRSA risk
anaerobes
Cefotetan, cefoxitin
ampicillin/sulbactam
metronidazole + cephalosporin
BLA:
metro + clindamycin
FQ
aminoglycoside
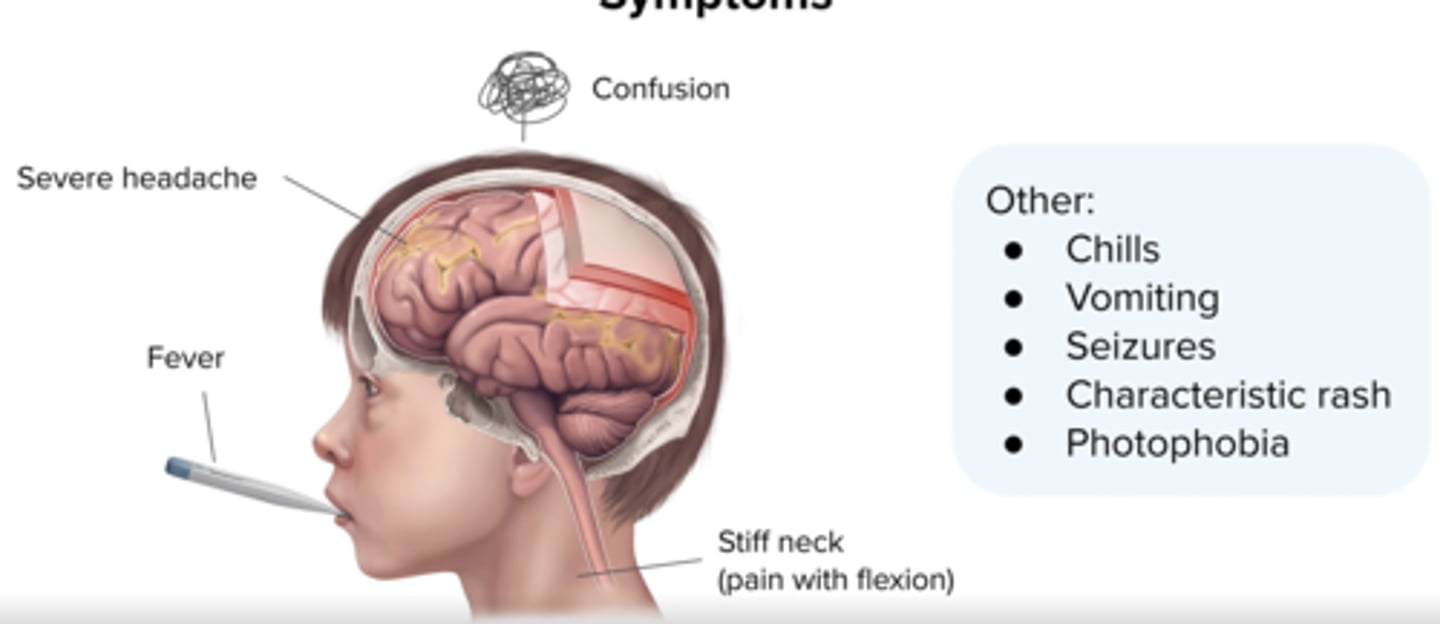
Meningitis:
Key Physical Findings 5
high fever,
Severe headache
stiff neck
altered mental status
rash (nisseria only)
Meningitis:
Diagnosis (what procedure/test + what to see in labs)
Lumbar puncture (CSF analysis)
Increased wbc, protein
decreased glucose
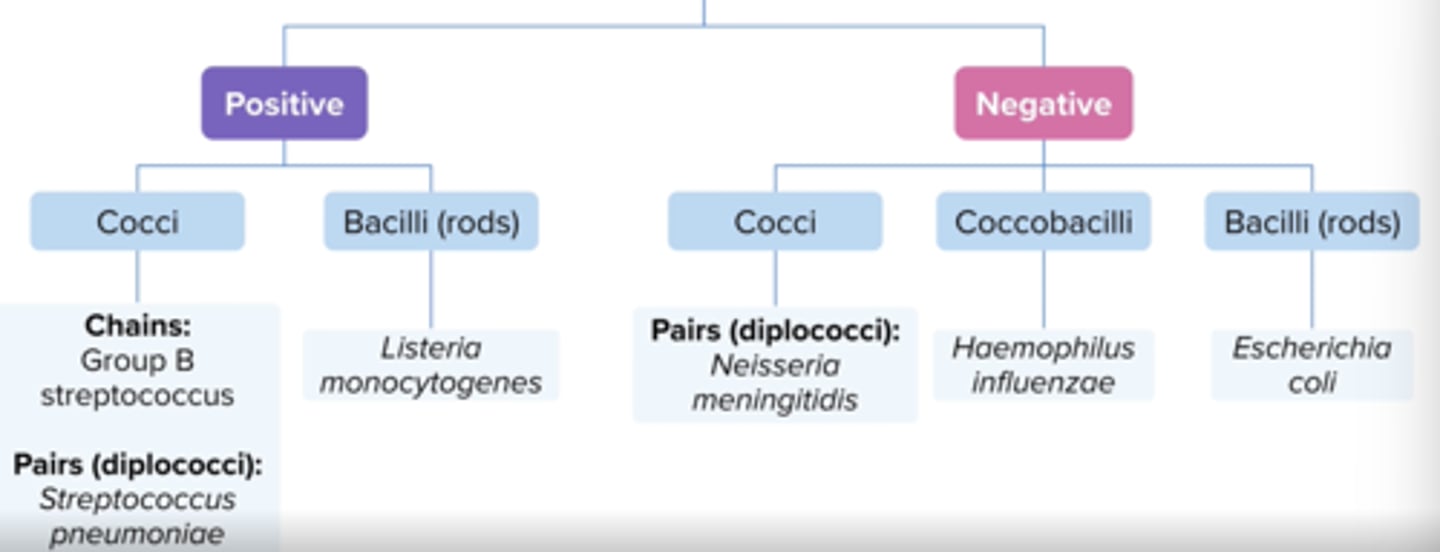
Meningitis:
Common Pathogens (5)
what about in special pops (age, immune, etc.)?
S. pneumoniae +
group B strep +
N. meningitidis -
H. influenzae -
e. coli -
Listeria monocytogenes + (neonates, adults > 50 years, any immunocompromised patient)
Meningitis:
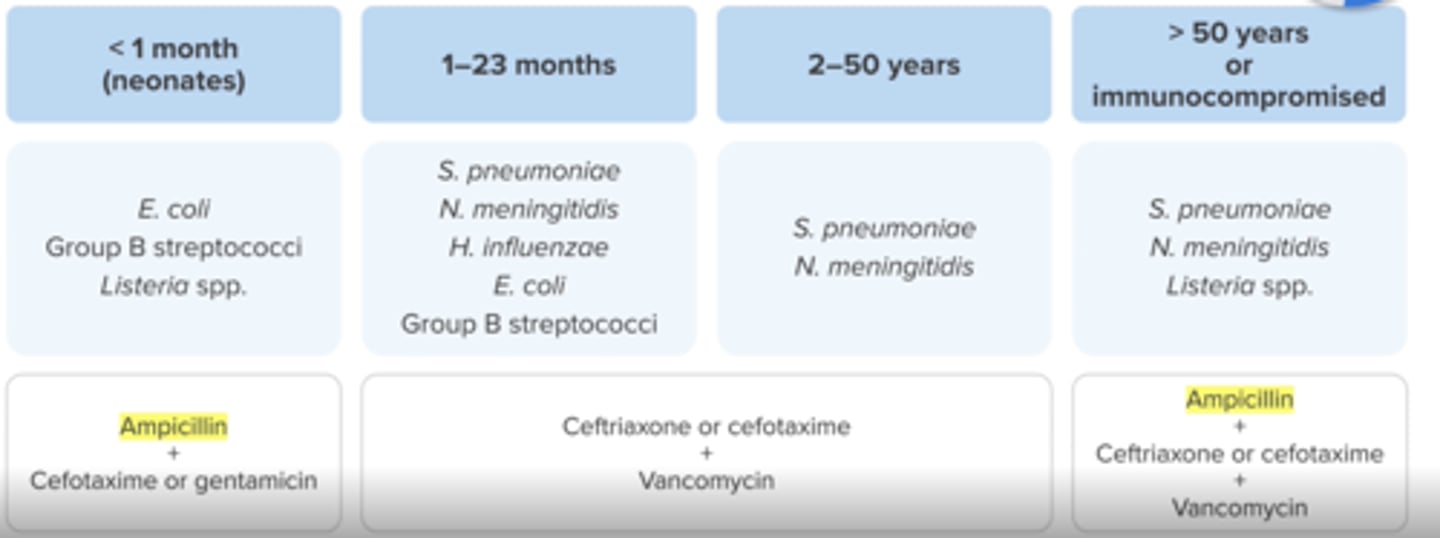
Treatment + which organism(s) + what to avoid
Age <1 month (28 days)
e.coli, group b strep, listeria
Ampicillin (for listeria) + (gentamicin or cefotaxime)
avoid ceftriaxone (causes biliary sludging)
Meningitis:
Treatment
Age 1 month - 50 years
Vancomycin (s.pneumo) + (ceftriaxone or cefotaxime 3rd gen cephs)
Meningitis:
Treatment
Age > 50 years or immunocompromised
Ampicillin (listeria)+ vancomycin (s.pneumo) + ceftriaxone or cefotaxime)
Meningitis:
Empiric Treatment
IV Dexamethasone
why?
when administer?
DOT? when d/c?
reduces neurological complications from excessive swelling
give prior to (15-20 min) or with the 1st dose of antibiotic (all pts)
x4 days
d/c if not s pneumo
Meningitis:
Empiric Treatment
when starting IV ABX, what conditions for selection are required? (+what to avoid)
MUST penetrate blood brain barrier (eg. avoid cefazolin, pip/tazo, clindamycin)
Meningitis
Treatment - DOT (by organism)
7 days: N. mening, H.flu
10-14: s. pneumo
14-21: group b strep (s.agal)
>21: listeria, gram - rods
Meningitis treatment overview
ALL: IV dexamethasone x4 days d/c if not s. pneumo
<1 month: Amp (listeria) + cefotaxime/gentamicin
>50/immunoc: Amp (listeria) + ceftriaxone/cefotaxime + vanc (s. pneumo)
everyone else: ceftriaxone/cefotaxime + vanc (s.pneumo)
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
Symptoms
Bulging tympanic membranes (ear drum)
otorrhea - drainage from ear
otalgia (ear pain - tugging/rubbing ears in kids)
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Viral/Bacteria Organisms
Many are viral
Common bacterial:
S pneumonia, H. influenzas, moroxella
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
Treatment
1st line + dose
+ when to use
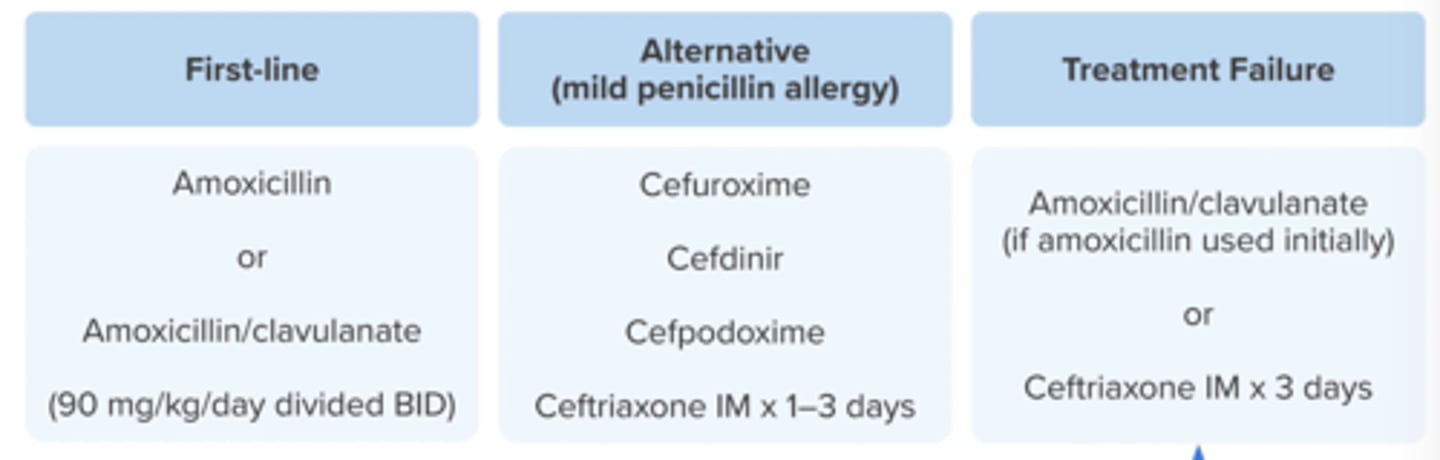
1st line:
High dose amoxicillin (90 mg/kg/day) split BID
Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 90 mg/kg/day (use lowest dose of clavulanate)
use amox/clav if amoxicllin has been taken w/i 30 days
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
Treatment
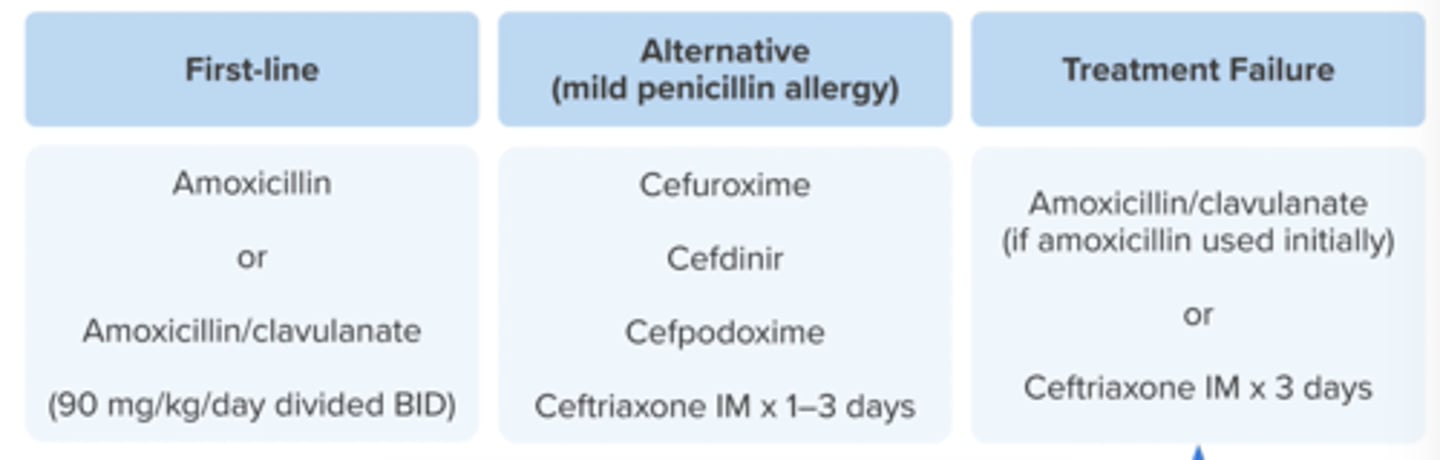
1st line alts (non-severe PCN allergy) 4
severe allergy
2/3rd gen cephs
cefuroxime
cefdinir
cefpodoxime
ceftriaxone IMx1-3 days
azith (poor effectiveness)
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
Treatment
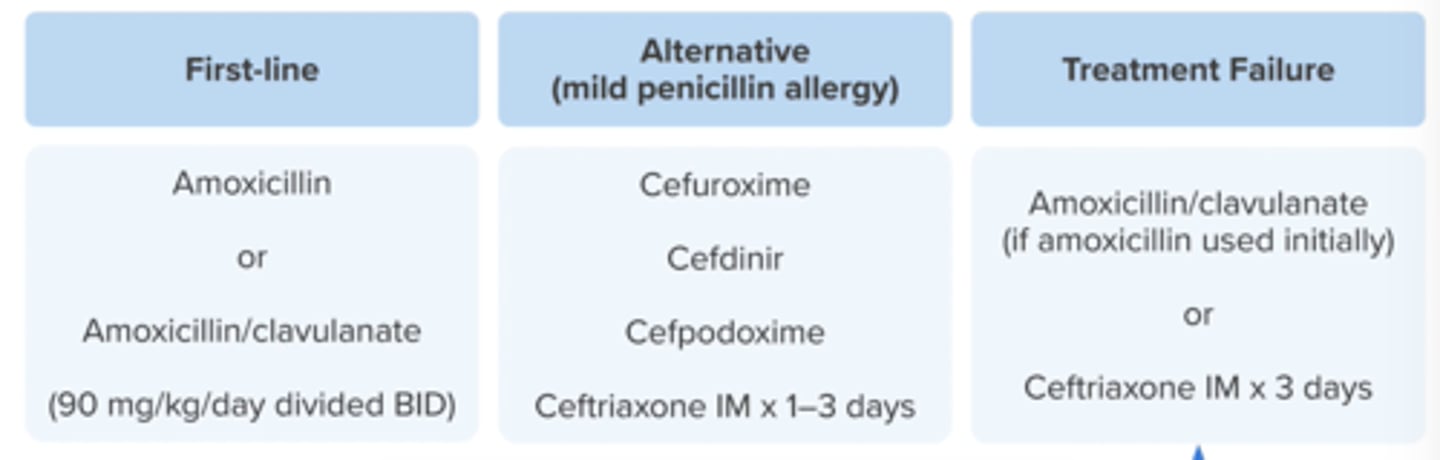
Treatment Failure (what classifies and treatment)
no improvement or worsening symptoms after 2-3 days of therapy
amox/clav (if amox used 1st)
ceftriaxone IM x 3 days
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
what is the amox/clavulanate ratio target + why?
14:1
minimizes toxicity and diarrhea
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Otitis Media
DOT for PO options
5-10 days
younger get longer
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
NON-AOM RTI
Prevention
Vaccinations:
Pneumococcal conjugate (Prevnar 13), and annual influenza vaccine
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
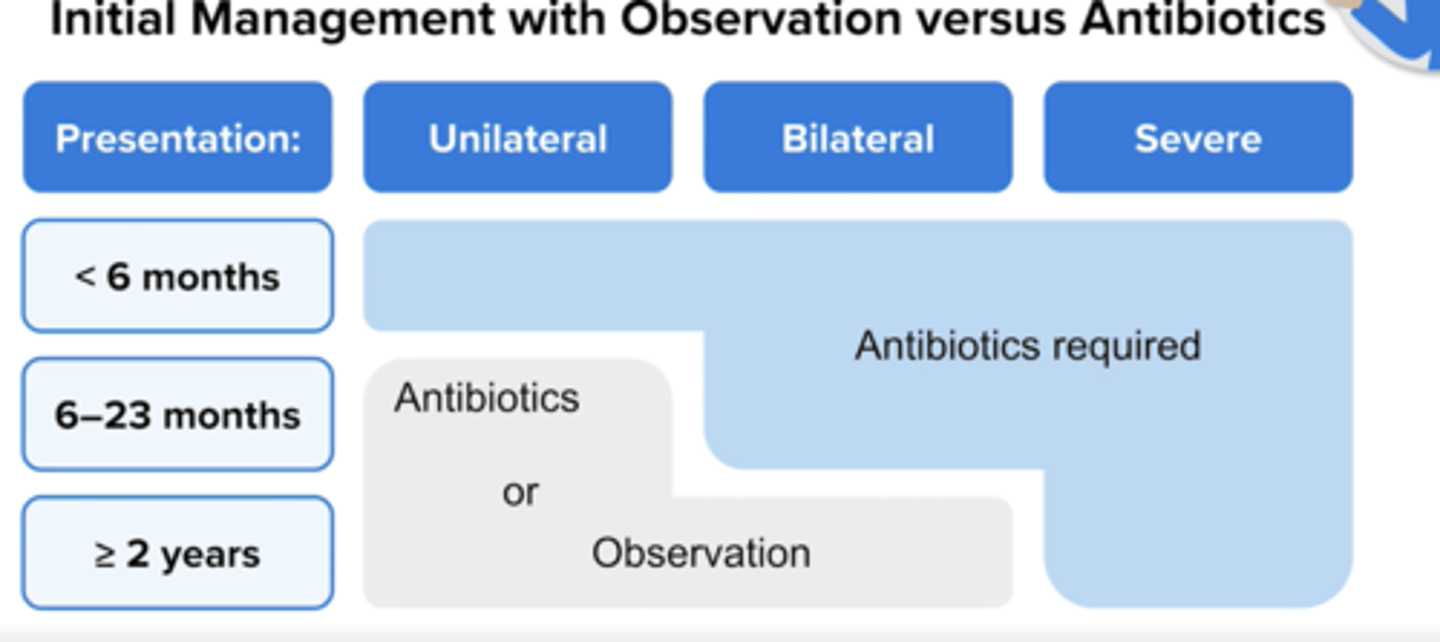
AOM Treatment in Kids - When to Consider Observation
Try observation for 2-3 days if symptoms NOT severe and:
- age 6-23 months: symptoms in only one ear
- age > or = 2 years: symptoms in one or both ears
DO NOT if <6 months, severe (otalgia >48h, otorrhea, temp 102.2F), bilateral if 6-23mos
NON-AOM
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Common Cold
Etiology: respiratory viruses
Clinical presentation: congestion, HA, sore throat, runny nose, cough
Criteria for Anti-infective Treatment: None
Treatment Options: None
NON-AOM
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Influenza
Etiology: influenza virus
Clinical Presentation: sudden onset of fever, chills, fatigue, body aches, dry cough, sore throat, HA
Criteria for Anti-Infective Treatment: < 48 hours of symptoms - severe illness, risks for complications, requires prophylaxis
Treatment options: Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
NON-AOM
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Pharyngitis
Etiology: Respiratory viruses, S. pyogenes
Clinical Presentation: sore throat, fever, HA, swollen lymph nodes, white patches on tonsils, no cough or runny nose
Criteria for Anti-Infective Treatment: Positive rapid antigen test (throat swab) or positive S. pyogenes culture
Treatment Options: PCN, amoxicillin, 1st/2nd generation cephalosporin
NON-AOM
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections:
Sinusitis
Etiology: Respiratory viruses, multiple bacterial etiologies
Clinical Presentation: Nasal congestion, purulent nasal discharge, pain/pressure in face/ears, HA, fever, fatigue
Criteria for Anti-Infective Treatment: > or = 10 days of symptoms; > or = 3 days of severe symptoms; worsening of symptoms
Treatment options: amoxicillin/clavulanate
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bronchitis
Symptoms
Inflammation of the mucus membranes of the bronchi
cough, with or without sputum, fatigue, headache, watery eyes
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bronchitis
Virus/Bacteria
Caused by respiratory viruses or bacteria
(M pneumoniae, H influenzae, Bordetella pertussis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bronchitis
Diagnosis
rule out other conditions
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bronchitis
Mild-Moderate Disease w/ pneumonia expected
Supportive Treatment (fluids, antipyretics, antitussives, vaporizers)
check chest X-ray and consider ABX
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bronchitis
Mild-Moderate Disease w/ confirmed or probably whooping cough
Supportive Treatment (fluids, antipyretics, antitussives, vaporizers)
and
Azithromycin, clarithromycin or SMX/TMP
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis
COPD is a primary underlying cause; COPD exacerbation
GOLD Guidelines
Look for sputum purulence, volume, worsening dyspnea or need for mechanical ventilation
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis
Treatment for COPD Patient with ABECB
Supportive Treatment (fluids, antipyretics, antitussives, vaporizers)
Antibiotics if:
- mechanically ventilated or
- purulent sputum + > or = 1 additional symptoms or
- all 3 of the following: increasing dyspnea, increasing sputum volume, and increasing sputum purulence
USE:
- amoxicillin/clavulanate, or azithromycin, or doxycycline
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Common Pathogens
S pneumoniae
H influenzae
atypicals (mycoplasma pneumoniae, chlamoydophila pneumoniae)
viruses
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Symptoms
Cough, chest pain, fever, dyspnea, tachypnea
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Diagnosis
new infiltrate, opacity, consolidation on chest X-ray
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment - Beta lactams
for coverage of typical pathogens
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment - Macrolides and doxycycline
for coverage of atypical and typical pathogens
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment - Respiratory quinolones
**for coverage of atypical and typical pathogens
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment - based on patient location:
Outpatient = PO
Non-ICU (IV or PO)
ICU (IV)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - OUTPATIENT
CAP Assessment and Treatment Approach
1. look for comorbidities (Chronic heart, lung, liver, or renal disease; DM; alcoholism; malignancy; asplenia)
2. check for MRSA or pseudomonas aeruginosa risk factors (prior respiratory isolation of either pathogen or hospitalization with receipt of parenteral antibiotics in the past 90 days)
3. decide whether patient falls into Category 1 or Category 2
4. choose one option with category; look for allergies, drug-disease interactions (quinolone and seizures), drug-drug interactions (qt prolongation) and culture results (if available)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - OUTPATIENT
Category 1 - NO Comorbidities
Amoxicillin high-dose (1 g TID), or
Doxycycline, or
Macrolide (azithromycin or clarithromycin) if local pneumococcal resistance is <25%
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - OUTPATIENT
Category 2 - WITH Comorbidities
Beta-Lactam + macrolide or doxycycline
- amoxicillin/clavulanate or cephalosporin (cefpodoxime, cefdinir, cefuroxime)
plus
- macrolide or doxycycline
Respiratory quinolone monotherapy
- moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - INPATIENT
Non-ICU, Nonsevere
Beta-Lactam + macrolide or doxycycline
- ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, ceftaroline, ampicillin/sulbactam
Respiratory quinolone monotherapy
- moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - INPATIENT
ICU, Severe
Beta-Lactam + macrolide
Beta-Lactam + respiratory quinolone (do NOT use quinolone therapy)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - INPATIENT
MRSA Risk Factors
add vancomycin or linezolid
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Treatment Regimens - INPATIENT
PSEUDOMONAS Risk Factors
Must cover S. pneumoniae and psedomonas
- piperacillin/tazobactam, cefepime, ceftazidime, imipenem/cilastatin, meropenem, aztreonam
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Definitions
HAP: pneumonia onset > 48 hours after admission
VAP: pneumonia onset > 48 hours after ventilated
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Common Pathogens
MRSA
Gram-negative nosocomial pathogens (p aeruginosa, acinetobacter, enterobacter)
Other gram-negatives (E. coli, Klebsiella)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Risk factors for MDR pathogens
IV antibiotics use within 90 days
High MRSA prevalence in unit or colonization
Additional risk factors for VAP (hospitalization > or = 5 days, septic shock, ARDS, HD)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP)
Identifying Risk factors for MRSA or MDR pathogens
look for:
- positive MRSA nasal swab
- high prevalence of resistant pathogen noted in hospital unit
- IV ABX use within 90 days
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP) - Antibiotics for Pseudomonas
piperacillin/tazobactam
cefepime, ceftazidime, or ceftolozane/tazobactam
levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin
imipenem/cilastatin or meropenem
tobramycin, gentamicin, or amikacin
colistimethate or polymyxin B
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP) - Antibiotics for MRSA
Vancomycin or linezolid
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
General Treatment Principles
Assess patient risk of MRSA, MDR Pseudomonas and death to determine the antibiotic regimen
(MRSA Coverage and double coverage of Pseudomonas is not required in every patient)
Treatment duration: 7 days
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Treatment for Pseudomonas and MSSA
One drug
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Treatment for Pseudomonas and MRSA
Two Drugs
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Treatment for MDR Pseudomonas and MRSA
Three drugs
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP) - Empiric Regimen
Choose 1 ABX to cover Pseudomonas and MSSA if:
low risk for MRSA or MDR pathogens
Cefepime or
Piperacillin/tazobactam
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP) - Empiric Regimen
Choose 2 ABX, one for MRSA and one for Pseudomonas if:
risk for MRSA (positive nasal swab), but low risk for MDR pathogens
Cefepime + vancomycin or
meropenem + linezolid
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
(HAP) and (VAP) - Empiric Regimen
Choose 3 ABX, one for MRSA and two for Pseudomonas, if:
risk for both MRSA and MDR pathogens (IV abs within past 90 days)
Piperacillin/tazobactam + ciprofloxacin + vancomycin or
Cefepime + gentamicin + linezolid
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
latent disease: no symptoms
active disease: highly contagious (requires isolation)
- transmitted by aerosolized droplets
- symptoms:
cough (hemoptysis), purulent sputum, fever, night sweats
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Latent TB diagnosis
Tuberculin skin test (TST), also called a PPD test (intradermal injection, interpreted in 48-72 hours)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Criteria for positive TST result
> or = 5 mm induration: close contacts of recent TB cases, significant immunosuppression
> or = 10 mm induration: recent immigrants, IV drug users, moderate immunosuppression, residents/employees of "high risk" congregate settings
> or = 15 mm induration: patients with no risk factors
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Latent TB treatment
CHECK WITH NEW BOOK
INH X 9 months
Rifampin x 4 months
INH and rifapentine once weekly x 12 weeks (DOT) (not recommended in pregnancy, children, HIV+ patients
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Active TB diagnosis
Acid-fast bacilli (AFB stain)
sputum culture (can take up to 6 weeks)
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Active TB Treatment
RIPE Therapy (6 months total)
Intensive Phase: 4 drugs for 2 months - rifampin, INH, pyrazinamide, ethambutol
Continuation Phase: 2 drugs for 4 months - rifampin and INH
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections:
Tuberculosis
Active TB Treatment
RIPE Therapy
Monitor infection - sputum sample, chest xray
ALL RIPE drugs - increase LFTs
Rifampin - orange bodily secretions, strong CYP450 inducer, flu-like symptoms
Isoniazid (INH) - peripheral neuropathy, DILE
Rifampin and INH - take on empty stomach, risk for hemolytic anemia (positive Coombs test)
Pyrazinamide - increase uric acid
Ethambutol - visual damage, confusion/hallucinations
Pyrazinamide/ethmabutol - increase dosing interval in renal impairment
Infective Endocarditis (IE):
Diagnosis
Infection of the heart valves
Echocardiogram
Blood cultures
Infective Endocarditis (IE):
Treatment
Varies by valve type, organism, MIC
(staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci)
IV antibiotics required
Gentamicin synergy (more common with prosthetic valves or enterococcal infections)
- peak: 3-4 mcg/ml
- trough: < 1 mcg/ml
vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid
Infective Endocarditis Dental Prophylaxis:
Why?
mouth contains bacteria that can infect the blood stream
Infective Endocarditis Dental Prophylaxis:
Who?
patients at high risk (prosthetic valve, congenital defects, h/o endocarditis) needing dental work (root canal)
Infective Endocarditis Dental Prophylaxis:
What?
Oral antibiotic x 1 dose 30-60 min prior to dental procedure (amoxicillin 2 g PO)
PCN allergy?
clindamycin 600 mg PO or azithromycin or clarithromycin 500 mg PO
Intra-abdominal Infections:
Primary Peritonitis: SBP
Liver disease, cirrhosis patients
DOC: ceftriaxone IV for 5-7 days
prophylaxis: Bactrim or ciprofloxacin
Intra-abdominal Infections:
Secondary peritonitis: usually polymicrobial
cover gram-negative pathogens, anaerobes, and in pseudomonas/CAPES organisms in critically ill patients
Intra-abdominal Infections:
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
Intra-abdominal Infections:
Cholangitis
infection of the common bile duct
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Mild infection
systemic signs absent
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Moderate infection:
systemic signs present
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Severe infection
failed I&D
purulent on oral ABX
deep infection
immunocompromised
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Systemic signs of infection
Fever > 100.4 F
HR > 90 BPM
WBC >12000 OR <4000 cells/mm3
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Superficial Infections: Impetigo
Honey-colored crusts
Tx: mupirocin (bactroban) or cephalexin
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Superficial Infections: Folliculitis/furuncles/carbuncles
often caused by staph. aureus
if systemic signs, use cephalexin
if not responsive, change to CA-MRSA coverage (Bactrim or Doxycycline)
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Superficial Infections: Folliculitis
hair follicle infection (looks like pimple)
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Superficial Infections: Furuncle
boil, infection involves hair follicle and surrounding tissue
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Superficial Infections: Carbuncle
group of infected furuncles
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Non-purulent Infections: cellulitis
Target streptococci and MSSA
Tx: cephalexin
beta-lactam allergy - clindamycin
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Outpatient Treatment
Purulent Infections: Abscess
No systemic signs: I&D
Systemic signs: I&D + antibiotics (cover CA-MRSA)
- bactrim, doxycycline, minocycline, clindamycin
Severe Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Severe purulent SSTIs
IV ABX active against MRSA
Vancomycin, daptomycin, lines-lid, ceftaroline, telavancin/oritavancin/dalbavancin
broad-spectrum if caused by animal or human bite
transition to oral abs once patient is stable
Severe Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs):
Necrotizing Fasciitis
fast moving infection
intense pain, tenderness over affect skin, purplish discoloration, edema
systemic illness
broad-spectrum ABX
Diabetic Foot Infections:
Polymicrobial
Prevention: proper foot care
Diabetic Foot Infections:
Treatment of Moderate-Severe
life or limb-threatening
broad-spectrum tx: cover pseudomonas and MRSA until susceptibilities are available
Osteomyelitis requires longer duration of therapy (usually IV)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Lower UTI
cystitis
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Upper UTI
Pyelonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Classification - uncomplicated
non-pregnant premenopausal women
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Classification - complicated
male patient, neurogenic bladder, obstruction, indwelling catheter
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Diagnosis:
urinalysis
urine culture
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Lower UTI (Cystitis) Symptoms
Urinary urgency and frequency
nocturne
dysuria
suprapubic heaviness
hematuria