Alcohols
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the functional group of an alcohol?
Hydroxyl group -OH
What is the general formula of an alcohol?
CnH2n+1OH
How do you name alcohols?
Use suffix -ol (or -diol/-triol)
If another functional group, use prefix hydroxy-
How do you classify alcohols?
By the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon bearing the -OH
1-primary
2-secondary
3-tertiary
What kind of intermolecular forces do alcohols have and why?
Hydrogen bonding due to the electronegativity difference in the OH bond
How do alcohols mp and bp compare to other hydrocarbons of similar carbon chain lengths?
They have higher bp/mp due to hydrogen bonding
Whats the trend in bp/mp for alcohols?
Bp increases with chain length - more VdWs forces
Bp decreases with branching - fewer contact points
Are alcohols soluble in water?
Yes because they form hydrogen bonds with water
What’s the trend in solubility for alcohols?
Decreases as chain length increases as the hydrophobic alkyl chain dominates (become insoluble at octonol)
How can ethanol be made from crude oil? What are the conditions?
Hydration of ethene via electrophilic addition
H3PO4 catalyst
High temperature (300C) and high pressure (60 atm)
What are advantages and disadvantages of making ethanol via hydration of alkenes?
Advantages:
Fast, continuous process, pure product
Disadvantages:
Non-renewable as from crude oil
How can ethanol be made by fermentation? What conditions are needed?
Plant carbohydrates broken down and fermented by enzymes in yeast to produce ethanol solution
Enzymes in yeast as catalyst
35C temp
Anaerobic conditions - no oxygen
Write an equation for the fermentation reaction which produces ethanol
C6H12O6 (aq) + (yeast cat.) → 2C2H5OH (aq) + 2CO2 (g)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of producing ethanol via fermentation of glucose?
Advantages:
Renewable
Disadvantages:
Slow, batch process, solution isn’t pure
Define carbon neutral
No net addition of CO2 to the atmosphere
CO2 taken in during a process = CO2 released during a process
Explain how using ethanol in petrol engines could be considered to be carbon neutral. Why would it probably not be entirely carbon neutral?
CO2 released in fermentation and combustion = CO2 absorbed during photosynthesis
However, other “carbon costs” associated with it eg transport and harvesting
What is an elimination reaction?
The removal of a smaller molecule from a larger one
What do alcohols lose in an elimination reaction?
OH from alcohol group
H attached to alcohol C
Overall = H2O
What conditions are needed for the elimination reactions from alcohols to alkenes? (2 alternatives)
1) Acid catalysed elimination:
Conc H2SO4/H3PO4 catalyst
Heat under reflux
2) Surface catalysed elimination
Pass alcohol vapour over Al2O3 catalyst
300C temp
Draw a mechanism for the dehydration/elimination of ethanol
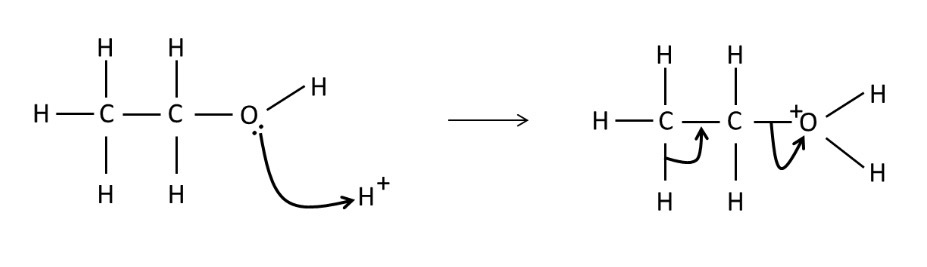
What forms if you partially oxidise a primary alcohol?
An aldehyde
What forms if you fully oxidise a primary alcohol?
A carboxylic acid
What conditions are needed to partially oxidise a primary alcohol?
Distillation
DILUTE H2SO4
Potassium dichromate (VI)
Gentle heating
What conditions are needed to fully oxidise a primary alcohol?
Reflux
Strong heating
CONC H2SO4
Excess potassium dichromate (VI)
What is reflux used for?
Ensures completion of a reaction by allowing you to heat a mixture for a long time at the boiling point of the chemicals without losing any volatile reactants or products
Write an equation for the partial oxidation of ethanol
CH3CH2OH + [O] → CH3CHO + H2O
Write an equation for the full oxidation of ethanol
CH3CH2OH (l) + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O
What forms if you oxidise a secondary alcohol?
A ketone
Write an equation for the oxidation of propan-2-ol (secondary alcohol)
CH3CH(OH)H3(l) + [O] → CH3COCH3(g) + H2O(l)
Why cant tertiary alcohols be oxidised?
The carbon attached to the -OH group has no hydrogen atoms on it
How would you test for an alcohol? What would a positive result show?
For primary or secondary alcohols:
-acidified K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 and WARM
-positive result - orange → green