Chapter 16 - Regulation of gene expression in prokayotes
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Positive Control
Increasing frequency of initiation; Activator proteins enhance binding of RNA polymerase
Negative Control
Decrease the frequency of transcription; repressor proteins bind to operators in DNA and block transcription; also includes the removing of a repressor
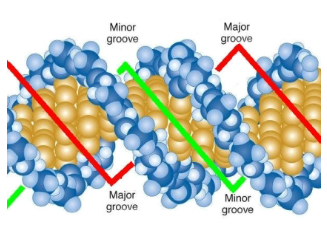
Major groove and Minor groove
Major groove is more accessible
A Operon
Prokaryotic cells; a series of genes that code for enzymes that are all part of a single metabolic pathway are where the expression is simultaneously controlled; Includes the operator and promoter
Inducible Operon
Usually OFF; Inducer turns it on by deactivating the repressor; usually catabolic;
Repressible operon
Usually ON;The repressor blocks gene expression by blocking RNA polymerase, and binding to the repressor turns it off; usually anabolic;
Operator
A gene that positioned next to the promoter
Represser
Binds to the operator and blocks RNA polymerase; what causes inducable operators to be off most of the time; A protein
Inducer
Binds to the repressor and prevents it from binding to the operator; causes Repressible operons to be on most of the time; not a protein
Co-repressor
a molecule that works with the represser to switch off a operon
Lac Operon
codes for an enzyme that consumes lactose; usually off but represser cant bind to operator when lactose is present; thus a induceable operon
Trp operon
produces trp; usually ON; turns off when trp is present; thus a repressable operon