BSTD Term 1 + Term 2
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Define ‘Effective Business Practice’
Defining a business’ core values and ingraining it in the business’ everyday activities. The business defines success by measuring the achievement of these values.
State 3 ways in which businesses may view themselves as successful.

State and explain the 6 different professionalism theories.
Principle-Based Theory - A set of values or rules will determine if an action is ethical or not.
Consequence-based Theory - The outcome of the situation will determine whether the action is ethical or not.
Utilitarian Theory - If the outcome benefits the majority of a group, the actions are justifiable.
Narrative Theories - Uses stories /folklore organisational culture (common beliefs) to illustrate to people what is acceptable behaviour or not.
Virtue-Based Theory - Judges a person by his/her character and reputation rather than on an individual action.
Dentology - If the person upholds his/her obligation towards another person or society, the action will be ethical.
What is Batho Pele?
A framework to ensure professional and ethical service delivery in the public service in South Africa.
State at least 2 aims of the Batho Pele framework.

State and briefly explain the 8 Batho Pele Principles.
Consultation - Listening to the needs of the people of the country. E.g Discussions, Surveys and Meetings.
Service Standards - Should be monitored to ensure the satisfaction of citizens.
Access to Public Services - Empower the people and increase the standard of living.
Courtesy, Consideration and Respect - Better communication and perception of government in public eye.
Relevant Information - Sharing important info about Service Delivery.
Openness and Transparency - Government is responsible for how resources are utilized.
Mechanisms in Place for Redress - Quick resolution to issues.
Citizens should feel they get the Value for their money
State at least 2 characteristics of Professional Behaviour.
Be honest and act with integrity
Act in a manner acceptable to society
Do what is right rather than what is easy or financially rewarding.
What is the difference between a Code of Ethics and a Code of Conduct?
A Code of Ethics is often defined as a set of rules that helps people when they have to make decisions, while a Code of Conduct will guide people’s actions.
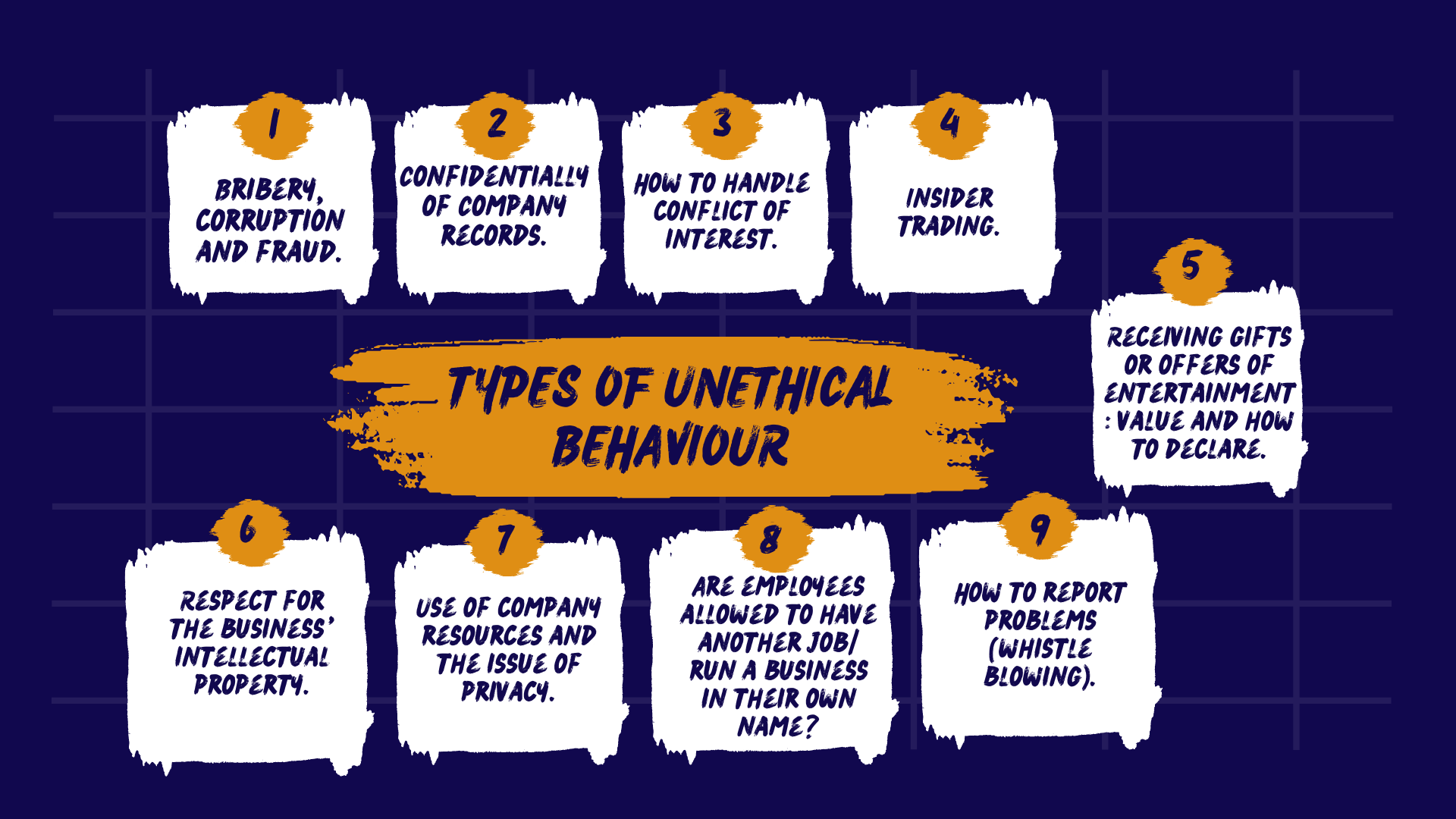
State at least 4 types of Unethical Behaviour.
State 3 methods that can be used to ensure staff members use the Code of Ethics / Code of Conduct as part of everyday business.
Obtain staff input. Prepare a draft document and allow employees to give feedback.
Managers must lead by example. There must be one set of rules for managers and one for employees.
Ensure the guidelines are written in easy to understand language.
Conduct regular training sessions to help employees to understand the guidelines. Provides examples of what is acceptable vs, unacceptable behaviour.
Ensure it is proofread and that the necessary language editing has been done.
Ensure employees are aware of the consequences by making an example of uncooperative employees.
State 2 consequences of Unethical Business Practices.
Leads to an atmosphere of mistrust in the workplace. Employees may act in the same conduct as superiors because they do not face consequences. Decreases productivity.
It may lead to some embarrassment for the individual, business and the family of the individual.
The business may end up with a class action suit with all consumers who feel they were treated in an unacceptable manner and take the company to court.
If customers become aware of unethical behaviour, the business’s reputation may suffer and customers could decide to boycott the business.
May even mean large fines for the business.
Lower profits may lead to investors losing confidence in the business.
Unethical behaviour by top management may lead to more regulations being introduced to try to govern behaviour.
State 1 advantages of being a good Corporate Citizen.
A healthier workforce with easier recruiting, because people want to work at a place.
Investor confidence makes it easier to raise capital.
An increased market share because of a higher satisfaction levels amongst customers
State the 4 different types of Problem Solving Strategies.
Corporate Strategies
Integration Strategies
Generic Strategies
Other Strategies
State the purpose of and the 3 strategies within the Corporate Strategies umbrella.
Corporate Strategies are used to create or defend a businesses competitive advantage.
Corporate Combination
Decline/Defensive Strategies
Growth Strategies
State and explain the 2 possible courses of action under Corporate Combination.
Corporate Combination:
Joint Venture [Two or more businesses agee to combine resources in order to create competitive advantage].
Merge/Takeover [Two or more different businesses form to create a single new business in order to create competitive advantage].
State and explain the 3 possible courses of action under Decline/Defensive Strategies.
Decline/Defensive Strategies:
Retrenchment Strategy [To reduce the size of the business or its range of products]
Divestiture [The business sells of assets that hinder financial performance]
Liquidation [The business sells all of its assets to pay of debt and as a result, the business will no longer exist]
State and explain the 4 possible courses of action under Growth Strategies.
Growth Strategies:
Market Penetration [Increasing sales of existing products to an existing market to gain a larger market share.]
Product Development [Introducing new products to existing markets.]
Market Development [Entering new markets with existing products.]
Diversification [Entering a new market with a new product.]
State the 3 strategies within the Integration Strategies umbrella.
Integration Strategies are used to align various aspects of the supply chain and operations to improve efficiency and competitiveness.
Forward Integration
Horizontal Integration
Backward Integration
Explain the purposes of Forward, Horizontal and Backward Integration.
Forward Integration [The business takes over its distributor to decrease final selling price to customers.]
Horizontal Integration [The business takes over one of its competitors.]
Backward Integration [The business takes over its suppliers or establishes their own production company in order to gain control over the production process and eliminate the power of suppliers.]
State the purpose of and 3 strategies within the Generic Strategies umbrella.
Generic Strategies are how a business responds to challenges in the internal and external business environments.
Low Cost Strategy
Focus/Niche Market
Differentiation
Explain the purposes of Low Cost Strategy, Focus/Niche Market Strategy and Differentiation Strategy.
Low Cost [Low Input Costs (Cheap Raw Materials), Low Cost Manufacturing (The use of mass production) and the discontinuity of non-beneficial activities. All in order to reduce operational costs.]
Focus/Niche Market [The business targets a smaller customer demographic with unique tastes in order to offer them premium products to build customer loyalty.]
Differentiation [Factors of product uniqueness include: Quality, After-sales service, Product brand and Marketing/Distribution efforts.]
State the purpose of and the 2 strategies under the Other Strategies umbrella.
Other Strategies are used to improve the overall performance of the business.
Revise Business Objectives
Teamwork
State the purposes of Revising Business Objectives and Teamwork.
Revise Business Objectives [The business must keep up with customer demand and the changes in the external business environment.]
Teamwork [Allows individuals within the business to flourish and complement individual strengths and compensate for individual weaknesses.]
State the 8 Problem Solving Tools of Overall Business Performance.
Total Quality Control & Total Customer Satisfaction
Benchmarking
Financial ratios
Performance Appraisals (360o) Self-Evaluation
Balanced Scorecard
Continuous Skill Development
Delphi Technique
Resource-Based Approach
State the 2 ways in which a business can implement the Total Quality Control & Total Customer Satisfaction tool.
Sampling [Checking the quality of every single product.]
Inspection [Checking the quality of one product out of a bach.]
State the purpose of the Benchmarking tool.
The business compares its current practices to the ideal of the industry and put measures in place to close the performance gap.
State the purpose of the Financial Ratios tool.
Financial ratios describe the businesses ability to adjust internal financial operations to increase profitability.
State the purpose of the Performance Appraisals (360o) Self-Evaluation tool and its characteristics.
A tool used to plan, evaluate and improve staff performance.
Planning Tool [Establish performance targets.]
Evaluation Tool [Self-evaluation and performance checks from several parties.]
Feedback Tool [Promotion or Development of Action Plans.]
State the characteristics of the Balanced Scorecard tool.
Financial Perspective [Focus on maximum utilization of assets and reduction of operation costs.]
Customer Perspective [Focus on customer demands and expectations.]
Internal Business Perspective [Focus on innovation of products/services.]
Learning and Growth Perspective [Focus on the creation of intellectual capital by human capital (employees).]
State the purpose of the Continuous Skill Development tool.
Business environments in which employees are encouraged to learn and equip new skills to adapt to market trends.
State the purpose of the Delphi Technique tool.
A method of survey anonymous experts on an issue faced by a business and implement their feedback.
State the purpose of the Resource-Based Approach tool.
When faced with a problem, a business must determine:
What resources are needed to solve the problem?
What resources are available?
What is the cost of those resources?
In order to manage the businesses tangible/intangible resources.
State and briefly explain the 4 pillars to the approach to creativity.
Fluency [The ability to produce multiple ideas.]
Flexibility [The ability to look at a situation through different perspectives.]
Originality [The ability to develop unique ideas.]
Elaboration [Adding detail and depth to ideas.]
State and briefly explain each letter of the SCAMPER method.
S ubstitute [Replace elements with alternatives]
C ombine [Merge different components]
A dapt [Update product to new preferences]
M odify [Change appearance/presentation]
P urpose [New function of a product]
E liminate [Reduction of useless elements]
R everse [Deconstruction of main pillars]
State difference between Resisting Forces and Driving Forces.
Resisting Forces are factors that hinder or create obstacles to change.
Driving Forces are factors that promote or support change.
State the steps of a Force Field Analysis.
Define Problem
Define Change Objective
Identify Driving Forces
Identify Resisting Forces
Develop Change Strategy
State at least 3 obstacles to creative thinking.
The belief of one correct solution.
Lack of Sleep.
Routine/Logical Thinking.
The “Why Change?” mindset.
Lack of Time.
Discouragement of creativity from superiors.
“Its not my job to be creative”.
Define the term Indigenous Thinking.
The local knowledge and way of thinking that is unique to a culture or to a particular society. These skills and experiences of a particular group can be applied to develop a product/service.
State one advantage and one disadvantage of Indigenous Thinking.
Advantage:
Indigenous Thinking can create competitive advantage by offering a unique product/service to a customer group.
Disadvantage:
Indigenous Thinking can be a threat/weakness in a market that is unfamiliar with their product/service.
Define Sole Trader.
A form of business ownership where one individual owns and operates the business.
Unlimited Liability
The owner is personally responsible for all debts incurred by the business.
State all 7 characteristics of ownership
Formation Procedures
Legal Persona
Continuity of Existence
Tax Implications
Capital Requirements
Management & Control
Owner’s Liability for Debt
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Formation Procedures of a Sole Trader.
Advantage.
There are no legal requirements for formation, making it quick and low cost.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Legal Persona of a Sole Trader.
Disadvantage.
The sole trader is the legal entity and must enter into contracts in their own name.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Continuity of Existence of a Sole Trader.
Disadvantage.
The business does not continue after the owner’s departure or death.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Tax Implications of a Sole Trader.
Can be an Advantage or Disadvantage.
The owner's tax rate is based on business profitability; lower profits lead to a lower tax rate than corporate rates. Conversely, higher profits subject the owner to a higher tax rate, which may result in a greater tax burden than corporate structures.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Capital Requirements of a Sole Trader.
Can be an Advantage or Disadvantage.
If the business does not require a large amount of capital that the owner can provide, it is not a problem.
If the business needs more capital than the owner can provide, they must consider another form of ownership.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Management and Control of a Sole Trader.
Advantage.
The sole trader has the ability to make quick decisions, providing flexibility.
Disadvantage.
Lacks collaborative opportunities.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Owner’s Liability for Debt of a Sole Trader.
Disadvantage.
The owner has unlimited liability.
Define Partnership.
A business structure where two or more individuals manage and operate a business together, sharing profits and liabilities.
State the purpose of a Partnership Agreement.
A formal contract between partners that outlines the terms of the partnership, including roles, responsibilities, and profit distribution.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Formation of Procedures of a Partnership.
Advantage.
No legal requirements – quick and low cost. Partnership Agreements are not legally necessary.
Disadvantage.
No Partnership Agreement may lead to disputes among partners that may need to be settled legally.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Legal Persona of a Partnership.
Disadvantage.
The owners are the legal entities and they enter into contracts in their own names.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Continuity of Existence of a Partnership.
Disadvantage.
The business does not continue if one owner departure, death or addition of a new owner. A new Partnership Agreement and new business must be created.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Owner’s Liability for Debt of a Partnership.
Disadvantage.
Partners have unlimited liability and are jointly liable for the debt of the business.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Tax Implications of a Partnership.
Can be an Advantage or Disadvantage.
The owner's tax rate is based on business profitability; lower profits lead to a lower tax rate than corporate rates.
Conversely, higher profits subject the owner to a higher tax rate, which may result in a greater tax burden than corporate structures.
State the Advantage(s)/Disadvantage(s) of Management and Control of a Partnership.
Advantage.
Good quality of decision-making because there are several people to give input. The business also benefits from the combination of skills and knowledge.
Disadvantage.
More people have to be consulted when a decision is made. This may mean slower decision-making.
Define the term Company.
A business structure where ownership is divided into shares, offering limited liability to its owners while being a distinct legal entity.
State at least 2 purposes of the Companies Act (Companies Act 71 of 2008).
To encourage entrepreneurship and stimulate the economy.
To promote the overall well-being of the economy.
To simplify the process of registering and managing a company as a form of ownership.
To ensure the rights and obligations of shareholders and directors are aligned and protected.
To ensure non-profit companies are established and managed in an effective manner and to ensure accountability.
State the 2 different companies (and their sub-categories) that are recognised by the companies act.
Profit Companies:
State-owned Co.
Private Co.
Public Co.
Non-Profit Companies
State the greatest difference between private and public companies.
Private Company:
MOI has to specify that no shares will be offered to the public.
Shares will be freely negotiable/transferable.
Public Company:
Allowed to list on JSE and offer shares to the public in order to raise capital.
State at least 1 rule in regards to naming a business.
Any company may reserve a name for the business, provided it is not the same or too similar to an existing business.
The name may not pretend to be associated with any person or business; may not be misleading or pretend to be associated with the South African government or any foreign government if it is not.
State at least 2 abbreviations that a company name must end with, what it means and what type of company uses it.
Pty Ltd.
Proprietary Limited
Private Company
Ltd.
Limited
Public Company
SOC Ltd
State-Owned Company Limited
State Owned Company
NPC
Non-profit Company
Non-Profit Company
State the two documents that are needed to formally register a company.
Notice of Incorporation
Memorandum of Incorporation (MOI).
State at least 2 characteristics of a Memorandum of Incorporation.
Founding document of a company.
Stipulates the shares that will be sold and the rights and responsibilities of shareholders.
Describes duties, responsibilities and liabilities of company directors.
May include stricter guidelines than the companies act, but must not violate the act.
May be changed by means of a special agreement among shareholders.
State the required minimum number of directors in a private and public company.
Public Company: 3 directors
Private Company: 1 director
Define the term prospectus.
The prospectus is a written invitation to the public to buy shares or other securities in the company.
State at least 1 characteristic of a prospectus.
Indication of the registration of the prospectus.
Dated signatures of all directors.
Statement indicating the extent to which it complies with the King Code.
The prospectus has to contain details of the transaction ie (purchase price, address of business, cash payment, customer goodwill payment)
State at least 1 characteristic of company meetings.
Public companies have to give 15 business days’ notice of an upcoming meeting.
Private companies have to give 10 business days’ notice.
The requirements to have a quorum for meetings is that 25% of shares with voting rights have to be in attendance.
State at least 1 duty of directors.
Directors have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of the company.
Directors should also act in good faith.
Director is obliged to disclose personal or financial interests to prevent a conflict of interest.
State at least 1 characteristics of a companies financial obligations.
Annual Financial Statements (AFS) that meet international financial reporting standards.
Public Companies must have their AFS audited. Private Companies do not.
State the advantage/disadvantage of formation procedures of a company.
Disadvantage:
Complicated and Costly.
State the advantage/disadvantage of Legal Persona of a comapany.
Advantage:
The business is its own legal identity.
State the advantage/disadvantage of Continuity of Existence of a company.
Advantage:
The business can continue to exist regardless of the live(s) of the owner(s).
State the advantage/disadvantage of Owner’s liability for debts of a company.
Advantage:
Owners have limited liability and therefore can only lose their capital investment if the business is insolvent.
State the advantage/disadvantage of Tax Implications of a company.
Can be an advantage or disadvantage:
The owner's tax rate is based on business profitability; lower profits lead to a lower tax rate than corporate rates. Conversely, higher profits subject the owner to a higher tax rate, which may result in a greater tax burden than corporate structures.
State the advantage/disadvantage of Capital Requirements of a company.
Can be an advantage/disadvantage:
A company is a suitable form of ownership, regardless of the size of the business.
State the advantage/disadvantage of Management and Control of a company.
Can be an advantage/disadvantage:
Separation of ownership and management can lead to professional management practices.
Define CSR.
Corporate Social Responsibility
A company's overall commitment to operate in an ethical and sustainable manner.
(Often involves the social, environmental, and economic impacts of business decisions.)
Define CSI.
Corporate Social Investment
A specific strategy within CSR where companies invest resources in social and environmental initiatives.
(Often involves addressing specific social issues like poverty, education, and healthcare.)
State at least 5 social responsibility areas.
Poverty
Crime
Lack of Education
Poor Health Services
Lack of/Poor Infrastructure
Unemployment
Inequalities + Human Rights Issues
Economic
Environment
State the 3 Ps of the Triple Bottom Line.
Profit
People
Planet
How can a business apply the triple bottom line to ensure that they are ethical and sustainable?
Profit:
A business must ensure that they are profitable, otherwise they are not sustainable.
All profit should not be distributed to internal stakeholders, a percentage must be invested in CSR campaigns.
A business needs to be ETHICAL and provide audit trails to ensure that they are transparent, accountable and compliant.
People:
A business must consider how their actions impact all their stakeholders.
A business should het involved in CSR activities that uplift the community in which they operate.
A business can get involved in CSR by providing healthcare to their workers, fair working hours and conditions as well as opportunities for growth within the company.
Planet:
A business should aim to minimise its carbon footprint.
A business can get involved in recycling etc. and buy into the 'going green' concept. Consumers tend to support businesses who are environmentally responsible and this will in turn increase the profits of the business.
What is considered ‘Going Green’
Reduce energy usage
Disposing of toxic waste safely
Not being involved in the production of goods that are unhealthy or unsafe for the environment or the people.
State all seven of the principles of the King Code 2 and explain how two of them can apply to contribute to good corporate governance.
Transparency
Accountability
Taking responsibility for one’s actions. accountability increases the level of confidence that stakeholders have in the business decisions taken.
Integrity or Honesty
Truthfulness will influence people or corporations to do the right thing because of the consequence of disciplinary action.
Independence
Discipline
Social Responsibility
Fairness in dealing with Stakeholders
Responsibility of Directors
What are a business’ level of responsibility and what do they entail from the business?
Primary
The business’s obligation to look after the interest of stakeholders which are directly affected by the success of the business.
Secondary
The business’ obligation towards stakeholders who are indirectly affected by the business’s activities, e.g. the community, government and the environment.
State Blowfield and Murray’s tool to measure the level of responsibility.
A pyramid.
From TOP to BOTTOM it reads:
Discretionary Responsibility
Ethical Responsibility
Legal Responsibility
Economic Responsibility
Explain each of Blowfield and Murray’s levels of responsibility.
Discretionary Responsibility
A business’ responsibility to not harm others and build a brand that has values and practices giving back to the community.
Ethical Responsibility
The business has to ensure it is making ethically sound business decisions that will not have a negative impact on stakeholders and the sustainable future of society and the environment.
Legal Responsibility
All businesses have the responsibility to ensure it is respecting the laws of the country in which it operates.
Economic Responsibility
A business is responsible to ensure that it is economically active, i.e. it produces goods / services that can be sold at a profit and from which employees and shareholders will benefit.
State at least 2 Argument for CSR.
Community members will become brand loyal to the business because of all the good work they have done within their community.
If businesses assist the community to increase its standard of living through education and health programs, it will benefit from a community that has a higher standard of living and a higher level of disposable income.
Investing resources into a community issue will cause less people to relocate and benefit the business by eradicating crime, which will make customers have more money to spend.
State at least 2 Argument against CSR.
CSR can distract a business from its core business activities.
Shareholders may think that investing in CSR is not profitable.
It is difficult to measure the benefits of CSR.
State the 4 elements of CSR sustainable business practice.
Making Operations Environmentally Sustainable
Making Operations Socially Sustainable
Making Society Sustainable
Influencing Suppliers
State all 9 steps to designing a CSR program.
Managements communicates need for CSR across business.
Management creates CSR policy.
Management communicates CSR policy throughout business and buy-ins take place.
Management links CSR policy to business success factors.
Employees brainstorm CSR initiatives.
CSR program is planned and necessary skills and resources are implemented.
Implement CSR project(s).
Monitor CSR initiatives.
Make necessary changes or brainstorm again.
State and explain the 6 principles of Implementing a CSR strategy.
Concepts of Citizenship
The business’ position within a community and its responsibility to different stakeholders.
Strategic Intent
How CSR forms part of the core values of the business i.e The business has to define what the purpose of the CSR initiative is going to be.
Leadership
CSR initiatives could be either offensive or defensive or a combination of the two.
Structure
CSR activities must be planned, organised, driven and controlled by management to ensure CSR goals are met.
Stakeholder Relationship
Has to maintain sound relationships with both internal and external stakeholders through communication.
Transparency
Communication to all stakeholders. Contingency plans must be put in place to overcome negative events or failures.
Define Environmental Scanning.
The process of obtaining information about possible current and future events that may have an impact on the performance of the business.
Which environment(s) make up the external environment of a business and how do we analyse them?
Macroenvironment and Market Environment.
Macroenvironment uses PESTLE to identify Opportunities and Threats.
Market Environment uses Porter’s model to identify Opportunities and Threats.
Which environment(s) make up the internal environment of a business and how do we analyse them?
Microenvironment.
Identify Strengths and Weaknesses.
Why are strengths and weaknesses considered to be internal to a business?
Because the business has complete control over them.
State at 4 strengths of a business.
Competitive Price
Location
Patent
Product Differentiation
Skilled Workforce
Business Culture
Good Marketing and Strong Brand
Access to finance and other resources
Operational efficiency and good quality
State at least 2 factors that contribute to the location of a business.
It is important that customers should have easy access to the business. Look at the availability of parking.
Security is an important aspect to consider, otherwise customers may not feel safe to come into the business.
The type of business has to “fit in with the neighbourhood”.
Also consider how a complementary business in close proximity may be considered a strength.