Unit 3 Study Guide
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
251 Terms
Cnidaria
Phylum of Eumetazoans “True animals”; have embryonic germ layers
Gastrodermis
the lining membrane of the alimentary tract of an invertebrate
Gastrovascular cavity
A central cavity with a single opening in the body of certain animals, including cnidarians and flatworms, that functions in both the digestion and distribu- tion of nutrients
Polyp
Mostly sedentary, can detach from surface; oral surface faces up; e.g. sea anemone, hydras
Oral surface
The surface of the body of an echinoderm where the mouth is situated; usually on the ventral side
Medusa
oral surface faces down; moves by drifting freely or body contractions; e.g. jellies
Cnidocytes
Stinging cells used for defense and capture of prey
Nematocysts
Organelle in Cnidocytes that eject a stinging thread to entangle or paralyze prey; some extremely harmful to humans
Medusozoa
Most spend majority of life in medusa form; jellies, box jelly, Portuguese Man O’ War
Anthozoa
exist only in polyp form; sea anemone corals; form symbiosis with zooxanthellae algae
Exoskeleton
a polyp secretion of hard calcium carbonate
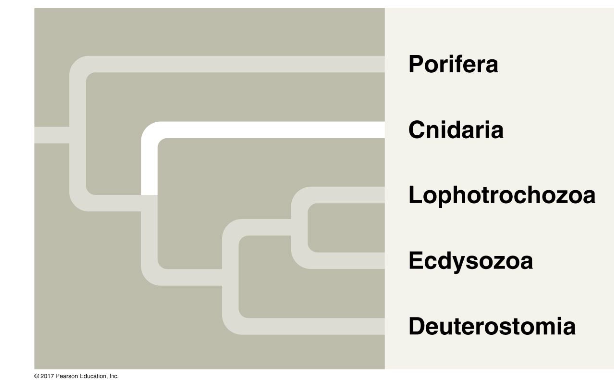
Lophotrochozoa
Bilateral animals with protostome development
Lophophore
ciliated feeding structure around mouth
Trochophore
a type of developmental larval stage
Platyhelminthes
“Flatworms” in Lophotrochozoa; Acoelomates; live in aquatic and damp terrestrial environmentsl; lack circulatory system; some species are free-living and others are parasites

Pharynx
extended through mouth to feed and take up food. Undigested waste ejected here too
Turbellaria
Platyhelminthes; free-living carnivores; aquatic and terrestrial flatworms; move by undulation or gliding along secreted mucus layer; Planarians common in ponds and streams; some reproduce asexually by splitting down the middle

Cestoda
Platyhelminthes; tapeworms; parasites of vertebrates
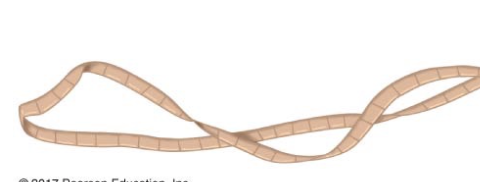
Scolex
on anterior end, has hooks and suckers attach to intestinal lining of host; absorb nutrients from host through body, causes malnutrition
Proglottids
repeating sacs containing sex organs; sexual reproduction fills up with fertilized eggs; are shed in feces
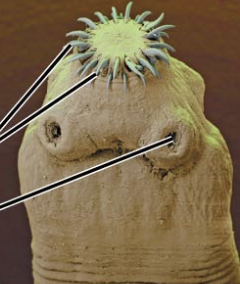
Syndermata
Rotifers; Microscopic “wheel animals”; live in freshwater, marine and damp soil environments; multicellular but smaller than most protists; pseudocoelomates; reproduce via parthenogenesis
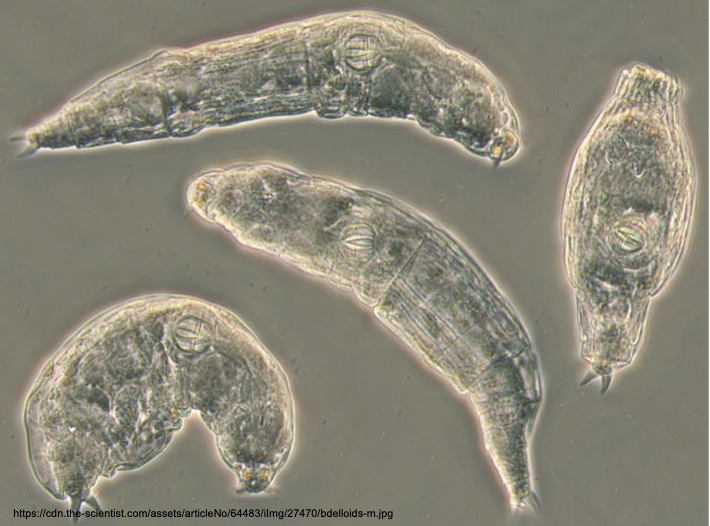
Rotifer
a tiny aquatic animal that is smaller than many unicellular protists
Alimentary canal
A complete digestive tract consisting of a tube running between a mouth and an anus.
Parthenogenesis
when females produce unfertilized eggs that develop into new females (asexual). Some species lack males entirely
Annelida
Segmented worms; live in aquatic and damp soil environments; Coelomates; have circulatory system, and alimentary canal; well developed nervous system; most have chaeta; segmented internally and externally
Chaeta
external bristles made of chitin; esp. on an annelid worm
Errantians
highly mobile marine worms
Sedentarians
less mobile worms; includes earthworms and leeches
Parapodia
lateral ‘paddles’ with several chaeta; used for movement and gas exchange

Hirudin
an anti-coagulant leeches inject
Earthworm
Annelid; Has a digestive system, nervous system, circulatory system; divided with septa; metanephridia; monoecious
Septa
partitions between segments
Metanphridia
used for waste removal and osmoregulation; invertebrate kidneys
Aboral Surface
The surface of the body of an echinoderm where the anus is situated; typically on the posterior side
Cnidarian Characteristics
Diploblastic; 10,000 species; Jellies, hydra, and corals; Radial symmetry
Cnidaria Anatomy
Diploblastic (epidermis and gastrodermis); Two body forms (Polyp and Medusa); No head or brain (rely on nerve net); Ring of tentacles around mouth/anus captures food and pushes into gastrovascular cavity
Diploblastic
To have two tissue types
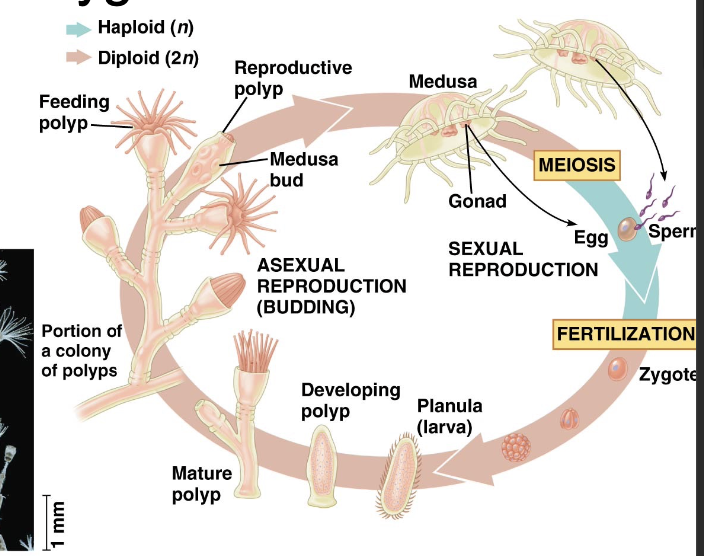
Cnidaria Phylogeny
Medusozoa: majority of life in medusa form
Anthozoa: exist only in polyp form
Corals
Anthozoa; live in colonies; excrete exoskeleton; symbiosis with zooxanthellae algae; also trap zooplankton in tentacles
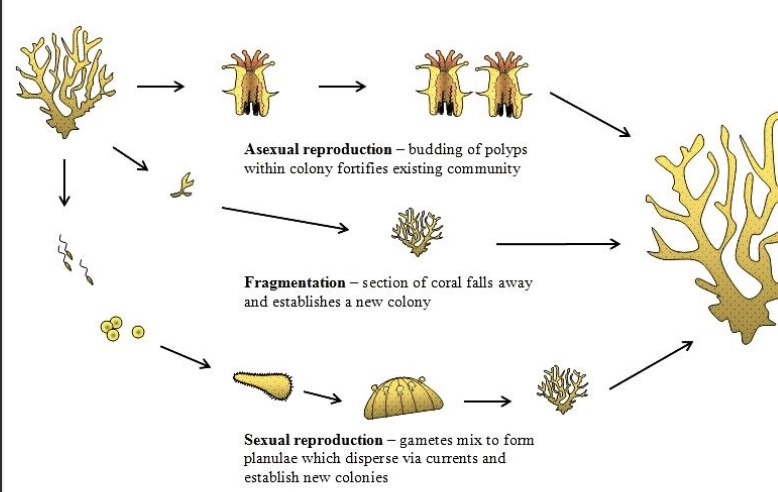
Medusozoa Reproduction
Polyp form (adult) produces tiny medusae via asexual budding. Medusae’s gametes fuse to produce zygote
Anthozoa Reproduction
Corals may reproduce sexually or asexually; coral spawning is when corals release eggs and sperm at the same time
Root
anchors plants in the soil, absorbs minerals and water, and stores carbohydrates
Lateral Root
a root that arises from the pericycle of an established root; spreading branch roots
Taproot system
Eudicot; one main vertical root, may be used for storage (e.g. carrot)

Fibrous root system
Monocot; many thin, branching roots with many lateral roots. Combats soil erosion

Root hair
tiny extension of a root epidermal cell growing just behind the root tip; increase surface area for absorption capability
stem
elongate the plant, elevate leaves and reproductive structures
Node
point of leaf attachment
Internode
stem sections between leaves
Apical bud
location of active cell division at shoot tips
Axillary bud
located at nodes, form lateral branches, thorns, etc.
Leaf
main photosynthetic organ in plants
Blade
broad portion of leaf
Petiole
joins leaf to the stem at a node
Dermal Tissue
outer protective covering, may be green, herbaceous, woody, etc.
Vascular tissue
xylem and phloem, found in a single cluster in roots or as vascular bundles in stems and leaves
Vascular bundles
clusters of xylem and phloem
Ground tissue
between dermal and vascular tissue; performs photosynthesis and storage
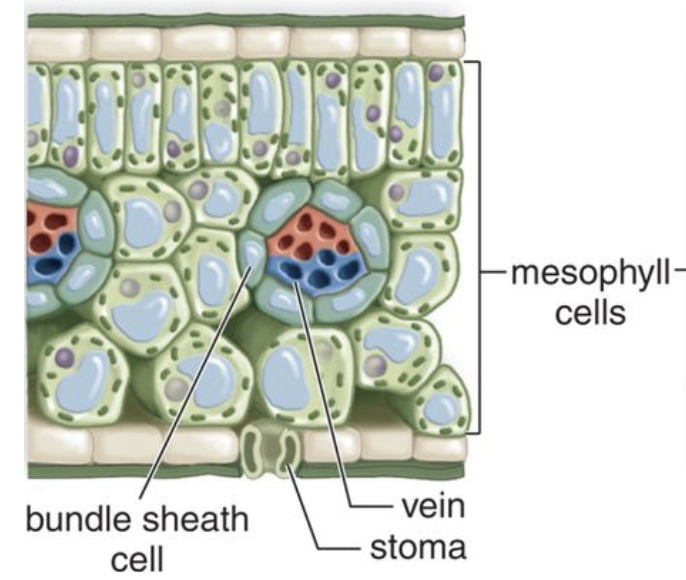
Guard cells
dermal tissue; pair of curved cells that surround stomata; open and close stomata by contracting and expanding
Xylem
moves water and minerals up from the roots
Tracheids
long, thin, tapered dead cells with pits that allow water to move through; in all vascular plants
Vessel elements
wider, shorter dead cells with perforated ends; in most angiosperms and some gymnosperms
Phloem
moves sugars down to other parts of the plant (e.g. roots)
Sieve-tube cells
living cells that make up ______; lack nucleus and ribosomes
Companion cells
cells connected to, and support metabolism of sieve tube elements
Active transport
pumping and cotransporting solutes across the cell membrane; traveling up the concentration gradiant
Passive transport
solutes flowing through ion channels and carriers down the concentration gradient
Osmosis
act of water molecules entering and exiting cells; includes Hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions
Parenchyma
cells with thin, flexible walls; contain large vacuole; used for photosynthesis (mesophyll of leaves) and storage (roots, fruits, etc.)
Apoplastic route
Movement outside cell membranes; through extracellular spaces and through dead xylem vessels
Symplastic route
movement of the cytosol continuum via plasmodesmata of interconnected cells
Casparian strip
waxy belt blocks apoplastic routes into the xylem; forces a merge into symplastic route
Xylem sap
water and minerals being transported
Bulk flow
xylem sap being transported long distances by pulling it up the plant
Transpiration
loss of water from leaves via bulk flow
Cohesion-tension hypothesis
as water molecules evaporate out of stomata they pull up the water molecules behind them with their hydrogen bonds
Stomata
Pore in epidermis of plant that allows gas exchange between environment and interior of plant; opening regulated by guard cells that either traps water or allows transpiration
Translocation
the phloem transport of sugar from sources to sinks
Phloem sap
sugar, amino acids, and vitamins
Sugar sources
organs that are net producers of sugar (e.g. mature leaves)
Sugar sinks
organs that are net consumers or depositories of sugar (e.g. growing buds and leaves, roots, stems, and fruits)
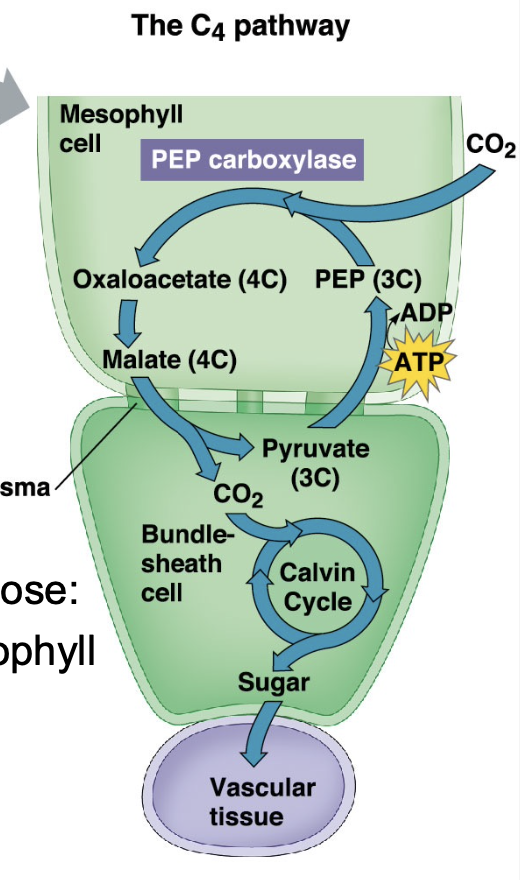
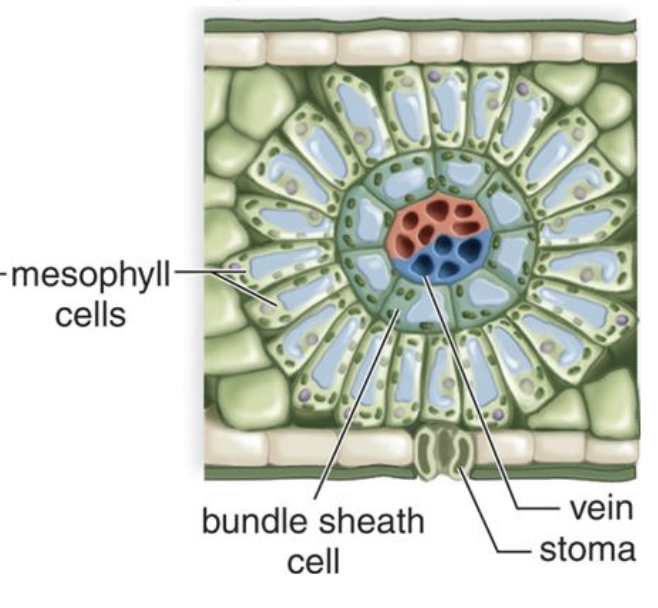
C4 photosynthesis
Hot/dry conditions when stomata partially close: CO2 is fixed by PEP carboxylase in Mesophyll cells as Oxaloacetate. Malate transported into bundle sheath cells; delivers CO2 to Rubisco
C3 plant leaf anatomy
Vascular plants’ two organ systems
Root system and Shoot system
3 types of plant tissues
Dermal tissues, Vascular tissues, Ground tissues
Pavement cells
dermal tissues; flat cells of epidermis; protect inner cells and generally lack chloroplasts (not active photosynthesizers)

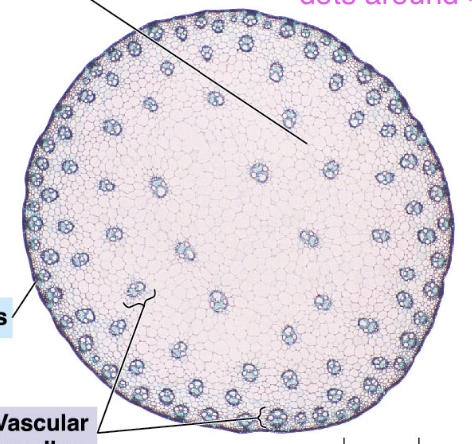
Monocot cross-section
scattered vascular bundles; little faces
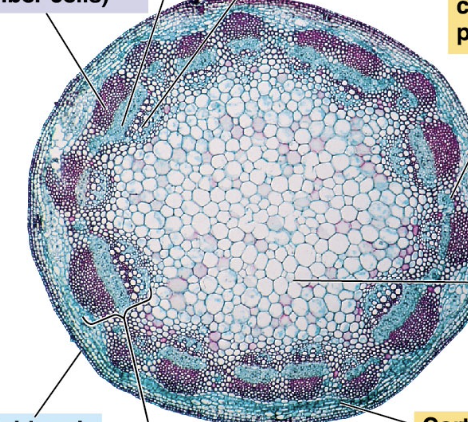
Eudicot cross-section
vascular bundles in a ring
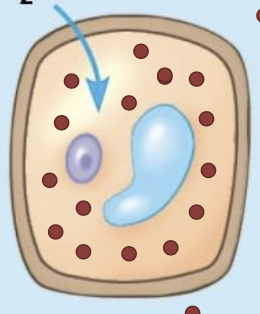
Hypotonic solution
A solution that will cause the cell to take up water; leads to turgid (normal) cell
Isotonic solution
A solution that causes no net movement of water into or out of a cell; leads to flaccid cell
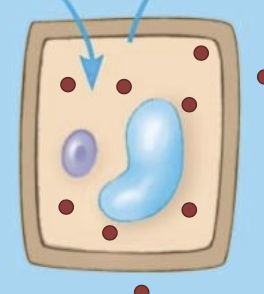
Hypertonic solution
A solution that will cause a cell to lose water; leads to plasmolyzed cell
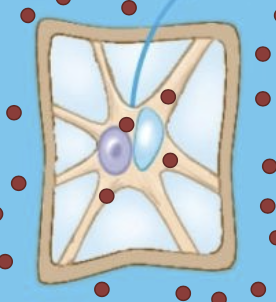
Long distance transport
Apoplastic route and Symplastic route
Short distance transport: Solutes
Movements of solutes and water across cell membranes; active and passive transport
Short distance transport: Water
water enters and exits cells via osmosis
C4 plant leaf anatomy
Heterotrophic
Must obtain organic compounds by consuming biomass. Ingest food and digest it inside the body.
Tissues
group cells that develop from embryonic layers and work as a unit
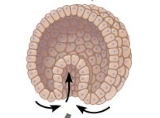
Blastula
A hollow ball of cells that marks the end of the cleavage stage during early embryonic development in animals
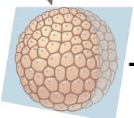
Gastrulation
The reorganization of cells into embryonic germ layers; a series of cell and tissue movement in which the blastula-stage embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo