Chem 116 Exam 4 WVU
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What does ∆S0 < 0 mean?
Entropy/disorder is DECREASING
∆S0 is negative
Which factors INCREASE entropy? ∆S0 > 0
MORE particles forming
A solid turning into a liquid or gas. A liquid turning into a gas.
A mixture being combined into the same area
What’s the formula for Δ S0rxn?
ΔSrxn∘=∑νiSproducts∘−∑νiSreactants∘
vi = Stoichiometric coefficient for that substance
What’s Gibbs Free Energy equation?
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
ΔH: Enthalpy change (essentially the sum of energy and pressure in a system)
T: Temperature in Kelvin
ΔS: Entropy change
What does ΔG < 0 mean?
Reaction is spontaneous
What does ΔG > 0 mean?
Reaction is nonspontaneous
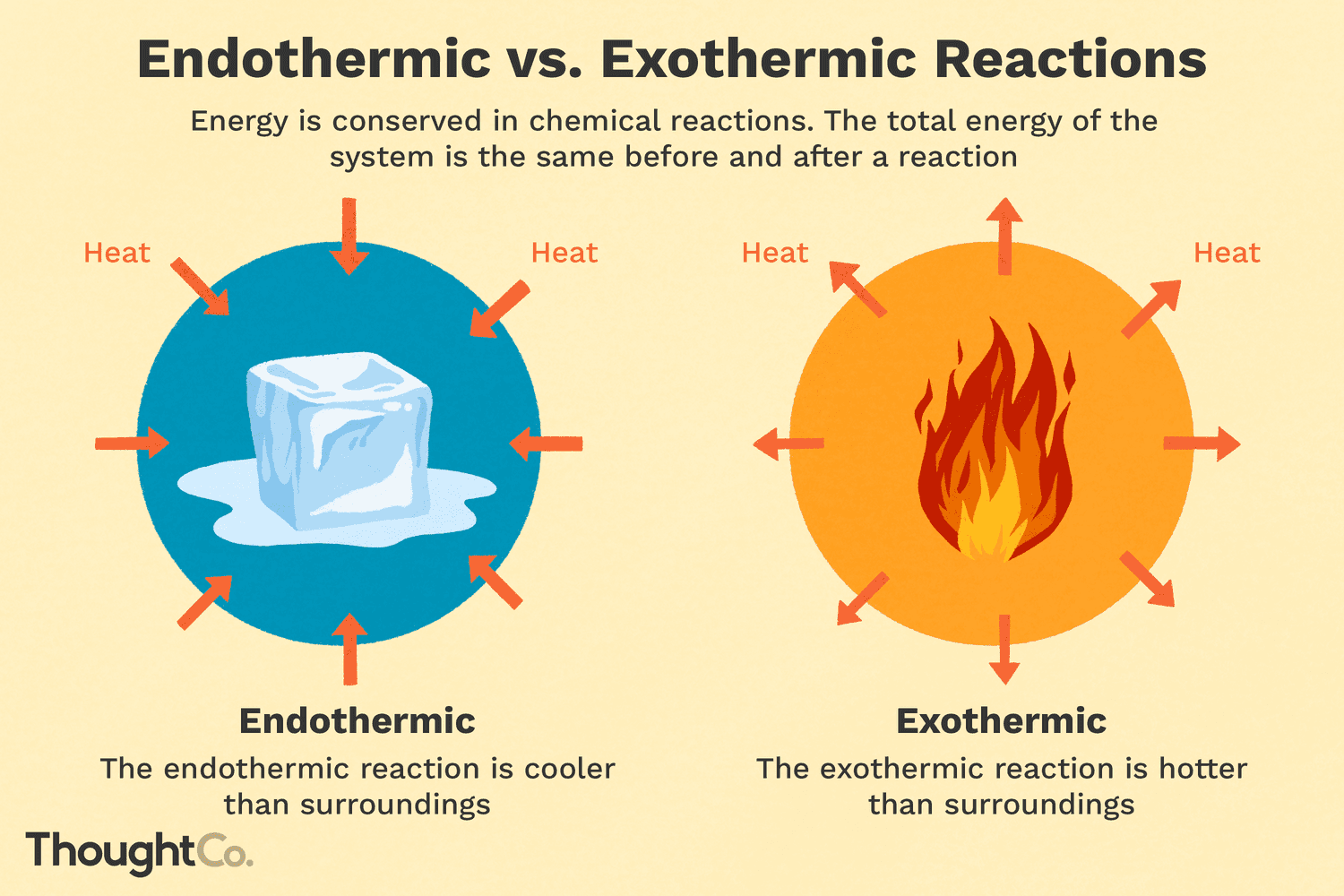
Endothermic
Heat is absorbed and enters the substance. The substance is cooler than the enviornment
ΔH > 0
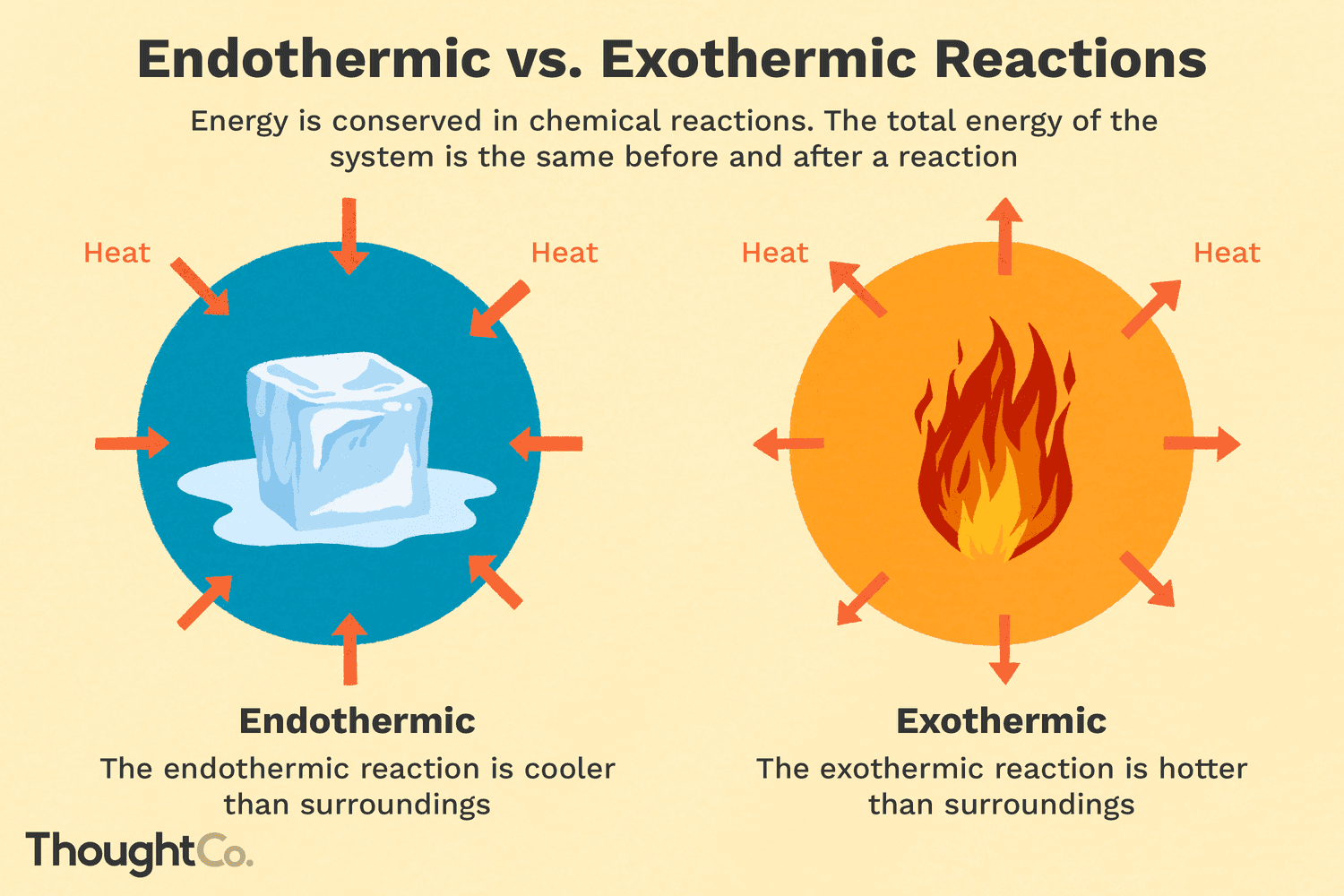
Exothermic
Heat exits to be absorbed by something else. Substance is hotter than the environment
ΔH < 0
What’s the formula for ΔH°rxn?
ΔHrxn∘=∑ΔHfproducts∘−∑ΔHfreactants∘
Whats the formula for ΔG° (Gibbs free energy under standard conditions)?
ΔG° = -RTlnK
R: Gas constant
K: Equilibrium constant
Alpha (a) decay
Emits an alpha particle (4/2He)
Decreases the atomic number (Z) by 2
Decreases the mass number (A) by 4
Beta-minus (B-) decay
Emits an electron (e-)
Increases the atomic number by 1. Turns a neutron into a proton.
No change to mass number
Beta-plus (B+) decay
Emits a Positron (e+)
Decreases the atomic number by 1. Turns a proton into a neutron
No change to mass number
What’s the formula for finding out how many half-lives have passed (n)?
n = total elapsed time/half life of the isotope
What’s the half life formula?
N = N0 (1/2)n
N0: Initial number of atoms
n: Number of half lives elapsed
What’s the mass defect equation?
(Mass of however many protons + neutrons are in the particle) - total mass of the particle
“Particle” refers neutrons (1/0n) and alpha particles (4/2He)