Lecture 4 Salivary Glands
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What are exocrine glands?
Glands that secrete products directly into a location via a duct.
What are the four characteristics used to classify exocrine glands?
Duct system, shape of secretory unit, mode of secretion, and nature of secretion.
What is the difference between simple and compound ducts?
Simple ducts do not branch, while compound ducts have branching.
1.
If you are looking at a gland under a microscope and see that the main duct branches into several smaller 'stems' like a tree, how would you classify its duct system?
Compound
Which type of secretion is described as 'thin and watery' and often contains enzymes?
Serous
What are the two shpaes of secretory units?
Multicellular and unicellular
Example of unicellular
Goblet cells
Examples of multicellular
Tubular, alveolar/acinus
Which gland type releases its product through exocytosis, leaving the secretory cell completely undamaged?
Merocrine
In a mammary gland, the secretory product contains small amounts of the cell's cytoplasm because the top part of the cell detaches. This is called:
Apocrine secretion
What is the mode of secretion for merocrine glands?
Secrete products through free surface with no loss of cytoplasm (e.g., salivary glands).
What is the mode of secretion for apocrine glands?
Secrete small amounts of cytoplasm with the secretory product; the apical portion pinches off
What is the mode of secretion for holocrine glands?
Entire cells are discharged as secretion
What are the three types of secretion in salivary glands?
Serous, mucous, and mixed.
What type of secretion contains mucin and is cloudy?
Mucous secretion.
If a salivary gland contains both serous and mucous cells, it is classified as a:
Mixed gland
What type of secretion is characterized by clear, watery fluid with protein?
Serous secretion.
Which type of secretion is specifically responsible for starting the digestion of carbohydrates in the oral cavity?
Serous
What is the functional unit of the salivary gland?
The alveolus or acinus.
What are the three major salivary glands?
Parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
What specific type of epithelial tissue makes up the single layer of secretory cells in an acinus?
Simple cuboidal epithelium
The 'lumen' of the acinus is best described as:
The central opening where saliva is deposited.
Where is an acinus located in relation to the rest of the glandular system?
At the terminal part of the duct system.
If multiple acini are grouped together within a larger section of a gland, that section is called a:
Lobule
If you are looking at a partition of connective tissue located specifically between two lobules, what is it called?
Interlobular septum
Which duct is the very first one to receive saliva directly from the acinus?
Intercalated Duct
Which duct type is characterized by 'striations' caused by a high concentration of mitochondria?
Striated Duct
What is the specific function of the striated duct beyond serving as a passageway?
Resorbing and excreting electrolytes.
As the excretory duct approaches and enters the oral cavity, what is the final type of epithelium it becomes?
Stratified Squamous
Match the duct to its lining: Which duct is lined with simple cuboidal epithelium and serves only as a passageway?
Intercalated Duct
Why does the excretory duct change from pseudostratified to stratified cuboidal and finally to stratified squamous?
To provide increasing protection as the duct reaches the oral environment.
What is the primary purpose of the connective tissue capsule in a salivary gland?
To provide support and protection for the lobes and lobules.
Approximately what percentage of total daily saliva is produced by the three pairs of major salivary glands?
90%
What is the specialized arrangement called when serous cells form a 'half-moon' cap over mucous cells?
Serous demilunes
How do minor salivary glands typically deliver their secretions to the oral cavity?
Directly into the oral cavity via very short ducts.
The 'functional unit' of a salivary gland, where the saliva is actually manufactured, is known as the:
Acinus (or Alveolus)
Which cell type is responsible for the 'clear, watery' portion of saliva often containing digestive enzymes?
Serous cells
A gland classified as 'compound tubular-alveolar' has which type of structure?
Branching ducts with a mix of tube-shaped and rounded secretory units.
Where is the parotid salivary gland located?
Behind the mandibular ramus, anterior and inferior to the ear.
What duct does the parotid gland use?
Stenson's duct.
What is the primary secretion type of the parotid gland?
Mainly serous, contributing approximately 25% of saliva.
Where is the submandibular salivary gland located?
In the floor of the mouth, posterior to the sublingual gland.
Which muscle does Stenson's duct pierce through to enter the oral cavity?
Buccinator muscle
The Parotid Papilla, the opening of Stenson's duct, is located opposite which tooth?
Maxillary 2nd molar
What is the unique characteristic of the internal duct system within the parotid gland?
Long intercalated ducts and short striated ducts
Where is the parotid gland located in relation to the ear?
Anterior and inferior
Mumps is?
Viral infection of the parotid gland
What duct does the submandibular gland use?
Wharton's duct.
What is the primary secretion type of the submandibular gland?
Mixed, but serous dominates, contributing approximately 60-65% of saliva.
Which of the following describes the anatomical location of the submandibular gland relative to the sublingual gland?
Posterior
The submandibular duct, also known as Wharton's duct, opens into the oral cavity at which specific landmark?
Sublingual caruncle
Which gland is responsible for the largest portion of total salivary volume, contributing approximately 60 to 65%?
Submandibular gland
How does the internal duct system of the submandibular gland compare to that of the parotid gland?
It has short intercalated ducts and long striated ducts.
Where is the sublingual salivary gland located?
In the floor of the mouth, anterior to the submandibular gland.
The submandibular gland is classified as a mixed gland. Which type of secretion is dominant in its output?
Serous
What is the clinical significance of the sublingual caruncle?
It is where the submandibular duct (Wharton's duct) exits.
Which of the following describes the capsule of the submandibular gland?
Medium capsulated
What is the primary secretion type of the sublingual gland?
Mainly mucous, contributing approximately 10% of saliva.
Which of the following is a unique structural feature of the sublingual gland compared to the parotid and submandibular glands?
It is the only gland that is unencapsulated.
What is the dominant type of secretion produced by the sublingual gland?
Mucous
Where do the 8-30 minor sublingual ducts (Ducts of Rivinus) empty into the mouth?
Along the sublingual fold on the floor of the mouth.
The main duct of the sublingual gland that often joins Wharton's duct at the caruncle is called:
Bartholin's duct
What are minor salivary glands?
Glands that empty their products directly into the oral cavity by short ducts.
What is xerostomia?
A condition of dry mouth due to decreased salivary flow.
What is a mucocele?
An accumulation of saliva in the mucosa due to trauma to a minor salivary duct.
What percentage of total salivary volume does the sublingual gland contribute?
10%
Which minor salivary gland is the exception to the rule and produces a mainly serous secretion instead of mucous?
Von Ebner's glands
Where would you find the Palatine minor salivary glands?
On the hard and soft palate
What is the primary functional role of Von Ebner's glands?
To rinse the taste buds at the circumvallate papillae.
Which of these minor glands would you find on the inner surface of the lips?
Labial glands
Most minor salivary glands share which of the following characteristics?
They produce a mainly mucous secretion.
What are Fordyce granules?
Ectopic sebaceous glands found in 60-70% of adults, considered a variation of normal.
What is a sialolith?
Salivary stones that block salivary flow.
What is Sjogren's syndrome?
An autoimmune disease that affects salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry mouth and eyes.
What is the daily saliva production in humans?
Approximately 640 ml (2.7 cups).
What are the functions of saliva?
Moistens food, begins digestion, cleanses the mouth, aids in swallowing, and regulates pH.
In which specific location are you most likely to find a mucocele during a clinical exam?
The lower lip
What is the most common primary cause for the development of a mucocele?
Trauma to a minor salivary duct
How does saliva contribute to the 'remineralization' of tooth enamel?
By providing calcium and phosphate ions.
Which enzyme found in saliva is responsible for beginning the digestion of carbohydrates?
Amylase
What is the 'favorable range' for salivary pH that allows enzymes to function correctly and protects the mouth?
6.5 to 7.5
Saliva plays a role in speech by:
Aiding in articulation and moisture for the tongue and lips.
What is the primary difference between a Mucocele and a Ranula?
A Mucocele typically involves minor glands, while a Ranula involves major glands in the floor of the mouth.
A ranula is most typically associated with which gland?
Sublingual gland
Which of the following describes the effect of xerostomia on the microbial environment of the mouth?
Bacteria flora increases significantly.
How does xerostomia typically affect the progression of periodontal disease?
The disease progresses much faster.
The rapid mineralization of plaque into a hard deposit in xerostomia patients results in an increase of:
Calculus
Which of the following is a common clinical term used interchangeably with xerostomia?
Dry mouth
Sjögren's syndrome is classified as which type of disease?
Autoimmune destructive disease
A patient with Sjögren's syndrome typically presents with which 'duo' of symptoms?
Dry eyes and dry mouth
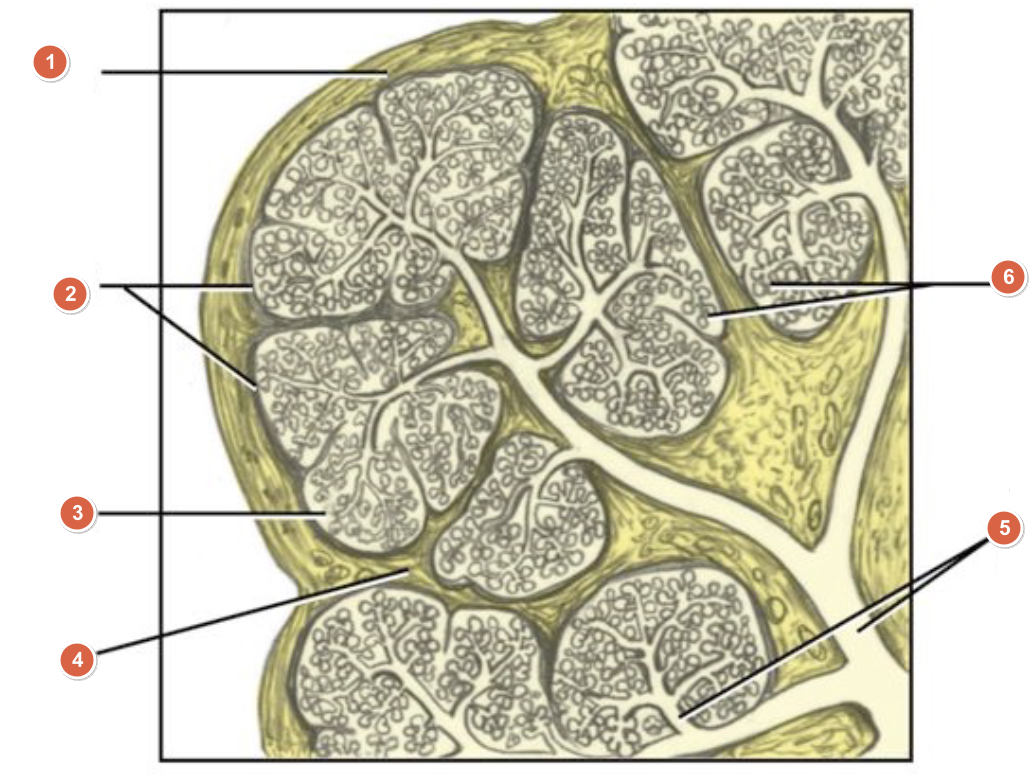
What is 1?
Capsule
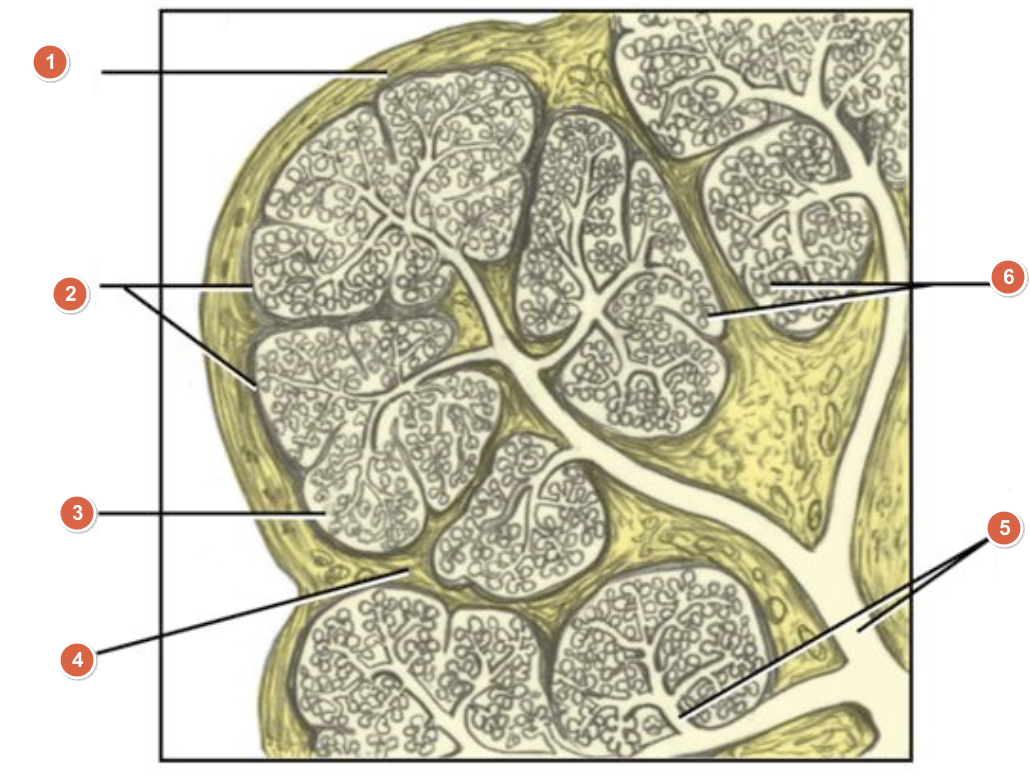
What is 2?
Lobes
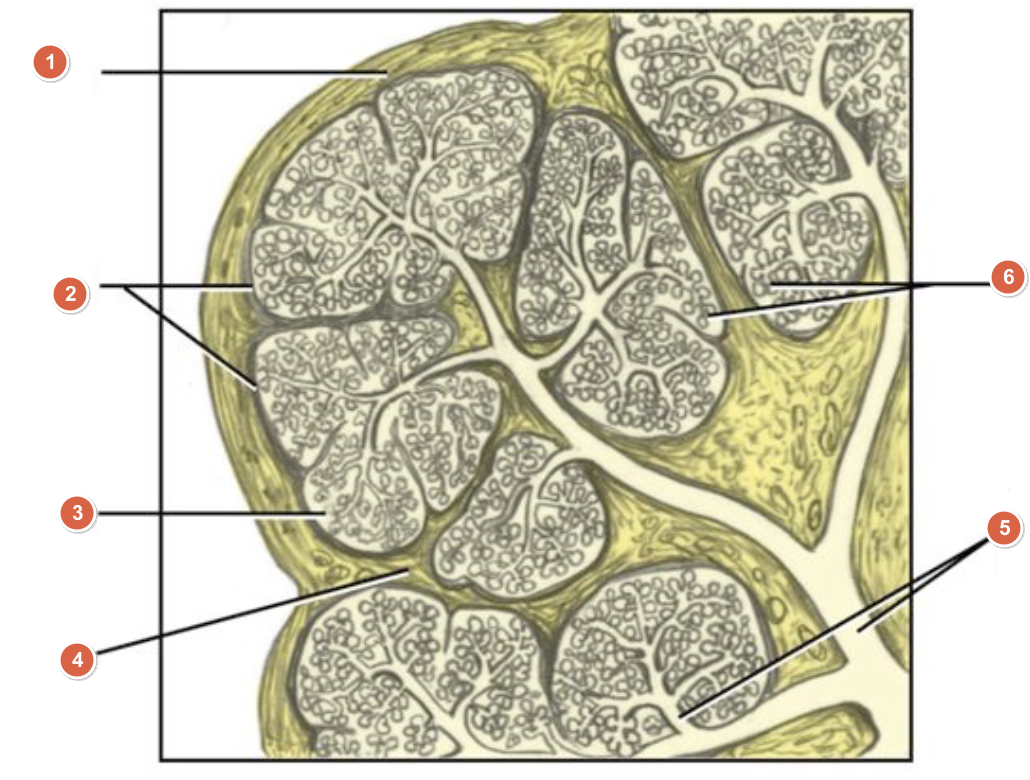
What is 3?
Lobule
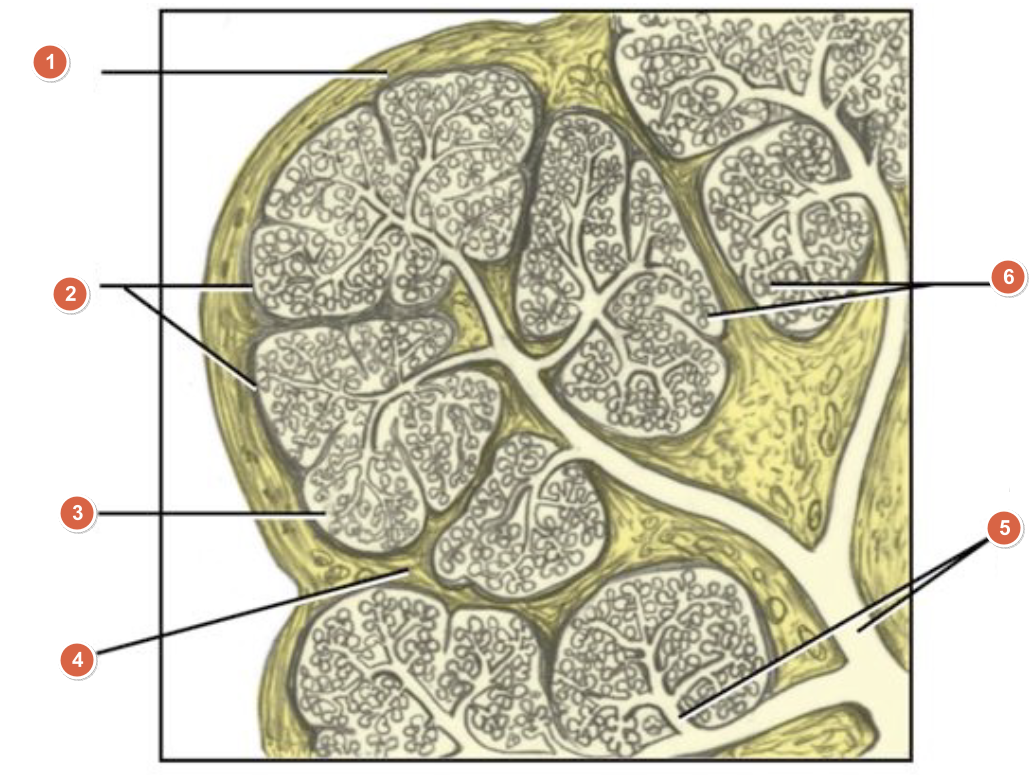
What is 4?
Septum
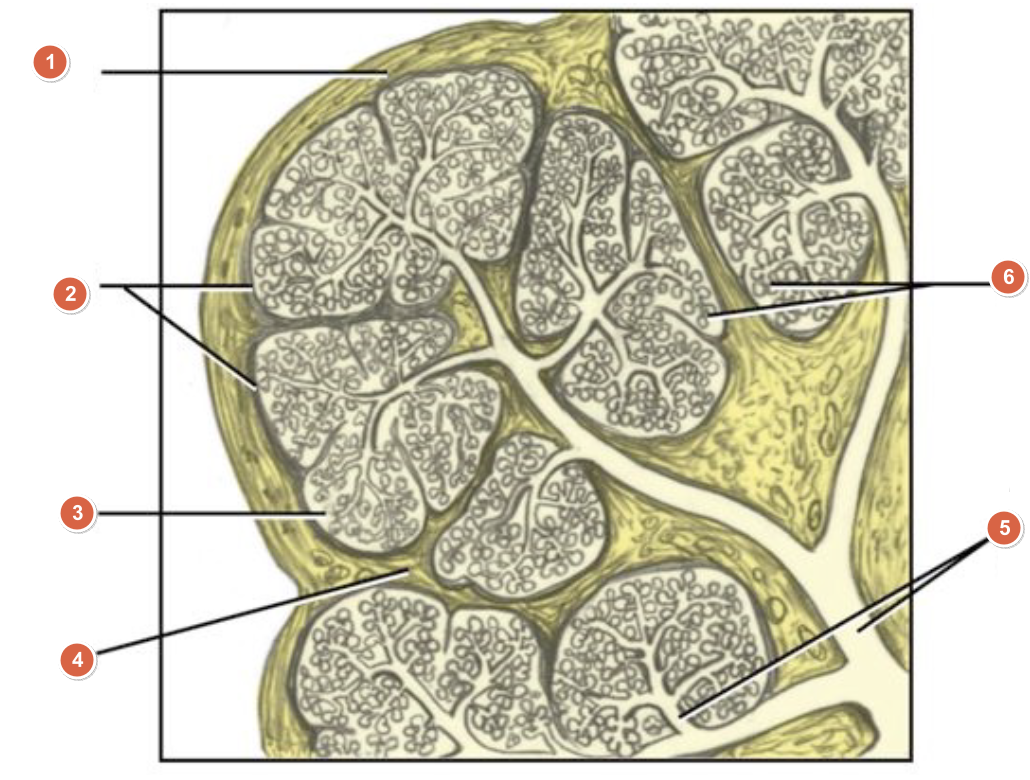
What is 5?
Duct system
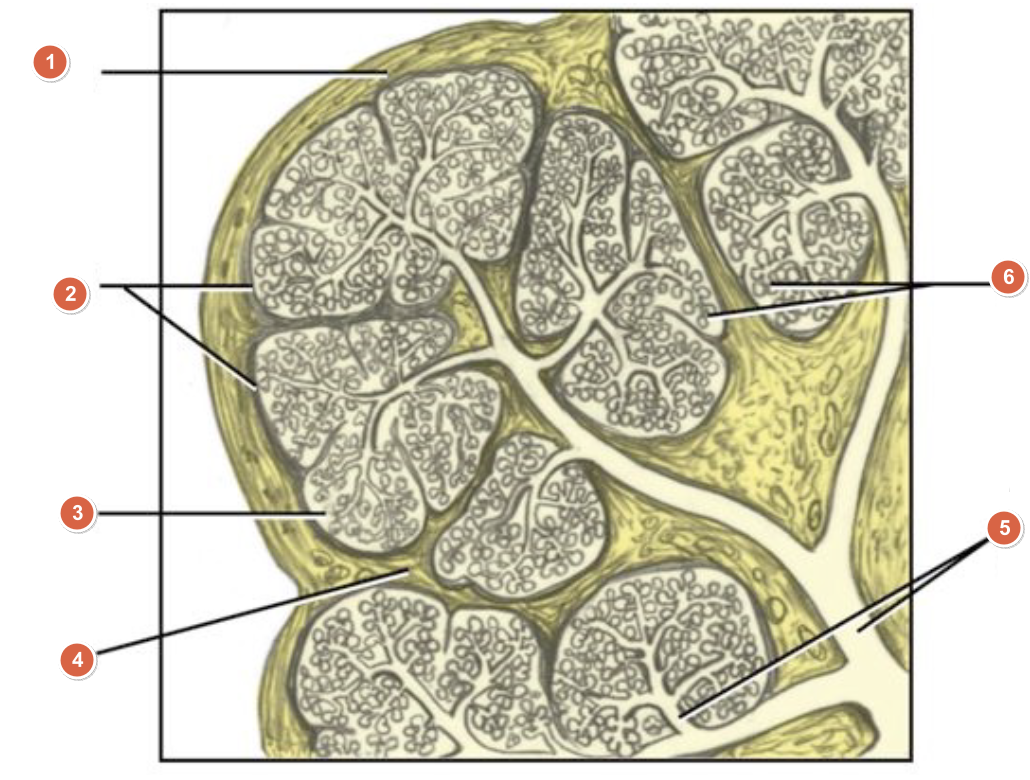
What is 6?
Acini
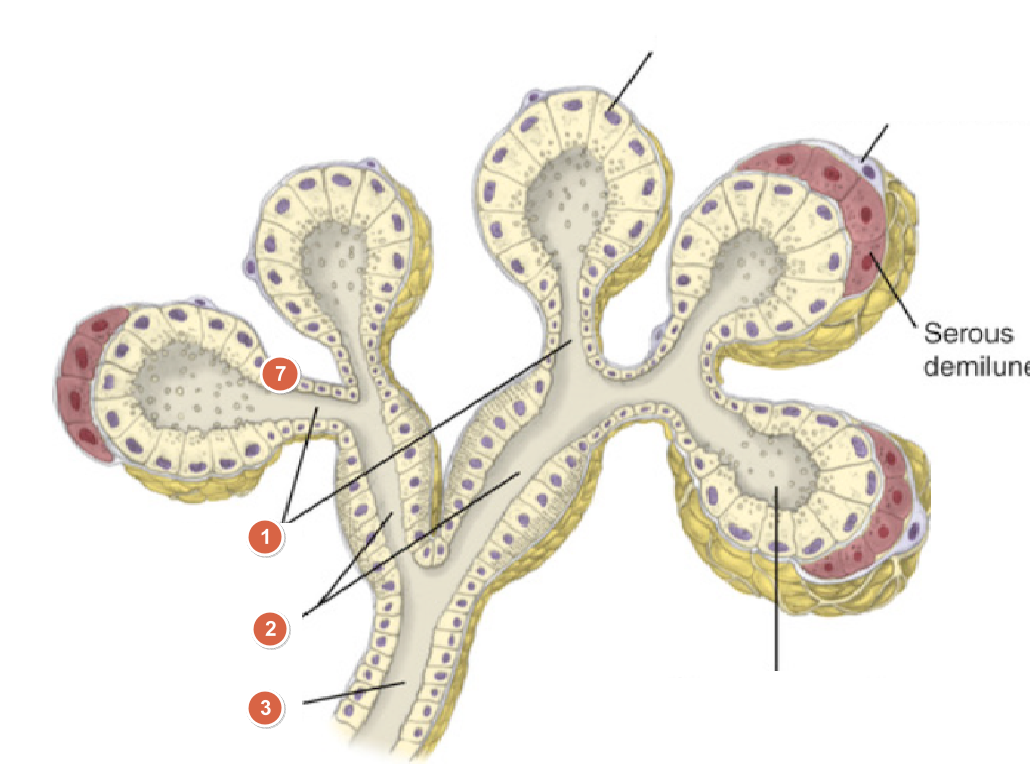
What is 1?
Intercalated ducts
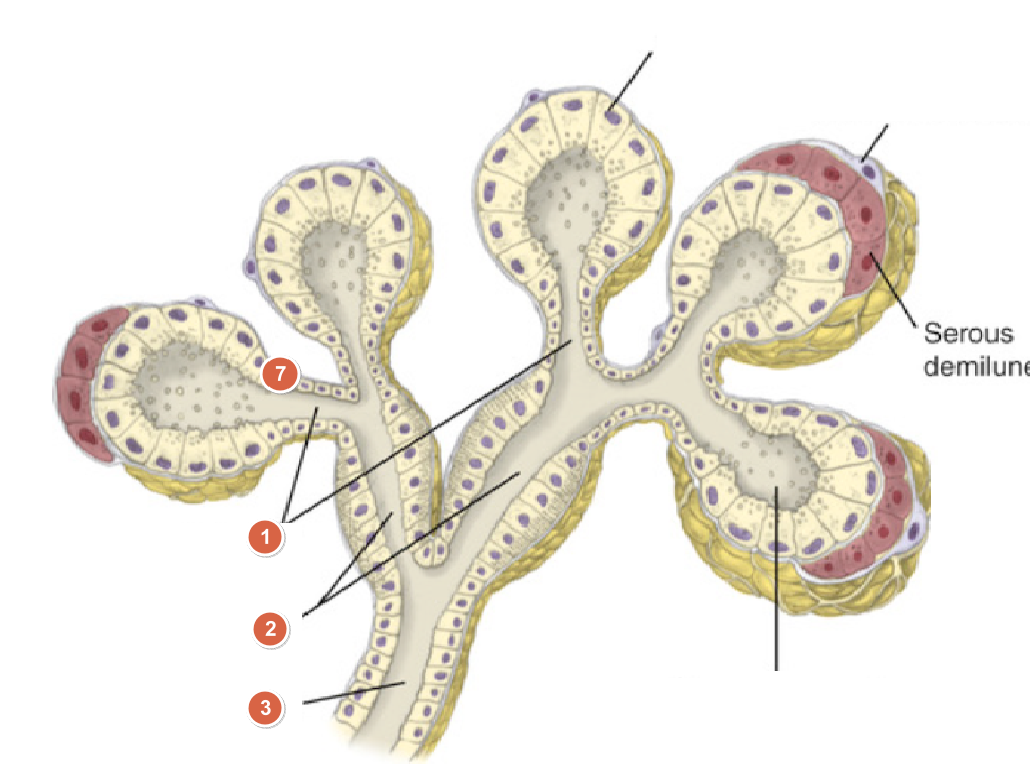
What is 2?
Stratied ducts
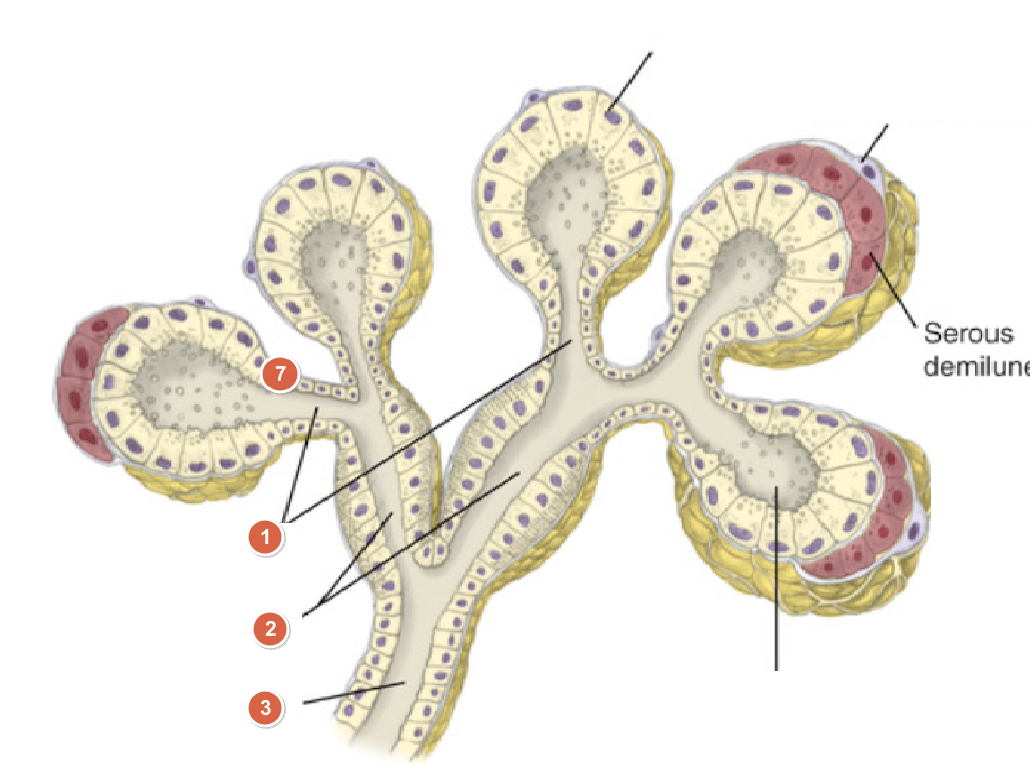
What is 3?
Secretory ducts