Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical antagonists
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
morphology of the adrenal gland from outside in
connective tissue capsule
Z.glomerulosa [aldosterone]
Z.fasciculata [cortisol] (largest part)
Z.reticularis [DHEA & estrogen]
medulla
![<ul><li><p>connective tissue capsule</p></li><li><p>Z.glomerulosa [aldosterone]</p></li><li><p>Z.fasciculata [cortisol] (largest part)</p></li><li><p>Z.reticularis [DHEA & estrogen]</p></li><li><p>medulla</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bf237775-ce6c-45b1-b4fd-ccc7ab6a6c9b.png)
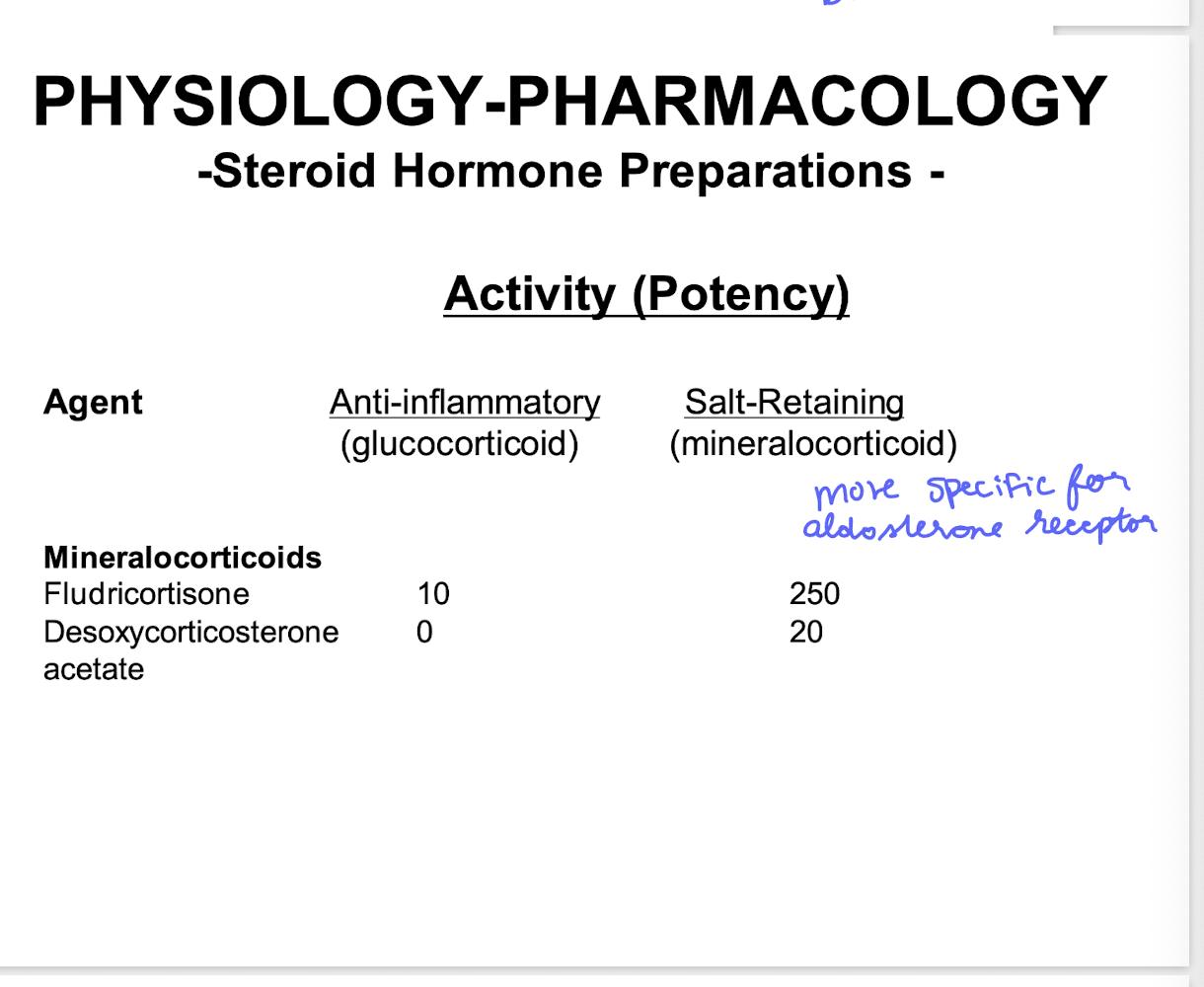
Aldosterone
steroid hormone from cholesterol
how many systems regulate aldosterone synthesis
3
what 3 systems regulate aldosterone synthesis
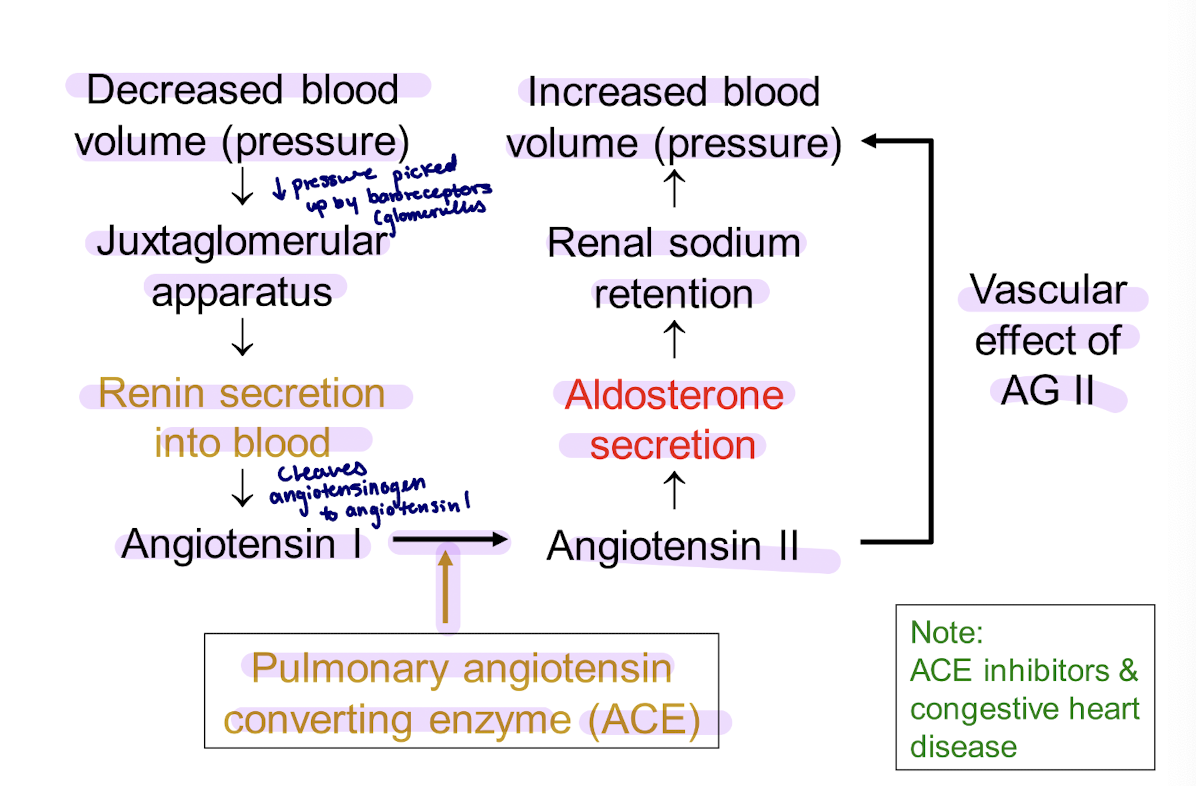
renin-angiotensin system (main system)
blood potassium levels
ACTH
what does the renin-angiotensin system regulate
Extracellular fluid (ECF) volume
steps of renin-angiotensin regulation
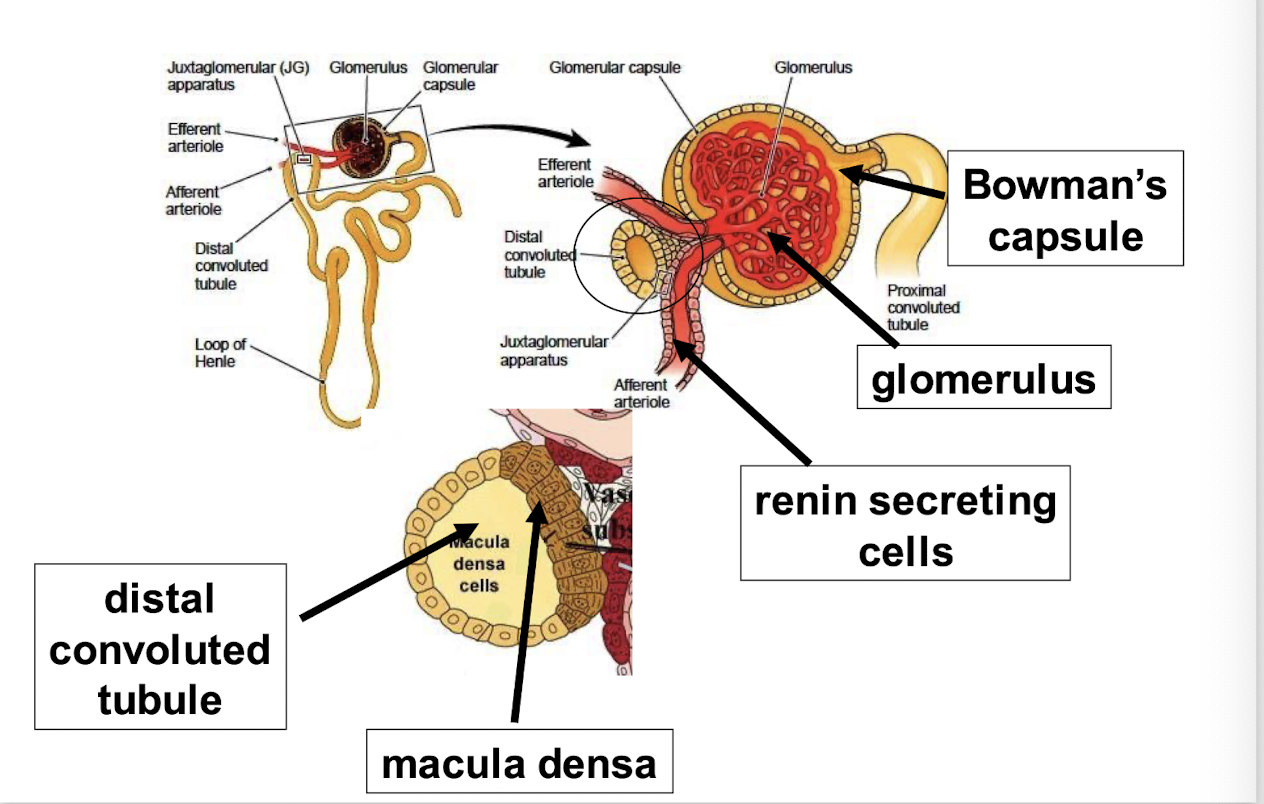
drop in ECF volume = drop in perfusion pressure at the afferent arteriole of the renal glomerulus (baroreceptor)
this stimulates the juxtaglomerular cells to secrete renin, a protease that cleaves angiotensinogen → angiotensin I → angiotensin II
angiotensin II has direct arteriolar pressure effects, and it stimulates aldosterone synthesis by binding to a G-protein coupled receptor in the zona glomerulusa
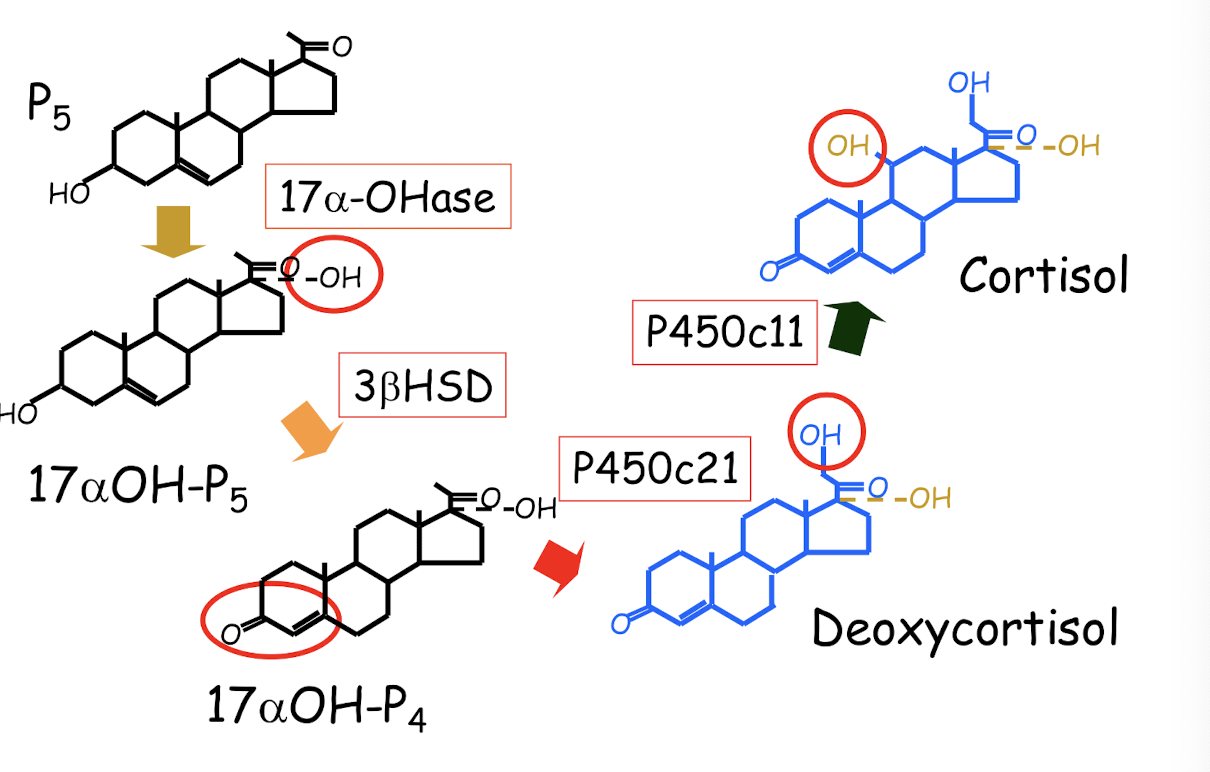
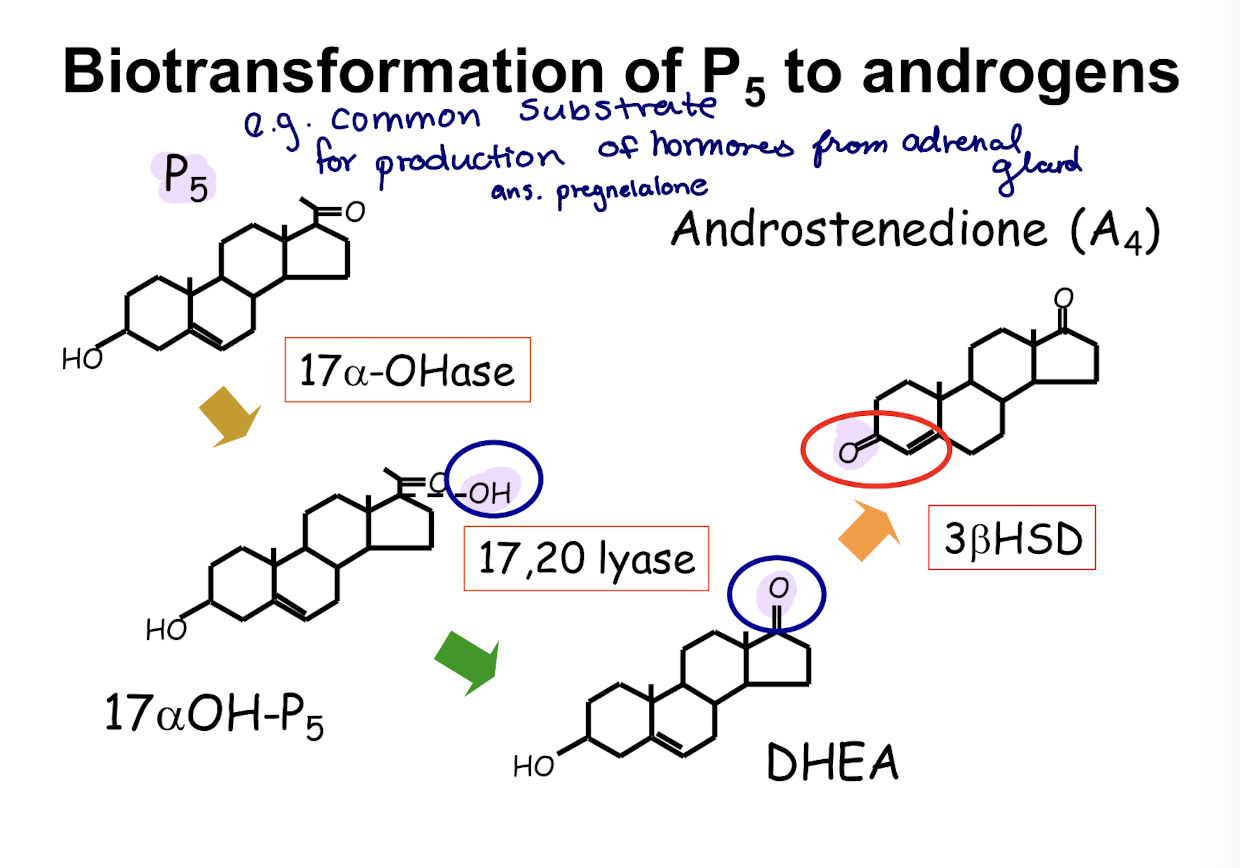
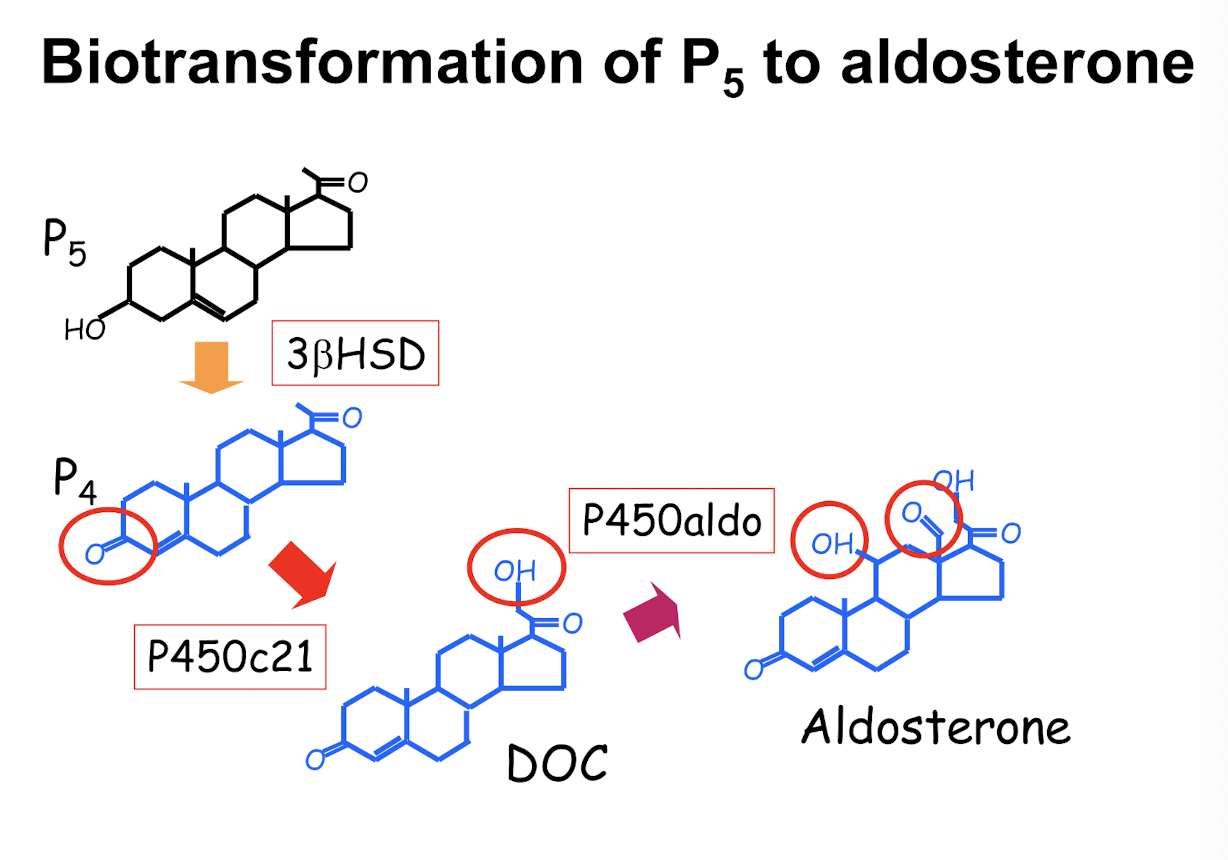
biotransormation of P5 to glucocorticoids
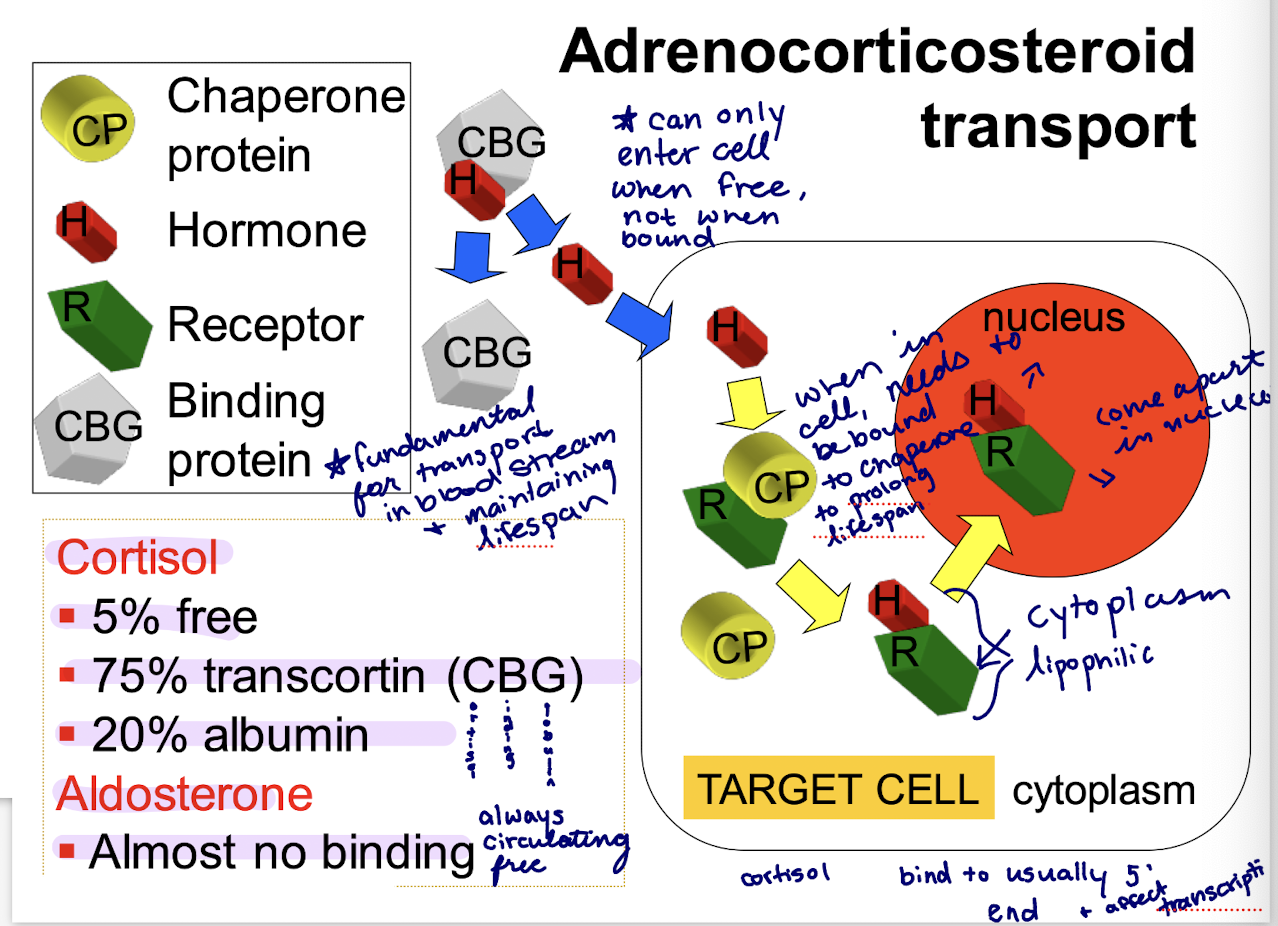
how does cortisol exist
5% free
75% transcortin (CBG)
20% albumin
how does aldosterone exist
almost no binding
what are binding proteins fundamental for
transport in bloodstream and maintaining lifespan
steps of adrenocorticosteroid transport
hormone bound to binding protein in the blood dissociates at cell membrane in order to enter
when inside the cell, the hormone needs to be bound to chaperone protein to prolong lifespan
binds to chaperone protein + receptor
eventually chaperone dissociates and hormone is bound to receptor
hormone and receptor enter the nucleus where they come apart
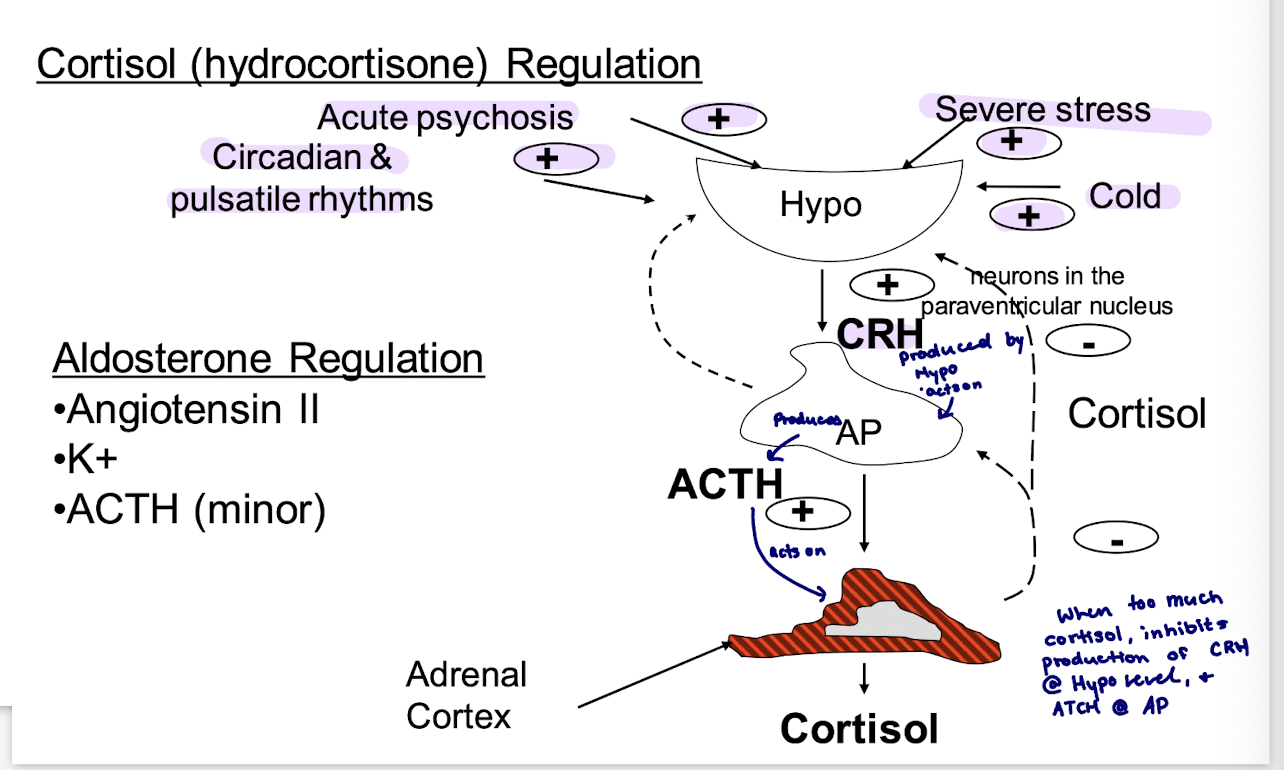
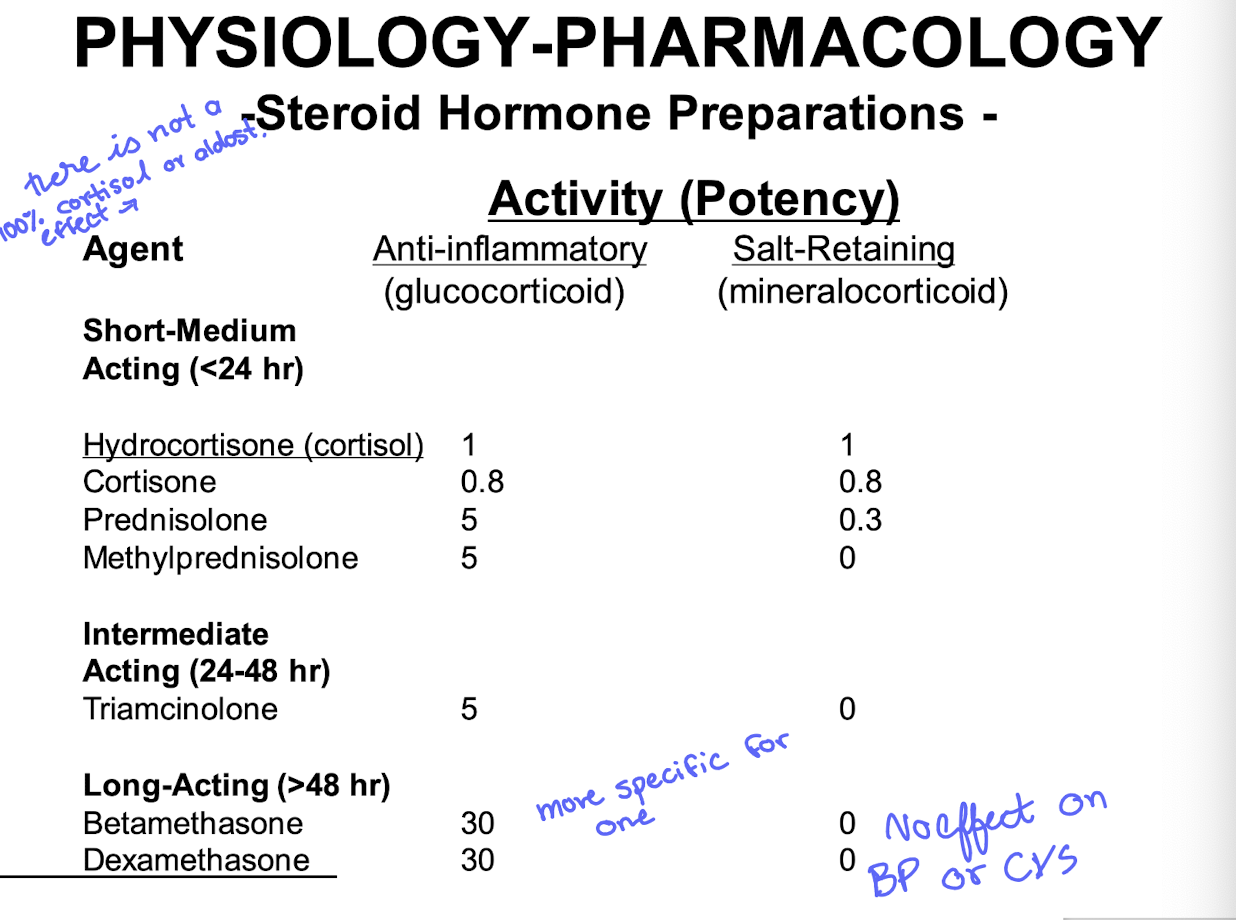
Cortisol (hydrocortisone)
numerous effects; direct and permissive
CHO, protein, and lipid metabolism
increase blood glucose overall; protects heart/brain
liver - gluconeogenesis, glycogen storage
periphery decrease glucose use, increase protein and lipid breakdown (to increase blood glucose)
anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects
inhibit production of proinflammatory mediators
stress coping support (stress increases cortisol)
CNS; sense of well-being, mood and behaviour
cardiovascular integrity
stimulation for development of fetal lung-surfactant (used in last trimester of pregnancy when risk of preterm labour)
what does aldosterone regulate
fluid and electrolyte balance; Na+ and K= homeostasis
rapid activation of Na+ channels in the apical membrane of principal cells (Distal Collecting Tubes + Collecting ducts)
promotes Na+ reabsorption, H+/K+ excretion
cardiovascular support; blood pressure
can aldosterone and cortisol have similar effects when working on receptors
Yes, aldosterone and cortisol receptors are very similar, thus cortisol can have similar effects when working on aldosterone receptors
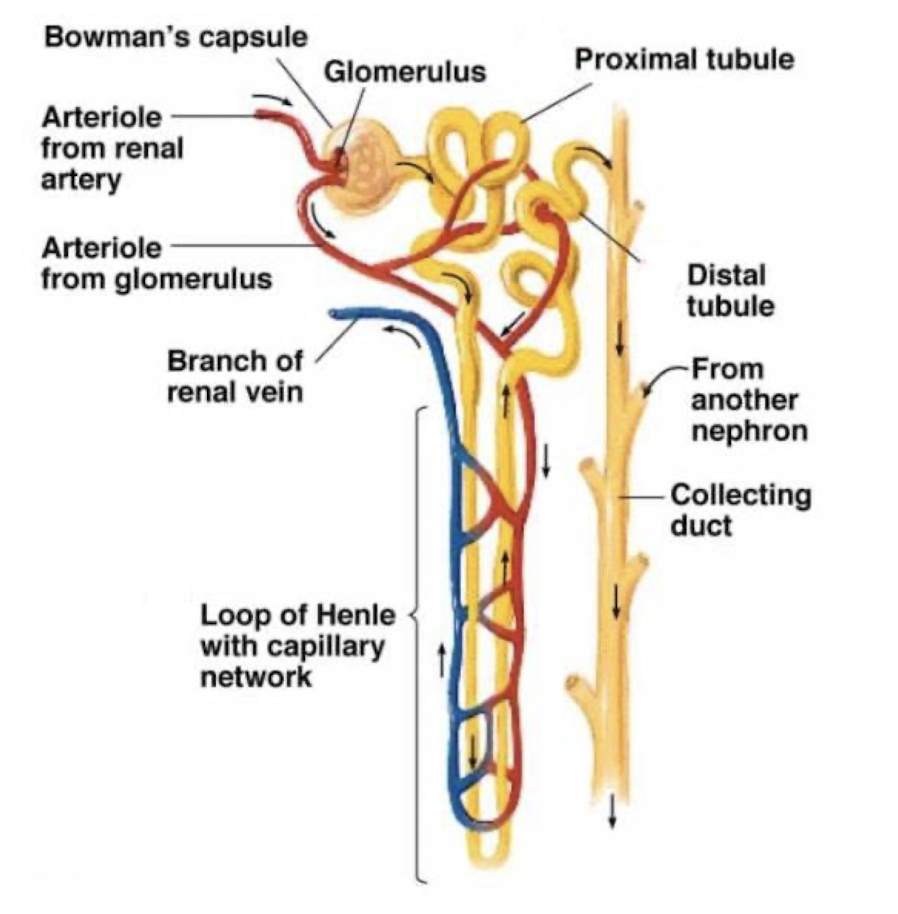
distal tubule
reabsorption of 7% of Na+
Impermeable to water → further decreases in concentration to a value lower than plasma
Collecting duct
reasborption of 2-3% of Na+; permeability to water and of concentrated vs. dilute urine dependent on presence of vasopressin (ADH)
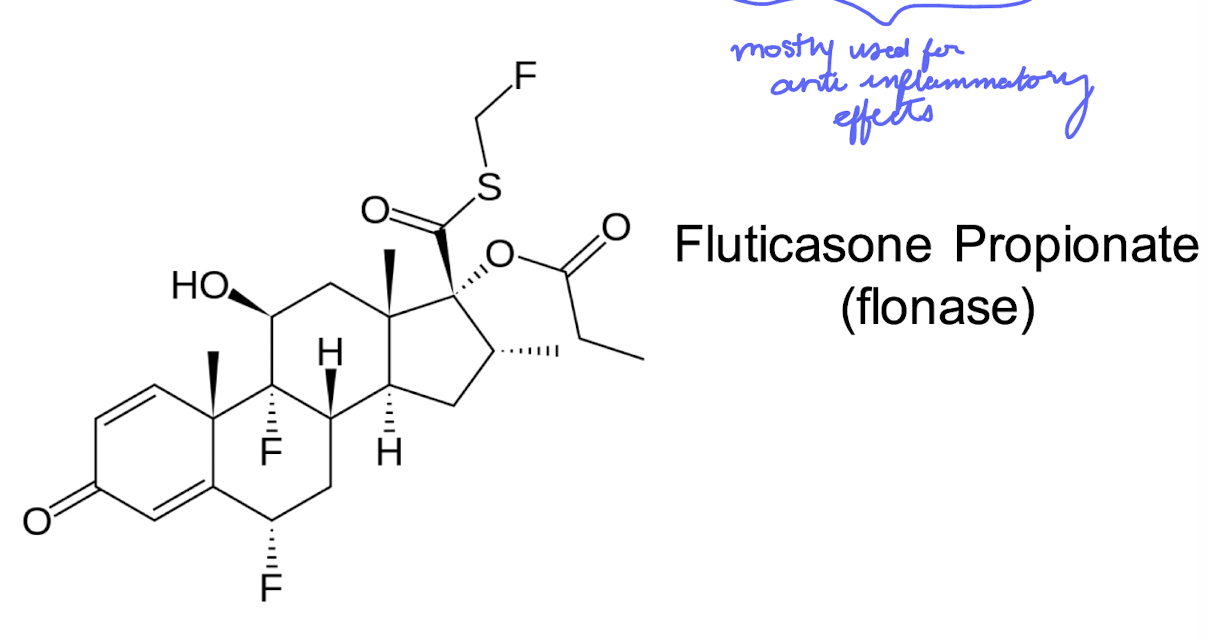
topically active glucocorticoid
Fluticasone Proprionate (flonase)
Glucocorticoid and Progesterone antagonist
Mifepristone (Ru486)
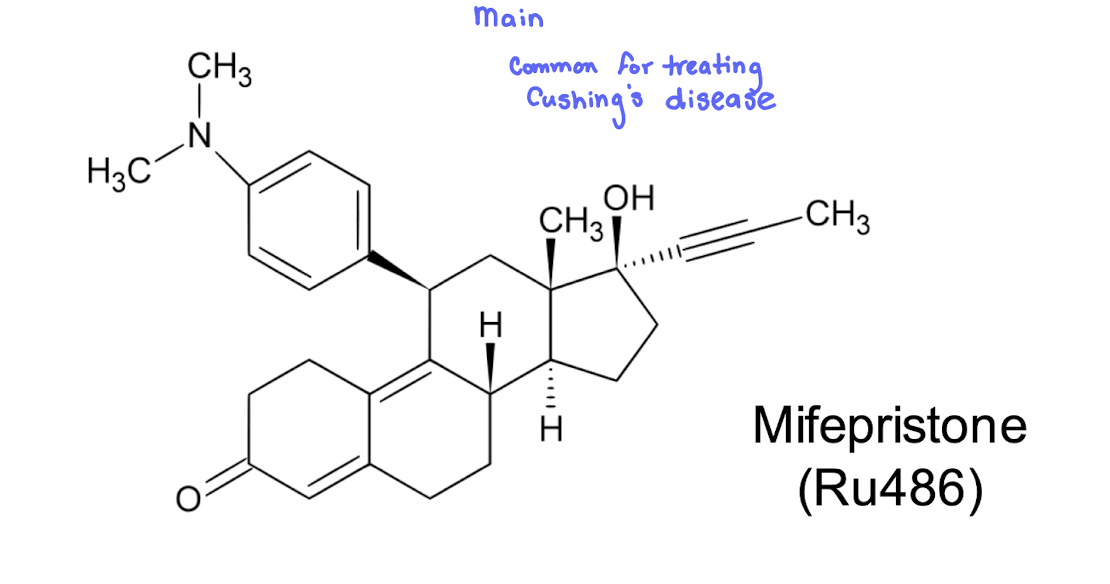
Hyperadrenocorticism a.k.a
Cushing’s syndrome
what is cushings syndrome marked by
the presence of elevated cortisol levels in the body — clinical signs of hypercortisolism
clinical signs of hypercortisolism
upper body obesity
moon face, buffalo hump
thinning of skin; easily bruised
muscle wasting (thinning) of arms and legs
weakening of bones; osteopenia
elevated liver enzymes
causes of hyperadrenocorticism (cushings)
pituitary adenoma; women>men by 5x
iatrogenic; long term steroid treatment for another problem
ectopic ACTH syndrome
adrenal gland tumors
diagnosis of cushings
clinical signs, blood tests, imaging
24 hr urine collection; elevated cortisol (if elevated @ one time, could just be a peak due to circadian, thus, monitor over 24 hours)
provocative tests to rule out adrenal vs. pituitary vs. ectopic
therapy for cushings
surgery (in case of tumor) → resectable tumors; pituitary, adrenal, ectopic
Radiation (if malignant) → alone or follow up to surgery of tumor
adrenocorticosteroid inhibitors → used when cortisol is elevated due to medical treatment → Mitotane, Adrenolytic; specific for adrenals
therapy for cushings
hormone synthesis inhibitors
glucocorticoid receptor antagonists
hormone synthesis inhibitors
ketoconazole; most effective inhibitor; liver damage
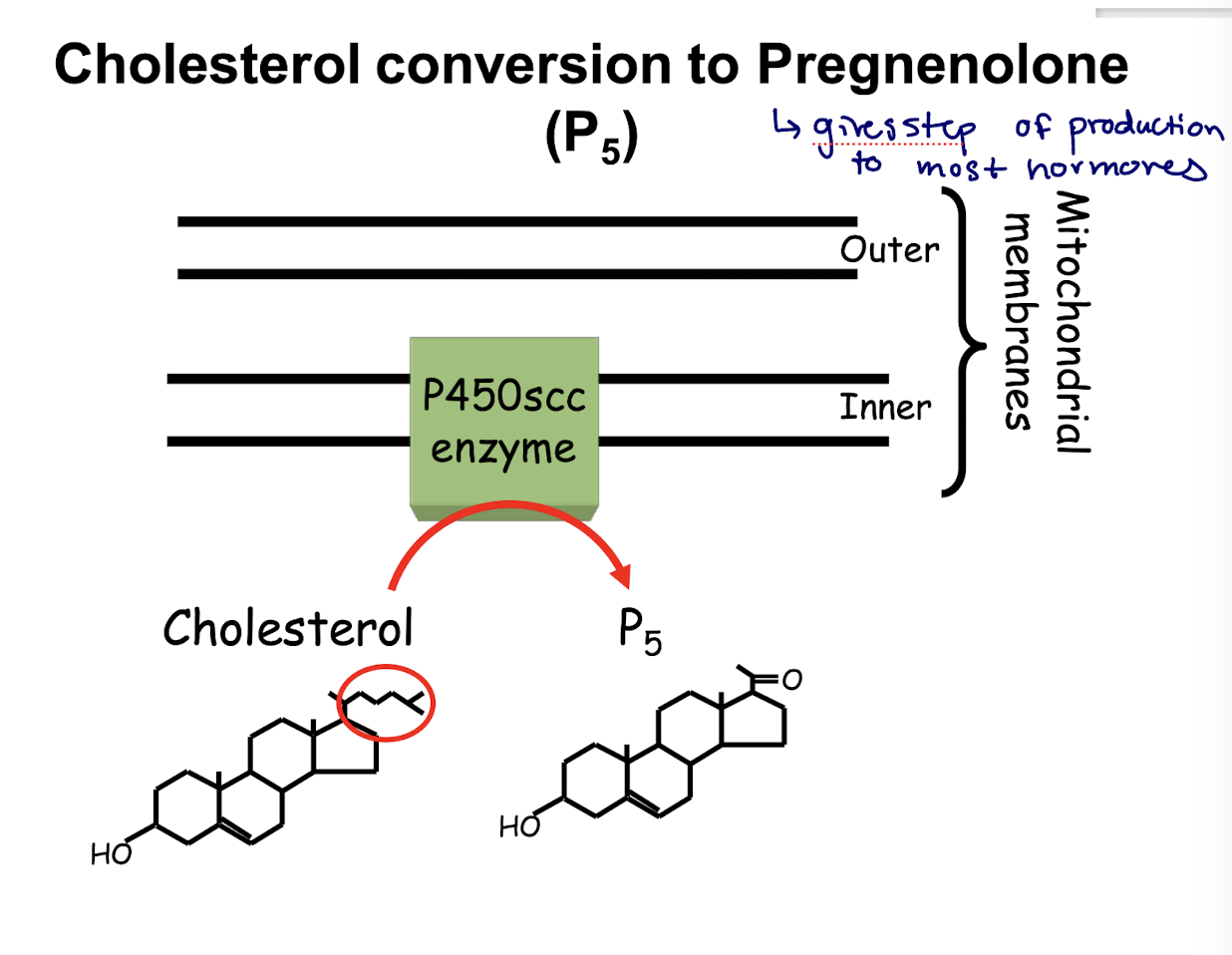
aminoglutethimide; inhibits conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone; adrenal tumors (1st limiting step)
trilostane; inhibits conversion of pregnenolone to progesterone (step down from above, less drastic side effects, but still lots)
what is the limiting step in production of lots of hormones
the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone
→ also stops the production of aldosterone and other hormones
glucocorticoid receptor antagonists
mifepristone; at higher doses may be effective
used on inoperable patients with ectopic or adrenal tumors not responding to other therapies
hypoadreocorticism
adrenal insufficiency → addison’s disease
what is primary adrenal insufficiency most commonly caused from
autoimmune disease and adrenal destruction (used to be common in cases of tuberculosis)
what are other possible causes of Addison’s diease
abrupt steroid withdrawal
possible following surgery for adrenal tumors or pituitary tumors
acute vs chronic adrenal insufficiency
acute adrenal crisis is often due to abrupt withdrawal of long-standing glucocorticoid therapy, but can also precipitate from exacerbation of chronic adrenal insufficiency
acute adrenal insufficiency treatment
emergency often
IV fluid support (isotonic NaCl) and IV corticosteroids (hydrocortisone), other supportive care as needed e.g. antibiotics
chronic adrenal insufficiency treatment
similar signs to acute but less severe
long-term glucocorticoid (hydrocortisone or prednisone) replacement therapy
Fludricortisone (mineralocorticoid) if primary addison’s disease present
Non-endocrine use of glucocorticoids
Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy therapy
mainstay of glucocorticoid use/misuse in medicine
plethora of allergic conditions; most organ systems
reduce proinflammatory mediators by multiple mechanisms
Intensive short-term or emergency therapy
anaphylaxis, shock, heat stroke
rapidly acting IV preparations of glucocorticoids
usually given in high doses for pronounced effects
more non-endocrine uses of glucocorticoids
immunosuppressive therapy
used to quiet an overzealous immune system that is detrimental - organ transplants (prevent rejection), autoimmune ds
Neoplasia
glucocorticoids have antilymphoproliferative effects
useful for certain hematologic malignancies such as lymphoma, certain leukemias
adjunct therapy for inflammation following radiation and with mast cell tumors
do glucocorticoids used in non-endocrine diseases treat the underlying problem?
No, they merely mask the symptoms of condition being treated; need to correct underlying problem
how can adverse effects of steroid therapy can be minimized
lowest dose possible
low potency steroids; prednisone
alternate day therapy; give HPA a day off
tapered reduction of steroid therapy to allow HPA axis time to recover following treatment
main cause of primary aldosteronism
adrenal adenoma is usual cause
what is primary aldosteronism a sign of
hypertension and hypokalemia
treatment of primary aldosteronism
usually surgical; can be curative
what else can treat primary aldosteronism
blockade of aldosterone can be accomplished also with drugs
spironolactone
eplerenone
what else can mineralocorticoid antagonists treat
hypertension and heart failure; increased aldosterone contributes to adverse effects
eplerenone
take home messages
adrenal steroids are very powerful, affecting entire body
aldosterone (Z. Glomerulosa)
cortisol and androgens (Z fasciculata and Z reticularis)
what are aldosterone and cortisol controlled by
aldosterone (mineralocorticoid) controlled by kidney renin-angiotensin system.
Cortisol (glucocorticoid) by hypothalamic-pituitary ACTH
what does aldosterone control
kidney sodium and water retention
what does cortisol control
metabolism, promoting glucose regeneration and entry to the blood
are cortisol and aldosterone carried in the blood bound to proteins
cortisol, but not aldosterone, largely carried bound to proteins in the blood
pharmacological targets
enzymes involved in steroid synthesis, as well as steroid receptors
are mineralocorticoid (MR) and glucocorticoid (GR) receptors similar?
yes, very similar, so high cortisol increases sodium retention
what types of different synthetic corticosteroids are available
MR as well as GR specific, differing in duration of action, some only surface active, as well as some antagonists (mifepristone, GR antagonist; spironolactone, MR antagonist)
what else are these drugs used for
widely used as anti-inflammatories, immune suppressants, treatment of glucocorticoid insufficiency, treatment of women in premature labour
what happens to those taking glucocorticoids long term
they are very powerful drugs, so long term glucocorticoids suppress ACTH, and must be tapered off slowly - or the patient may suffer an adisonian crisis when the glucocorticoid is stopped