Chapter 27
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are amines?
Organic compounds derived from NH3 in which one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia have been replaced by a carbon chain or ring
What is an aliphatic amine?
An amine where the nitrogen atom is attached to at least one straight or branched carbon chain
What is an aromatic amine?
An amine where the nitrogen atom is attached to an aromatic ring
What is a primary amine?
An amine where there is only one alkyl groupn
How do you name a primary amine which has the amine group on any other carbon but carbon 1?
It is named using the prefix amino, and a number is added to indicate the position of the amine group along that chain.
How do you name a secondary or tertiary amine with two or more different groups attached to a nitrogen atom?
It is named as an N-substituted derivative of the larger group, for example N-methylpropylamine and N-ethyl-N-methylpropylamine
How do amines behave in reactions?
They act as bases as the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom can accept a proton. When this happens, a dative covalent bond is formed between the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom and the proton.
What are the reactions that take place in the formation of primary amines?
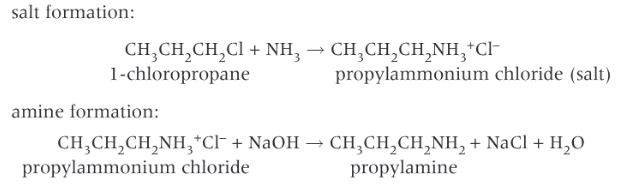
What are the conditions for the preparation of primary amines?
Ethanol is used as a solvent, which prevents any substitution of the haloalkane by water to produce alcohols. Excess ammonia is used, which reduces further substitution of the amine group to form secondary and tertiary amines
How is phenylamine produced?
Nitrobenzene is heated under reflux with tin and hydrochloric acid to form the ammonium salt, which is then reacted with excess sodium hydroxide to produce the aromatic amine
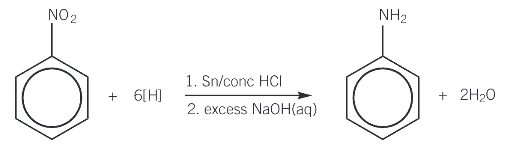
What is an amino acid?
An organic compound containing both amine and carboxylic acid functional groups. The body has 20 of them
How will the amine group in an amino acid react?
It is basic so will react with an acid
How will the carboxylic acid group in an amino acid react?
It will react with alkalis to form salts and with alcohols to form esters
What are the conditions of esterification of amino acids?
Heating with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid
What is a switterion?
An ion that contains both a positive and negative charge. It has no overall charge
What is the isoelectric point?
The pH at which the zwitterion is formed, with each amino acid having its own unique isoelectric point
What are amides?
The products of reactions between acyl chlorides and ammonia/amines. They contain a carbon double bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to an NH2 group.
What is optical isomerism?
When two isomers have the same structural and molecular formula, but different 3D arrangements, creating non-superimposable mirror images
What are enantiomers?
Two molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images
What special type of carbon atom creates optical isomerism?
Chiral carbons
How should you draw optical isomers?
As 3D mirror images of each other
What is condensation polymerisation?
The joining of monomers with loss of a small molecule, usually water or hydrogen chloride
What are the two ways polyesters can be made?
One monomer containing both a carboxylic acid and an alcohol group
Two monomers, one containing two carboxylic acid groups and the other containing two alcohol groups
What are polyamides?
The condensation polymers formed when monomers are joined together by amide linkages in a long chain to form the polymer
How can polyesters and polyamides be hydrolysed?
Using hot aqueous alkalli or acid