First Exam Anatomy and Physiology
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
Anatomy
study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another
Physiology
study of the function of body parts how they work to carry out life sustaining activities
Superior (cranial)
towards the head end or upper part of a structure or the body above
example: The head is superior to the abdomen
Inferior (caudal)
away from the head end or towards the lower part of a structure or the body: below
example the naval is inferior to the chin
Anterior (ventral)
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
example: the breastbone is anterior to the spine
Posterior (dorsal)
toward or at the back of the body: behind
example the heart is posterior to the breastbone
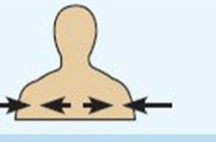
medial
toward or at the midline of the body on the inner side of
example: the heart is medial to the arm
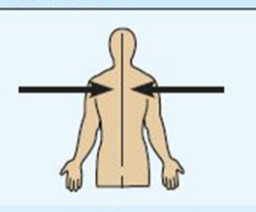
lateral
away from the midline of the body on the outer side of
example the arms are lateral to the chest
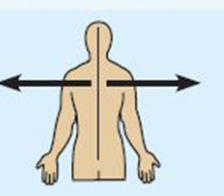
intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
example: the collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder
Proximal
closer to the origin of the body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
example: the elbow is proximal to the wrist
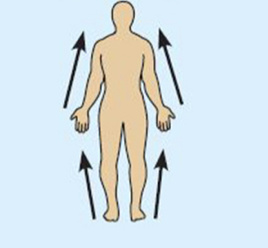
Distal
father from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
example: The knee is distal to the thigh
Superficial (external)
toward or at the body surface
example: The skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles
Deep (internal)
away from the body surface: more internal
example: the lungs are deep to the skin
Sagittal plane
Divides body vertically into right and left parts. Produces a sagittal section if cut along this plane

Midsgaital (median) plane
cut was made perfectly on midline
Parasagittal plane
cut was off centered, not on midline

Frontal (coronal plane)
divides body vertically into anterior and posterior parts (front and back).
Produces a frontal or coronal section

Transverse (horizontal) plane
divides body horizontally (90° to vertical plane) into superior and inferior parts (top and bottom). Produces a cross section
Axial
head, neck and trunk
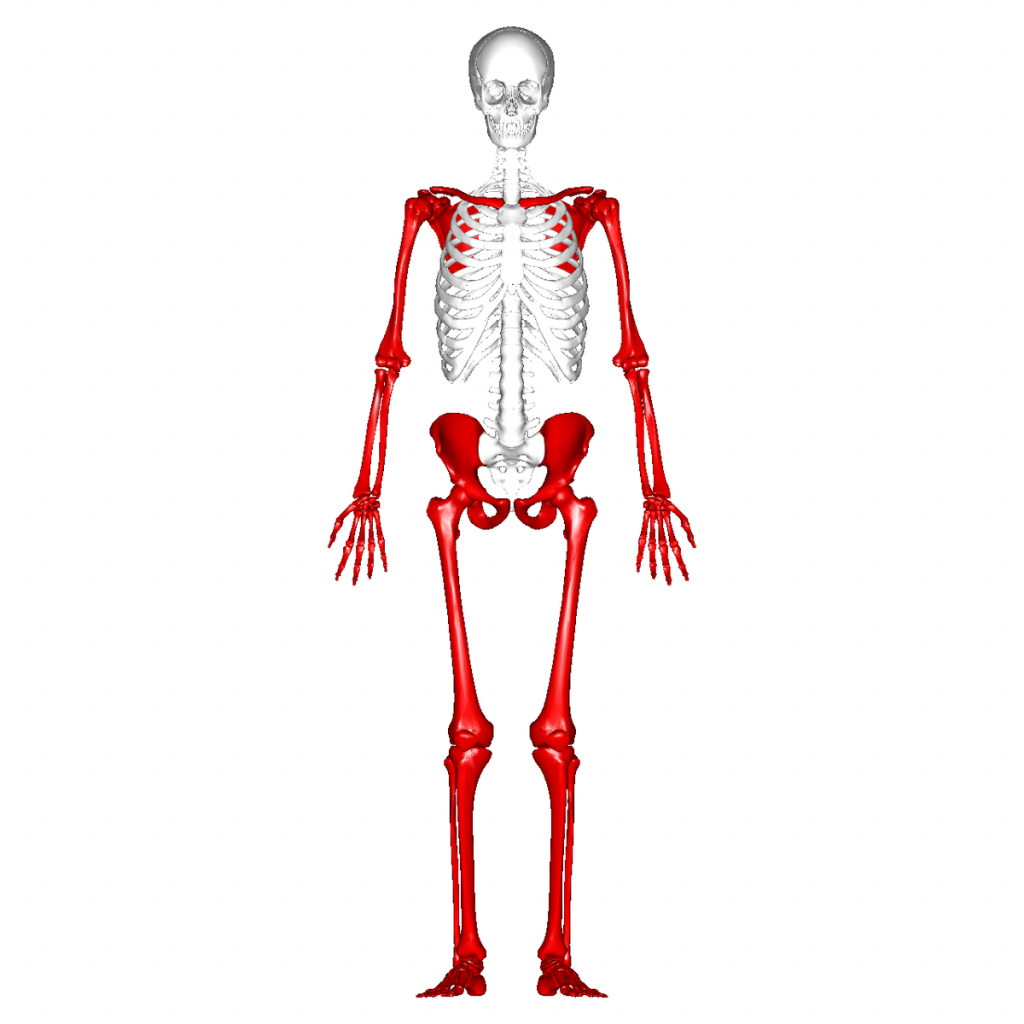
Appendicular
limbs
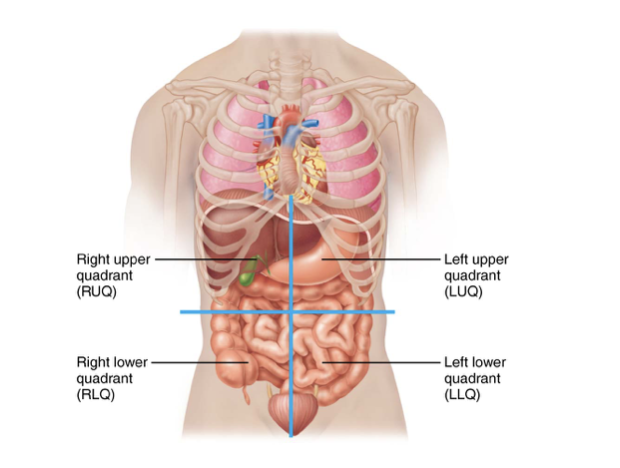
Four Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Maintaining boundaries
separation between internal and external environments’s must exit
plasma membranes separate cells
skin separates organism from environment
Movement
muscular system allows movement
of body parts via skeletal muscles. Of substances via cardiac muscle (blood) and smooth muscle (digestion or urination )
Responsiveness
ability to sense and response to stimuli. withdrawal reflex prevent injury. control breathing rate, which must change in response to different activities
Digestion
breakdown of ingested foodstuffs, followed by absorption of simple molecules into blood
Metabolism
all chemical reactions that occur in body cells.
catabolism
breakdown of molecules
anabolsim
synthesis of molecules
Excretion
removal of wastes from metabolism and digestion.
Urea (from breakdown of proteins) carbon dioxide (from metabolism) and feces (unabsorbed foods)
Reproduction
at the cellular level reproduction involves division of cells fro growth or repair
at the organismal level, reproduction is the production of offspring
Growth
increase in size of a body part or of organism
What do human need to survive?
Human need many different factors in order to survive, but need to be appropriate amounts; too much or too little can be harmful
nutrients
oxygen
water
normal body temp
appropriate atmospheric pressure
How do we maintain appropriate levels of these requirement?
Homestasis
Homestasis
is the maintenance of relatively stable internal condition despite continuous changes in environment.
A dynamic state of equilibrium, always readjusting as needed. Maintained by contribution of all organ system
Homeostatic controls
Body must constantly be monitored and regulated to maintain homeostasis
nervous and endocrine system, as well as others play a major role in maintaining homeostasis
Variable are factors that can change (blood sugar, body temp, and blood volume)
Receptor (sensor)
monitor environment
responses to stimuli (thing that cause changes in controls variables)
Control center
determine set point at which variable is maintained
receives input from receptor
determines appropriate response
Brain or spinal cord
Effector
receives output from control center, provides the means to respond, response either reduces stimulus (negative feedback) or enhances stimulus (positive feedback)
Negative feedback
most used mechanism in body. Response reduces or shut off original stimulus
variable changes in opposite direction of initial change
negative feedback examples (Blood Glucose)
Receptors sense increased blood glucose (blood sugar)
Pancreases (control center) compares level to set point and secretes insulin into the blood
Insulin causes body cells (effectors) to absorb more glucoses, which decrease blood glucose levels
Positive feedback
response enhances or exaggerates the original stimuli
may exhibit a cascade or amplifying effect as a feedback causes variable to continue in same direction as initial change
Positive feedback examples
enhancement of labor contraction by oxytocin
platelet plug formation and blood clotting
Integumentary system
skin (largest organ of the body)
surface area= 20 square feet
weight= 10 pounds
Skin (protection)
Skin is exposed to microorganism, abrasions, temperature extremes, and harmful chemicals
3 barriers are chemical, physical and biological
Chemical barrier
skin secretes many chemicals such as:
sweat, which contains antimicrobial protein (defensin)
Sebum and defensins, which kill bacteria
Melanin provides a chemical barrier against UV radiation damage
Acid mantle
low pH of skin inhibits bacterial multiplication
Physical barriers
flat dead, keratinized squamous cells of stratum corneum, surrounded by glycolipids, block most water and water soluble substances
Physical barriers (some chemical have limited penetration of skin)
lipid-soluble substances
plant oleoresins (poison ivy)
organic solvents (acetone or paint thinner)
salts of heavy metals (lead, mercury)
Physical barriers (administration route of medication/drugs)
nitroglycerin
nicotine
fentanyl
estrogen and testoerone
Biological barriers
cells breakdown biological invader and activate immune system
epidermis (contains dendritic cells)
dermis (contains macrophages)
Integumentary stem is made up:
skin
accessory organs
Hair
nails
glands
sweat
sebaceous
Sensory Receptors
Epidermis
superficial region (surface)
consists of epithelia tissues and is avascular (no blood vessels)
Dermis
underlies (deep) epidermis
mostly fibrous connective tissues and vascular
contains accessory organ structures
Hypodermis
subcutaneous layer deep to skin
not part of skin but shares some functions
mostly adipose tissues that absorbs shock and insulates
anchors skin to underlying structures (most muscles)
Cells of the Epidermis
consist mostly of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Four cell types
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes
Dendritic (langerhans) cells
Tactile (Merkel cells)
Keratinocytes
Produce fibrous keratin (protein that gives skin its protective properties)
Major cells of epidermis
Tightly connected by desmosomes
Millions slough off every day
Melanocytes
Spider-shaped cells located in deepest epidermis
Produce pigment melanin:
Melanin is transferred to keratinocytes, where it protect the nucleus from UV damage
Dendritic (langerhans) cells
star-shaped macrophages that patrol deep epidermis
Are key activators of immune system
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
sensory receptors that sense touch
Layers of the Epidermis
Thick skin contains five layers (strata) and is found in high-abrasion areas (hands, feet)
Thin skin contains only four strata
Five layers of skin:
Stratum basale
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
Stratum corneum
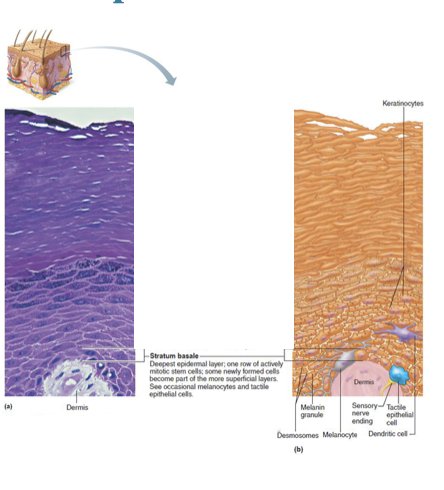
Stratum Basale (basal layer)
Deepest of all epidermal layers (base layer)
Layer that is firmly attached to dermis
Consists of a single row of stem cells that actively divide
One cell is pushed superficially from basal layer to surface,
Cell dies as it moves toward surface
Contains melanocytes, tactile cells
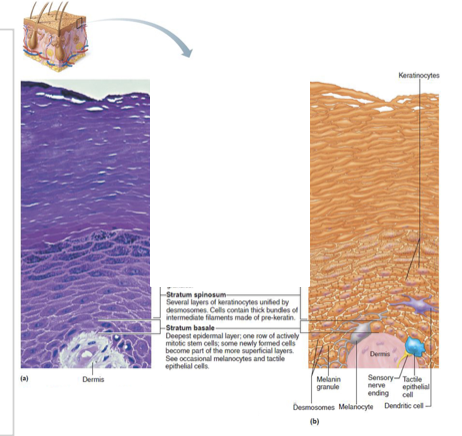
Stratum Spinosum (prickly layer)
Several cell layers thick
Cells contain desmosomes
Allows them to resist tension and pulling
Keratinocytes in this layer appear spikey, so they are called prickle cells
Scattered among keratinocytes are abundant melanosomes and dendritic cells
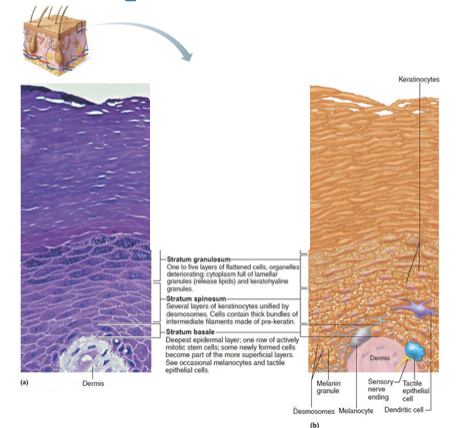
Stratum Granulosum (granular layer)
Four to six cells thick, but cells are flattened, so layer is thin
Cell appearance changes
Cells flatten, nuclei and organelles disintegrate
Keratinization begins
Cells also accumulate a water-resistant glycolipid that slows water loss
Cells above this layer die
Too far from dermal capillaries to survive
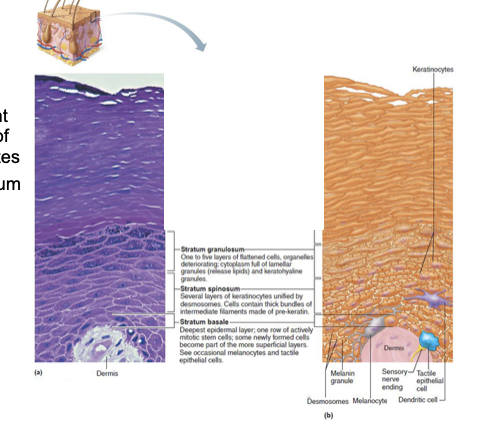
Stratum Lucidum (clear layer)
found only in thick skin ( hands, soles of feet)
Consists of thin, translucent band of two to three rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes
Lies superficial to the stratum granulosum
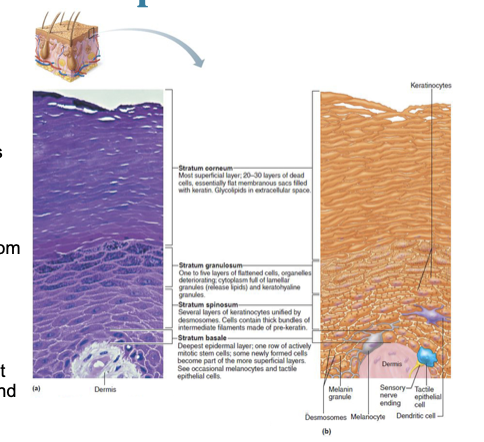
Stratum Corneum (horny layer)
Rows of flat, anucleated, keratinized dead cells
Accounts for three-quarters of epidermal thickness
Though dead, cells still function to:
Protect deeper cells from the environment
Prevent water loss
Protect from abrasion and penetration
Act as a barrier against biological, chemical, and physical
Apoptosis
cells change by going through controlled cell death
dead cells slough off and are replaced by deeper cells
Humans can shed- 50,00 cells every minutes
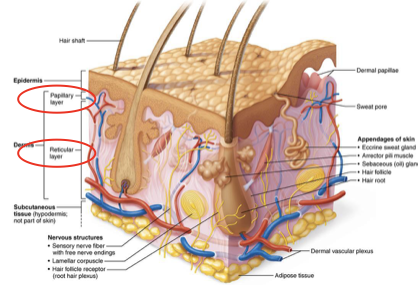
Demis
strong flexible connective tissue
vascular (blood vessels and lympatic vessels)
contains nerves
contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat galnds
two layer (papillary and reticular)
Papillary layer
Superficial layer of connective tissue consisting of loose, interlacing collagen and elastic fibers and blood vessels
Dermal papillae: superficial region of dermis that sends fingerlike projections up into epidermis
Projections contains capillary loops, free nerve endings, and touch receptors (tactile corpuscles, also called Meissner’s corpuscles)

Papillary layer (in thick skin)
dermal papillae lie on top of dermal ridges, which give rise to epidermal ridges
Collectively ridges are called friction ridges
Enhance gripping ability
Contribute to sense of touch
Sweat pores in ridges
Reticular layer
Makes up ~80% of dermal thickness
Consists of coarse, dense fibrous connective tissue
Many elastic fibers provide stretch-recoil properties
Collagen fibers provide strength and resiliency
Bind water, keeping skin hydrated
Network of blood vessels that run between reticular layer and hypodermis
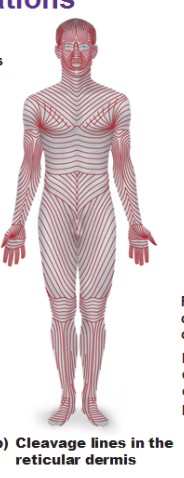
Cleavage (tension) lines
in reticular layer are caused by many collagen fibers running parallel to skin surface
Externally invisible
Important to surgeons because incisions parallel to cleavage lines heal more readily
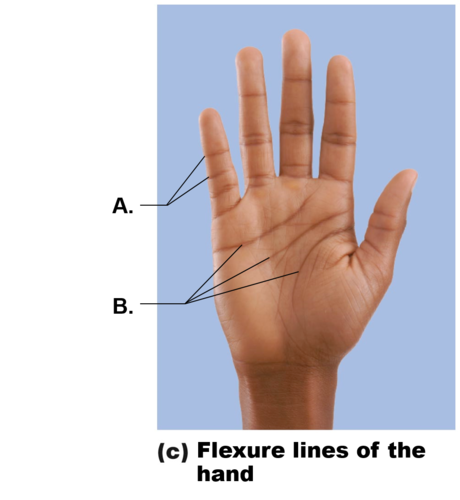
Flexure lines
of reticular layer are dermal folds at or near joints
Dermis is tightly secured to deeper structures
Skin’s inability to slide easily for joint movement causes deep creases
Visible on hands wrists, fingers, soles, toes
Hair
(also called pili): flexible strands of dead, keratinized cells
Produced by hair follicles
Contains hard keratin, not like soft keratin found in skin
Hard keratin is tougher and more durable, and cells do not flake off
Functions:
Hair on head guards against physical trauma
Protect from heat loss
Shield skin from sunlight
Nails
Scale-like modifications of epidermis that contain hard keratin
Act as a protective cover for distal, dorsal surface of fingers and toes
Abnormal color or shape can be an indicator of disease
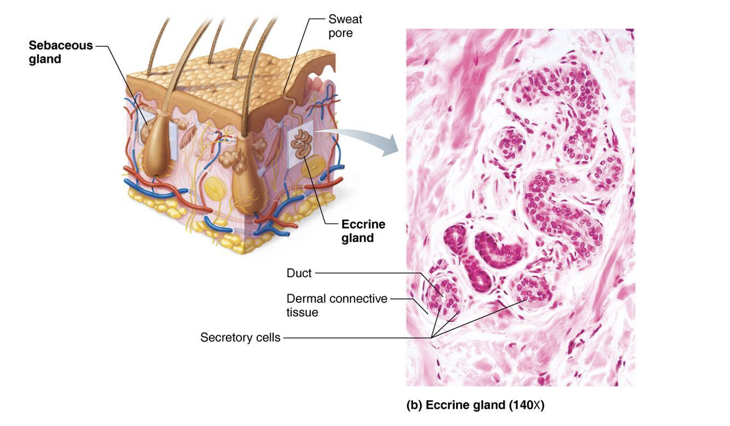
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Most abundant type
High density on palms, soles, and forehead
Ducts connect to pores
Function in thermoregulation
Regulated by sympathetic nervous system
Secretion of sweat
99% water, salt, vitamin C, antibodies, dermcidin (microbe-killing peptide) metabolic wastes
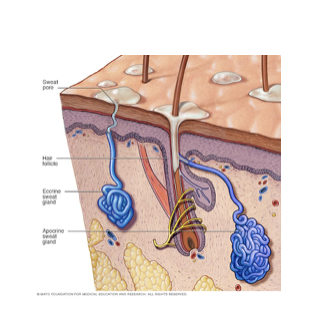
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Confined to axillary and anogenital areas
Secrete viscous milky or yellowish sweat that contains fatty substances and proteins
Bacteria break down sweat, leading to body odor
Larger than eccrine sweat glands with ducts emptying into hair follicles
Modified apocrine glands
Ceruminous glands: lining of external ear canal; secrete cerumen (earwax)
Mammary glands: secrete milk
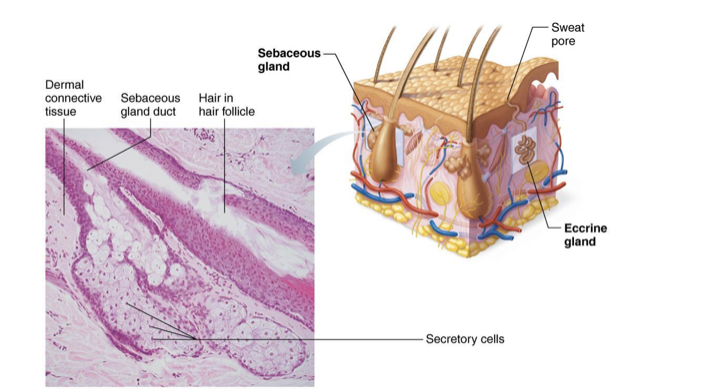
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
widely distributed, except for thick skin of palms and soles
Most develop from and secrete into hair follicles
Relatively inactive until puberty
Stimulated by hormones, especially androgens
Secrete sebum
Oily secretion
Bactericidal (bacteria-killing) properties
Softens hair and skin
Melanin
Pigment made in skin; made by melanocytes (two forms: reddish yellow to brownish black)
Packaged into melanosomes that are sent to shield DNA of keratinocytes from damaging UV sunlight
The more sun the more melanin will be produced
Skin color differences are due to amount and form of melanin
Freckles and pigmented moles are local accumulations of melanin
Carotene
yellow to orange pigment
most obvious in palms and soles
accumulates in stratum corneum and hypodermis
Hemoglobin
pinkish hue of fair skin (main coloring in those with lower levels of melanin)
Homeostatic imbalance
Cyanosis
Blue skin color: low oxygenation of hemoglobin
Pallor (blanching or pale color)
Anemia, low blood pressure, fear, anger
Erythema (redness)
Fever, hypertension, inflammation, allergy
Jaundice (yellow cast)
Liver disorders
Bruises (black-and-blue marks)
Also referred to as ecchymoses or hematomas, are a result of clotted blood beneath skin
As clot is broken down, color of bruise changes
Brown or black “necklace” or bruises
Hyperpigmented dark areas in axillae and around neck may be a sign of insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels
Skin cancer
Most skin tumors are benign (not cancerous) and do not spread (metastasize)
Risk factors
Overexposure to UV radiation
Three major types of skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Melanoma
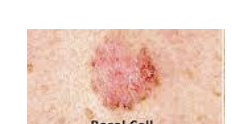
Basal cell carcinoma
Least malignant and most common
Stratum basale cells proliferate and slowly invade dermis and hypodermis
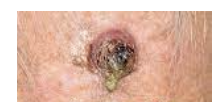
Squamous cell carcinoma
Second most common type; can metastasize
Involves keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
Usually is a scaly reddened papule on scalp, ears, lower lip, or hands
Melanoma
Cancer of melanocytes; is most dangerous type because it is highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy

What does our skeletal system do?
support, protection, movement, mineral and growth factors, blood cell formation (hemotopoesis), triglyceride (fat) storage (used for an energy source, is stored in bone cavities, and Hormone production
How many bones do we have?
206 named bones in human skeleton
86 paired (having left and right0 34 paired
Long bones
longer than they are wide
limb bones
Short bones
cube shaped bones (in wrist and ankle)
Sesamoid bones form within tendons (example patella)
vary in size and number in different individuals
Flat bones
thin flat slightly curved
sternum, scapulae’s, ribs and most skull bones
irregular bones
complained shaped
vertebrae and hip bones
Osseous
bone tissues predominates, but a bone also has nervous tissue, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue, muscle cells, and epithelial cells in its blood vessels
2 region of osseus
Compact bones
Spongy bones
Compact bones
dense outer layer on every bone that appears smooth and solid

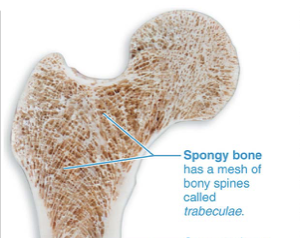
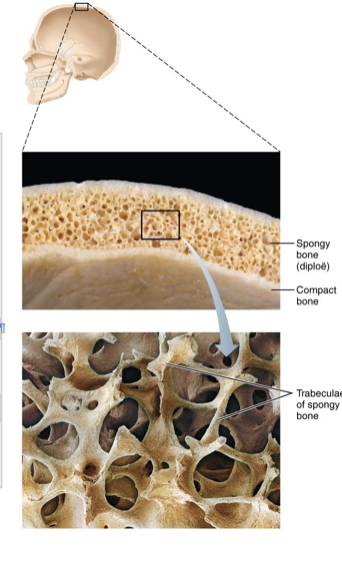
Spongy bone
made up of a honeycomb of small, needle-like or flat pieces of bone called trabeculae
Open spaces between trabeculae are filled with red or yellow bone marrow
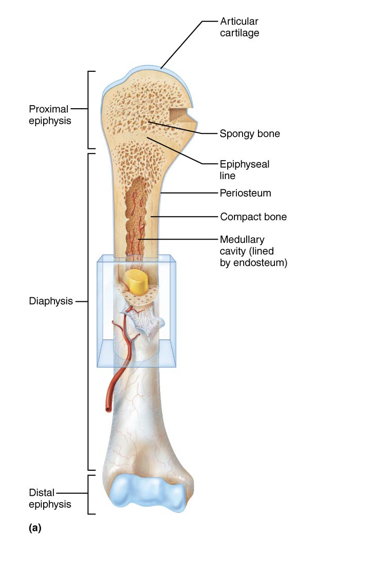
Structure of typical long bones
Diaphysis: tubular shaft that forms long axis of bone
Consists of compact bone surrounding central medullary cavity that is filled with yellow bone marrow in adults
Epiphyses: at the proximal and distal ends of long bones -consists of compact bone externally and spongy bone internally
Articular cartilage covers articular (joint) surfaces
Between diaphysis and epiphysis is epiphyseal line
Remnant of childhood epiphyseal plate (growth plate) – a disc of hyaline cartilage
Structure of short, irregular, and flat bones
Consist of thin plates of spongy bone covered by compact bone
Compact bone sandwiched between connective tissue membranes
Periosteum covers outside of compact bone, and endosteum covers inside portion of compact bone
Bone marrow is scattered throughout spongy bone; no defined marrow cavity
Hyaline cartilage covers area of bone that is part of a movable joint
Periosteum
double-layered membrane that covers outer surface expect joints
contains many nerve fibers and blood vessels that continue to the shaft through nutrient foramen openings
anchoring points for tendons and ligaments
Fibrous layer
outer layer consisting of dense irregular connective tissue that secure to bone matrix
osteogenic layer
inner layer abutting bone and contains primitive osteogenic stem cells that give rise to most bone cells '