EXAM: AP USA government and politics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/234
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:05 AM on 12/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
1
New cards
elitism
model of democracy where a small number of people, usually wealthy and educated, influence political decision making
2
New cards
elitist democracy
the electoral college is an example of what kind of democracy?
3
New cards
Elitism
Pluralism
Participatory
Pluralism
Participatory
What are the theories of democracy?
4
New cards
pluralist democracy
a model of democracy where no one group dominates politics and individuals work through organized groups to compete to influence policy
5
New cards
pluralist democracy
interest groups, like march for life, are an example of what kind of democracy?
6
New cards
participatory democracy
a model of democracy where citizens have the power to decide directly on policy and politicians are responsible for implementing these decisions
7
New cards
participatory democracy
town hall meetings are an example of what kind of democracy?
8
New cards
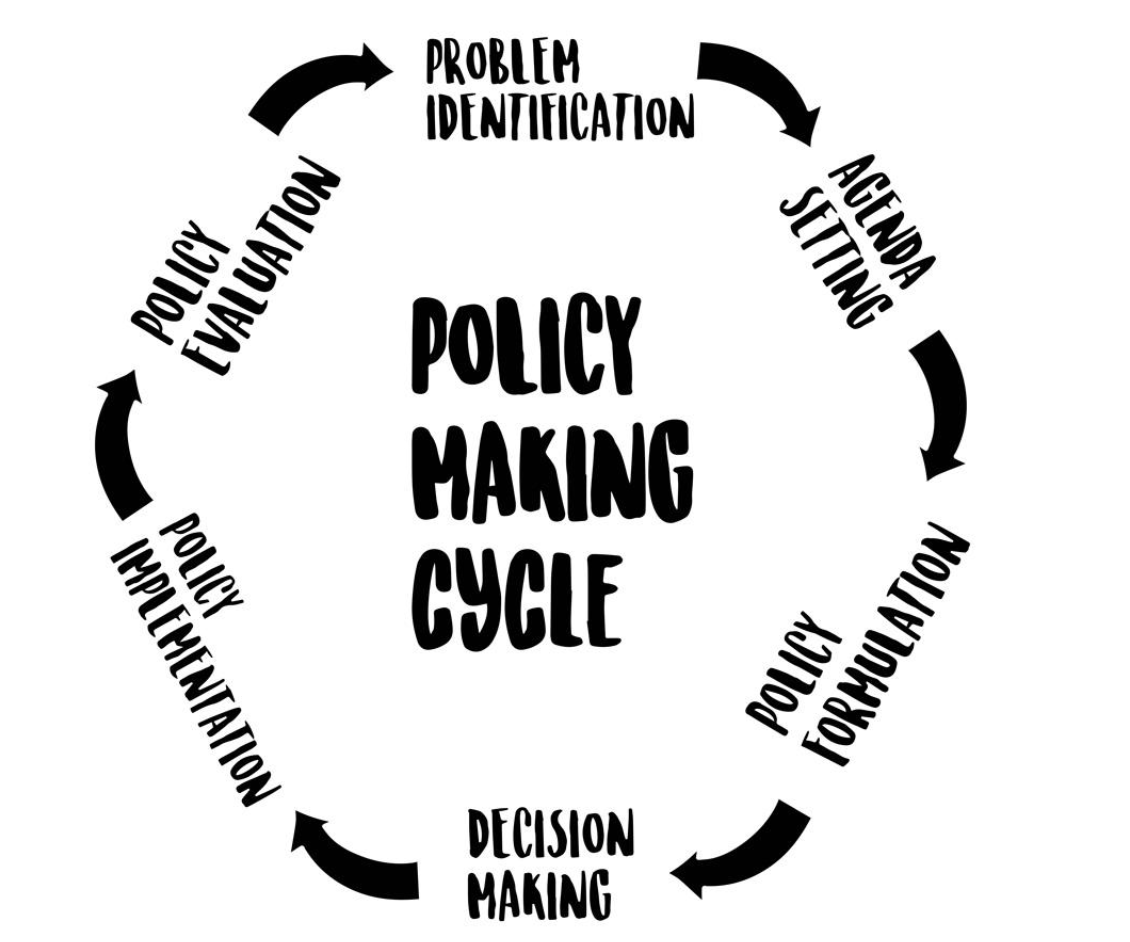
Issue Identification
Policy Formulation
Decision Making
Implementation
Evaluation
Issue Identification
Policy Formulation
Decision Making
Implementation
Evaluation
Issue Identification
What is the policymaking process?
9
New cards
ratify treaties
confirm appointments for the cabinet, justices, and judges)
try impeachments
foreign relations
confirm appointments for the cabinet, justices, and judges)
try impeachments
foreign relations
What are the enumerated powers of senate?
10
New cards
power to initiate revenue bills
impeach federal officials
elect the President in the case of an electoral college tie
impeach federal officials
elect the President in the case of an electoral college tie
What are the enumerated powers of the House?
11
New cards
* Executive (administrative powers)
* Take care that the laws are faithfully executed
* Nominate officials (with 51%agreement of the Senate)
* Request written opinions of administrative officials \n fill administrative vacancies during congressional recesses
* Legislative
* Present info on state of the union to congress
* Recommend legislation to congress
* Convene both house on extraordinary occasions
* Adjourn congress if house and senate can't agree
* Veto legislation (congress may overrule with a 2/3 vote
* Foreign/military (national security or military powers)
* Commander-in-chief of the armed forces
* Make treaties (with ratification by 67% of senate
* Nominate ambassadors (with the agreement of 51% of senate)
* Receive ambassadors/diplomatic recognition on other governments
* Judicial
* Reprieves and pardons for federal offenses (except impeachment)
* Nominate federal judges (with confirmation of 51% of senate)
* Take care that the laws are faithfully executed
* Nominate officials (with 51%agreement of the Senate)
* Request written opinions of administrative officials \n fill administrative vacancies during congressional recesses
* Legislative
* Present info on state of the union to congress
* Recommend legislation to congress
* Convene both house on extraordinary occasions
* Adjourn congress if house and senate can't agree
* Veto legislation (congress may overrule with a 2/3 vote
* Foreign/military (national security or military powers)
* Commander-in-chief of the armed forces
* Make treaties (with ratification by 67% of senate
* Nominate ambassadors (with the agreement of 51% of senate)
* Receive ambassadors/diplomatic recognition on other governments
* Judicial
* Reprieves and pardons for federal offenses (except impeachment)
* Nominate federal judges (with confirmation of 51% of senate)
What are the enumerated powers of the President?
12
New cards
* Bargaining/persuasion: setting priorities for congress and attempting to get majorities to put them through the president's legislative agenda
* Issuing executive orders: relations to run government and direct the bureaucracy
* Issuing signing statements: giving president's intended interpretation of bills passed by congress
* Negotiating executive agreements: agreement with the heads of foreign governments that aren't ratified by the senate
* Issuing executive orders: relations to run government and direct the bureaucracy
* Issuing signing statements: giving president's intended interpretation of bills passed by congress
* Negotiating executive agreements: agreement with the heads of foreign governments that aren't ratified by the senate
What are the implied powers of the President?
13
New cards
regulate commerce
collect taxes
raise an army
establish post offices
collect taxes
raise an army
establish post offices
What are the implied powers of Congress?
14
New cards
amendment
the process by which changes may be made to the Constitution
15
New cards
American Political Culture
the set of beliefs, customs, traditions, and values that Americans share
16
New cards
Antifederalist (ex: Brutus)
Those opposed to the proposed Constitution, who favored stronger state governments.
17
New cards
Bicameral (ex: we have the Senate and the House of Reps.)
Two house legislature
18
New cards
Bill of Attainder
when the legislature declares someone guilty without a trial
19
New cards
Block Grants (evidence of devolution)
a grant that gives the states a big chunk of money, and the states get a lot of flexibility in how they want to spend it
20
New cards
Categorical Grants
Federal grants provided to states used only for specific purposes
21
New cards
Commerce Clause
grants Congress the authority to regulate interstate business and commercial activity
22
New cards
Checks and Balances
Aspects of the Constitution that require each branch of the federal government to gain the consent of the other two in order to act.
23
New cards
Concurrent Powers (ex: lawmaking and taxation)
Powers shared by the federal government and state governments
24
New cards
Constitutional Convention
a meeting attended by state delegates in 1787 to fix the Articles of Confederation
25
New cards
Constitutional Republic
a democratic system with elected representatives in which the Constitution is the supreme law
26
New cards
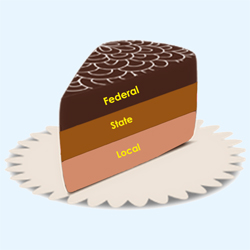
Cooperative Federalism (ex: marble cake federalism)
a form of American federalism in which the states and the national government work together to shape public policy

27
New cards
Democracy
system where the power of the government is vested in the people who rule directly through elected representatives
28
New cards
Devolution
returning more authority to state or local governments
29
New cards
Dual Federalism (ex: layer cake federalism)
a form of American federalism in which the states and the nation operate independently in their own areas of public policy
30
New cards
Elitist Democratic Theory (elitism)
a theory of democracy that the elites (usually the wealthy/those of higher rank) have a disproportionate amount of influence in the policymaking process
31
New cards
Ex Post Facto Law
a law punishing people for acts that were not crimes at the time they were committed
32
New cards
Executive Branch (the president)
the branch of government that carries out/enforces laws
33
New cards
Expressed (Enumerated Powers)
authority specifically granted to a branch of the government in the Constitution-found in Article 1, section 8
34
New cards
Faction (Madison spoke of the dangers of faction in Federalist Number 10)
a group of self-interested people who use the government to get what they want, trampling the rights of others in the process
35
New cards
Federal Revenue Sharing
when the federal gov. apportions tax money to the states with no strings attached
36
New cards
Federalism
the sharing/division of power between the national gov. and the states
37
New cards
Federalists (ex: Publius)
supporters of the proposed Constitution, who called for a strong central govt
38
New cards
Federalist Papers
a series of 85 essays written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay (using the name "Publius") published between 1787 and 1788 that lay out the theory of the Constitution, for the ratification and convincing people to vote for it
39
New cards
Federal System
a system where power is divided between the national and state govs.
40
New cards
Fiscal Federalism
Federal government using money (grants) to influence & control states.

41
New cards
Full Faith and Credit Clause
constitutional clause requiring states to recognize the public acts, records, and civil court proceedings from another state
42
New cards
Government
the rules and institutions that make up that system of policymaking
43
New cards
Grants-in-aid
federal money provided to states to implement public policy objectives
44
New cards
Great Compromise (Connecticut Compromise)
an agreement for a plan of government that drew upon both the Virginia and New Jersey Plans; it settled issues of state representation by calling for a bicameral legislature with a House of Representatives apportioned proportionately and a Senate apportioned equally
45
New cards
Implied Powers (the Necessary and Proper Clause fulfills these)
powers that congress has that are not stated explicitly in the constitution, goes beyond expressed powers
46
New cards
Institutions
the structure of gov, including the executive, legislature, and judiciary
47
New cards
Judicial Branch
Interprets the laws, hears and decides cases through the federal courts
48
New cards
Legislative Branch
the branch of government that makes/writes the laws, can override veto by pres.
49
New cards
Liberty
social, political, and economic freedoms
50
New cards
Limited Government
The idea that certain restrictions should be placed on government to protect the natural rights of citizens.
51
New cards
Mandates (AKA "unfunded mandates")
federal gov. declares/requires that a state must do something, but provides no money for it
52
New cards
Natural Rights
the idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property, that the gov. cannot take away
53
New cards
Necessary and Proper Clause (Elastic Clause)
language in Article 1, section 8 that allows Congress to carry out all powers necessary to carry out their enumerated powers
54
New cards
New Jersey Plan
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for equal representation of each state in Congress regardless of the state's population (unicameral legislature)
55
New cards
Participatory Democratic Theory
a theory that widespread political participation is essential for democratic government
56
New cards
Pluralist Democratic Theory
a theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of interest groups in the policy making process
57
New cards
Politics
the process of influencing the actions and policies of government
58
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
idea that the government’s power comes from the will of the people or the consent of the governed
59
New cards
Privileges and Immunities Clause
constitutional clause that prevents states from discriminating against people from out of state
60
New cards
Republicanism
a government where elected leaders represent the interests of the people
61
New cards
Reserved Powers
powers not given to the national gov. which are retained by states and the people
62
New cards
Separation of Powers
a design of government that distributes powers across institutions in order to avoid making one branch too powerful on its own
63
New cards
Shay's Rebellion
a popular uprising against the government of Massachusetts due to raised taxes the farmers couldn't pay, led by the farmer Daniel Shays, due to the Articles of Confederation
64
New cards
Social Contract
An agreement between people and government in which citizens consent to be governed so long as the government protects their natural rights (people allow their gov. to rule over them to ensure an orderly society)
65
New cards
Supremacy Clause
constitutional provision declaring that the Constitution and all national laws and treaties are the supreme law of the land (States are BOUND)
66
New cards
Three Fifths Compromise
an agreement reached by delegates at the Constitutional Convention that a slave would count as three-fifths of a person in calculating a state's representation (south wanted slaves to count as a whole person to raise populational data and rewards)
67
New cards
Unicameral
One house legislature (what the New Jersey plan wanted)
68
New cards
Virginia Plan
a plan of government calling for a three-branch government with a bicameral legislature, where more populous states would have more representation in Congress
69
New cards
Writ of Habeas Corpus
the right of people detained by the government to know the charges against them
70
New cards
STEP ONE : Proposal
A) 2/3 of the House and the Senate or
B) 2/3 of State Legislatures call a convention to propose
STEP TWO : Ratification
A) 3/4 of the State Legislatures approve
or
B) 3/4 state ratifying conventions (separate convention at each state)
A) 2/3 of the House and the Senate or
B) 2/3 of State Legislatures call a convention to propose
STEP TWO : Ratification
A) 3/4 of the State Legislatures approve
or
B) 3/4 state ratifying conventions (separate convention at each state)
How do you make an amendment?
71
New cards
false (EXECUTIVE AND JUDICIAL BRANCHES HAVE NO FORMAL ROLE IN THIS PROCESS-it’s just for Congress)
true or false? the executive and legislative branches have roles in the amendment process
72
New cards
Rule of Law
the principle that governmental authority is legitimately exercised only in accordance with written and publicly disclosed laws
73
New cards
Federalism
the sharing/division of power between the national gov. and the states
74
New cards
evidence of devolution
What is the significance of block grants?
75
New cards
McCulloch (federal) v. Maryland (state)
Argument between federal and state governments debating if congress has the power to make a bank, and if states have the power to tax that federal bank. (**FEDERALISM)**
76
New cards
US (federal) v. Lopez (state)
Argument between federal and state governments debating whether congress had the authority to pass the Gun-Free School Zones Act
77
New cards
electoral college
you need 51% of votes from the _____________ to win the presidency
78
New cards
YES! Congress has the power to make a bank through the necessary and proper clause and their implied powers
NO! Maryland thought they had the power to tax the bank, as it is one of their implied powers through the Constitution. Maryland doesn't have the power to tax in this instance because of the Supremacy Clause-federal government is supreme over the state government in terms of conflict
NO! Maryland thought they had the power to tax the bank, as it is one of their implied powers through the Constitution. Maryland doesn't have the power to tax in this instance because of the Supremacy Clause-federal government is supreme over the state government in terms of conflict
What did the Supreme Court rule on the fundamental questions from McCulloch v. Maryland? And Why? (Does Congress have the power to make a bank? and Does the state of Maryland have the power to tax that federal bank?)
79
New cards
McCulloch (federal) v. Maryland (state)
What supreme court case established the existence of implied powers, clarified how the USA federal system would work, and greatly increased the powers of Congress and the federal government
80
New cards
US (federal) v. Lopez (state)
What supreme court case held that the Congress had overstepped its power under the Commerce Clause for the first time in half a century, preserved federalism, and limited the power of the federal government in relation to the states
81
New cards
NO! Congress exceeded its constitutional authority under the Commerce Clause when it passed a law prohibiting gun possession in local school zones and also said that it wasn't an economic issue (congress thought they could pass this law using commerce clause to their advantage)
What did the Supreme Court rule on the fundamental question from Lopez v. USA? And Why? (Does Congress have the power to pass the Gun-Free School Zones Act?)
82
New cards
Apportionment
The process of determining the number of representatives for each state using census data
83
New cards
Cloture
A procedure through which senators can end debate on a bill and proceed to action, provided three-fifths (60) of Senators agree to it.
84
New cards
Committee Chair
leader of a congressional committee who has authority over the committee’s agenda
85
New cards
Committee of the Whole
Consists of all members of the House and meets in the House chamber but is governed by different rules, making it easier to consider complex and controversial legislation
86
New cards
Conference Committee
A temporary joint committee that resolves differences between the House and Senate versions of a bill, which is required by the Constitution before a president can sign the bill into law
87
New cards
Constituencies
A body of voters in a given area who elect a representative or senator
88
New cards
Delegate
The idea that the main duty of a member of Congress is to carry out constituents' wishes
89
New cards
Select/Special Committee
Temporary committees that are usually called upon to investigate an issue, sometimes in response to a crisis or scandal.
90
New cards
Senate Majority Leader
The person who has the most power in the Senate and is the head of the party with the most seats
91
New cards
Speaker of the House
The leader of the House of Representatives, chosen by an election of its members
92
New cards
Standing Committees
Where most of the work in Congress gets done. They are permanent committees that are divided by policy area, and members tend to serve on them for multiple terms, developing expertise. They consider legislation and exercise oversight of bureaucratic agencies, usually recommending funding levels for them. They are divided into subcommittees, which specialize even further, usually considering parts of legislation under instructions from their parent committees.
93
New cards
Trustee
The idea that members of Congress should make decisions based on their knowledge and judgement
94
New cards
Unanimous Consent
an agreement in the Senate that sets the terms for consideration of a bill.
95
New cards
Unified Government
the political condition in which the same political party controls the presidency and BOTH houses of Congress
96
New cards
Veto
formal rejection by the president of a bill that has passed both houses of Congress.
97
New cards
Whip
A member of Congress, chosen by his or her party members, whose job is to ensure party unity and discipline
98
New cards
Discharge Petition
A motion filed by a member of Congress to move a bill out of committee and onto the floor of the House of Representatives for a vote
99
New cards
Divided Government
Control of the presidency and one or both chambers of Congress split between the two major parties
100
New cards
Filibuster
A tactic through which an individual senator may use the right of unlimited debate to delay a motion or postpone action on a piece of legislation