AP Chemistry Units 4, 5, 6
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
SNAP
Sodium (NA), Nitrate (NO3), Ammonium (NH4), Potassium (K) are always soluble
When doing stoichometry, never forget..
the limiting reactant
Percent error equation
actual-theoretical/theoretical
Oxidation
Loses Electrons
Reduction
Gains Electrons
amphoteric
substance that can act as both an acid and a base
To find rate orders..
find where concentrations are constant, check for double/triple/quadruaple. Set it up by putting x with the power of two = the amount it multipled by.
Zero order reaction
The graph is a straight line equal to -k and concentration vs. time.
First order reaction
The graph is the natural log of [A] vs. Time. This creates a straight line with a slope of -k and y-interest of ln[A] at time 0.
Second order reaction
The inverse concentrations vs. time create a straight line, where the slope is k and y-intercept is (1/[A]) at time zero
Half life equation
For first order reactions, the half-life is constant and is given by the equation t1/2 = 0.693/k.
Collision Theory
Collision theory states reactions only occur when chemicals collide with each other with sufficient energy (activation energy).
They can react more..
if there's a higher concentration of aqueous or gaseous
substances, or a high surface area of a solid substance.
Molecules will only react if they collide
with the correct orientation.
Where is activation energy on a graph?
Activation energy is represented as the peak of the energy barrier that reactants must overcome during a chemical reaction on an energy vs. reaction coordinate graph.
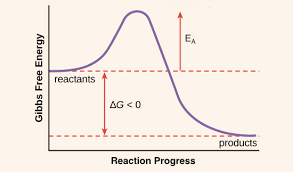
Intermediate
formed and then consumed
Catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy without being consumed in the process. consumed and then formed
unimolecular
reaction involving a single reactant molecule that undergoes a change in structure or composition.
slow step is the
rate determining step
if the slow step has an intermediate
replace it by using other steps
The reaction rate is written with the
reactants (not products)
In a multistep energy diagram, the highest peak
is the slowest step
first law of thermodynamics
states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
Enthalpy
Change in H, positive is endo, negative is exo
Entropy
Change in S
specific heat
of substance is how much heat is required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius (or one degree kelvin)