Botany Exam 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
6 Characteristics that all organisms share.
Order - Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, ecosystems
Sensitivity - Living things respond to stimuli, Different stimuli for different organisms
Growth and Development - Seed → Seedling → Plant
Energy Processing - Asexual/ Sexual
Regulation/ Homeostasis - Maintain internal conditions dispite environmental changes, like temp and pH
Evolution/ Adaptation - Change over time, have characterisitics that help with survival and reproduction
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for observed phenomena
Theory
An idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events
Law in science
A statement that describes an observable occurence in nature that appears to always be true
Independent v Dependent variables
Value is indepedent of the experiment outcome; Variable that is set by the experimenter.
VS
Value is dependent on the experimental outcome; What we are testing.
Are controlled experiments the only valid scientific experiments?
No, sometimes it is not possible to run a controlled experiment to collect data.
How do you define a control group/ experimental group?
Group that does not have the independent variable, tests to ensure the value of the dependent variable is affected by the value of the independent variable
What other kindss of experiments can you do?
Quasi-experimental - Est. a cause and effect relationship between an independent and dependent variable
What kinds of data are qualitative ?
Descriptions rather than measurements
Quantitative?
Recorded measurements, organized into tables and graphs
What is a monomer?
A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
What reaction is used to build polymers?
Dehydration synthesis
What reaction is used to breakdown polymers?
Hydrolysis reactions
Why aren’t lipids, polymers?
Because they are not made of repeating smaller molecules
What are the smaller molecules of fats, phospholipids, and steriods?
Glycerol, triglycerol, phospholipids, and sterols
What is the monomer and function of Carbs?
Monosaccharide and act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism, and help with fermentation.
Monomer and function of proteins?
Amino acids and helps repair and build your body's tissues. It drives metabolic reactions, maintains pH and fluid balance, and keeps the immune system strong. It also transports and stores nutrients and can act as an energy source.
Monomer and function of nucleic acids?
Nucleotide and storage and expression of genomic information. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, encodes the information cells need to make proteins.
What are the structural components of amino acids?
Carboxlyic acid, anime, R group, and central C-H backbone
Glucose
Structure
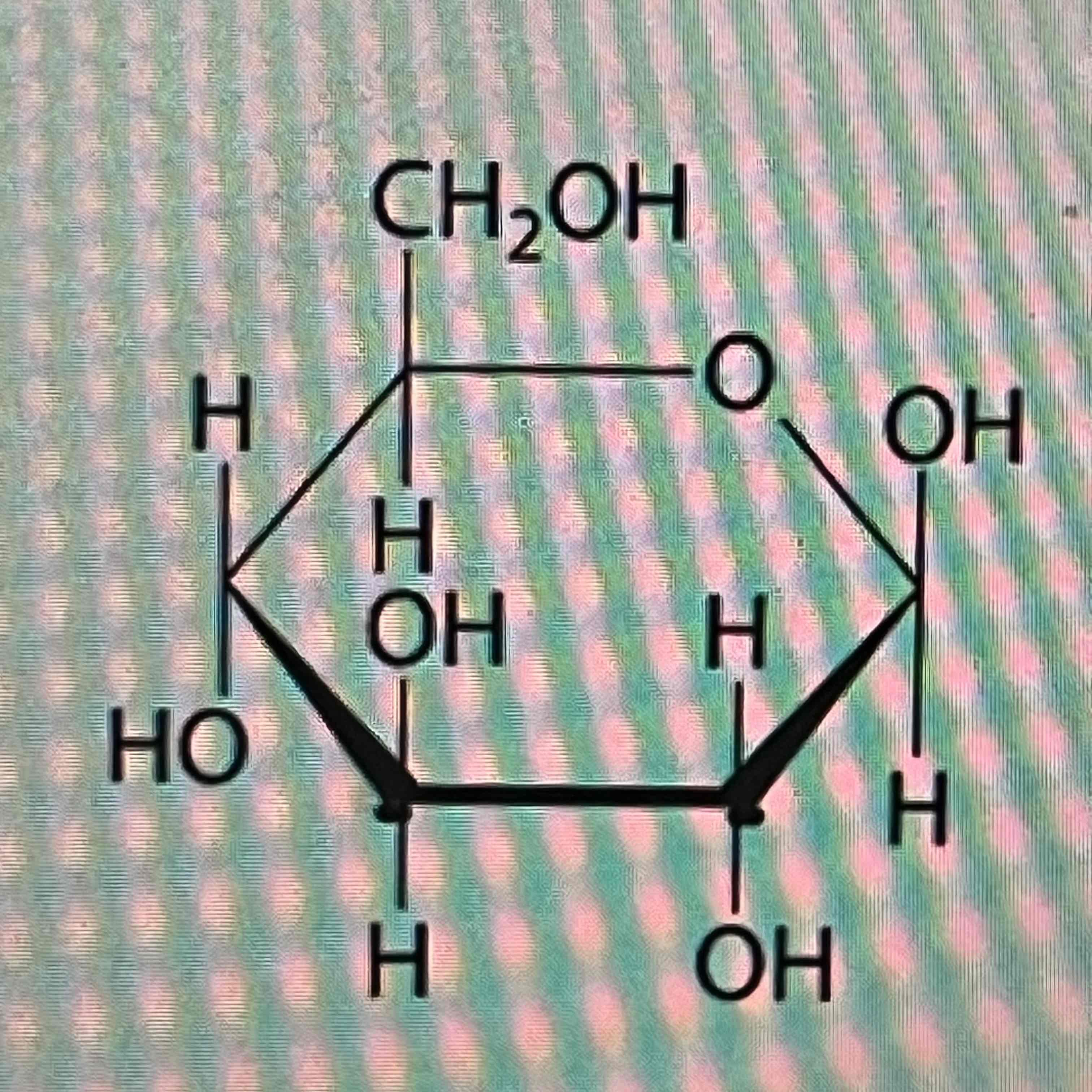
Cysteine
Structure
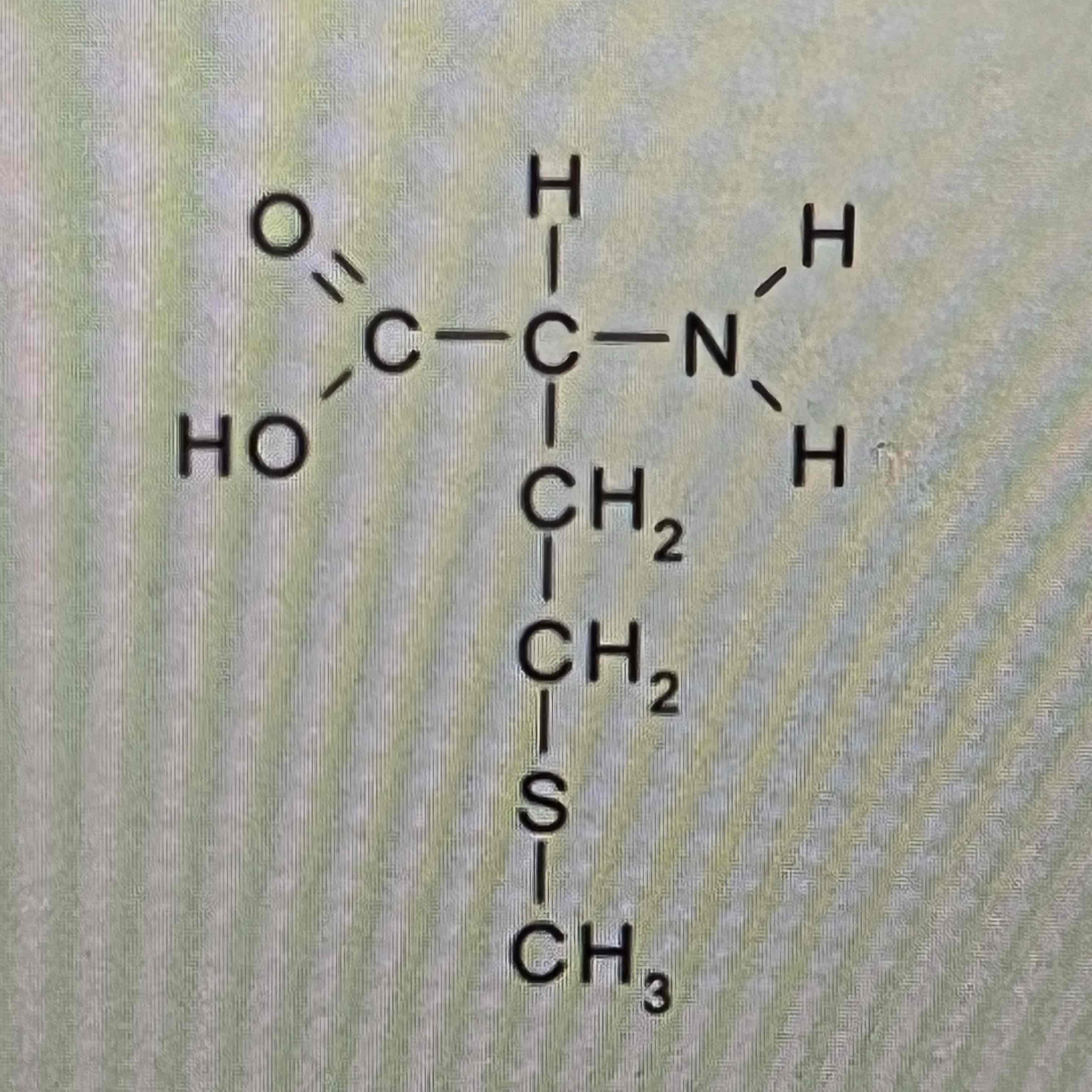
Triglycerol
Structure
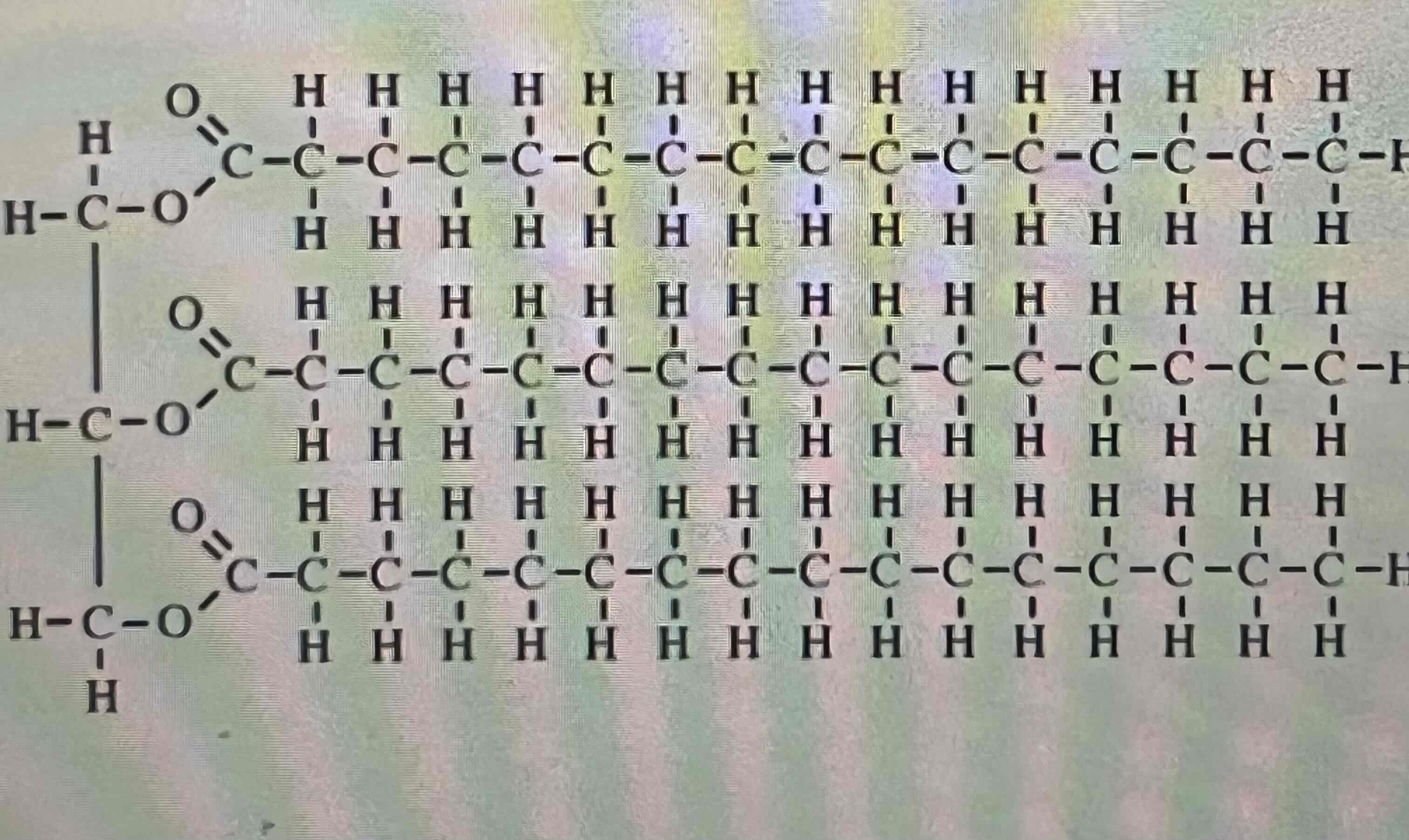
Nucleotide
Structure
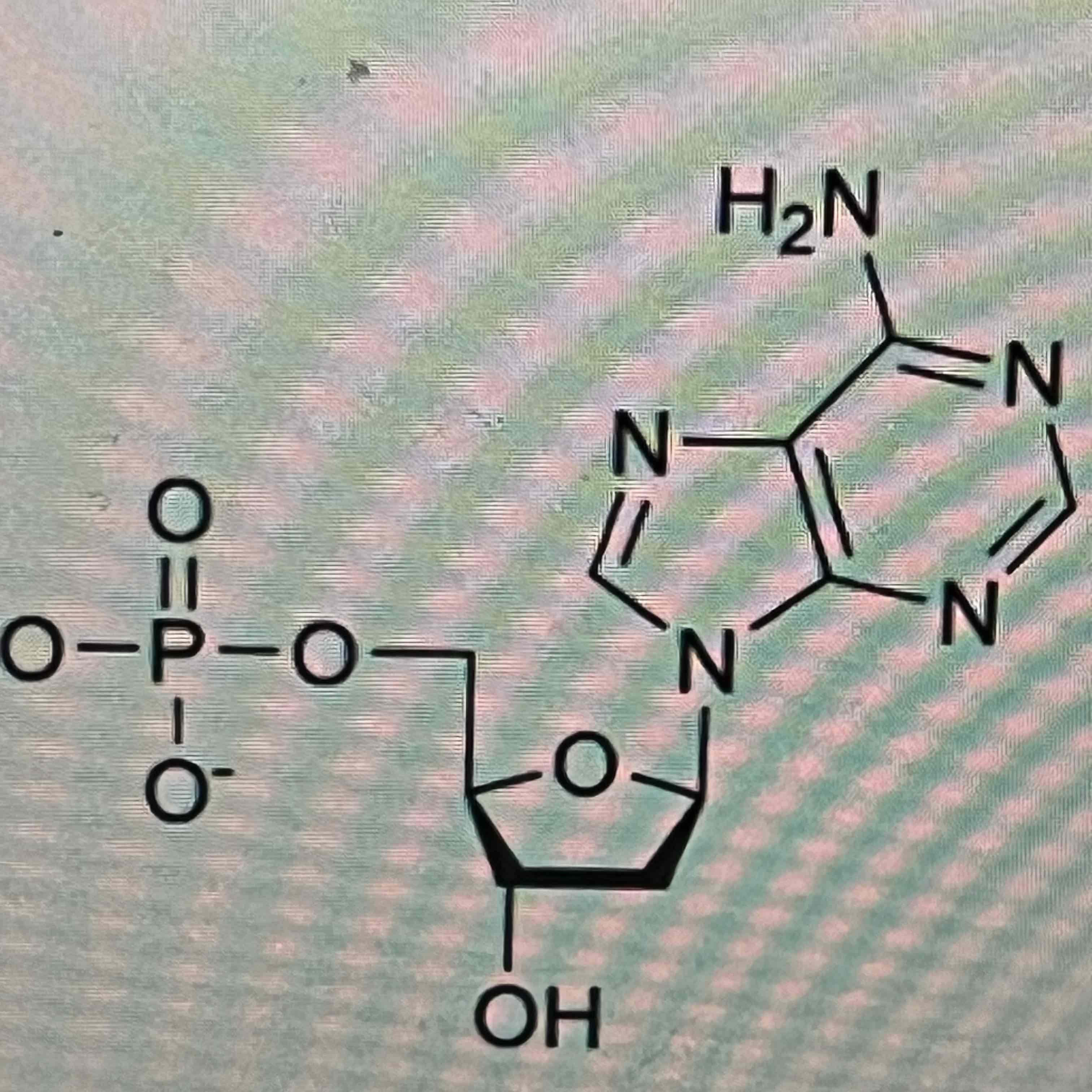
What makes each amino acid unique?
It’s R group
Primary structure of proteins
Chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Secondary structure of proteins
Alpha helix or Beta pleated sheet
Tertiary structure of proteins
3D globular shape
Interactions with water, acids, and bases attracted to each other
Quarternary structure of proteins
Only occurs when the protein is made of more than one polypeptide chain
Function of proteins
Enzymes - Speed of chemical rxns
Structure - Storage of amino acids
Transport- Transport materials across materials
Components of a nucleotide?
Phophate group
Sugar
Base
What are the differences and similarities between DNA and RNA?
DNA:
RNA:
What are the three components of the cell theory?
Cells are the basic units of life
All living things are made up of cells
All cells come from other cells
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and do not have any organelles
Similarities between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
DNA, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Region inside the cell, metabolism of the cell, cytoskeleton provides shape and structure to the cell and organelles
Nucleus
Control center of the cell (contains DNA), surrounded by nuclear envelope to control what enters through nuclear pores, chromatin contains DNA and proteins, Nucleoli produce ribosomes
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis, surrounded by double membrane, thylakoids are stacked into grana, Stoma is liquid between DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes
Mitochondria
SIte of cellular respirattion, double membrane, folds called cristae and liquid space in b/w is the matrix, has own DNA and ribosomes
Plastids - Leucoplasts
Double membrane bound, 3 types, colorless and used for storage
Amyloplast (store starch)
Tannosomes (store tannins)
Elaioplasts (store oils)
Plastids - Chromoplasts
Store red, orange, yellow pigments
Microbodies
Small, spherical, single membrane, contain enzymes
Peroxisomes
Role in metabolism, development and stress responses
Nuclear Pores
Membrane of nucleus
Nucleoplasm
DNA + Proteins → chromatin
Maintain shape and structure of nucleus
Rough ER
Have RIBOSOMES
Protein production ends here
Transport of proteins
Tonoplast
Membrane surrouding central vacuole
Microtubulues/Microfilaments
Cytoskeleton
Support structure
Movement internally
Desmotubule
Tube passes through cell wall
Allows cytoplasm to pass through multiple cells lined w/ plasma membrane
Cell wall
Structure/suppport for outside of the cell
Neighboring cell wall
Central vacoule
Used for storage of H2O, Na+, C6H12O6, and waste products
Middle lamella
Glue between cell walls
Plasma membrane
Regulate materials going in and out of the cell
Plasmodesmata
Connections between cells
Transport of material in cytoplasm
Smooth ER
No RIBOSOMES
Lipid production/membrane assemby
Cytosol
H2O, Na+, enzymes, metabolic processes
Dictoyosomes
Similar to golgi body
Package, process, and transport proteins
Works through vesicles
Nuclear envelope
Surround nucleus
Nucleolus
Ribsomes are produced
protein production
Components and their functions of a cell wall
Cellulose form microfibrils
Pectin, lignin and Hemicellulose to the microfibrils together
Lignin - Support/Structure provides tension for full central vacoule for tugor pressure
Phospholipid bilayer - provides protection to the
Plasmodesmata - Transport of nutrients, water, and other molecules
Fluid mosaic model components and roles in the plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer - regulate what can pass through the membrane
Proteins - transport in/out of membrane
Carbs - glycolipids and glycoproteins used for identification
Sterols - maintain fluidity of the membrane
What does it mean that the plasma membrane is selectively permeable
Allows some substances to cross more easily than others
Subatomic particle, location in atom, charge
+
Proton, nucleus, positive
Subatomic particle, location in atom, charge
-
Electron, orbits nucleus, negative
Subatomic particle, location in atom, charge
Neutron, inside of nucleus, neutral
Difference between covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bond?
Covalent: sharing of electrons
Ionic: transferring of electrons
Hydrogen: water type bonds (involves a hydrogen)
Property of water that makes it behave special compared to other molecules
Adhesion, cohesion, high heat of vaporization, and high polarity
Organic molecule?
Molecules made of carbon and hydrogen (can include other elements)
The different functional groups and types of molecules they are found in
Hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl groups
Proteins, carbs, and lipids
How can molecules pass through the membrane without using energy
Passive transport
What is diffusion?
Simple diffusion - movement of molecules across the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane
Facilitated diffusion - movement of molecules through proteins in the plasma membrane
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water across the across a selectively permeable membrane
Hypertonic
Solution has a high [] of solutes and a low concentration of water
water leaves, turgor pressure decreases, cytoplasm shrinks, plant wilts
Isotonic
Solution has a similar solute to water [] ratio
same amount of water flows in as out, equilibrium
Hypotonic
Solution has a low [] of solute and a high [] of water
water enters, turgor pressure increases, plant is upright