Early Lit II midterm
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Which of these is an example of reading fluency?
A student reads a text slowly and accurately decodes every word.
Student accurately reads text at a conversational rate with expression.
A student reads a text quickly without pausing between phrases.
None of these are correct
Student accurately reads text at a conversational rate with expression.
In order to read at a fluent rate, what must students be able to do?
Increase their working memory by 90 percent
Read a great number of words with automaticity
Attain a high level of WCPM
None of these are correct
Read a great number of words with automaticity
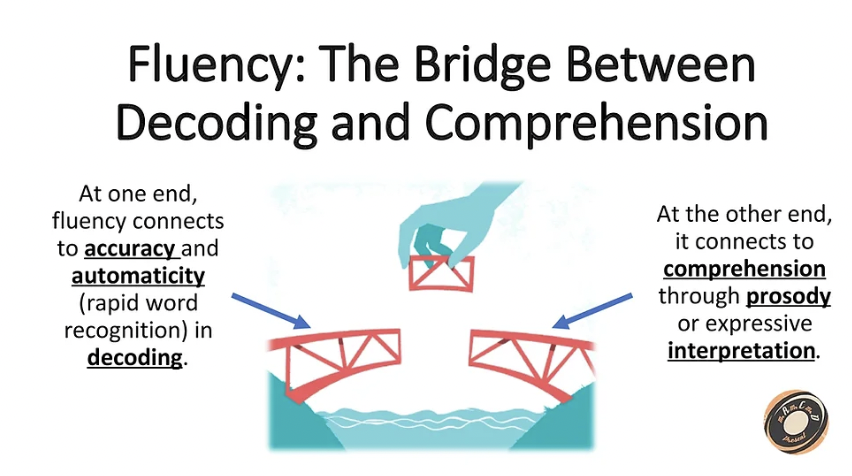
Fluency has been described as a bridge between what two reading components?
Phonics and vocabulary
Vocabulary and comprehension
Decoding and comprehension
None of these are correct
Decoding and comprehension
Which of these is the most important variable in explaining the differences in reading fluency?
The reader’s motivation and level of interest in the text
The proportion of words that the reader recognizes by “sight”
The size of the reader’s oral vocabulary
None of these are correct
The proportion of words that the reader recognizes by “sight”
ORF CBM measures overall reading proficiency. What are ORF scores based on?
Comprehension of connected text
Expressiveness of oral reading
Words read correctly per minute
None of these are correct
Words read correctly per minute
All of the following statements about ORF CBM are true except for which one?
Data from ORF CBM identify students who are at risk of reading failure.
Data from ORF CBM provides diagnostic information about the cause of dysfluency.
Data from ORF CBM identify which students are not making adequate progress.
None of these are correct
Data from ORF CBM provides diagnostic information about the cause of dysfluency.
How might a teacher use ORF norms?
To compare students’ ORF scores to the performance of others in their grade
To see if students’ ORF scores are valid and reliable
To identify the cause of a student’s dysfluent reading
None of these are correct
To compare students’ ORF scores to the performance of others in their grade.
Which of these is an example of prosodic reading?
A student pauses at the end of clauses and sentences.
A student often pauses after every word and within words.
A student equally stresses each word in a sentence.
None of these are correct
A student pauses at the end of clauses and sentences.
All of the following statements describe possible causes of dysfluent reading except for which one?
Lack of vocabulary
Lack of intonation
Limited content knowledge
Lack of sufficient decoding skills
Lack of intonation
When administering ORF CBM, which of these would be scored as an error?
Self-correcting an error within three seconds
Pausing after each word
Adding a word
Leaving out a word
Leaving out a word
All of the following are instructional methods for developing reading fluency except which one?
ORF digital graphing
Partner Reading
Repeated oral reading
Assisted reading
ORF digital graphing
Which of the following is an example of assisted reading?
Round robin reading
Two students reading aloud in unison
A teacher reading aloud a story to the class
A student reading aloud a story over and over
A teacher reading aloud a story to the class
In repeated oral reading, how many times do students have to reread the same passage aloud to obtain the most benefit?
six
Nine or ten
One or two
Three or four
Three or four
During timed repeated oral reading, how many minutes do you listen to a student read?
The time varies with the passage.
One minute
Seven minutes
Five minutes
One minute
All of the following are criteria for selecting the right text for fluency practice except which one?
Choosing a passage with an interesting topic
Using a passage that is less than 200 words in length
Using a nonfiction passage
Making sure a passage is difficult for the reader
Making sure a passage is difficult for the reader
Which level of text difficulty is described as “challenging but manageable for the reader”?
Frustration level
Instructional level
Decodable level
Independent level
Instructional level
In what major way does timed repeated oral reading differ from timed reading used to measure ORF rate and accuracy?
The text used for timed repeated oral reading is at a student’s grade level, not instructional level.
The purpose of timed repeated oral reading is to build a student’s oral reading fluency, not assess it.
Timed repeated oral reading is designed for skilled readers, not struggling readers.
There is no difference.
The purpose of timed repeated oral reading is to build a student’s oral reading fluency, not assess it.
Which instructional strategy might best benefit a student whose oral reading is characterized by staccato, or word-by-word reading?
Partner reading
Phrase-cued reading
Readers Theatre
Phrase-cued reading
Which is the formula for calculating an ORF score?
Total words read + errors
Total words read – errors
Total words read × errors
Total words read - erros
Not all students need instruction focused on building fluency. How would a teacher determine which students need fluency instruction?
Timed repeated oral reading
Assessment of a decodable passage
Assessment of word reading automaticity
Assessment of ORF and prosodic reading
Assessment of ORF and prosodic reading
Which is a description of receptive vocabulary?
Words we use when we talk or write
Words we use daily
Words we understand when heard or read
Words we understand when heard or read
According to Dale, what is the highest level of word knowledge?
The student can explain the meaning of a word and use it
The student has heard the word before but doesn’t know its meaning.
The student can associate a word with a concept or context.
The student can explain the meaning of a word and use it
How many root words can be taught directly during a school year?
About 8 per day
About 20 per day
About 2 per day
About 2 per day
Which statement describes the relationship between vocabulary knowledge and word recognition?
A student cannot decode a word if its meaning is unknown.
Each time a student sounds out a word, it is easier to remember what it means.
If a word is part of a reader’s oral vocabulary, the reader can more easily decode and understand it.
If a word is part of a reader’s oral vocabulary, the reader can more easily decode and understand it.
Which is a critical element in specific word instruction?
Focus on introducing words found on word lists
Focus on memorization of definitions of words
Focus on contextualized words that are useful to know
Focus on contextualized words that are useful to know
All of the following are primary goals of specific word instruction except for which one?
Use instructed words in understanding a text containing those words.
Find each instructed word in the dictionary, and use it in a sentence.
Recall instructed words well enough to use them when speaking and in writing.
Find each instructed word in the dictionary, and use it in a sentence.
In the three-tier system for selecting vocabulary words to teach, which word tier is best suited for explicit instruction?
Tier One
Tier Two
Tier Three
Tier Two
When selecting specific words to directly introduce to ELLs, which modification of the three-tier system should be considered?
Introduction of Tier-One, concrete words
Introduction of all Tier-Three words
Introduction of function words.
Introduction of function words.
All of the following are research-based methods for introducing specific vocabulary words except which one?
Providing dictionary definitions of the words
Providing short, playful opportunities for word engagement
Providing student-friendly explanations of the words
Providing dictionary definitions of the words
What is the purpose of using graphic organizers for specific word instruction?
To help students visualize word relationships
To encourage students to use new words at home
To provide students with a different context
To help students visualize word relationships
Which statement describes the purpose of independent word-learning strategies?
Contextualized words are harder to teach.
There are many more words to learn than can be directly taught.
During independent reading, new words are more easily learned.
There are many more words to learn than can be directly taught.
What should be a primary focus of instruction in dictionary use?
How to use the dictionary pronunciation key to properly pronounce the word
How to choose the dictionary entry that fits the context in which the word was used
How to use information in a dictionary definition to write a complete sentence
How to choose the dictionary entry that fits the context in which the word was used
Which is a term that describes “using word-part clues to figure out a word’s meaning”?
Phonemic analysis
Morphemic analysis
Contextual analysis
Morphemic analysis
Which set of words is an example of a word family?
predict, preview, prepare
lightning, bright, highlight
equal, equality, equalize
Equal, equality, equalize
Which pair of words illustrates that morphemic analysis does not always work?
painless and repay
mister and distance
nonfat and unpack
Mister and distance
Which is an example of explicit instruction on using word-part clues to derive the meaning of a word?
Explicitly teaching open and closed syllables
Explicitly teaching about false cognates
Explicitly teaching the meaning of prefixes
Explicitly teaching the meaning of prefixes
Which set of words is composed of two Greek roots?
telescope, photograph
riverbank, sweatshirt
predict, transport
Telescope, photograph
Some context clues are misdirective, or point readers to an incorrect meaning. Which type of context clue appears in the preceding sentence in this item?
Example
Synonym
Definition
Definition
Unlike helpful context clues, nondirective clues may confuse readers. In the preceding sentence in this item, which word acts as a signal word to the meaning of nondirective?
unlike
may
helpful
Unlike
Which statement about combined morphemic and contextual analysis instruction is the most accurate?
Combined instruction is only effective in Grades 1 and 2.
Combined instruction is just as effective as separate instruction.
Combined instruction is not as effective as separate instruction.
Combined instruction is just as effective as separate instruction.
Which is a general characteristic of word consciousness?
A student’s skill in sorting words into categories
A student’s interest in and awareness of words
A student’s ability to define academic words
A student’s interest in and awareness of words
All of the following strategies can be used for improving students’ word consciousness except which one?
Creating a word-rich classroom environment
Playing new word games with students
Using only basic vocabulary in classroom conversation
Using only basic vocabulary in classroom conversation
Which of these describes adept diction?
The ability to speak clearly and concisely
The ability to derive a word’s meaning from text
The skillful use of words in speech and writing
The skillful use of words in speech and writing
Which of these is an example of a complementary antonym pair?
sink and float
break and brake
ugly and beautiful
Sink and float
What is a connotation?
The literal meaning of a word
The dictionary definition of a word
The feeling a word evokes
The feeling a word evokes
What do similes, metaphors, and idioms have in common?
They are all figures of speech.
They are all palindromes.
They are all synonyms.
They are all figures of speech.
Which of these is an example of a metaphor?
Our star basketball player is an absolute machine.
That user’s manual is as clear as mud.
When we saw the diving board, we got cold feet.
Our star basketball player is an absolute machine.
There are three layers of the English language. Which set of words represents the Anglo-Saxon layer?
biology, morpheme, telephone
transport, spectator, credible
father, doghouse, happiness
Father, doghouse, happiness
Which layer of English is characterized by specialized words found mostly in science and technology?
The Latin layer
The Anglo-Saxon layer
The Greek layer
The Greek layer (remember telescope)
What do you call the expression “to pay through the nose”?
An idiom
Slang
A proverb
An idiom
What are the three layers of the English language?
Greek
Anglo-Saxon
Latin
What are complementary antonyms?
Complementary antonyms are pairs of words that represent opposite meanings, where the presence of one term necessarily excludes the other. For example, the words "alive" and "dead" are complementary antonyms, as something cannot be both alive and dead at the same time.
True or false?
Root words are always English words.
False; telephone → tele (Greek)
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“A habitat is the place where animals live.”
Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Definition
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“The tiny puppy was so small it fit in my hand.”
Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Synonym
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“Unlike his quiet friend, Ben was very loud.”
Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Antonym
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“There are many insects, like butterflies, ants, and bees.”
Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Example
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“After walking in the rain, her shoes were soaked.”
Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
General
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“A conga is a barrel-shaped drum.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Definition; the author provides a direct definition of an unfamiliar word, right in the sentence.
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“At night you can see constellations, or groups of stars, in the sky.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Appositive Definition; a type of definition clue; When a word or phrase that defines or explains an unfamiliar word that comes before it.
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“My dog Buck travels everywhere with me. My friend’s canine buddy travels everywhere with him, too.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Synonym; The author uses another word or phrase that is similar in meaning, or can be compared, to an unfamiliar word.
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“I thought the movie would be weird, but it turned out to be totally mundane.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Antonym; The author uses another word or phrase that means about the opposite of, or is in contrast with, an unfamiliar word.
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“In science we are studying marine mammals such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
Example; The author provides several words or ideas that are examples of an unfamiliar word.
What type of context clue is the following sentence:
“Einstein rode his bike everywhere. He though driving a car was way too complicated.”
Definition, Appositive Definition, Synonym, Antonym, Example, General
General; The author provides several words or ideas that are examples of an unfamiliar word.
What do the components of effective vocabulary instruction include?
Incidental vocabulary learning, intentional vocabulary teaching, and word consciousness.
Are the following examples of receptive or productive vocabulary?
Listening and reading.
Receptive vocabulary
Are the following examples of receptive or productive vocabulary?
Speaking and writing.
Productive vocabulary
What is receptive vocabulary?
The set of words to which a student can assign some meaning when listening or reading.
What is productive vocabulary?
The set of words students use frequently in their speaking and writing.
Which is generally larger, receptive or productive vocabulary?
Receptive; people usually recognize more words than they regularly use.
Which component of effective vocabulary instruction do the following fall under:
Rich oral language experiences
Wide reading (Teacher read-alouds, independent reading)
A. Incidental vocabulary learning
B. Intentional vocabulary teaching
C. Word consciousness
Incidental vocabulary learning
Which component of effective vocabulary instruction do the following fall under:
Specific word instruction (Rich and robust instruction of words in text)
Word-learning strategies (Dictionary use, morphemic analysis, contextual analysis, cognate awareness [ELL])
A. Incidental vocabulary learning
B. Intentional vocabulary teaching
C. Word consciousness
Intentional vocabulary teaching
Which component of effective vocabulary instruction do the following fall under:
Adept diction
Word play
Word origins
A. Incidental vocabulary learning
B. Intentional vocabulary teaching
C. Word consciousness
Word consciousness
What are the four levels of Dale’s Levels of Word Knowledge?
(1) Have never seen or heard the word before
(2) Have seen or heard the word before, but don’t know what it means
(3) Vaguely know the meaning of the word; can associate it with a concept or context
(4) Know the word well; can explain it and use it
How is vocabulary linked to comprehension?
When students know the meanings of words, they can more easily decode sentences and grasp the overall message of the text. In return, understanding the overall meaning of a text helps students learn new words in context.
Components of vocabulary instruction
Wide reading, word consciousness, word learning strategies, specific word instruction