All 27 Amendments of the U.S Constitution
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Bill of Rights (1791)
A collective name for the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1791.

1st Amendment
Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, Petition

2nd Amendment
Right to Bear Arms / Possess Weapons

3rd Amendment
Quartering soldiers / prohibition against forcing citizens to house soldiers.

4th Amendment
Protection against Unreasonable Search and Seizure

5th Amendment
The Right to Remain Silent/Double Jeopardy, right to due process

6th Amendment
The right to a Speedy Trial by jury, representation by an attorney for an accused person

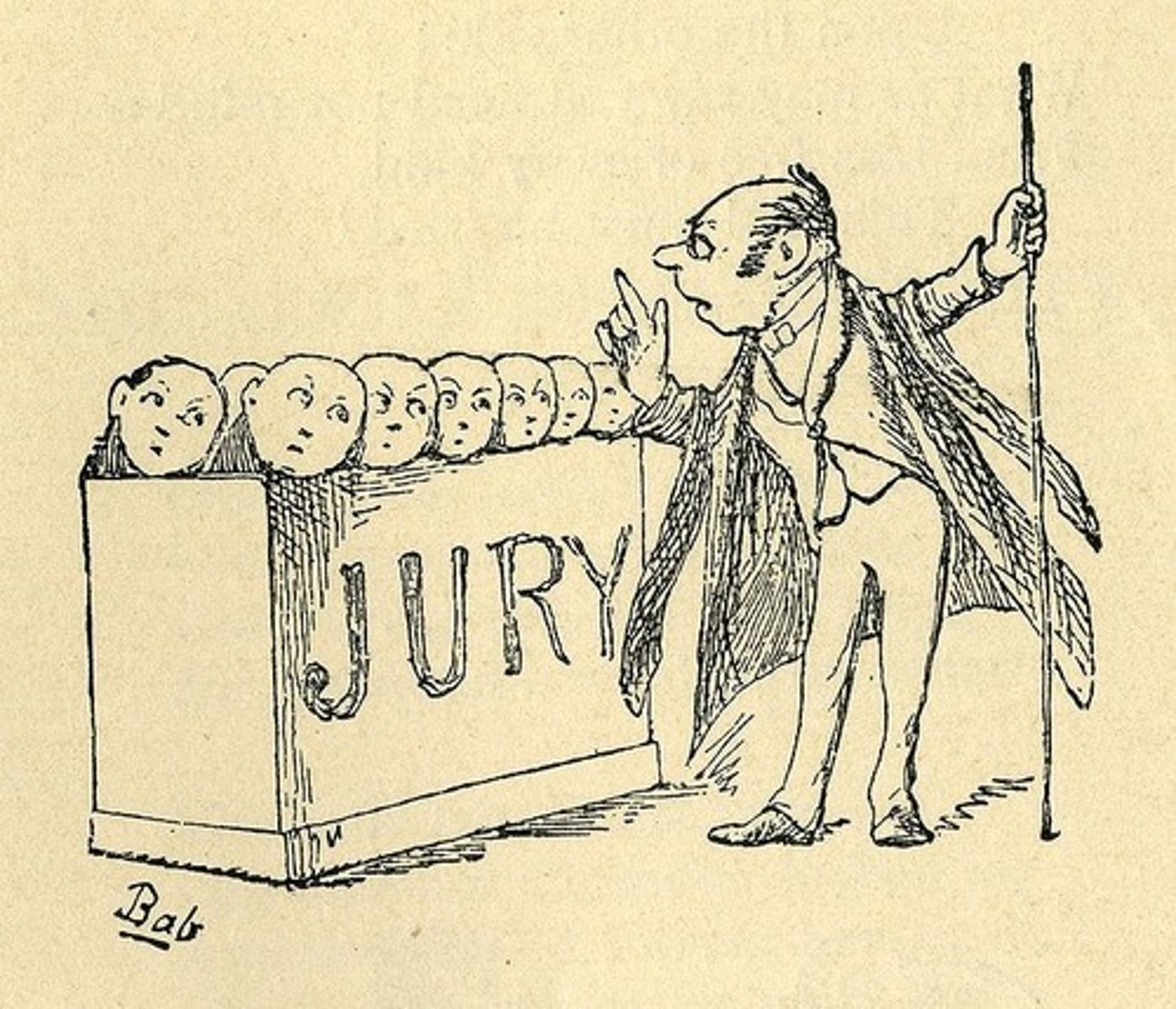
7th Amendment
Right to a trial by jury in civil cases
8th Amendment
No Excessive Bail or Cruel and Unusual Punishment

9th Amendment
Assertion that the enumeration of certain rights does not deny or disparage others retained by the people.

10th Amendment
Declaration that powers not delegated to the federal government are reserved for the states or the people.

Early Amendments
(11th and 12th Amendments) 1795-1804
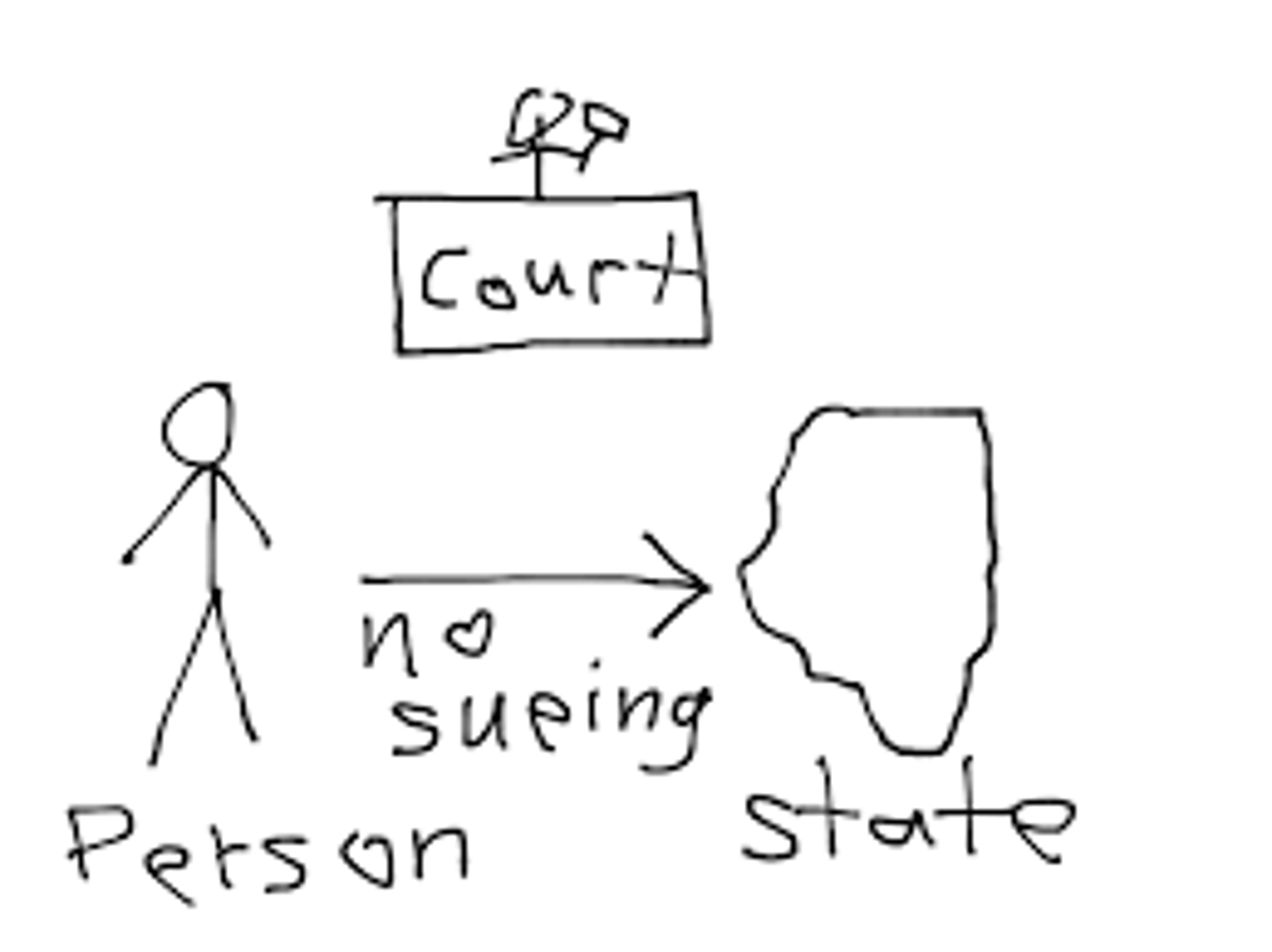
11th Amendment (1795)
Prohibits citizens of one state or foreign country from suing another state. Ratified in 1795.
12th Amendment (1804)
Separation of votes for President and Vice President. Ratified in 1804

Civil War and Reconstruction Amendments
13th, 14th, and 15th amendments - established rights no matter of race.

13th Amendment (1865)
Abolition of slavery and involuntary servitude, ratified in 1865.

14th Amendment (1868)
Guarantee of citizenship, equal protection under the law, and due process, ratified in 1868.

15th Amendment (1870)
Guarantee that the right to vote cannot be denied based on race, ratified in 1870.

Progressive Era Amendments
16th, 17th, 18th, and ents - instituting a variety of social reforms

16th Amendment (1913)
Authorization of a federal income tax, ratified in 1913.

17th Amendment (1913)
Provision for the direct election of U.S. Senators, ratified in 1913.
18th Amendment (1919)
The ban on the manufacture, sale, and transportation of alcohol, ratified in 1919. Later repealed by 21st amendment.

19th Amendment (1920)
Guarantee of women's suffrage / right to vote, ratified in 1920.

Repeal & Modernization Amendments
20 - 27 last amendments (1933 - 1992)

20th Amendment (1933)
Congress begins on January 30th; President starts on January 20th. "Lame-duck" Amendment, ratified in 1933.

21st Amendment (1933)
Repeal of prohibition for alcohol (18th Amendment), ratified in 1933.

22nd Amendment (1951)
Limitation of presidents to two terms, ratified in 1951.

23rd Amendment (1961)
Provision for presidential voting rights for residents of Washington, D.C., ratified in 1961.

24th Amendment (1964)
Prohibition of poll taxes in federal elections, ratified in 1964.

25th Amendment (1967)
Provisions for presidential succession and disability, ratified in 1967.

26th Amendment (1971)
Establishment of 18 years old as the minimum voting age, ratified in 1971.

27th Amendment (1992)
Stipulation that congressional pay raises take effect only after the next election, ratified in 1992.
