Geography: water and carbon
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Sublimation
The change of state of water from solid to a gas, without being a liquid

Storm hydrograph
Variation of river discharge over a short period of time (days).

Smart irrigation
Providing crops with water supply less than optimal, to make crops resistant to water shortages.

Secondary energy
The product of primary energy, mostly electricity

Saltwater encroachment
The movement of salt water into freshwater aquifers or soils, this may be caused by sea level rise, storm surges or over extraction

Salinisation
Where salt water contaminates freshwater stores or soil, creating saline conditions and reducing human use/consumption.

River regime
The patterns of river discharge over the year

Respiration
Process of converting glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy. Some organisms rely on respiration to survive

Renewable
Energy source that cannot runout(eg: wind, waves,biomass,hydroelectric solar etc)

Relief precipitation
When air masses are forced to rise over high land determined by the relief, Morphology of the land.

Primary energy
The initial source of energy, as it is naturally found. This could be the natural ores, water,crops and radioactive material

Phytoplankton
Small organisms that rely on photosynthesis to survive, does intake CO2. From the atmosphere

Physical water scarcity
Physical lack of available freshwater which cannot meet demands

Precolation
Water moving vertically from soil into permeable rock

Outgassing
Release of dissolved carbon dioxide (eg: at plate boundaries, warming the oceans).

Organic carbon
Carbon stored in plant material and living organisms

Open system
System affected by external flows and inputs (such as a drainage basin).

OPEC
Oil and Petroleum exporting countries. An organisation that supports and coordinates fossil fuel exporting countries.

Nuclear fusion
The process of joining atomic nuclei together to produce energy

Non-renewable
Source of energy that can only be used once (coal, gas, oil etc)

Monsoon
The drastic variation between wet and dry seasons for sub-tropical areas, caused by. Changed prevailing wind. Can lead to annual flooding

Meteorological droughts
When long erm precipitation trends are below average

Interception
When rainwater is prevented from hitting the ground due to the leaves of the trees catching them

In-organic carbon
Carbon stored in carbonated rocks

Integrated Drainage basin management
Establishing a frame of coordinated efforts between administration (eg: local governments) and stakeholders (eg: businesses) to achieve balanced management of a basin (world bank).

Hydrological drought
Insufficient soil moisture to meet the demands of vegetation (crops,trees,plants) at a particular time.

Groundwater flow
Water flowing slowly through rocks towards the sea.

Throughflow
Water flows downhill within the soil

Surface runoff
Water flows across the surface of earth becoming a stream.

Infiltration
The downward movement of water from the surface into the soil.

Global hydrological cycle
The continuous transfer of water between land, atmosphere and ocean. The Earth is a closed system.

ENSO-cycles
EL Nino Southern Oscillations-naturally occurring phenomena that involves the movement of warm water in the Equatorial Pacific.

Economic water scarcity
When water resources are available but insufficient economic wealth limits access to it.

Drainage Basin
The area of land drained by the river and its tributaries.

De-sublimation
The change of state of water form gas to solid. Without being a liquid.

Desalination plant
The conversion of seawater to freshwater, suitable for human consumption.

Depression
A system of low pressure, with fronts of precipitation wher low and high pressure air masses meet.

Decomposition
The break down of matter.

Cryosphere
Where water an be stored as ICE or snow

Lithosphere
When a source is stored in the ground/earth.

Biosphere
When a source is stored in a living organism/organic. (Eg: plants, animals)

Hydrosphere
A source is stored in water (eg: rivers,oceans,lakes,streams, etc)

Conventional precipitation
Solar radiation heats the air above the ground, causing it to rise,cool & condense forming precipitation (often as thunderstorms)

Combustion
The process of burning a substance,in the presence of oxygen, to release energy.

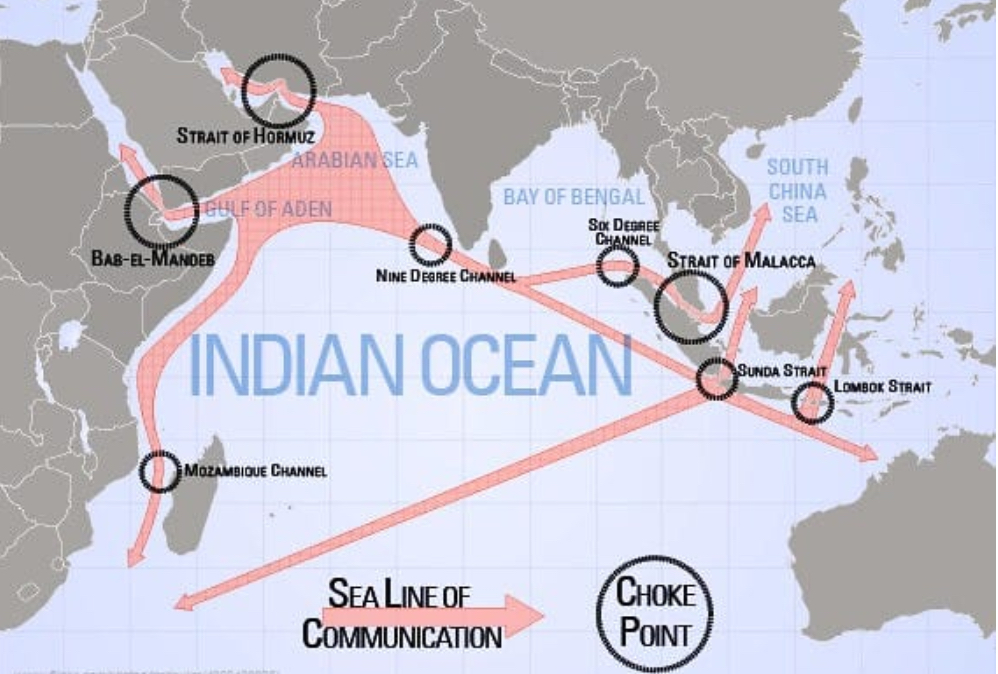
Choke points
The process of burning a substance, in the presence of oxygen, to release energy.

Choke point
A location with tactical and strategic importance such as a narrow land or sea passage, a bridge, or a tunnel, the destruction of which would hamper flows of trade and people

Channel flow
Water flows in a rivulet,stream or river

Carbon stores
Places where carbon accumulates for a period of time such as rocks and plant matter.

Carbon neutral
A process that has no net addition of carbon dioxide to the environment.

Carbon fluxes
The movement of carbon between stores

Carbon capture and storage (CCS)
The capture of carbon dioxide emissions directly from the factory, pumped into discussed mines rather than being released into the atmosphere.

Biofuel
Burning crops and vegetation for electricity and heat.

Aquifer
A permeable or porous which stores water.

Anticyclone
A system of high pressure, causing high temperatures and unreasonably high evaporation rates

Afforestation
Planting trees an vegetation in aim of increasing forest cover.

Acidification
The gradual reduction of PH of the oceans, due to dissolving carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

Evaporation-transpiration
The combined total moisture transferred from the earth to the atmosphere, through evaporation and transpiration
