EXAM 3 Patho 2 CH 43, 44, 45, 46
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:59 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Name the 3 principal systems and what each consist of:
CNS: brain, spinal cord
PNS: 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 12 pairs of cranial nerves(CN)
ANS: sympathetic(SNS) and parasympathetic(PSNS)
PNS: 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 12 pairs of cranial nerves(CN)
ANS: sympathetic(SNS) and parasympathetic(PSNS)
2
New cards
State the function of the CNS:
-receiving and processing sensory information
-creating appropriate responses to be relayed to muscles and glands.
-Coordinates emotion, memory, cognition, and learning
-creating appropriate responses to be relayed to muscles and glands.
-Coordinates emotion, memory, cognition, and learning
3
New cards
Name the 3 layers of Meninges: (outer to inner) hint: DAP
a. Which layer is collagenous?
b. Where does CSF flow?
a. Which layer is collagenous?
b. Where does CSF flow?
-Dura Mater (collagenous)
-Arachnoid Mater (CSF flows here)
-Pia Mater
-Arachnoid Mater (CSF flows here)
-Pia Mater
4
New cards
Blood supply of the brain:
Internal carotid arteries → → → Anterior circulation
Vertebral arteries → → → Posterior circulation
Circle of Willis→ → →Anterior and Posterior circulation at the base of the brain
Vertebral arteries → → → Posterior circulation
Circle of Willis→ → →Anterior and Posterior circulation at the base of the brain
5
New cards
State the functions of CSF:
-Mechanical support
-Remove metabolic products from the brain
-Transport chemical messenger compounds
-Maintain the chemical environment of the brain
-Remove metabolic products from the brain
-Transport chemical messenger compounds
-Maintain the chemical environment of the brain
6
New cards
State the functions of BBB:
a. What factors affect its permeability?
a. What factors affect its permeability?
Functions:
-physiological barrier
-separates brain and CSF from substances in the blood
-allows the brain and CSF composition to be maintained at different levels than blood
Factors affecting permeability:
-Inflammation
-Neovascularity (formation of microvascular networks in and around tendon tissue)
-Toxins
-Infants < 6 months of age BBB is immature and more permeable
-physiological barrier
-separates brain and CSF from substances in the blood
-allows the brain and CSF composition to be maintained at different levels than blood
Factors affecting permeability:
-Inflammation
-Neovascularity (formation of microvascular networks in and around tendon tissue)
-Toxins
-Infants < 6 months of age BBB is immature and more permeable
7
New cards
Names the 4 principal structures of the brain: (C-CBD)
a. What does the cerebrum consist of?
b. What does the brainstem consist of?
a. What does the cerebrum consist of?
b. What does the brainstem consist of?
-Cerebrum: cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic cortex, corpus callosum
-Cerebellum:
-Brainstem: midbrain, pons, medulla
-Diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland
-Cerebellum:
-Brainstem: midbrain, pons, medulla
-Diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland
8
New cards
State the function of the hypothalamus:
-Regulatory center for the ANS
-Along with the pituitary, produces and secretes hormones
-Sleep, body temperature, appetite, and sex drive
-Along with the pituitary, produces and secretes hormones
-Sleep, body temperature, appetite, and sex drive
9
New cards
State the function of the flocculonodular lobe:
-maintains equilibrium
-mediates the eye movements needed for visual tracking
-mediates the eye movements needed for visual tracking
10
New cards
State the function of the brainstem:
-Critical for transmission of impulses between the brain and spinal cord
-Vital centers for regulating respiratory and cardiovascular function
-Midbrain contains motor tracts to spinal cord
10/12 CN originate from nuclei of brain stem
-Vital centers for regulating respiratory and cardiovascular function
-Midbrain contains motor tracts to spinal cord
10/12 CN originate from nuclei of brain stem
11
New cards
State the function of the Spinal cord:
-Conveys nervous impulses between the brain and 31 pairs of spinal nerves
-Mediates spinal reflexes involved in the maintenance of posture, protective responses to pain, urination, and muscle tone
-Mediates spinal reflexes involved in the maintenance of posture, protective responses to pain, urination, and muscle tone
12
New cards
What is protected by CSF and meninges?
Brain and Spinal Cord
13
New cards
Which CN do not originate in the brainstem? Hint: there are 2.
CN I and II, which originate in the diencephalon.
14
New cards
What causes hydrocephalus?
When CSF becomes obstructed.
↑ amount of CSF
↑size of ventricles
↑ amount of CSF
↑size of ventricles
15
New cards
PNS contains how many spinal nerves?
31 pairs
16
New cards
mnemonic for 12 cranial nerves and their type (sensory or motor)
Some Say Money Matters But My Big Brother Says Big Books Matter More
17
New cards
State the rate of production/ reabsorption of CSF per day:
It is produced and reabsorbed at a rate of 500 ml/day (0.35ml/min).
18
New cards
The pineal gland is a part of which principle structure?
Diencephalon
19
New cards
What is the specialized function of the basal ganglia?
motor control
20
New cards
Name the 3 types of neurons:
-multipolar
-bipolar
-unipolar
-bipolar
-unipolar
21
New cards
Name the 4 types of neuroglia and state their functions:
-Oligodendrocytes: Form myelin sheath that wraps around nerve axons
-Astrocytes: Maintain the integrity of the BBB, regulate the ionic balance of the interstitial fluid, and transfer nutrients from capillaries to neurons
-Microglia: Provide phagocytic functions
-Ependymal cells: Produce CSF and maintain CSF-brain barrier
-Astrocytes: Maintain the integrity of the BBB, regulate the ionic balance of the interstitial fluid, and transfer nutrients from capillaries to neurons
-Microglia: Provide phagocytic functions
-Ependymal cells: Produce CSF and maintain CSF-brain barrier
22
New cards
Explain the process of synaptic transmission:
-Electrical impulses reach the presynaptic terminal
-Electrical impulses trigger release of neurotransmitters
-Neurotransmitters cross the synapse from vesicles
-neurotransmitters combine with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
-Stimulation of postsynaptic receptors by neurotransmitters result in either excitation
or inhibition of the postsynaptic membrane.
-Electrical impulses trigger release of neurotransmitters
-Neurotransmitters cross the synapse from vesicles
-neurotransmitters combine with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
-Stimulation of postsynaptic receptors by neurotransmitters result in either excitation
or inhibition of the postsynaptic membrane.
23
New cards
What does receptor stimulants alter?
They speed up messages travelling between the brain and body
24
New cards
Comparison: Ipsilateral vs. Contralateral
-Ipsilateral: in the Dorsal column (medial lemniscal) tract. touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception
-Contralateral: Anterolateral tract. pain, itch, and temperature
-Contralateral: Anterolateral tract. pain, itch, and temperature
25
New cards
State all of the spinal reflexes and their function:
Hint: there are 2
Hint: there are 2
-Stretch reflex: tests reflex arc between sensory muscle spindles and alpha motor neurons
-Withdrawal reflex: a protective mechanism that allows the withdrawal of a body part from a physical threat while maintaining balance
-Withdrawal reflex: a protective mechanism that allows the withdrawal of a body part from a physical threat while maintaining balance
26
New cards
What part of the neuron generates action potential?
Axon
27
New cards
Compare primary vs. secondary brain injury
Primary brain injury: occurs as a direct result of the initial insult.
Secondary injury: progressive damage resulting from the body's physiological response to the initial insult.
Secondary injury: progressive damage resulting from the body's physiological response to the initial insult.
28
New cards
What is critical in determining the neuronal cell fate after injury?
Critical factor in determining the neuronal cell fate after injury:
-degree of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depletion
-ischemia and hypoxia
-increased intracranial pressure
-degree of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depletion
-ischemia and hypoxia
-increased intracranial pressure
29
New cards
Ischemia vs. Hypoxia
ischemia: decreased oxygenated blood flow
hypoxia: decreased O2 at cellular level
(usually occur together)
hypoxia: decreased O2 at cellular level
(usually occur together)
30
New cards
What are the two mechanism that result in the death of brain cells?
Anaerobic metabolism and Deterioration of ion gradients
31
New cards
What is reperfusion?
restoration of the flow of blood to a previously ischemic tissue or organ.
32
New cards
Explain the Monroe-Kellie Hypothesis:
Intra-cranial pressure is in a state of dynamic equilibrium between the brain, CSF and blood.
An increase in any one of these necessitates a decrease in the others if normal intracranial pressure (ICP) is to be maintained.
An increase in any one of these necessitates a decrease in the others if normal intracranial pressure (ICP) is to be maintained.
33
New cards
Name 2 common causes that results in an increase in CSF volume:
obstructive hydrocephalus, nonobstructive hydrocephalus, pseudotumor celebri
34
New cards
Name 2 common cause that results in an increase in brain tissue volume:
tumor, hemorrhage, infection, cytotoxic edema, vasogenic edema, ischemia and necrosis
35
New cards
State the 3 elements that make up the volume of the cranium:
-brain tissue
-CSF
-blood
-CSF
-blood
36
New cards
What is autoregulation influenced by?
normally influenced by PaCo2 and PaO2
37
New cards
State the clinical manifestations of increased intracranial pressure:
-Headache, vomiting
-altered level of consciousness (drowsiness)
-Blurry vision and edema of the optic disk
-altered level of consciousness (drowsiness)
-Blurry vision and edema of the optic disk
38
New cards
Treatment of brain injury focuses on managing...
cerebral oxygenation
39
New cards
Explain Cushing Reflex (Ischemic response):
It is the last ditch to re-establish cerebral perfusion.
-increase BP>>>200mmHg
-bradycardia
-widening PP
-increase BP>>>200mmHg
-bradycardia
-widening PP
40
New cards
What does the level of consciousness(LOC) indicate?
Change in level of consciousness (LOC) is most sensitive indicator of altered brain function.
41
New cards
A patient's state of alertness and attentiveness to their environment depends on what?
State of alertness and attentiveness to one's environment and situation is dependent on activity in the RAS neurons
42
New cards
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)?
GCS is a standardized tool for assessing LOC in acutely brain-injured persons.
43
New cards
What is the scoring of the GCS based on?
Numeric scores are given to arousal-directed responses of eye-opening, verbal utterances, and motor reactions.
44
New cards
Know the GCS (which range is considered mild/ moderate/severe)
Mild (12-15), moderate (9 to 12), severe (
45
New cards
What is considered the most powerful predictor of patient's outcome?
Motor response is the most powerful predictor of patient outcome.
46
New cards
Differentiate between focal, polar, and diffused injury:
Focal: localized to site of impact
Polar: due to acceleration-deceleration movement of the brain within the skull (double injury)
Diffused: due to movement of the brain within the skull (widespread axonal injury) ex) shaken baby Sx
Polar: due to acceleration-deceleration movement of the brain within the skull (double injury)
Diffused: due to movement of the brain within the skull (widespread axonal injury) ex) shaken baby Sx
47
New cards
Which traumatic brain injury does not show any evidence of brain damage on a CT scan?
Concussion
48
New cards
Explain three types of intracranial hematoma:
-epidural: fracture of temporal bone>>>middle meningeal artery. Bleeding expands rapidly>>>acute deterioration of neurologic function
-subdural: rupture of bridging vein
-subarachnoid: both arterial and venous
-subdural: rupture of bridging vein
-subarachnoid: both arterial and venous
49
New cards
What is considered a secondary injury?
Body's response to initial injury may cause more harm than the initial injury.
50
New cards
How would you treat a patient suffering from a traumatic brain injury with elevated ICP?
-administration of mannitol (osmotic diuretic),
-sedation, hypothermia, and mild hyperventilation
-sedation, hypothermia, and mild hyperventilation
51
New cards
Embolic stroke vs. Thrombotic stroke:
Both are types of Ischemic Stroke.
Embolic: cardiac dysfunction or dysrhythmias (atrial fibrillation)
Thrombotic: Atherosclerosis and coagulopathies
Embolic: cardiac dysfunction or dysrhythmias (atrial fibrillation)
Thrombotic: Atherosclerosis and coagulopathies
52
New cards
What are the clinical manifestations of ischemic stroke?
-contralateral hemiplegia
-hemisensory loss
-contralateral visual field blindness>>>homonymous hemianopsia
-global aphasia (dominant hemisphere)
-hemisensory loss
-contralateral visual field blindness>>>homonymous hemianopsia
-global aphasia (dominant hemisphere)
53
New cards
What is hemorrhagic stroke?
a. Where does it occur?
b. How should it be treated?
a. Where does it occur?
b. How should it be treated?
Hemorrhage within the brain parenchyma that usually occurs secondary to severe, chronic Hypertension.
Most occur in basal ganglia or thalamus.
Treatment:
-Blood pressure management (keep mildly hypertensive at first)
Most occur in basal ganglia or thalamus.
Treatment:
-Blood pressure management (keep mildly hypertensive at first)
54
New cards
Broca vs Wernicke aphasia:
Broca aphasia (verbal motor/expressive) consists of poor articulation and sparse vocabulary.
Wernicke aphasia (sensory, acoustic, receptive) is characterized by impaired auditory comprehension and speech that is fluent but does not make sense
Wernicke aphasia (sensory, acoustic, receptive) is characterized by impaired auditory comprehension and speech that is fluent but does not make sense
55
New cards
Damage to the dominant cerebral hemisphere causes what to occur?
The dominant cerebral hemisphere controls language, so therefore aphasia will occur if damage is caused.
56
New cards
What is homonymous hemianopsia?
loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes
57
New cards
Recovery of motor function occurs with onset of ____________.
Spasticity
58
New cards
What are the most common causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Cerebral aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
59
New cards
What type of infections are associated with meningitis?
bacterial
60
New cards
What is encephalitis?
a. What is it commonly caused by?
a. What is it commonly caused by?
Inflammation of the brain, commonly caused by
West Nile virus, western equine encephalitis, and herpes simplex
West Nile virus, western equine encephalitis, and herpes simplex
61
New cards
What is a brain abscess?
a. What is it caused by?
b. How is it treated?
a. What is it caused by?
b. How is it treated?
-Localized collection of pus within the brain parenchyma
-Usually from pus-forming bacteria (pyogenic)
Treatment:
-drainage and/or excision of the abscess with IV antibiotic therapy
-Usually from pus-forming bacteria (pyogenic)
Treatment:
-drainage and/or excision of the abscess with IV antibiotic therapy
62
New cards
State some of the risk factors for CNS infections:
Risk factors:
-immunocompromise
-debilitation
-poor nutrition
-radiation
-steroid therapy
-contact with vectors
-immunocompromise
-debilitation
-poor nutrition
-radiation
-steroid therapy
-contact with vectors
63
New cards
State the pathogenesis of seizure:
alteration in membrane potential that causes certain neurons to become abnormally hyperactive and hypersensitive to changes in their environment
64
New cards
What are the possible causes of seizures?
-cerebral injury / lesions
-metabolic/nutritional disorders
-Idiopathic
-triggered by specific stimuli
-Seizures are a component of many diseases
-metabolic/nutritional disorders
-Idiopathic
-triggered by specific stimuli
-Seizures are a component of many diseases
65
New cards
What is status epilepticus?
Continuing series of seizures without a period of recovery between episodes
*Can be life-threatening
*Can be life-threatening
66
New cards
Partial vs. generalized seizures:
Partial: one hemisphere
Generalized: both hemispheres
Generalized: both hemispheres
67
New cards
State the type of seizure that affects children and causes staring spell:
Absence seizures (spell last a few seconds)
68
New cards
What are atypical absence seizures?
characterized by myoclonic jerks, automatisms with the staring spell
69
New cards
Differentiate between myoclonic, atonic, and tonic-clonic:
Myoclonic: single/several jerks
Atonic: fall down
Tonic-clonic: jerking of many muscles
Atonic: fall down
Tonic-clonic: jerking of many muscles
70
New cards
Be able to differentiate between simple partial and complex partial seizures:
Simple: No change in level of consciousness;
motor, sensory, and/or autonomic symptoms common
Complex: Change in consciousness
motor, sensory, and/or autonomic symptoms common
Complex: Change in consciousness
71
New cards
What is aura/prodrome?
subjective sense of an impending seizure
*A clue to the location of the epileptogenic focus*
*A clue to the location of the epileptogenic focus*
72
New cards
What steps should you take when someone is experiencing a seizure?
During a seizure:
-maintain airway
-protect from injury
-document course of seizure
-maintain airway
-protect from injury
-document course of seizure
73
New cards
How long should anticonvulsant medication be used?
Continued until no seizures for at least 2 years and then gradually withdrawn
*Not a cure*
*Not a cure*
74
New cards
What is dementia?
a. What are the types of dementia?
b. Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are indicators of what disease?
a. What are the types of dementia?
b. Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are indicators of what disease?
Sx characterized by progressive deterioration and continuing decline of memory and other cognitive changes
Types:
-Alzheimer's (has amyloid plaques/neurofibrillary tangles)
-Vascular
Types:
-Alzheimer's (has amyloid plaques/neurofibrillary tangles)
-Vascular
75
New cards
Deficient synthesis of ____________ is seen in people with Alzheimer.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
76
New cards
What is delirium?
A disoriented reaction with restlessness and confusion that may be associated with fear and hallucinations
77
New cards
What are the clinical manifestations of early Alzheimer? What are activities of daily
living (ADLs)?
living (ADLs)?
Clinical Manifestations:
Early
-Early memory loss. long-term memory may be preserved.
-Thinking ability declines
-↓ ability to function at work and in social settings
-Anxiety, agitation
Later
-Increasing difficulty with judgment, abstract thinking problem-solving, and communication
-Assistance with ADLs
-Difficulty with eating/swallowing
-Weight loss
-Loss of bladder and bowel control
-Complete loss of the ability to ambulate
-Personality and behavior changes
ADLs: eating, walking, dressing, and bathing
Early
-Early memory loss. long-term memory may be preserved.
-Thinking ability declines
-↓ ability to function at work and in social settings
-Anxiety, agitation
Later
-Increasing difficulty with judgment, abstract thinking problem-solving, and communication
-Assistance with ADLs
-Difficulty with eating/swallowing
-Weight loss
-Loss of bladder and bowel control
-Complete loss of the ability to ambulate
-Personality and behavior changes
ADLs: eating, walking, dressing, and bathing
78
New cards
How is Alzheimer diagnosed?
-Ruled out all manageable causes for dementia or delirium
-CBC, chemistry panel, thyroid function, vitamin B12 levels, and syphilis serology
-Chest x-ray, CT, MRI
-Lumbar puncture
-Mental status examinations
-clock drawing test
-tests of functional status
-CBC, chemistry panel, thyroid function, vitamin B12 levels, and syphilis serology
-Chest x-ray, CT, MRI
-Lumbar puncture
-Mental status examinations
-clock drawing test
-tests of functional status
79
New cards
Which medication is used to treat moderate Alzheimer?
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Indicated for patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's Dx.
Tacrine (Cognex), donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon), and galantamine (Reminyl)
Indicated for patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's Dx.
Tacrine (Cognex), donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon), and galantamine (Reminyl)
80
New cards
What is Parkinson's disease?
Motility Disorder
-Dopamine deficiency in the basal ganglia
>>Motor impairment
>>Lewy bodies
-Difficulty initiating and controlling movements results in:
-Akinesia: absence or loss of power of voluntary movement
-Tremor: occurs at rest and hand tremors exhibit pill-rolling movements.
-Rigidity: Attempts to passively move the extremities
-Dopamine deficiency in the basal ganglia
>>Motor impairment
>>Lewy bodies
-Difficulty initiating and controlling movements results in:
-Akinesia: absence or loss of power of voluntary movement
-Tremor: occurs at rest and hand tremors exhibit pill-rolling movements.
-Rigidity: Attempts to passively move the extremities
81
New cards
State some of the clinical manifestations of Parkinson's Dx.
General lack of movement
Loss of facial expression
Drooling
Propulsive (shuffling) gait
Absent arm swing
micrographia
bradykinesia/dyskinesia
paradoxical kinesia
orthostatic hypotension
daytime sleepiness
Loss of facial expression
Drooling
Propulsive (shuffling) gait
Absent arm swing
micrographia
bradykinesia/dyskinesia
paradoxical kinesia
orthostatic hypotension
daytime sleepiness
82
New cards
How is Parkinson's Dx treated?
No cure, but measures can be taken to ease the life of the patient.
-Restoring brain dopamine levels
-Administration of dopamine precursors
-dopamine receptor agonists
-Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (slow metabolism of dopamine)
-Anticholinergic
-Antidepressant
-Ablative surgical procedures may be helpful for motor symptoms
-Restoring brain dopamine levels
-Administration of dopamine precursors
-dopamine receptor agonists
-Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (slow metabolism of dopamine)
-Anticholinergic
-Antidepressant
-Ablative surgical procedures may be helpful for motor symptoms
83
New cards
What is Cerebral Palsy?
A permanent impairment affecting automatic postural control and movement as a result of a non-progressive brain disorder.
It is a permanent childhood Dx that causes damage to motor control areas of the brain.
It is a permanent childhood Dx that causes damage to motor control areas of the brain.
84
New cards
What is the most common type of Cerebral Palsy?
Spastic
85
New cards
How does Botox help treat Cerebral Palsy?
for pain and range of motion
86
New cards
Be able to differentiate between normal pressure, obstructive, and communicating hydrocephalus:
Normal Pressure:
-caused an increased volume of CSF
>>Triad of symptoms: gait instability, urinary incontinence, and dementia
Obstructive:
-a result of an obstruction to the flow of CSF
>>Blocked aqueduct of Sylvius, from premature closure before birth
Communicating:
-abnormal absorption of CSF
>>Blockage of fluid flow in subarachnoid space or blockage of the arachnoid villi themselves
-caused an increased volume of CSF
>>Triad of symptoms: gait instability, urinary incontinence, and dementia
Obstructive:
-a result of an obstruction to the flow of CSF
>>Blocked aqueduct of Sylvius, from premature closure before birth
Communicating:
-abnormal absorption of CSF
>>Blockage of fluid flow in subarachnoid space or blockage of the arachnoid villi themselves
87
New cards
How is hydrocephalus treated?
Medical treatment is limited*
Surgically:
-ventriculoperitoneal shunt: CSF flows into the peritoneal cavity. (MOST effective)
-Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: making a hole in the third ventricle to allow free flow of CSF into the basal cisterns for reabsorption
Surgically:
-ventriculoperitoneal shunt: CSF flows into the peritoneal cavity. (MOST effective)
-Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: making a hole in the third ventricle to allow free flow of CSF into the basal cisterns for reabsorption
88
New cards
What is multiple sclerosis(MS)?
a. What is it marked by?
b. Describe the treatment for MS.
a. What is it marked by?
b. Describe the treatment for MS.
-Chronic demyelinating disease of the CNS. Autoimmune disorder causes inflammation and scarring (sclerosis) of myelin sheaths
-Marked by exacerbations and remissions
Treatment:
*No cure*
-Short-term steroid therapy may be helpful during acute exacerbations
-Immune-modifying drugs may slow the progression of symptoms
-Marked by exacerbations and remissions
Treatment:
*No cure*
-Short-term steroid therapy may be helpful during acute exacerbations
-Immune-modifying drugs may slow the progression of symptoms
89
New cards
Be able to differentiate between spina bifida occulta and spina bifida cystica:
Spina Bifida Occulta: (oculta=hidden)
Invisible anomaly
Spina Bifida Cystica: (cyst=sac)
External protrusion of the saclike structure
Invisible anomaly
Spina Bifida Cystica: (cyst=sac)
External protrusion of the saclike structure
90
New cards
What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)? What is the prognosis for patient with ALS?
Progressive disease affecting both the upper and lower motor neurons. unknown cause
ALS prognosis is that most die within 3 to 5 years of diagnosis
ALS prognosis is that most die within 3 to 5 years of diagnosis
91
New cards
What are the mechanisms of spinal cord injuries?
hyperflexion, hyperextension, and/or compression.
92
New cards
Explain spinal shock.
-occurs immediately. characterized by temporary loss of reflexes below the level of injury
>>Muscles flaccid
>>Skeletal/autonomic reflexes lost
>>End of spinal shock: reflexes return and flaccidity is replaced by spasticity
>>Muscles flaccid
>>Skeletal/autonomic reflexes lost
>>End of spinal shock: reflexes return and flaccidity is replaced by spasticity
93
New cards
Explain neurogenic shock.
-the result of peripheral vasodilation
-Hypotension, bradycardia, and circulatory collapse>>>life-threatening
-high spinal cord injuries can affect respiratory muscles>>>ventilatory failure
-Hypotension, bradycardia, and circulatory collapse>>>life-threatening
-high spinal cord injuries can affect respiratory muscles>>>ventilatory failure
94
New cards
Explain autonomic dysreflexia.
Autonomic dysreflexia is a Sx in which there is a sudden onset of excessively high BP. It is more common in people with spinal cord injuries that involve the thoracic nerves of the spine or above (T6 or above).
-Acute reflexive response to sympathetic activation below the level of injury
-Visceral stimulation (full bladder or bowel) and activation of pain receptors below the injury are common stimuli.
-Acute reflexive response to sympathetic activation below the level of injury
-Visceral stimulation (full bladder or bowel) and activation of pain receptors below the injury are common stimuli.
95
New cards
What is the purpose of high-dose methylprednisolone in treating spinal cord injury?
may be used to decrease secondary injury.
96
New cards
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
a. What are the clinical manifestations?
b. How does someone recover from it?
a. What are the clinical manifestations?
b. How does someone recover from it?
-Inflammatory demyelinating disease of the PSNS
Lower motor neuron disorder
Clinical Manifestations:
-Muscle weakness that begins in the lower extremities and spreads to the proximal spinal neurons
-Progressive ascending weakness or paralysis, may affect respiratory muscles.
Spontaneous recovery usually occurs!
Lower motor neuron disorder
Clinical Manifestations:
-Muscle weakness that begins in the lower extremities and spreads to the proximal spinal neurons
-Progressive ascending weakness or paralysis, may affect respiratory muscles.
Spontaneous recovery usually occurs!
97
New cards
How does bell's palsy manifest? How does it resolve?
Clinical Manifestations:
-develop rapidly over 24 to 48 hrs; unilateral facial weakness/facial droop
-diminished eye blink
-hyperacusis (a disorder of loudness perception)
-decreased lacrimation
*often, it resolves within 3 weeks*
-develop rapidly over 24 to 48 hrs; unilateral facial weakness/facial droop
-diminished eye blink
-hyperacusis (a disorder of loudness perception)
-decreased lacrimation
*often, it resolves within 3 weeks*
98
New cards
What are the general structures of the eyes?
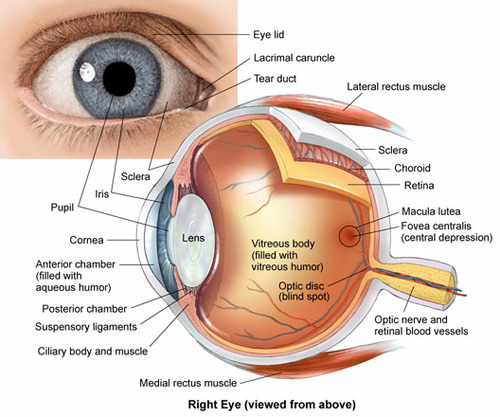
99
New cards
How do the aqueous and vitreous humor differ?
aqueous: transparent, protein free fluid. (front of eye)
vitreous: gelatinous (in vitreous body of eye)
vitreous: gelatinous (in vitreous body of eye)
100
New cards
What is the retina? What happens in the retina? What kind of neurons are present here?
a. What is the difference between cones and rods?
a. What is the difference between cones and rods?
Retina: where light waves are transformed into nerve impulses
There are five types of neurons in the retina: photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells.
Cones: daylight and color vision, visual acuity
Rods: nighttime and peripheral vision
There are five types of neurons in the retina: photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells.
Cones: daylight and color vision, visual acuity
Rods: nighttime and peripheral vision