Infectious Diseases
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Chain of Transmission: Pathogenic agent
Any organism that can cause disease
Chain of Transmission: Resevoir
Is an environment where an organism can live/multiply
Chain of Transmission: Portal of exit from the reservoir
Organism leaves the reservoir
Chain of Transmission: Mode (mechanism) of transmission
Direct (physical contact)
Indirect: through a “fomite”like a telephone, tray table, countertop
Chain of Transmission: Portal of entry into the host
Invasion
Chain of Transmission: Susceptible host
Lots of reasons that may increase/decrease the chances of infection
Signs and symptoms of infectious diseases
Systemic: fever, chills, sweating, malaise, nausea, and vomiting
Abscess, rash, red streaks, and inflamed lymph nodes
Red streaks
As bacteria travels to the lymph nodes or blood stream, leads to rapid systemic deterioration
Pathogenicity
Capacity of microbes to cause disease
Invasiveness
Concept of pathogenicity that refers to the ability to spread
Toxicity
Concept of pathogenicity that refers to the ability enzyme, endotoxin, exotoxin production. Damage cells or interfere with host functions
Adherence to/compatibility with tissue
Concept of pathogenicity that refers to how compatible the microbe is to the tissue
Pili (different tools that bacteria are going to use to adhere to tissue)
Streptococci in respiratory system
Avoidance of host defenses
Concept of pathogenicity that refers to mutations and “shields”
Local Infection symptoms
Organism enters the body and is confined to a specific location.
Ex: Abscess → leukocytes form wall around infection to prevent spreading
Systemic infection symptoms
Spreads to several sites and tissues
Ex: fever, chills, sweating, malaise, nausea, and vomiting
Standard Precautions
Type of microogranisms (bloodborne pathogens/all clients)
Hand hygiene
PPE
Clean patient care area/equipment with disinfectant
Handle laundry carefully
Ensure proper handling of sharp objects
Airborne Precautions
Transmission through small particles that suspend in air and dispersed by air current
Private room
Door closed
Patient isolation
PPE when enter room with. a fit-tested respirator
Droplet Precautions
Transmission through sneezing, coughing, talking within 3 feet of patient
Private room or housed with others with same infection
Door can remain open
PPE to include mask
Contact Precautions
Transmissions through direct contact with patient
Private room
PPE (gloves /gown) on entry and all interactions
Limit transporting patient
Disinfect equpipment
Hand Hygiene: When to wash with soap and water
Visibly soiled with blood/bodily fluid
After eating
After using restroom
Exposure to patients with clostridiodes difficile (c-diff)
Hand Hygiene: When to use alcohol-based rub
Before and after having contact with a patient
Before and after putting on gloves for patient care
After contact with objects in the patient room
Bacteria
Unicellular organisms that do NOT require living tissue to survive their own metabolic processes
Target for drugs as human cells do not have cell walls but this organism does
Viruses
Require a living host for replication
Hard to treat because they hide inside human cells
Lack own metabolic processes that drugs may interfere with and replicate/mutate frequently
Protozoa
Unicellular, with nucleus and more cell structure than bacteria
Parasites (ex. malaria)
Fungi
Unicellular, promoted by warmth and moisture
Reproduce by budding or spores
Some are pathogenic
Athlete’s Foot → invasion of superficial layers of skin
Histoplasma → causes lung infection
How does infectious disease differ in aging adults compared to younger adults?
Older adults are MORE susceptible to infectious diseases
Changes in cell-mediated or T-cell function → slower to respond and require a stronger stimulus
Changes in skin elasticity/strength
Cough and gag reflexes make it more difficult to control secretions
Decreased bronchiolar elasticity and mucociliary activity
Possible increased exposure when living in assisted living communities
Clostridiodies difficile (c-diff)
Anaerobic, spore-forming bacillus caused by antibiotic medication
Can live for weeks or months without a host in water, soil, animal and human feces
Most common causes of healthcare-associated diarrhea
With antibiotic treatment, good bacteria is killed, but this bacteria is RESISTANT
Can be influenced by chemotherapy, GI surgery, enteral feeding
Sign/ symptoms/ Clinical manifestations of c-diff
Mild diarrhea to severe colonic inflammation leading to death
Persistent diarrhea/loss stools (3 or more times a day for 24 hours)
Abdominal cramping and tenderness
Severe infections may include fever and sepsis
Preventative measures for c-diff
Proper handwashing: 1-2 minutes of soap and water followed by proper hand drying
Gloves, gowns
Chlorine-based or high-concentration hydrogen peroxide to clean surfaces
Use of disposable equipment
Responsible use of antibiotics
Staphylococcal Infections
Bacterial infection that is among most common microorganisms that colonize on skin and mucous membranes
Most common infection site is in the nostrils
Spreads by direct contact with surfaces, or people, or inhalation of infected droplets
Stimulate a strong host immune response
Neutrophils are recruited to a local infection to attempt to contain the infection
Can spread to bloodstream (systemic)
Signs/Symptoms/Clinical Manifestations of Staphylococcal infections
Can range from mild skin infections to life-threatening systemic disease (sepsis)
Preventative measures for Staphylococcal infections
Washing hands
Gloves/gown
Mask (if infection site is the nostrils)
MRSA
Antibiotic resistant staph infection that requires extremely strong drugs (vancomycin)
Streptococcal Infections: Group A (GAS)
Airborne, contact transmission
Present in nasal cavity and pharynx
Rheumatic fever
Carditis
Arthritis
Nodules
Chorea-choreiform movements
Erythema marginatum (non-itchy rash)
Progresses rapidly
Causes severe tissue damage as it spreads and destroys the soft tissue in its path (necrotizing fasciitis and strep gangrene)
Streptococcal Infection: Group B (GBS)
Infections in pregnant women and neonates
Leading cause of neonatal pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis
Streptococcal cellulitis
Acute spreading inflammation of the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissues
Usually results from infection of burns, wounds, or other breaks in the skin
Painful, warm, and swollen with accompanying erythema
May have systemic symptoms such as fever and chills
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Bacterial infection that colonizes in the upper respiratory tract
Invasive (meningitis)
Intracranial pressure/brain edema, headache, nausea, altered metnal status, stiff neck, fever
Noninvasive (pneumonia)
Fever, chills, pleuritis/chest pain, fatigue, productive cough
Preventative measures for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Droplet:
Private room or housed with other with same infection
Door can remain open
PPE to include mask
Direct contact;
Private room
PPE (gloves/gown) on entry and for all interactions
Limit transporting patient
Disinfect equipment
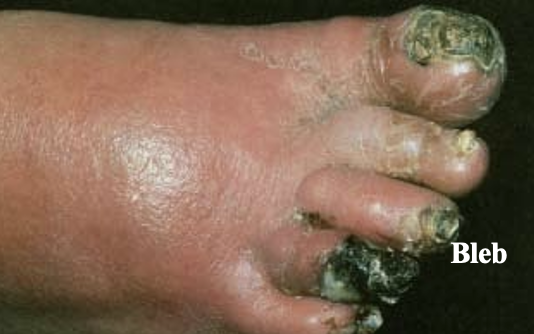
Dry Gangrene
Line of demarcation
Poor blood supply causing necrosis
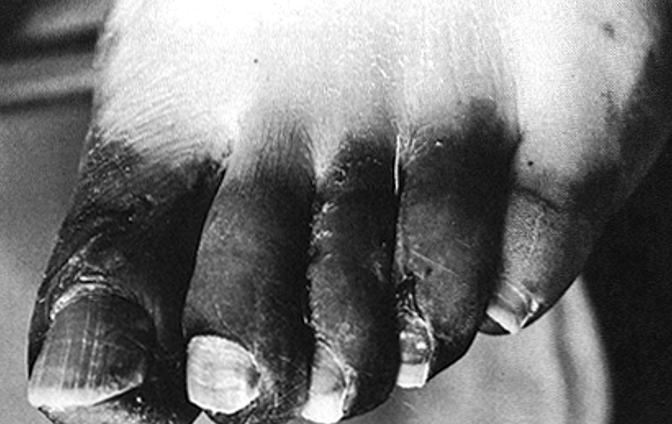
Wet Gangrene
Moist, progressive
Bacterial infections
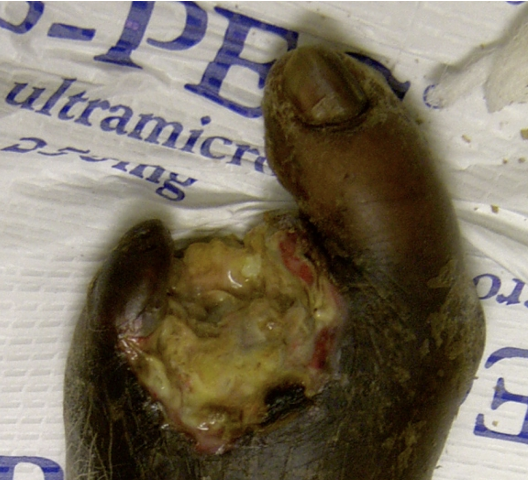
Gas Gangrene
Edema, gas pockets, foul odor
Caused by anaerobic bacteria
Preventative measures for Gas Gangrene
Look for signs of ischemia:
Cool skin
Pallor or cyanosis
Sudden severe pain/edema
Loss of pulse in involved limb
Psychological support
Pseudomonas
Opportunitistic pathogen, one of the most aggressive
Early diagnosis and detection is important
Clinical manifestations of Pseudomonas
Skin or wound infections
green-pigmented discharged at the infected site
Urinary tract infections
Pneumonia
Can cause sepsis
Herpes Simplex-1
Transmitted by direct contact
Oral herpes (cold sores or “fever blisters”)
Herpes Simplex-2
STD, Genital herpes
Transmitted by direct sexual contact
Herpes Type 3
Varicella Zoster Virus
Causes chicken pox and shingles
Clinical manifestations of Herpes Type 3
Chicken pox
Rash (“dew drop on a rose petal”) presentation
Shingles
Blisters erupts unilaterally on a specific dermatome supplied by dorsal root ganglia
Herpes Type 4
Epstein Barr
Spread by saliva → “kissing disease”
Causes infectious mononucleosis
Fever, sore throat, headache, malaise, abdominal pain (enlarged spleen of liver)
Excellent prognosis, but symptoms persist for 1-3 months
Pyrogens
Substances that result in
activation of the hypothalamus to
increase heat production
104
Temperatures ______ and above degrees Fahrenheit may causes delirium and seizures (irreversible cell damage)