Alkanes Chapter 12
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Alkane defintion
a hydrocarbon with C-C and C-H single bonds only
general formula alkanes
CnH2n + 2
saturated hydrocarbon
a compound containing only hydrogen and carbon with C-C and C-H single bonds
unbranched chains
straight hydrocarbon chains
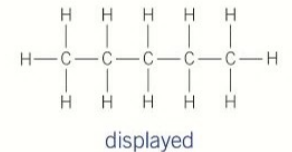
bond angle of unbranched chains
109.5
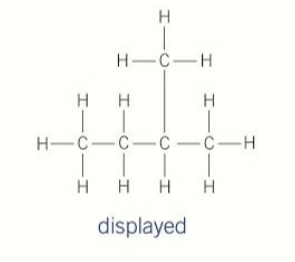
branched chains
straight chain with a substuent bonded to the main chain
general formula of ring alkanes
CnH2n
naming straight chain alkanes
identitfy the longest unbranched chain of carbons
compounds that dont have isomers
methane,ethane, propane
pattern for the number of isomers in an alkane
4 carbon atoms = 2 isomers
5 carbon atoms = 3 isomers
physical poperties
polarity
boiling point
solubility
polarity of alkanes
non polar, because there is a small difference in electronegativity
intermolecular forces in alkanes
weak van der waal’s forces only
longer chain = stronger van der waal’s forces
boiling points of alkanes
as chain length increases so does the boiling points
factors affecting boiling points of alkanes
chain length → more van der waal’s forces
branching→ less branching allows the atoms to pack together closely
solubility of alkanes
insoluble because the strong hydrogen bonds dont interact with alkanes in water
reactivity of alkanes
unreactive due to strong covalent bonds
burn in excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide
burn in abcence of 02 to form carbon monoxide
can react with halogens
crude oil formation
breakdown of animal and plant remains at high pressures and temperatures very slowly
crude oil
mixture of branched and unbranched alkanes
other elements in crude oil
sulfur burns to form sulfur dioxide
effect: reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere to form sulfur trioxide and then with water creating sulfuric acid
fractions definition
a mixture of hydrocarbons collected over a particular range of boiling points during fractional distillation of crude oil with similar boiling points and properties
steps of fractional distillation in a fractionating tower
crude oil gets heated in a furnace
the vapour rises and gets condensed in a cooler fractionating tower
short chain compounds are condensed at the top of the tower
the residue remaining is collected at the bottom
uses of natural gases
fuel
uses of petrol
cars
uses of naptha and kerosene
jet fuel
gas oil uses
lubrication
fuel oil and waxes uses
roads and roofing
fracking
extraction of natural gas by drilling into the shale and litting it mix with the water releasing trapped natural gas
HCl is added to break up the shale
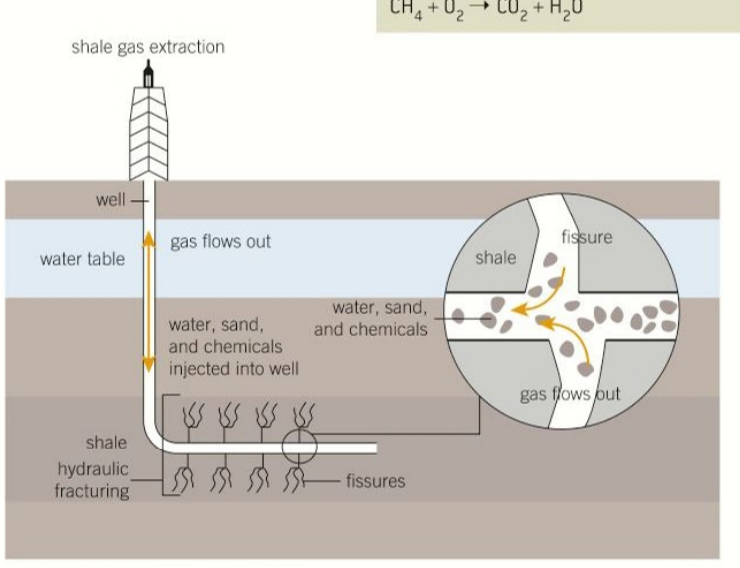
ethical concerns with fracking
visual pollution
water wastage
concern for chemical additives
causes small earthquakes
releases CO2 into the atmosphere
contributes to global warming
why is cracking used
longer chain fractions are not as usefull or high in demand so they are broken down to form shorter chains which are worth more economically
uses of alkenes
chemical feedstock (starting materials for different products)
converted into polymers
petrol
starting material for polyethene
conditions for thermal cracking
temperature:700-1200 kelvins
pressure: 700 kilopascals/ KPa
what occurs in thermal cracking
the C-C bond is broken so an electron from the covalent bond goes to each carbon atom forming a free radical
free radical definition
an atom with an unpaired electron which are highly reactive
products of thermal cracking
hydrogen
alkenes
short chain alkanes
conditions of catalytic cracking
temperature: 720 kelvins
pressure: slightly higher than 101KPa
catalyst used in catalytic cracking
silicon dioxide
aluminium oxide
products of catalytic cracking
motor fuels
branched alkanes
cycloalkanes
aromatic compounds
word equation for the combustion of alkanes
alkane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
chemical equation for combustion of alkanes
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
features of the combustion of alkanes
release heat
negative enthalpies of combustion
more carbons = greater heat output
fuel definition
substances that release heat energy when they undergo combustion
incomplete combustion
a combustion reaction where there is insufficient oxygen for all carbon in the fuel to burn to carbon dioxide
carbon monoxide forms
what is formed in the complete abcence of oxygen
soot
in what type of chain alkanes does incomplete combustion occur
long chain because they require more energy and more oxygen than shorter chain alkanes
example of incomplete combustion
alkane + oxygen → carbon monoxide + H2O
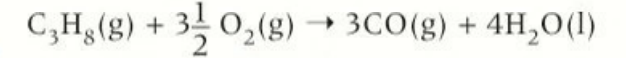
common pollutants
carbon monoxide
nitrogen oxides
sulfur dioxides
carbon particulates
carbon dioxide
water vapour
carbon monoxide
It is a toxic, colorless, and odorless gas that contributes to air pollution.
dangers of carbon monoxide
Binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, reducing oxygen transport in the body.
Can cause headaches, dizziness, unconsciousness
reacting with other pollutants to form harmful ground-level ozone (smog).
equation for the formation of nitrogen oxides
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
how are nitrogen oxide formed
when the temperature of petrol engines reaches high temperatures forming the oxides
dangers of nitrogen oxide (2)
react with water vapour and oxygen to form nitric acid
contribute to acid rain and petrochemical smog
dangers of sulfur dioxide
reacts with water to produce sulfuric acid which contributes to acid rain
dangers of carbon particulates
exacerbate asthma and cause cancer
effect of carbon dioxide on the atmosphere
necessary to keep earth habitable
large amounts increase earths average temperature
leads to climate change
uses of fossil fuels
burned to generate electricity
flue gas definition
a mixture of gases given out by power stations
formation of sulfur dioxides
natural gas contains sulfur impurities which form sulfur dioxide. this reacts with the water in the atmosphere to form acid rain
chemical and word equation of sulfur dioxide forming sulfuric acid
sulfur dioxide + oxygen + water → sulfuric acid
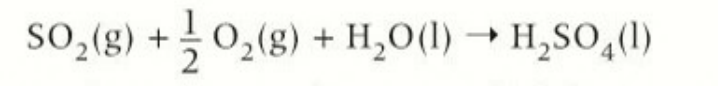
flue gas desulfurisation
process pf removinng SO2 from flue gas
2 methods of removing flue gas desulfurisation
uses calcium oxide
uses calcium carbonate
method 1 of desulfurisation using calcium oxide
a slurry of calcium oxide and water are sprayed into the flue gas to form calcium sulfite (gypsum)
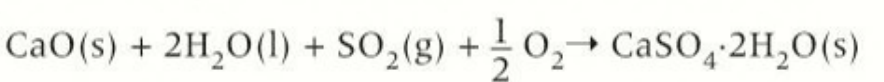
method 2 of desulfurisation using calcium carbonate
flue gas is passed through a suspensions of calcium carbonate
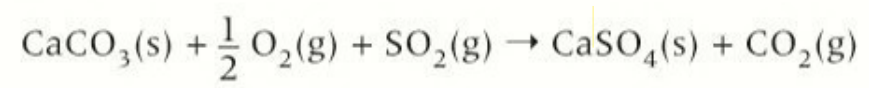
uses of catalytic converters
reduce the output of carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and unburnt hydrocarbons in the exhaust
shape of catalytic converters and the benefit of this shape
honeycomb shape that provides a large surface area. the honeycomb is made of ceramic material that is coated with platinum and rhodium
reactions that occur in catalytic converters
carbon monoxide + nitrogen monoxide →nitrogen + carbon dioxide
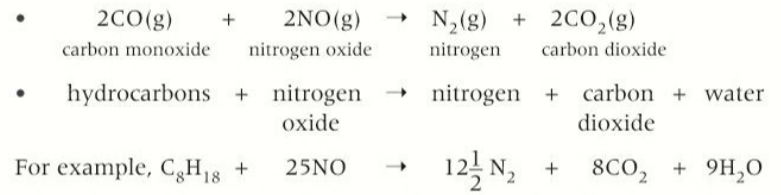
greenhouse effect explanation
visible rays pass through the atmosphere and the energy gets absorbed and reradiated.
aenergy with longer wavelengths and infrared cannot escape the atmosphere
uses of the greenhouse effect
maintain earth’s average temperature keeping it warm enough to sustain life
what do green house gases do
absorb infrared heating up the earth
why has the concentration of CO2 increased in recent years
due to the industrial revolution where fossil fuels have been used and burned for energy in industrial plants
effect of increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
a general increase in the earth’s average temperature contributing to global warming
explain water as a greenhouse gas
very abundant but doesnt affect the earth as the levels of H2O in the atmosphere are constant
increase in earths average temperature increases water vapour and greater cloud formation
carbon neutral activities defintion
activities that produce no carbon dioxide emissions overall
reaction type of formation of halogenoalkanes
nuclephillic substitution reactions
substitution word equation
alkane+ halogen → halogenoalkane + hydrogen halid
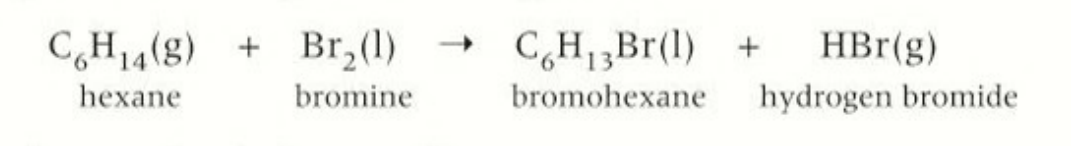
conditions for substitution
1 photon of ultra violet light
observations of substitution reactions
red/brown liquid goes colourless
3 key steps of free radical substitution
initiation
propagation stage 1 and 2
termination
free radical
a chemical species with an unpaired electron that makes it highly reactive
how does intitation occur
Cl2 absorbs energy from uv that breaks the covalent bond
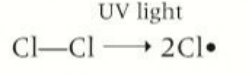
equation to show initiation
Cl-Cl→ 2CL.
propagation stage 1
the free radical reacts with a hydrogen atom to form a HCl and methyl free radical
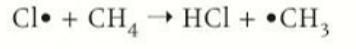
propagation stage 2
methyl radical is formed and reacts with Cl2 to form a halogenoalkane such as chloromethane
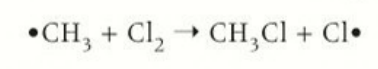
termination 3 types
forming a halogen
forming an alkane
forming a halogenoalkane
termination by forming a halogen
2 free radical halogen atoms required
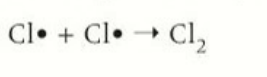
termination by forming a alkane
2 free radical alkanes required
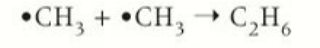
termination by forming a halogenoalkane
a mixture of both a chlorine radical and alkane radical
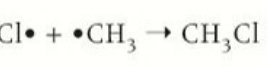
limitations of chain reactions
not as usefull
mixture of products
can occur in the abundance of light
effect of CFC on the environment
destroys the ozone layer as CFC contribute to ozone layer decomposition increasing exposure to UV
role of ozone
absorbs infrared radiation and protect from exposure that can cause cancer
break down of ozone
radicals act as a catalyst to decompostion
