ch 2 atomic structure
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
extent of deflection depends on
|charge| / mass ratio of the particle
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
nucleon number
total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
isotopes
atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different nucleon number
atomic orbital (contains 2 electrons)
region of space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron at any moment in time
s orbital shape
spherical
p orbital shape
dumb-bell
d orbital shape
butterfly
type of d orbitals
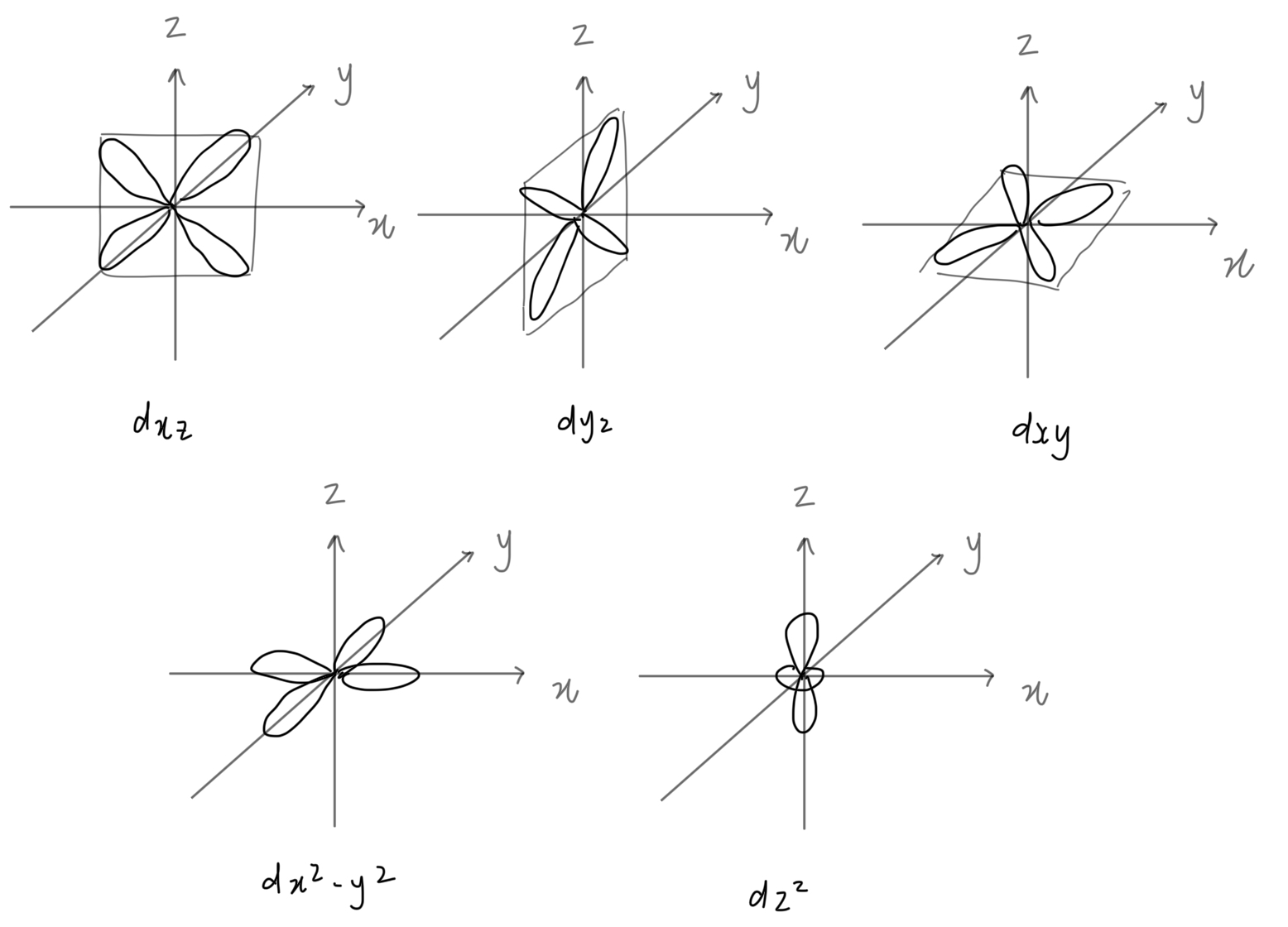
subshell (contains spdf orbitals)
group of orbitals with the same energy level and shape but different orientation in space
principal quantum shell
a group of subshells that are about equal distance from the nucleus
first principal quantum shell is closest to the nucleus and has the
lowest energy
as distance between orbital and nucleus increases, size of orbital
increases
electronic configuration of Cu
[Ar] 3d5 4s1 as half filled subshell is more stable than 3d4 4s2
electronic configuration of Cr
[Ar]3d10 4s1 as more symmetrical 3d electron cloud that shields the nucleus more effectively
first ionisation energy
of an element is the amount of energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of singly-charged gaseous cations
second ionisation energy
of an element is the amount of energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from a singly-charged gaseous cations to form one mole of doubly-charged gaseous cations
factors influencing ionisation energy
1) nuclear charge
2) shielding effect
ionisation energy ……… across a period
generally increases
IE trend across period explanation
no. of protons increase, nuclear charge increase
successive electrons are added to the same outermost shell, shielding effect remains approximately the same
effective nuclear charge increases
attraction between nucleus and outermost electron increases
more energy needed to remove outermost electron
exceptions for IE increase over period
ns2 and ns2np1
ns2np3 and ns2np4
reason for exception across period
2s2(Be) and 2s2 2p1(B)
less energy needed to remove 2p electron in B as it is removed from higher energy subshell, and filled 2s subshell in Be provide shielding, less energy needed to remove outermost electron in 2p1
2s2 2p3 (N) and 2s2 2p4 (O)
less energy required to remove the paired 2px electron in O as it experiences inter-electronic repulsion
1st ionisation energy ……… down the group
deceases
reason for trend down the group
no. of protons increase, nuclear charge increase
number of principal quantum shell increases, shielding effect increases significantly
outermost electron is further away form nucleus, attraction between nucleus and outermost electron decreases
less energy required to remove outermost electron
1st IE between periods ……
decreases significantly
reason for trend between periods
nuclear charge increases
one/two more principal quantum shell, shielding effect increases significantly
outermost electron is further away form nucleus, attraction between nucleus and outermost electron decreases
less energy required to remove outermost electron
successive IE always…… and why?
increases, because each electron is removed from an ion becoming more positively charged, harder to remove the negatively charged electron from a positively charged ion due to electrostatic attraction
atomic radius
half the shortest inter-nuclear distance found in the structure of an element
atomic and ionic radii……. down the group
increases
reason for atomic/ionic radii trend down the group
no. of protons increases, nuclear charge increases
no. of principal quantum shells increases, shielding effect increases significantly
outermost electron is further away form nucleus, attraction between nucleus and outermost electron decreases
less energy required to remove outermost electron
atomic radius ….. across a period
decrease
reason for atomic radii trend across a period
atoms have same number of principal quantum shells
as no. of protons increase, nuclear charge increases
as successive electrons are added to the same outermost shell, shielding effect remains approximately the same
effective nuclear charge increases
outermost electron is attracted more closely to the nucleus
ionic radius ……. across a period for ions with same isoelectronic configuration
decreases
reason for trend of ionic radius across a period for ions with same isoelectronic configuration
as no. of protons increase, nuclear charge increases
as the species are isoelectronic(same no. of electrons), shielding effect remains (
approximately)the sameeffective nuclear charge increases
outermost electron is attracted more closely to the nucleus
within the same period, anions are ……. than cations
larger because anions have one shell more of electrons
cations have …… radii than their respective atoms
smaller, as there is one shell less of electrons
anions have …… radii than their respective atoms
larger, as there more more electrons than protons, net attractive force for ve by nucleus decreases
electronegativity
of an atom is a measure of its ability to attract the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond (or electron density) towards itself
electronegativity …… across the period and why?
increases, as effective nuclear charge increases
electronegativity…… down the group and why?
decreases, as attraction between the outermost electron and nucleus decreases