Organs of Special Sense Pathology Image-Based Learning
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Investigating deathness - BAER test
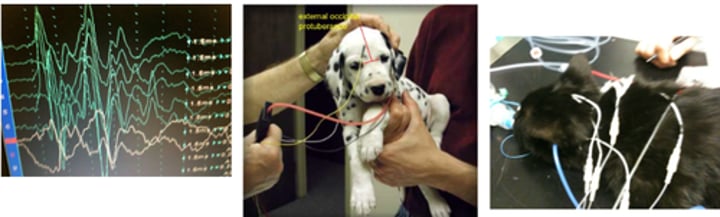
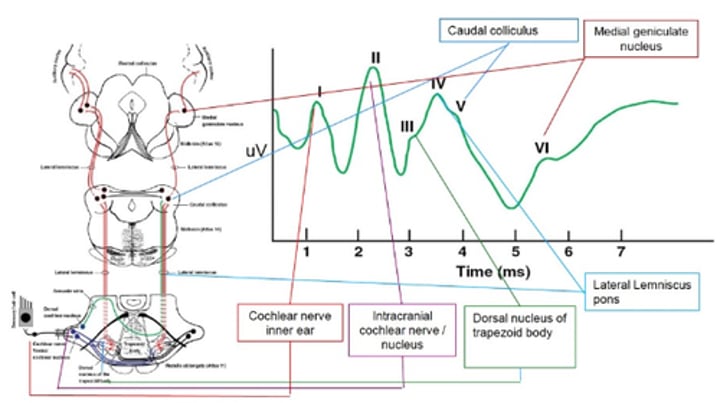
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response Results
I – cochlear nerve of the inner ear
II – intracranial cochlear nerve/ nucleus
III – dorsal nucleus of trapezoid body
IV – lateral lemniscus pons
V – caudal colliculus
VI – medial geniculate nucleus
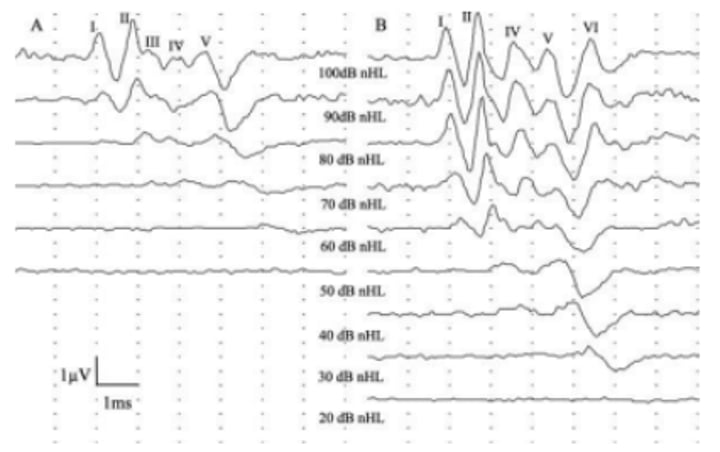
BAER slope shifted to the right with conductive hearing loss
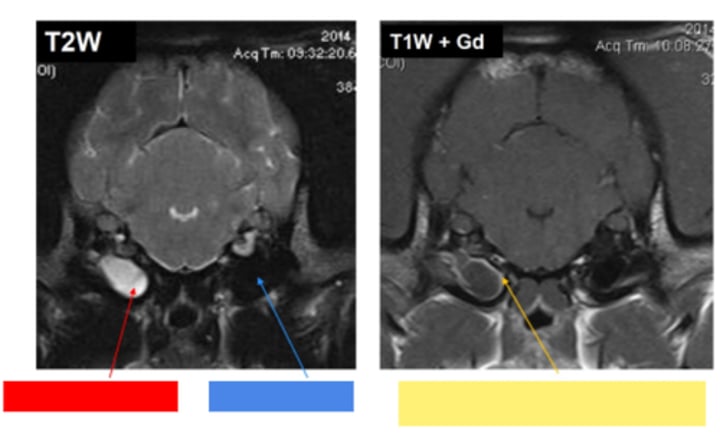
Otitis media/interna
Red - fluid filled bullae
Blue - air filled bullae
Yellow - gadolinium enhancement (increased blood supply with inflammation)
Bulla radiographs - Loss of air filled bullae
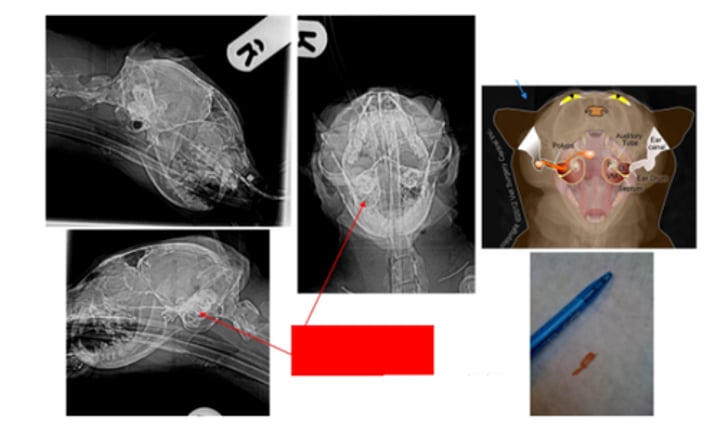
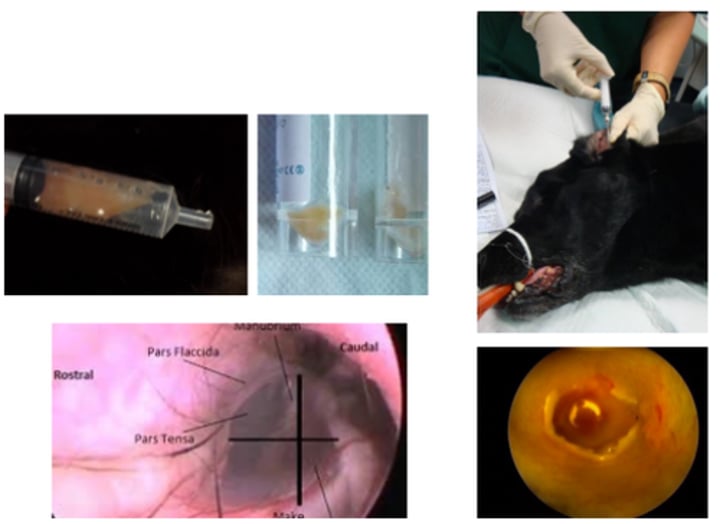
Myringotomy
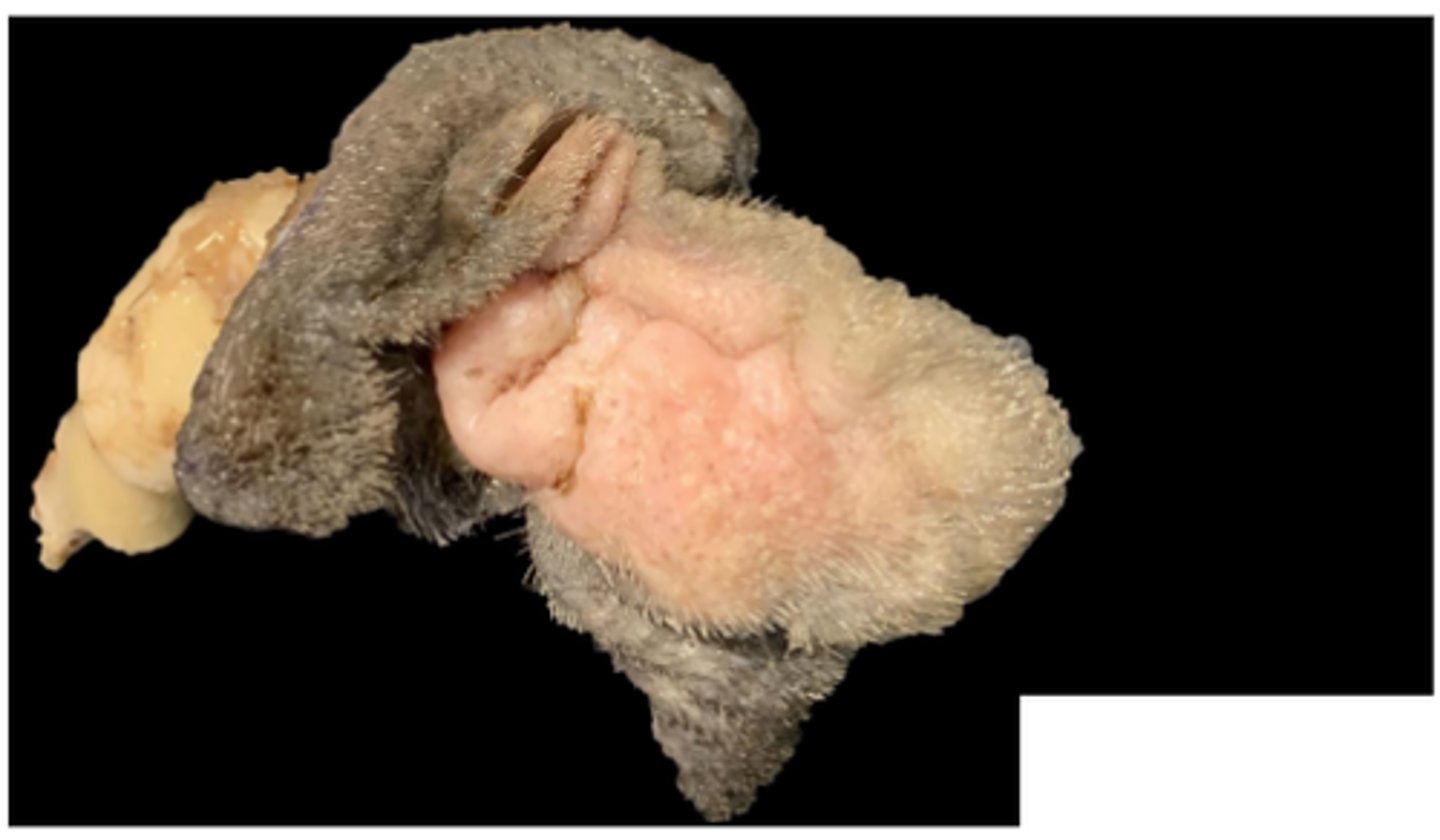
Feline nasopharyngeal polyp
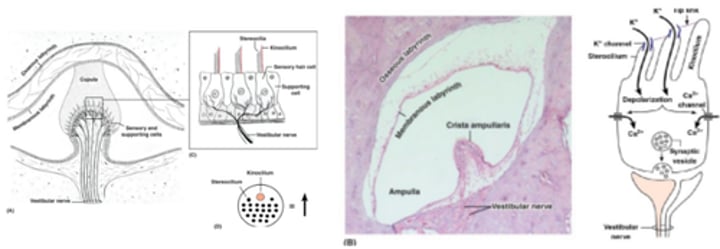
Sensory hair cells of crista ampulla (semicircular canal)
Movement: endolymph bends hair cells
Different orientations mean directionally sensitive
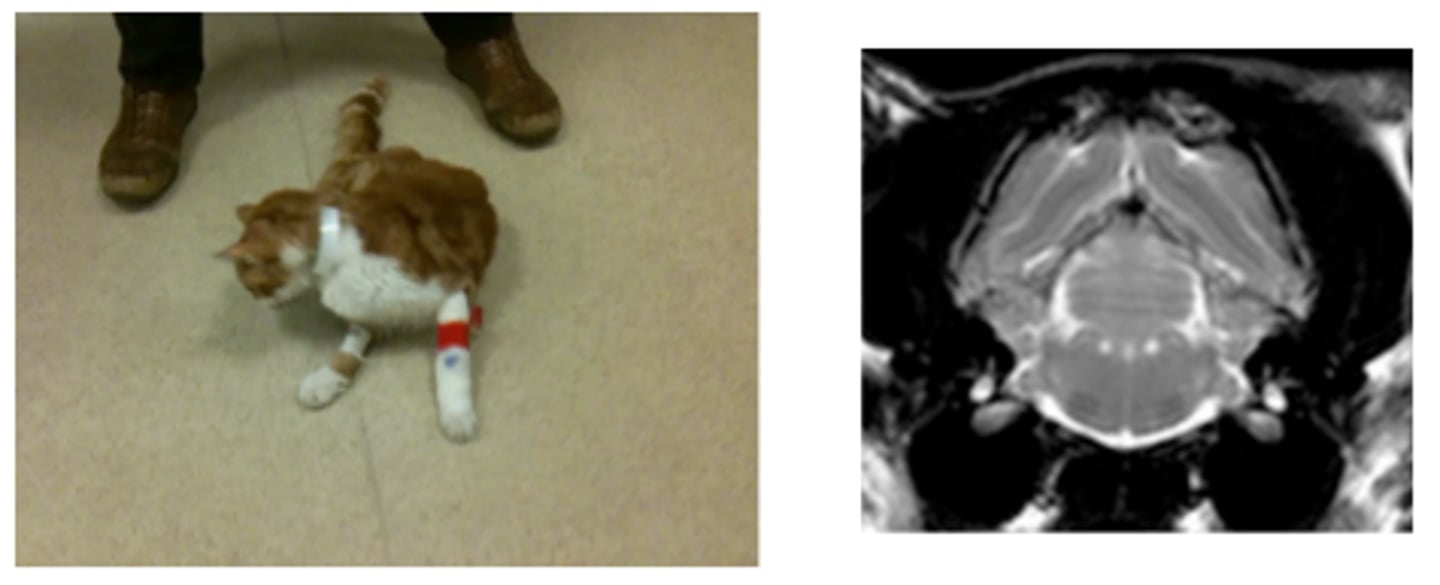
Peripheral vestibular disease
Peripheral vestibular disease - hypothyroidism
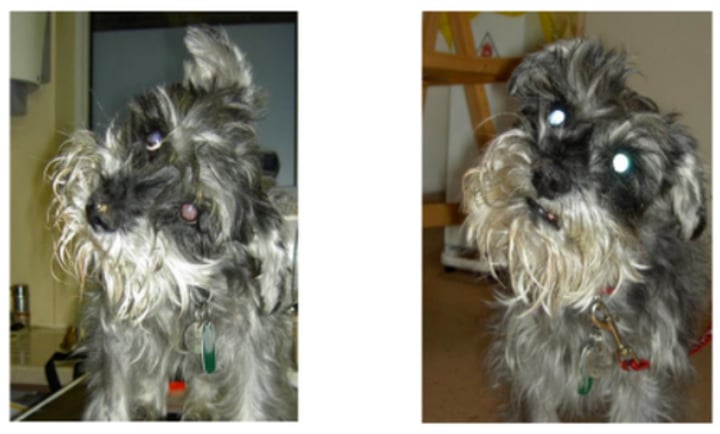
Vestibular disease and bilateral facial palsy
Second image: after 2 weeks of Levothyroxine therapy

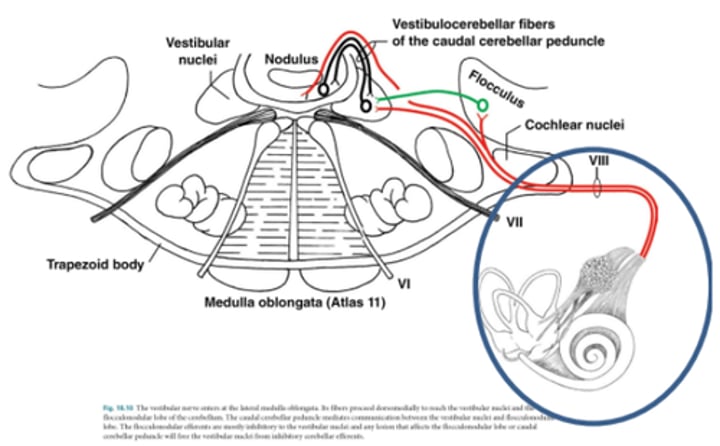
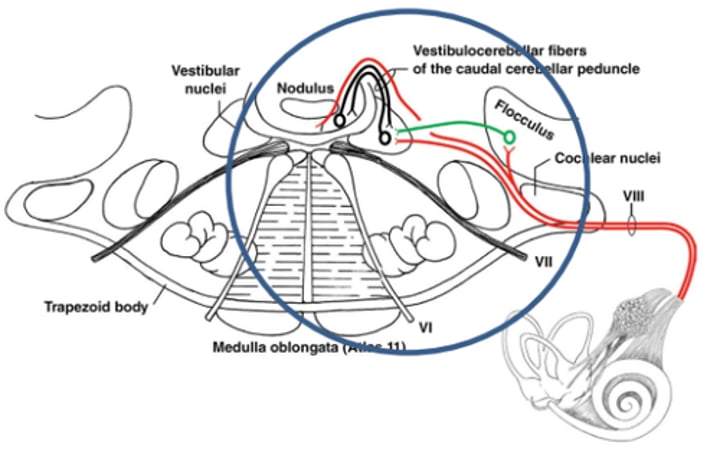
Central vestibular disease
Paradoxic vestibular syndrome
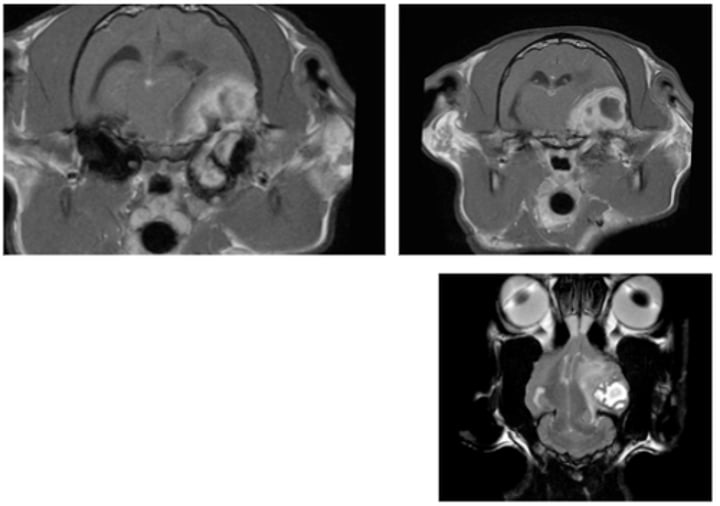
Carcinoma in 4th ventricle
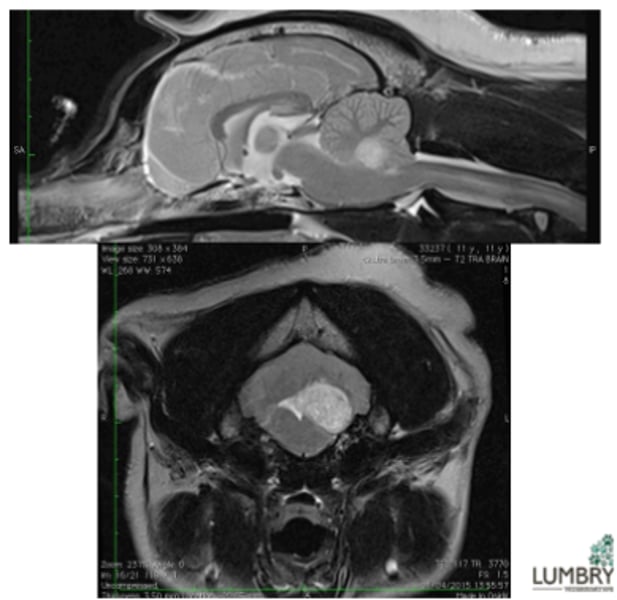
Otitis media-interna – secondary meningoencephalitis
Infection of middle ear cavity where peripheral disease has progressed to central disease
Paradoxical vestibular disease
Lesions resulting in loss of inhibitory influence of cerebellum
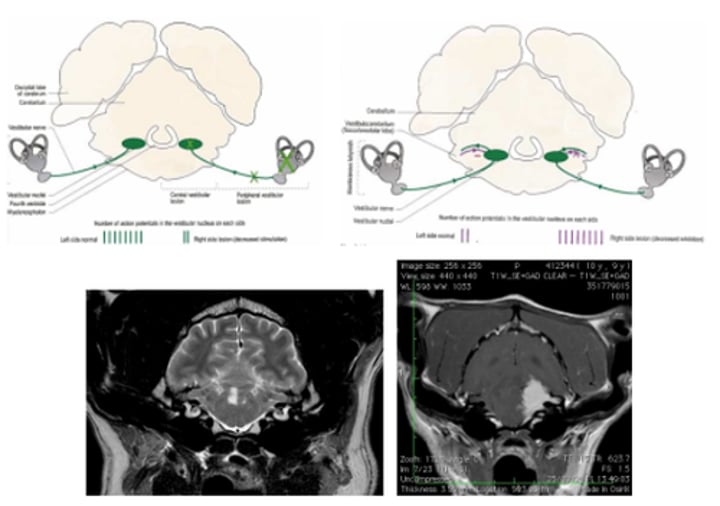
Paradoxical vestibular disease
Cystic tumour between the feedback from the cerebellum and brainstem
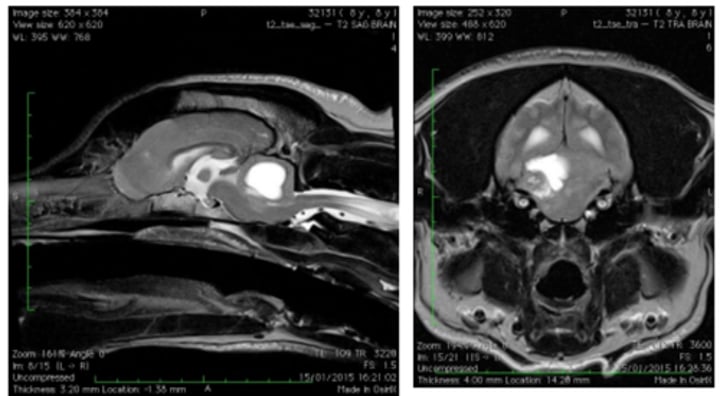
Tilting of the head due to nerve impulses firing only on one side resulting in contraction of extensor muscles on the other side
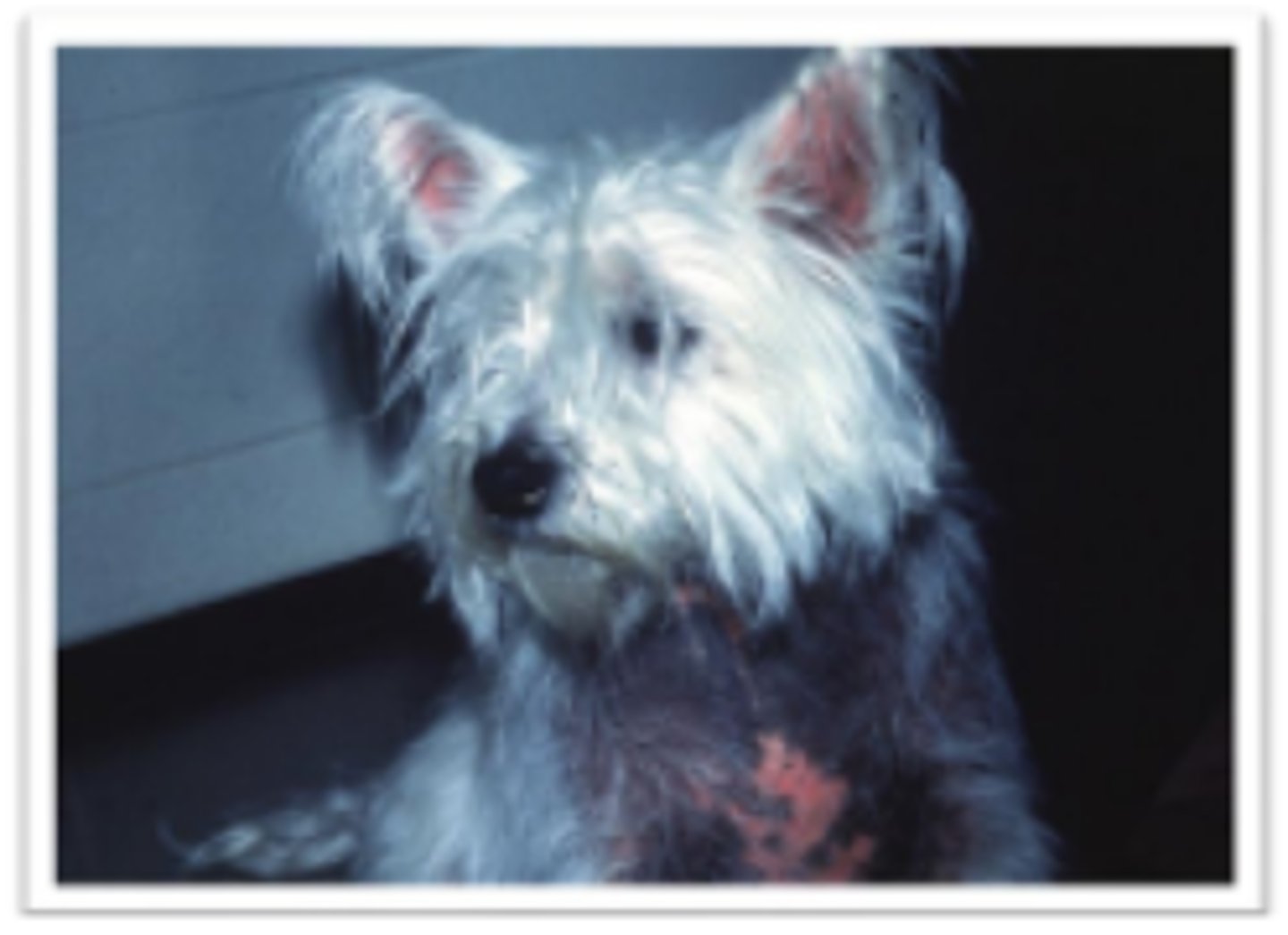
Thiamine deficiency - Bilateral vestibular disease
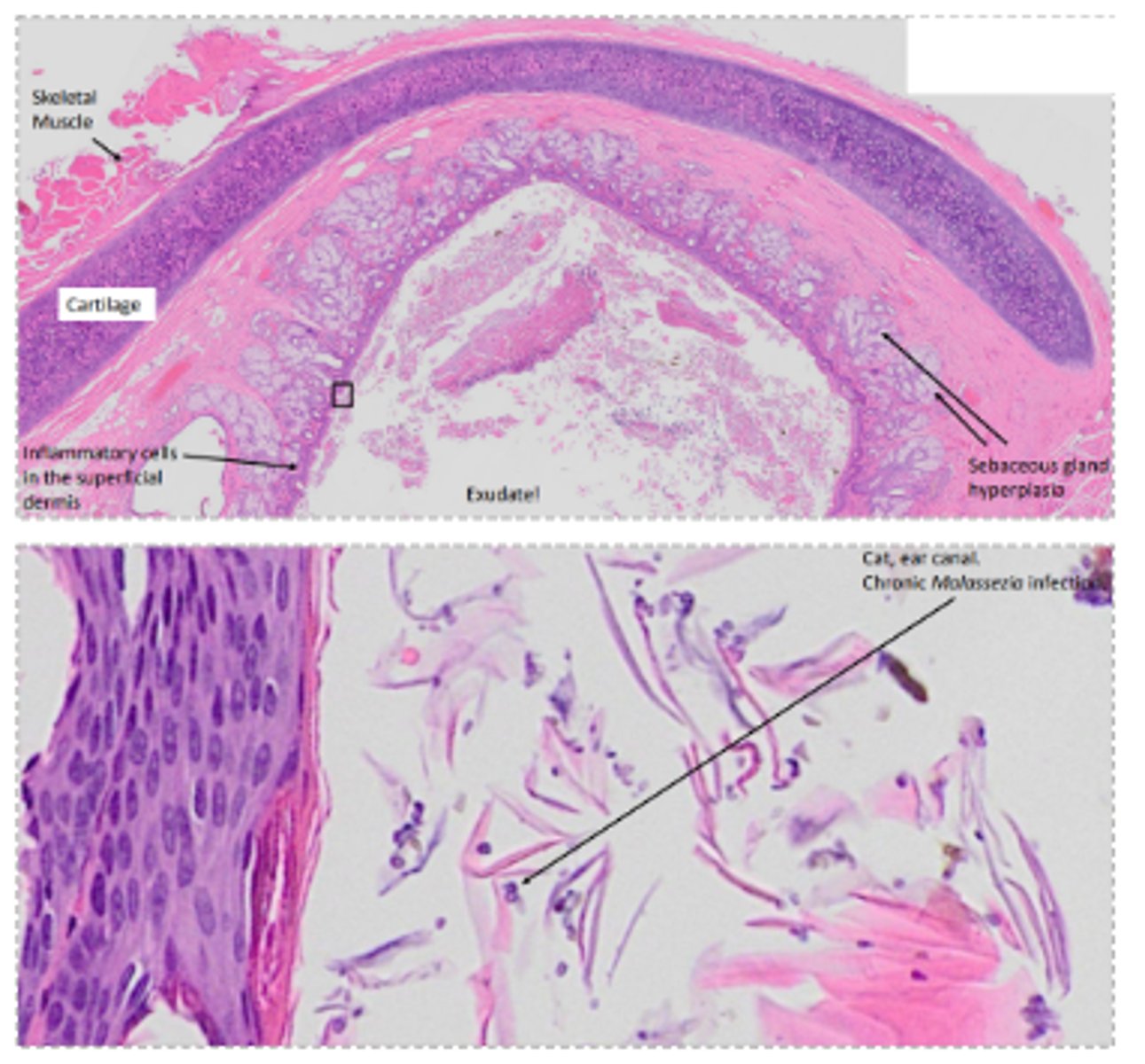
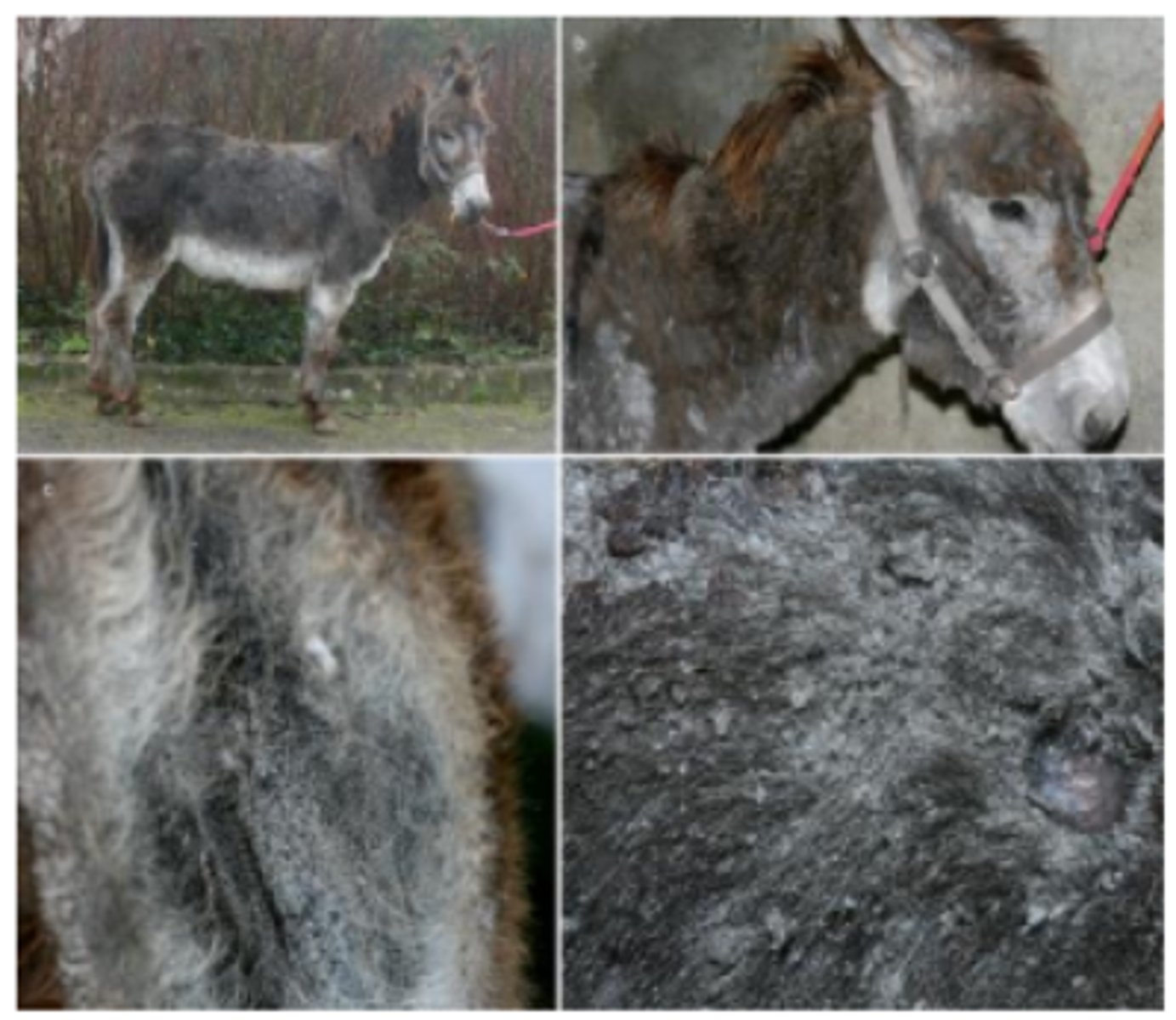
Malassezia infection
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, ceruminous debris
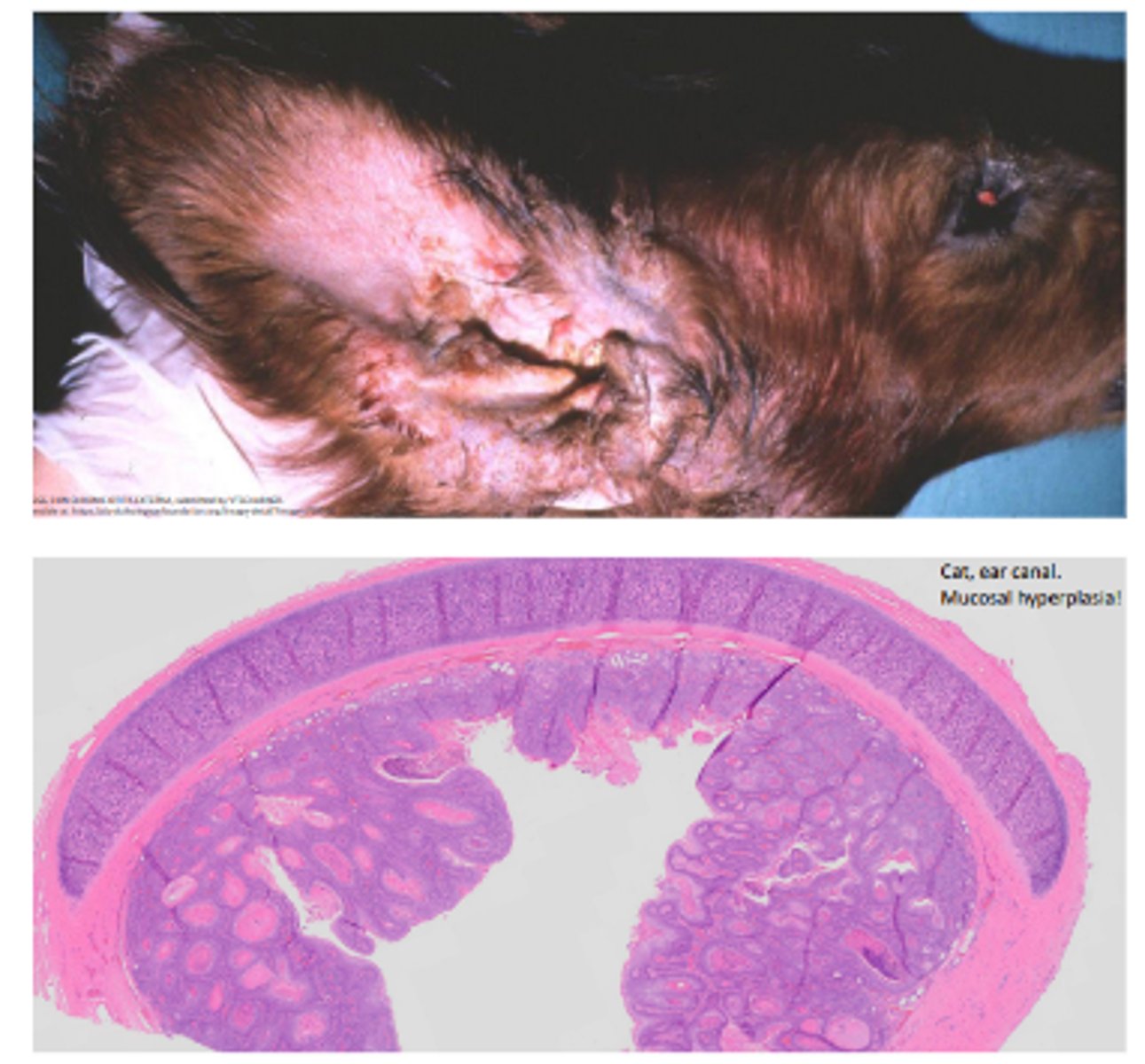
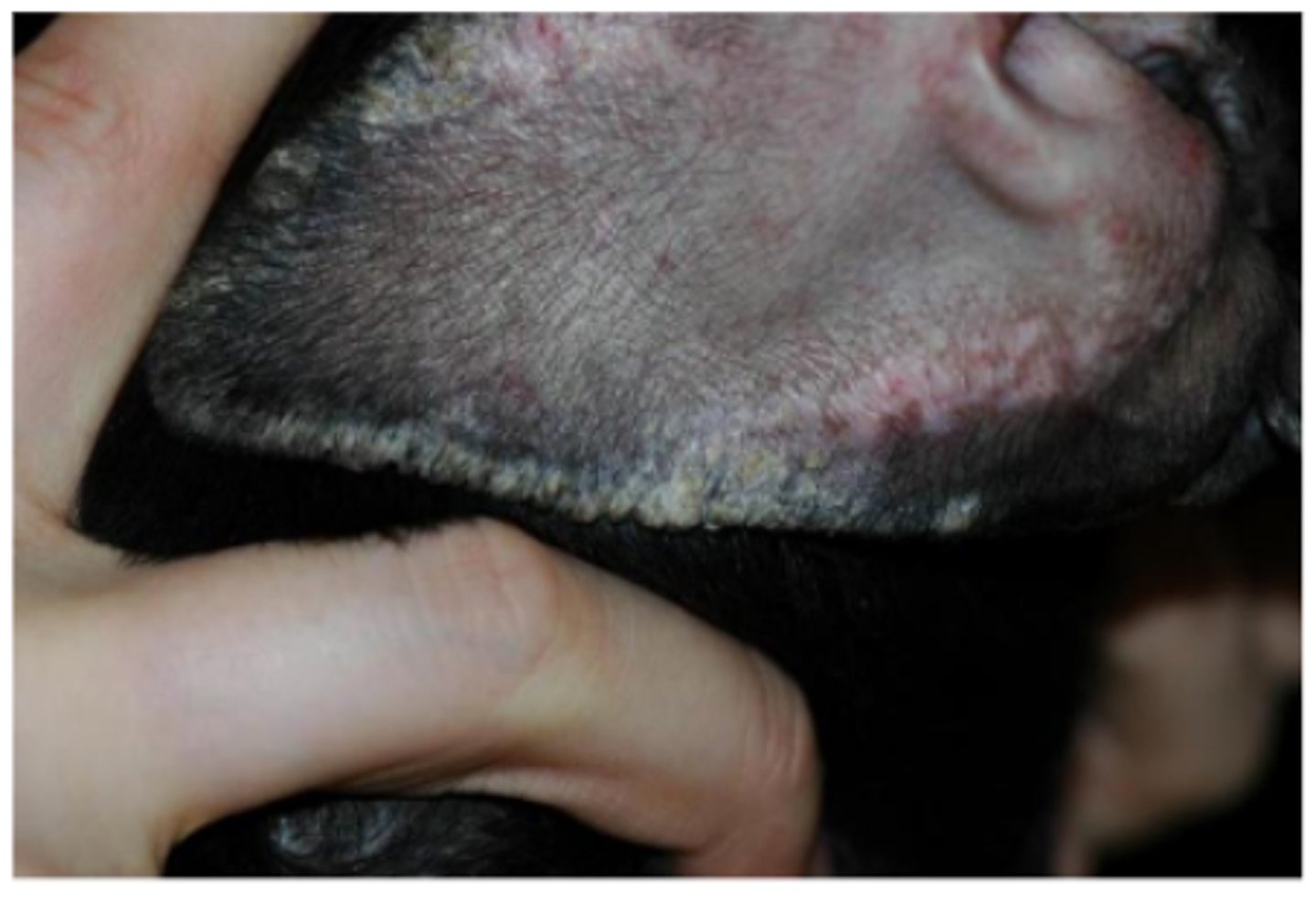
Otitis externa - chronic
Thickened, leathery, narrowing of the external acoustic meatus (stenosis), hyperplasia, dermal changes, osseous metaplasia of soft tissues
Otitis externa
Narrowing of the external acoustic meatus (stenosis), hyperplasia, dermal changes, oedema (acute), fibrosis (chronic), mixed inflammation (plasma cells, lymphocytes, mast cells, neutrophils), osseous metaplasia of soft tissues
Otitis externa
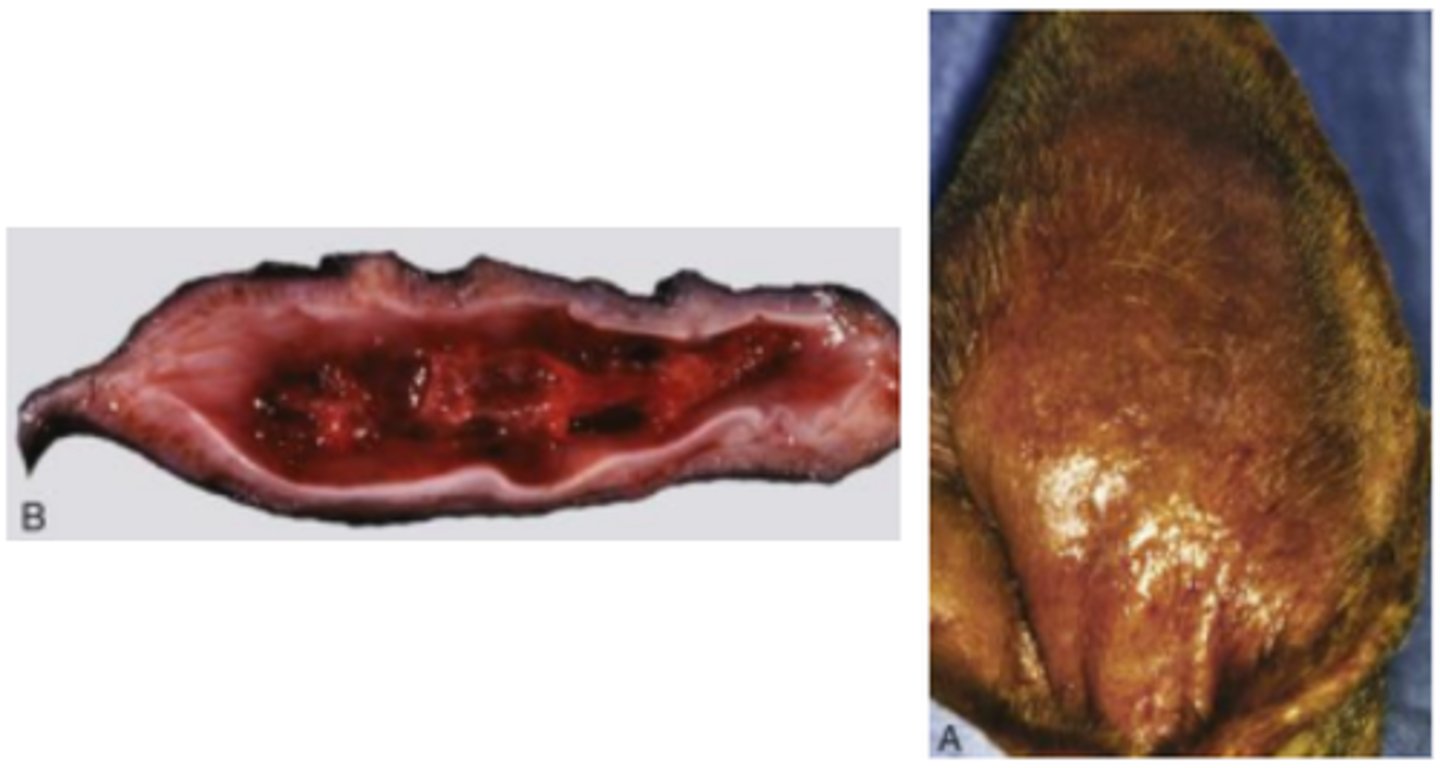
Cartilage splitting (fracture), fibrosis, healed haematoma
Aural haematoma
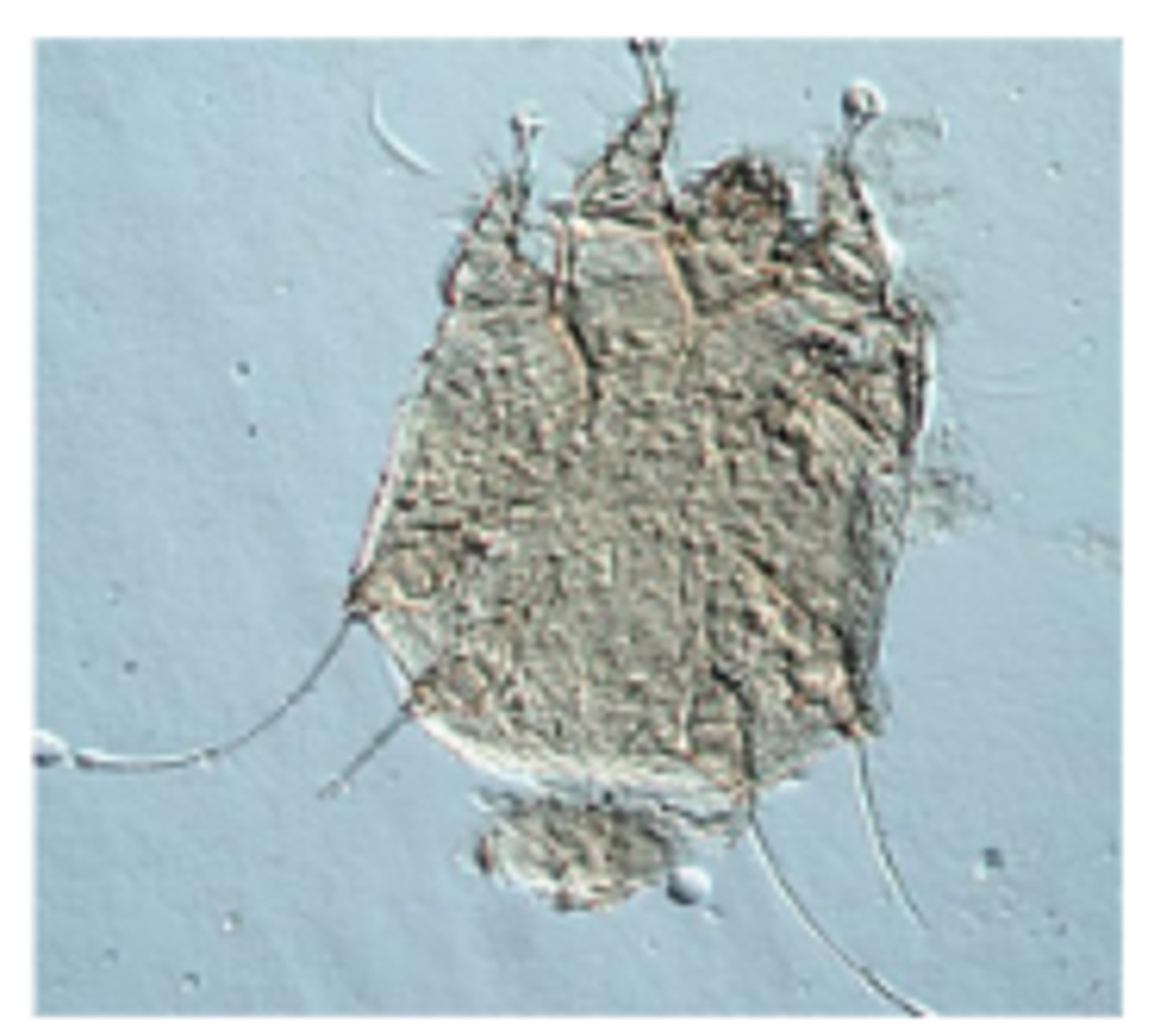
Notoedres cati
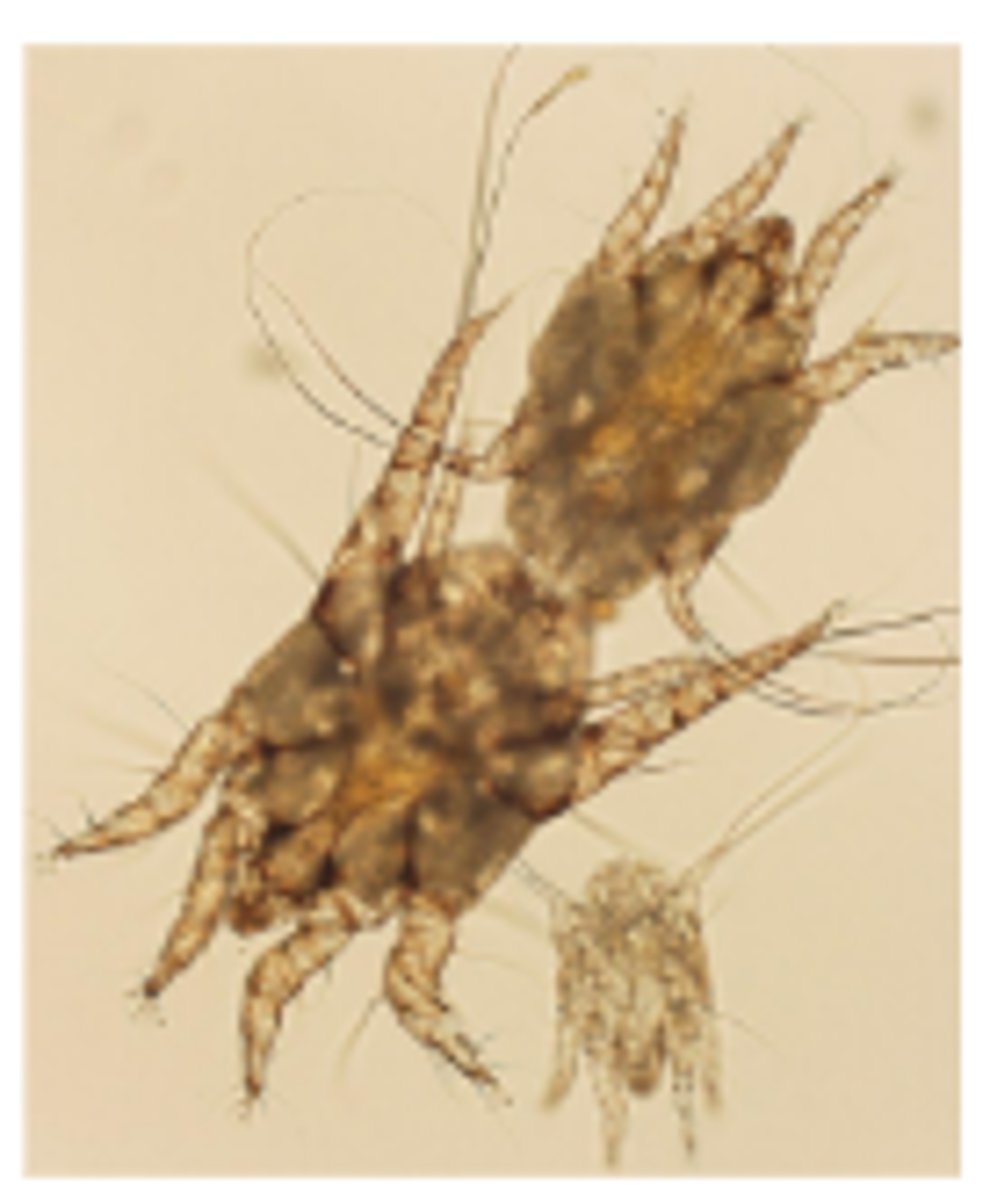
Otodectes cyanotis
Psoroptes cuniculi
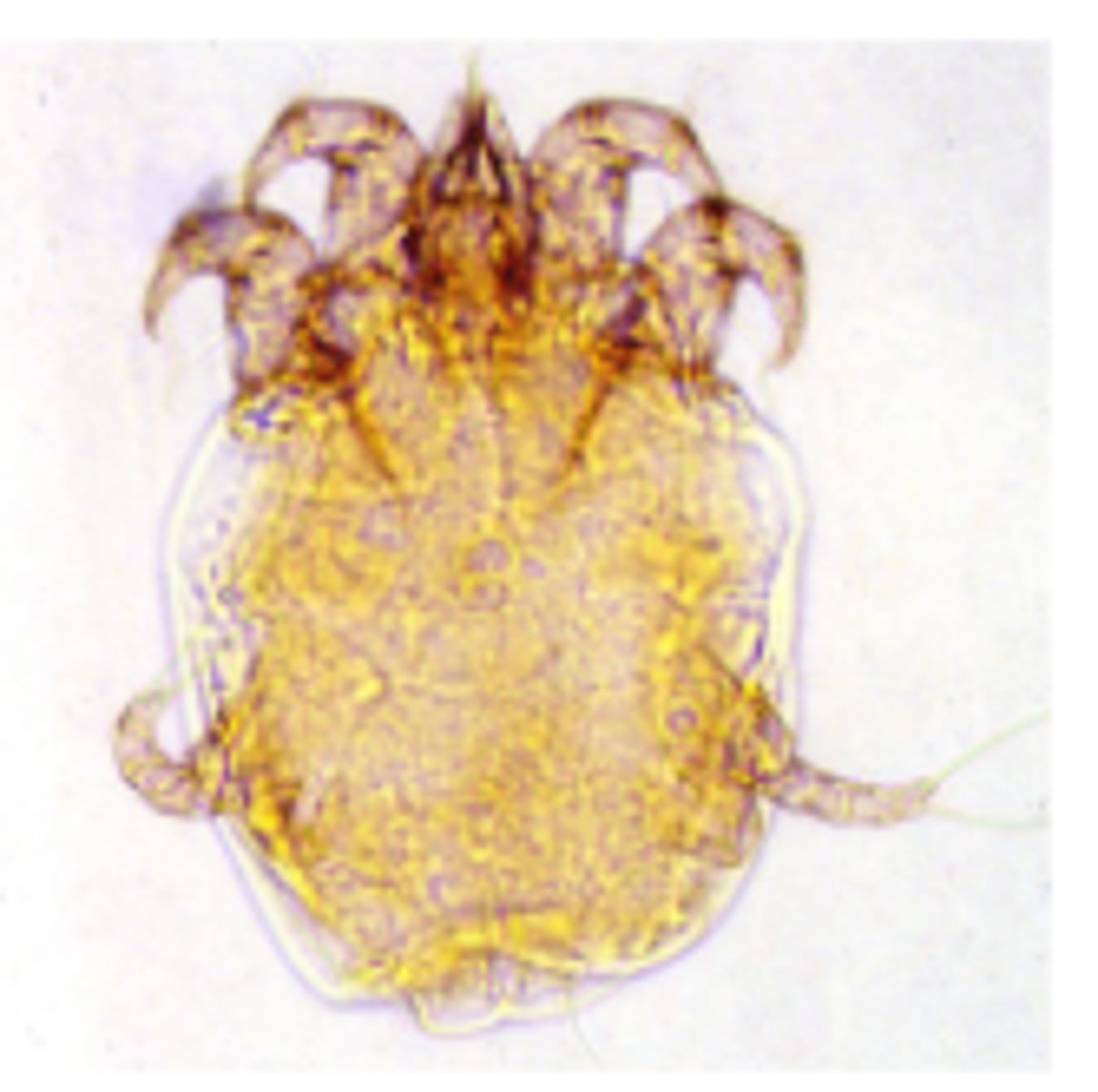
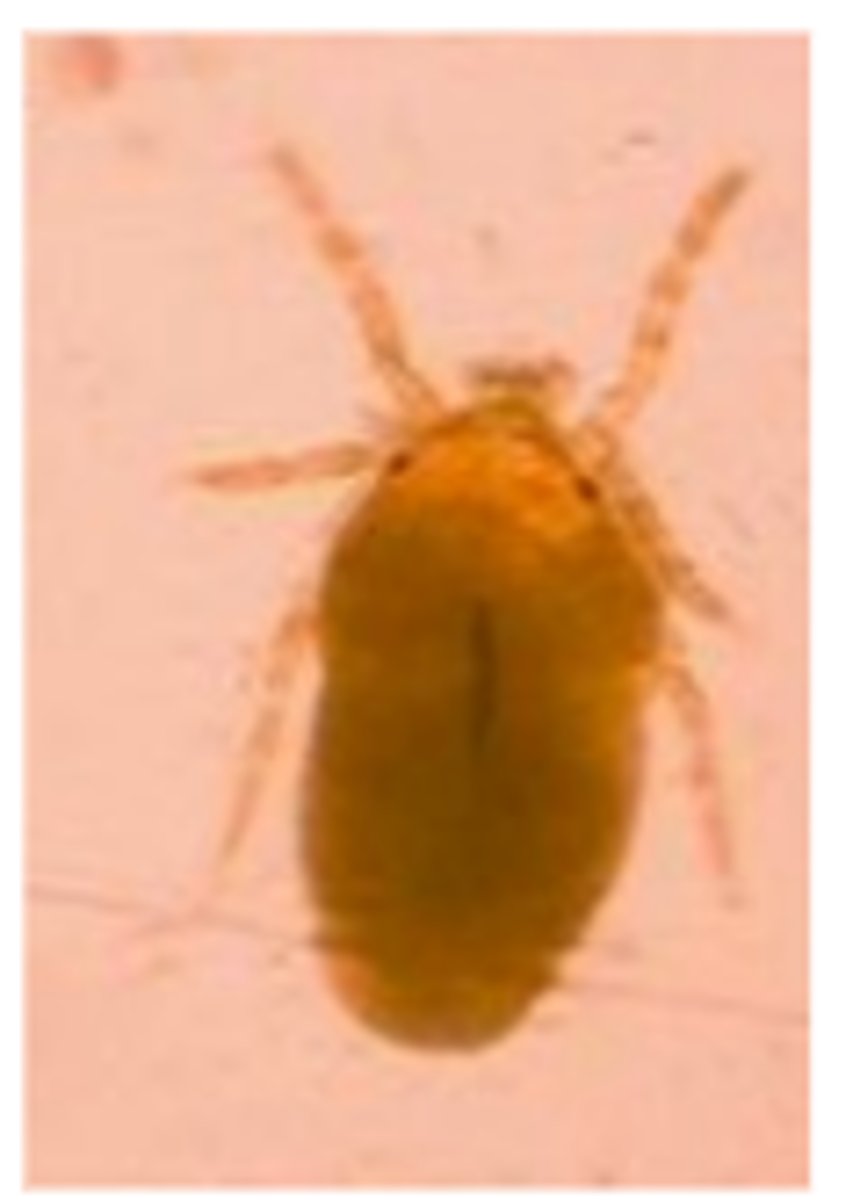
Neotrombicula autumnalis (Harvest mite)

Atopic dermatitis - Primary cause of otitis externa (OE)
Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, pyoderma secondary to pruritus

Allergic skin disease - Primary cause of otitis externa (OE)
Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, pyoderma secondary to pruritus
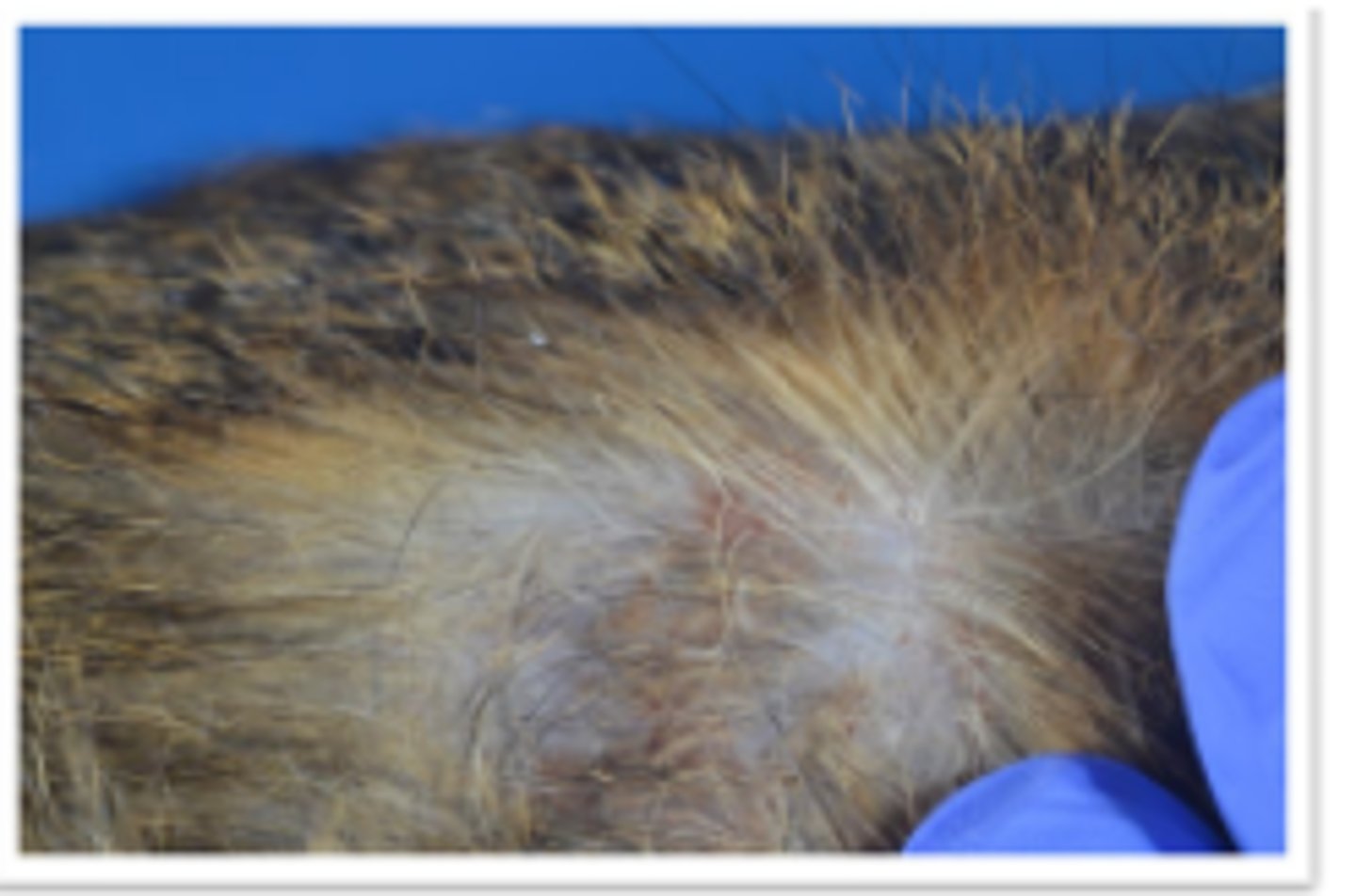
Ear margin seborrhea
Waxy crusts, small fissures
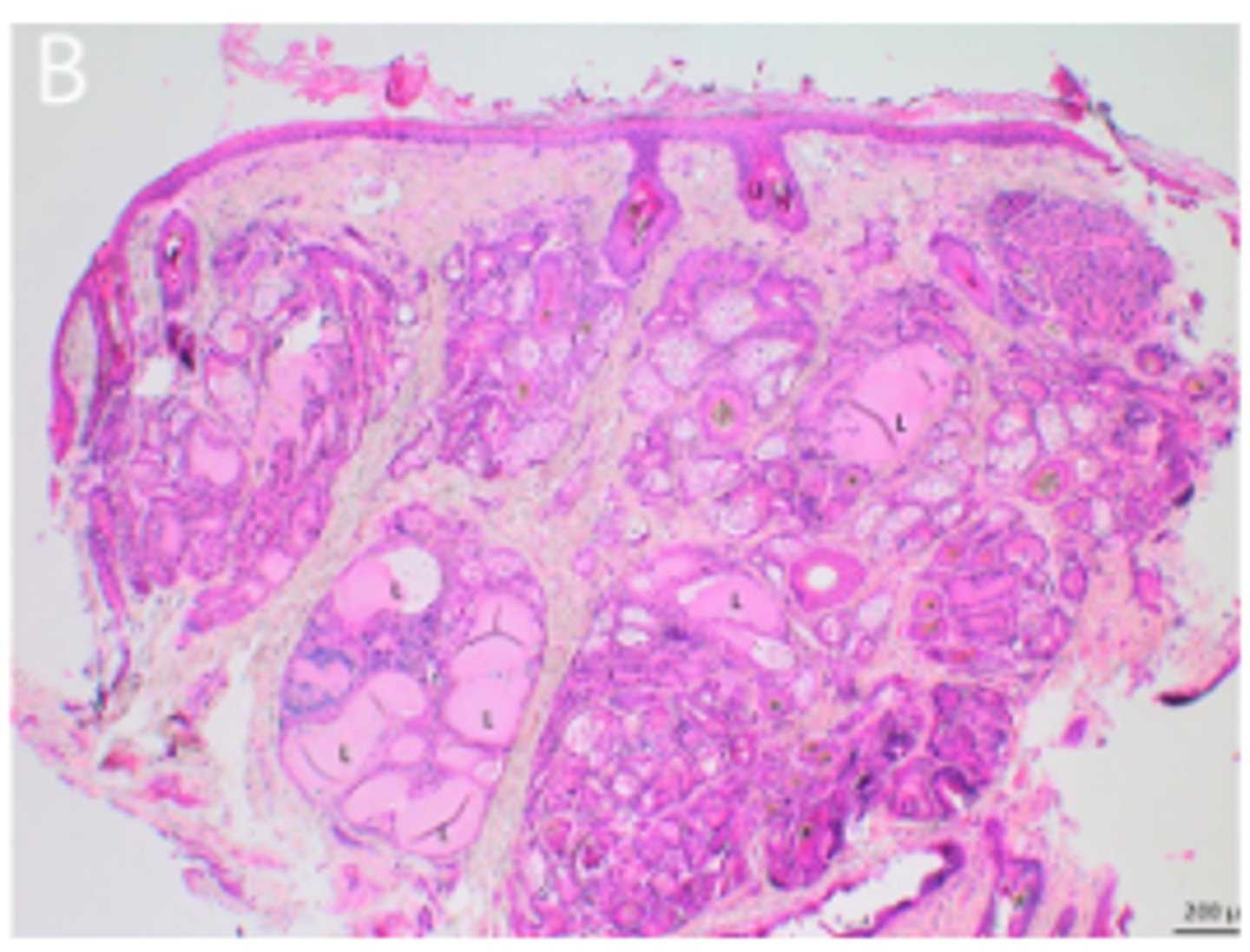
Dog, ears. Normal ceruminous glands in clinically healthy dog
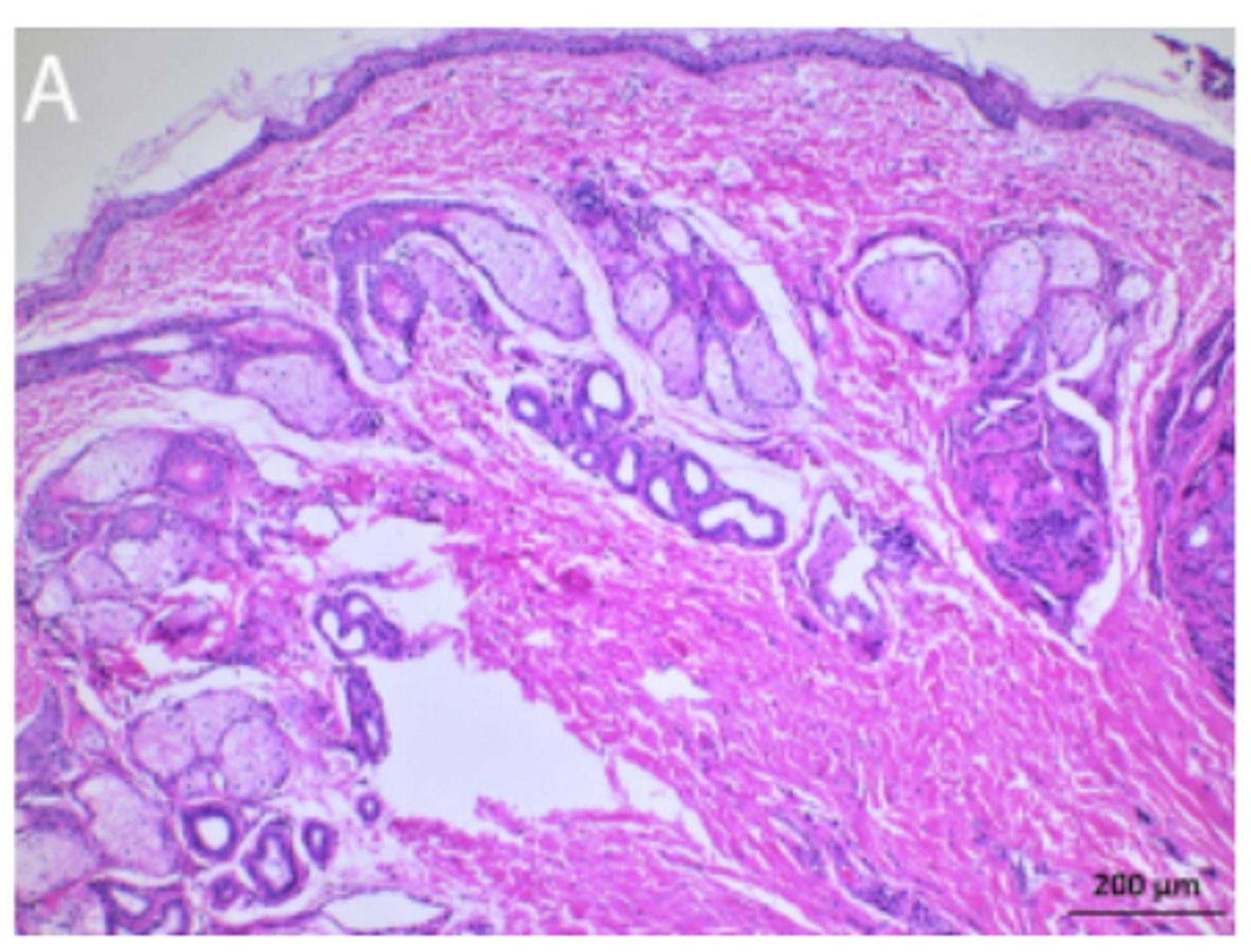
Increased keratin thickness layers, increased size and numbers of glands
Mild epidermal hyperplasia and compact orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, mild infundibular hyperkeratosis, numerous sebaceous glands and multifocal ceruminous gland ectasia (L)
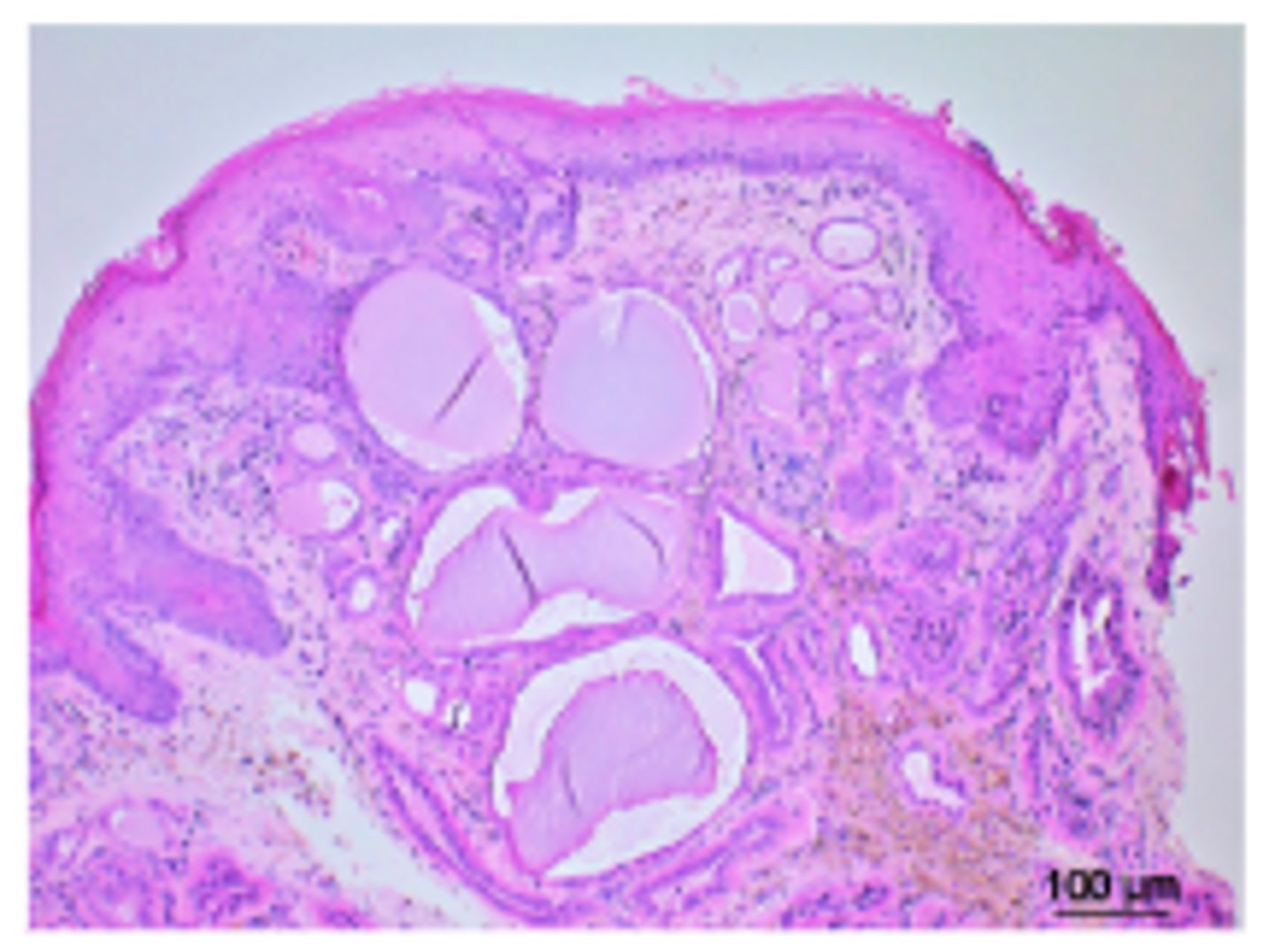
Otitis externa, dog pinna
Marked multifocal ceruminous gland hyperplasia and ectasia, and periadnexal pigment-laden macrophages
Lupus erythematosus
Scaling, crusting (multifocal to coalescing)

Pemphigus foliaceus
Scaling, crusting (multifocal to coalescing)
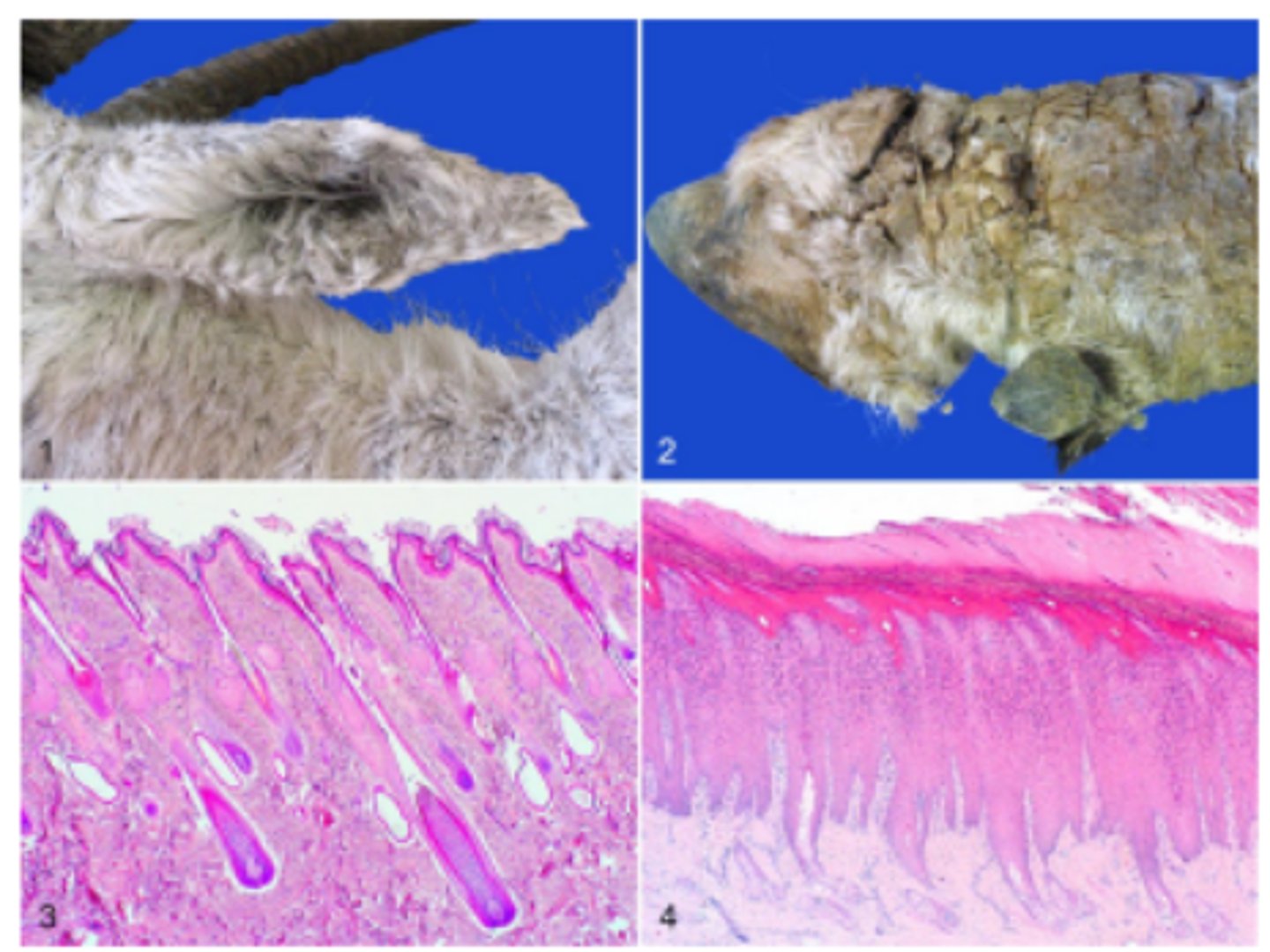
Vascular disease leading to primary otitis externa
Auricular infarction, frost bite, Goat. Dry gangrene. Note the clear line of demarcation between dead and living tissue
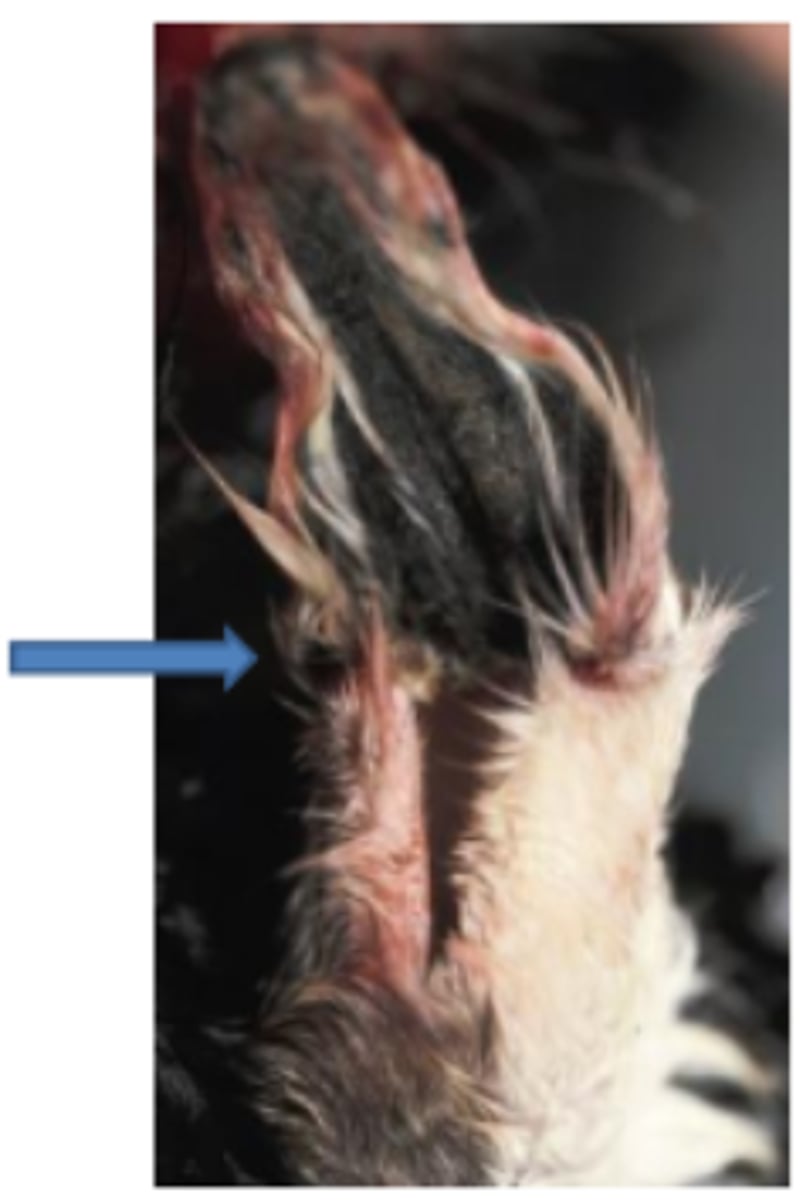
Cat ear canal, Malassezia chronic infection
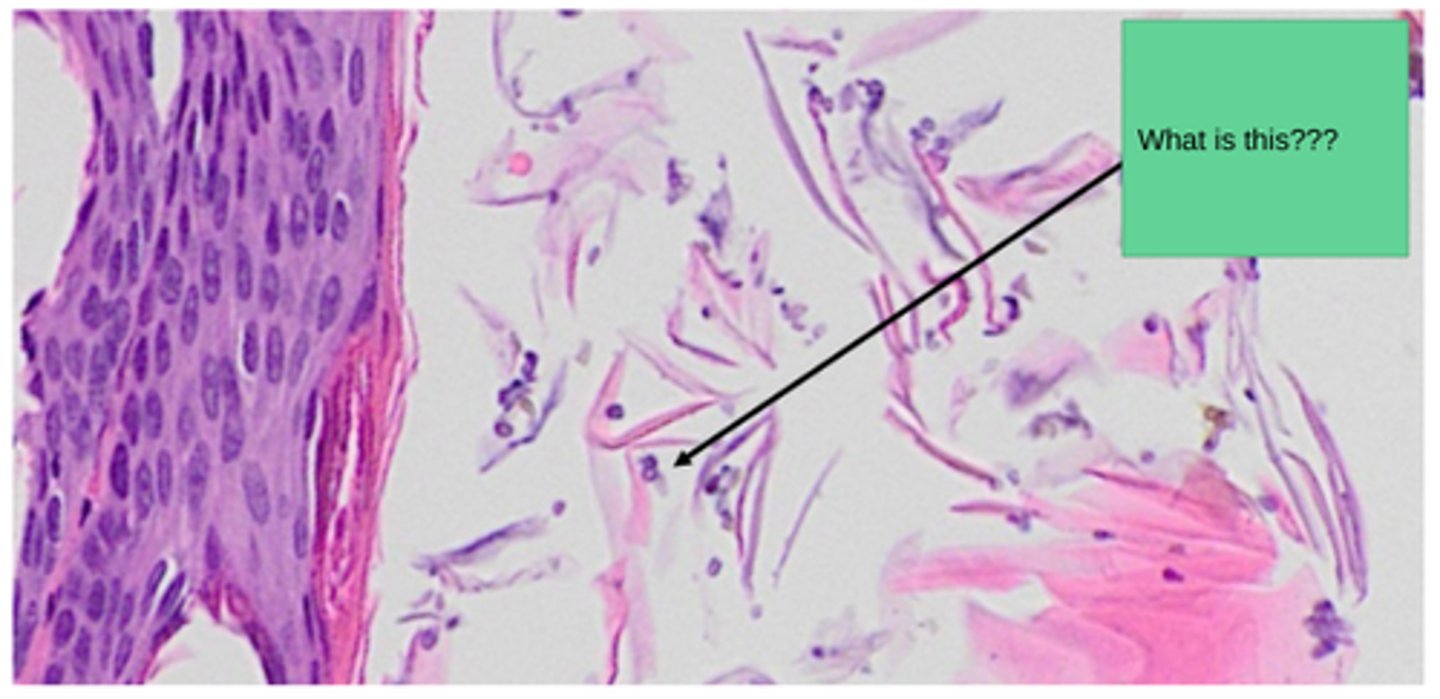
Otitis media
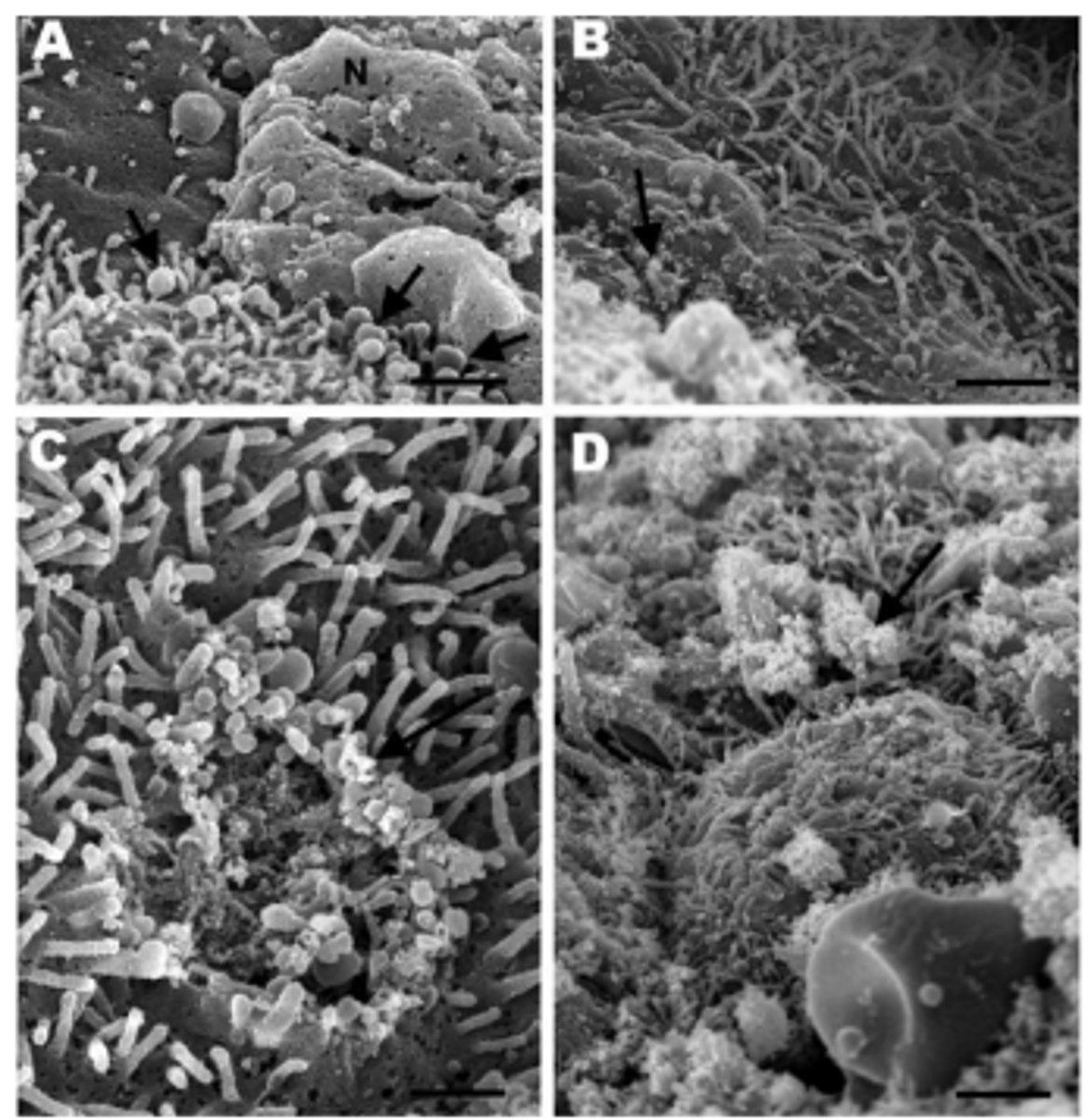
Ferret, ciliated epithelium (lung) with mycoplasmosis
Multifocal loss of cilia with mycoplasma-like organisms (arrows)
Mycoplasm trying to blend in with the cilia, but ultimately causing cilia death (c)
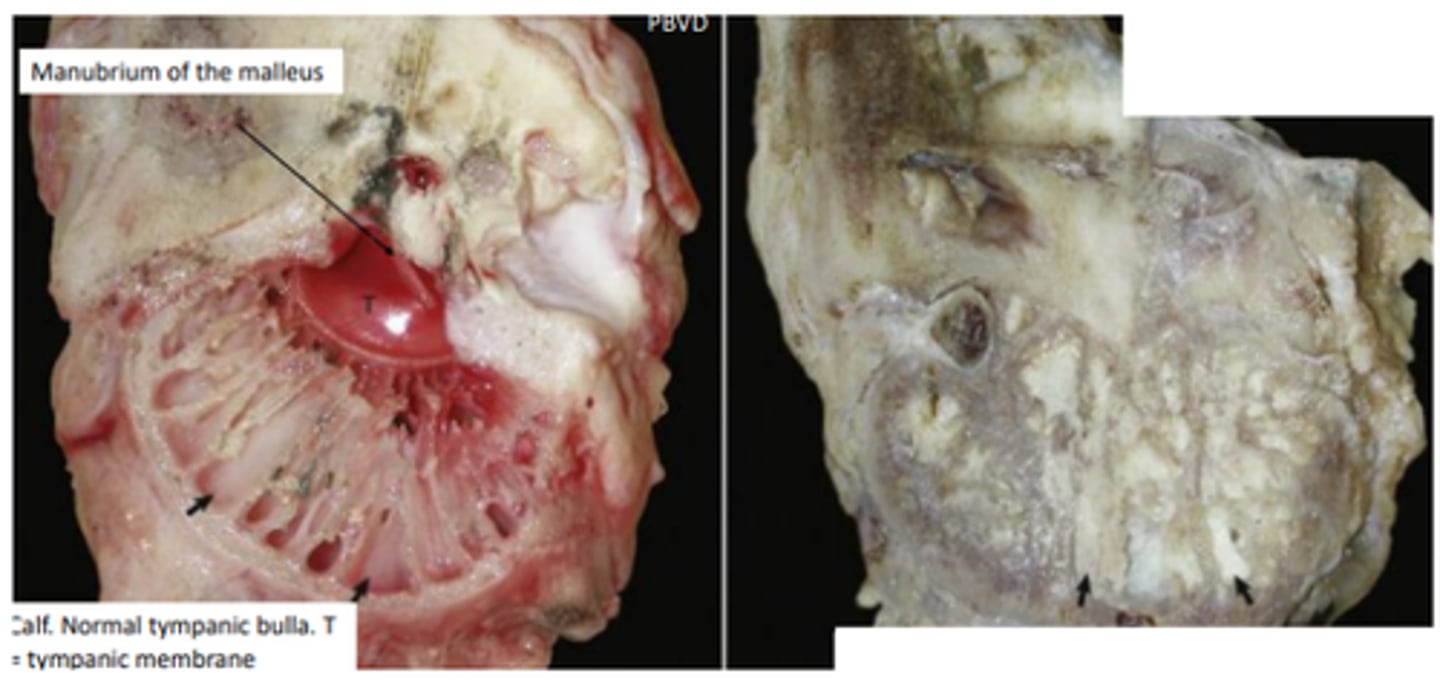
Otitis media gross pathology (Mycoplasma bovis)
Caseous, necrotic exudate, suppurative inflammation
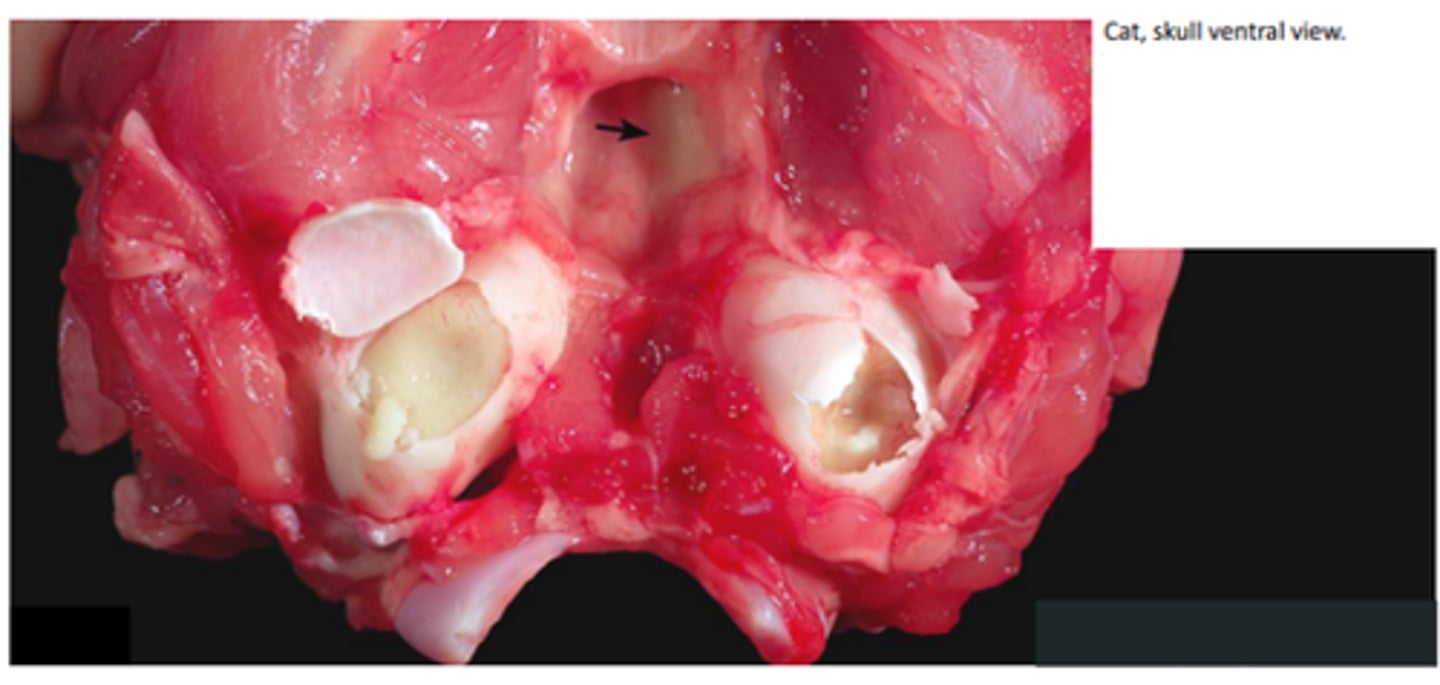
Bilateral suppurative otitis media
Tympanic cavities bilaterally filled with soft, yellow-tan exudate (pus; otitis media).
Arrow; eustachitis
Otitis media
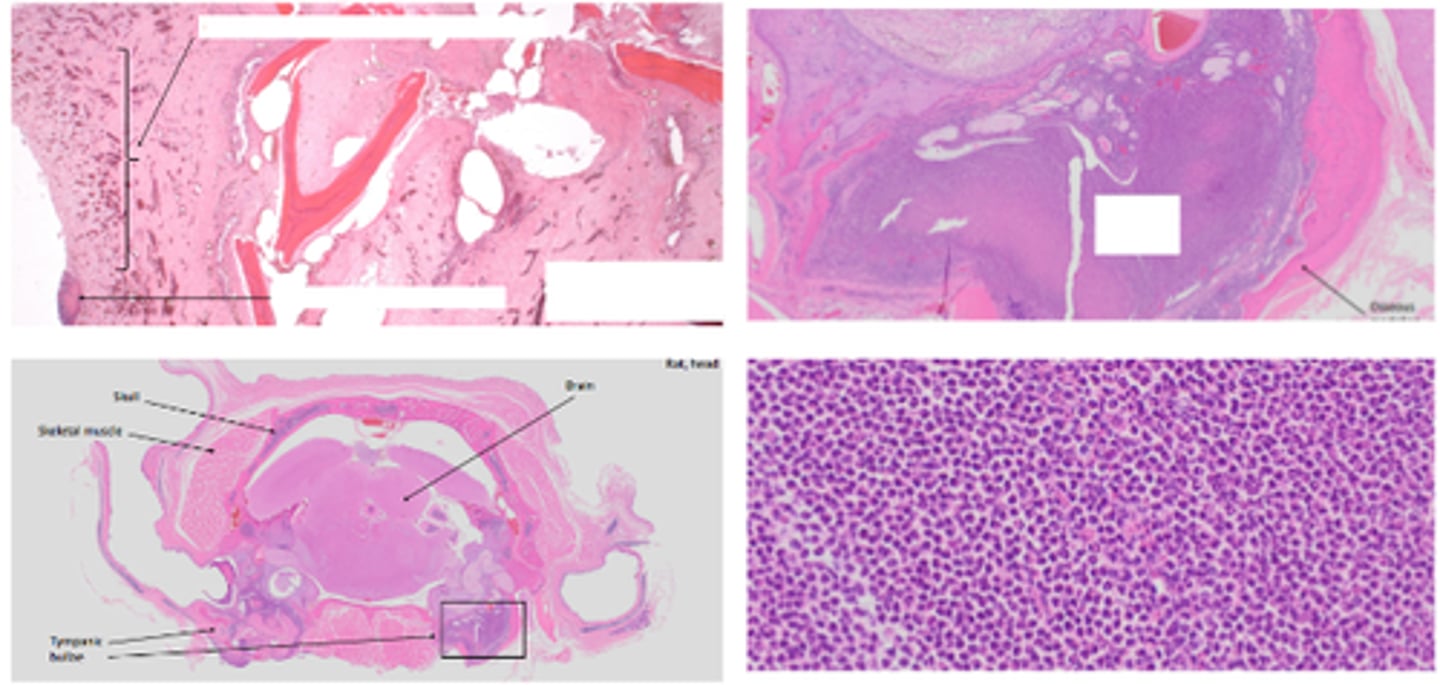
Microtia
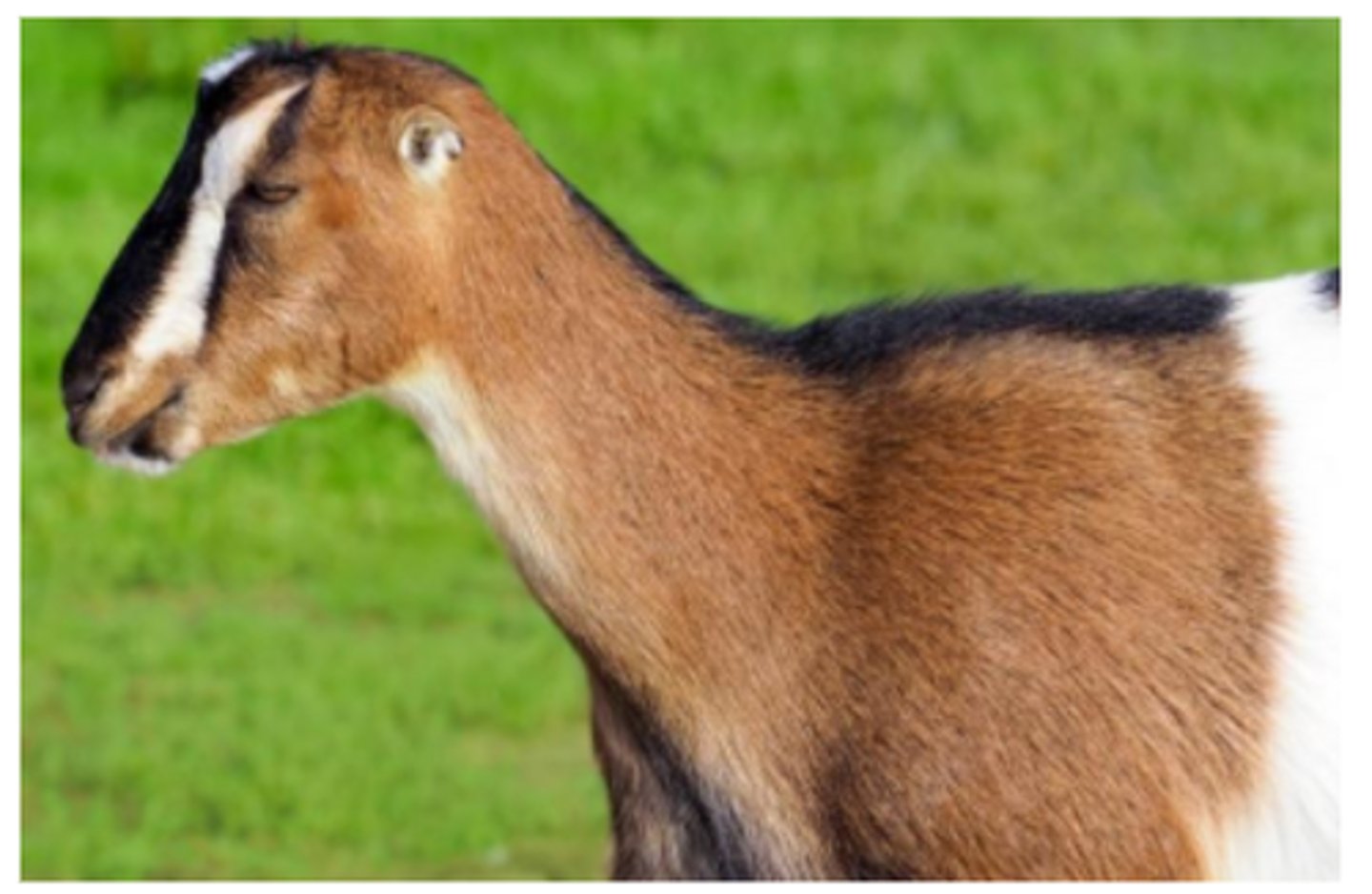
Small pinna - La Mancha goat

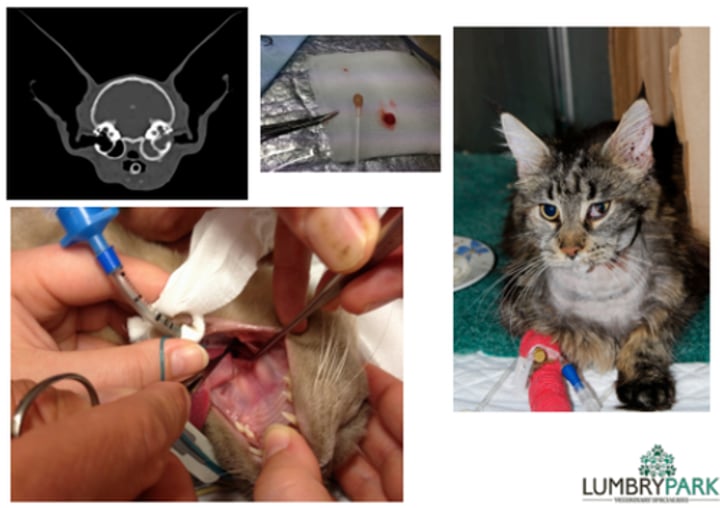
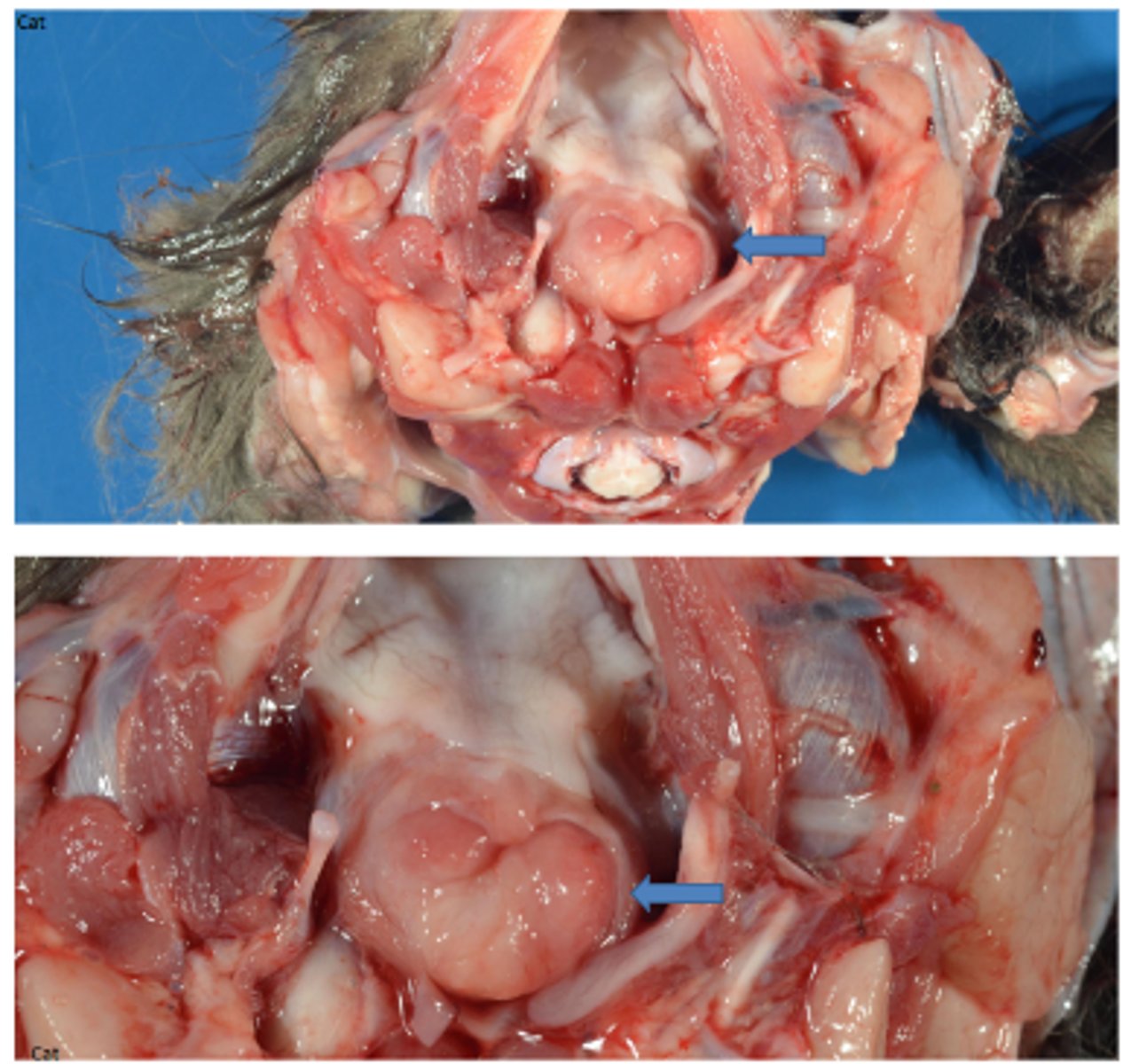
Nasopharyngeal polyps
Gross pathology: pedunculated to polypoid mass with smooth surface, variably ulcerated mucosal surface
Histopathology: fibrovascular core, lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes
Nasopharyngeal polyps
Hyperplasia
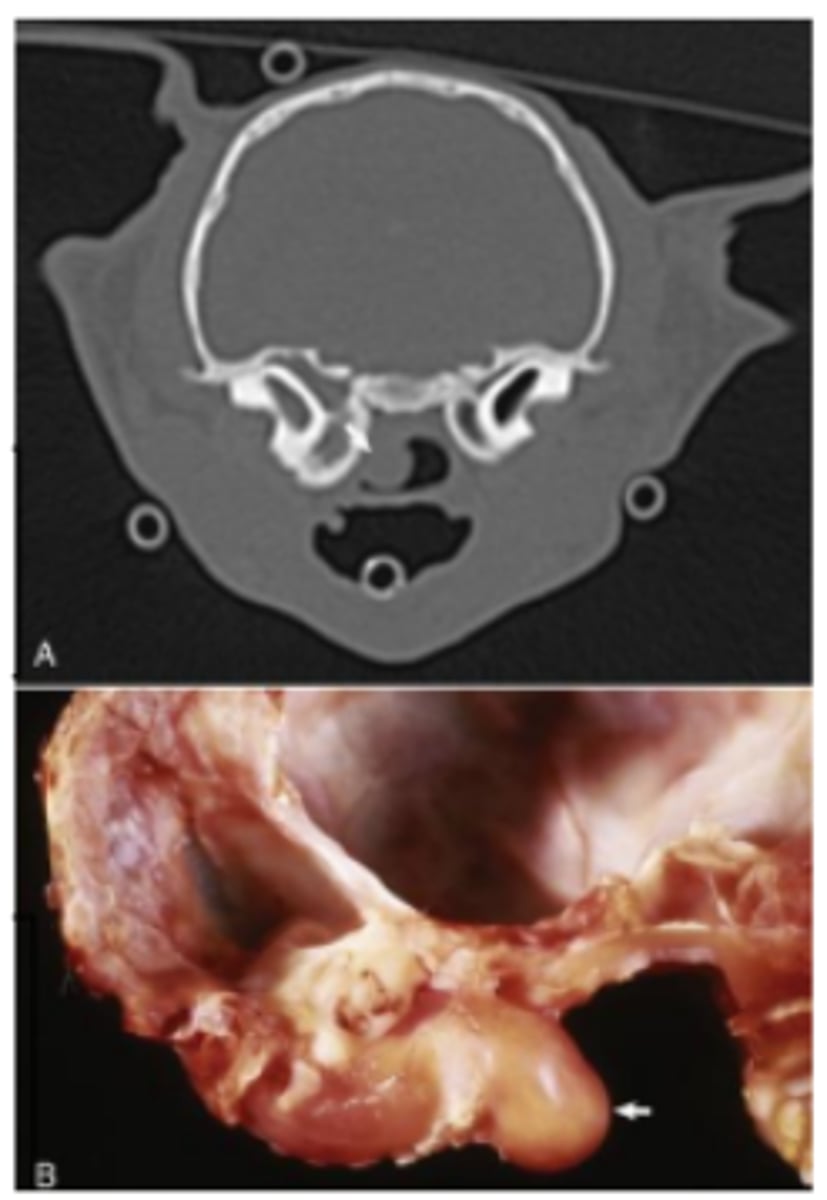
Tympanokeratoma
Gross pathology: tympanic cavity filled and expanded with pasty, yellow to pale-tan material, loss of normal structures (ossicles)
Histopathology: keratin surrounded by squamous epithelium, granulation tissue +/- otitis media (+/-) cholesterol clefts and granulomatous inflammation (cholesterol granulomas)
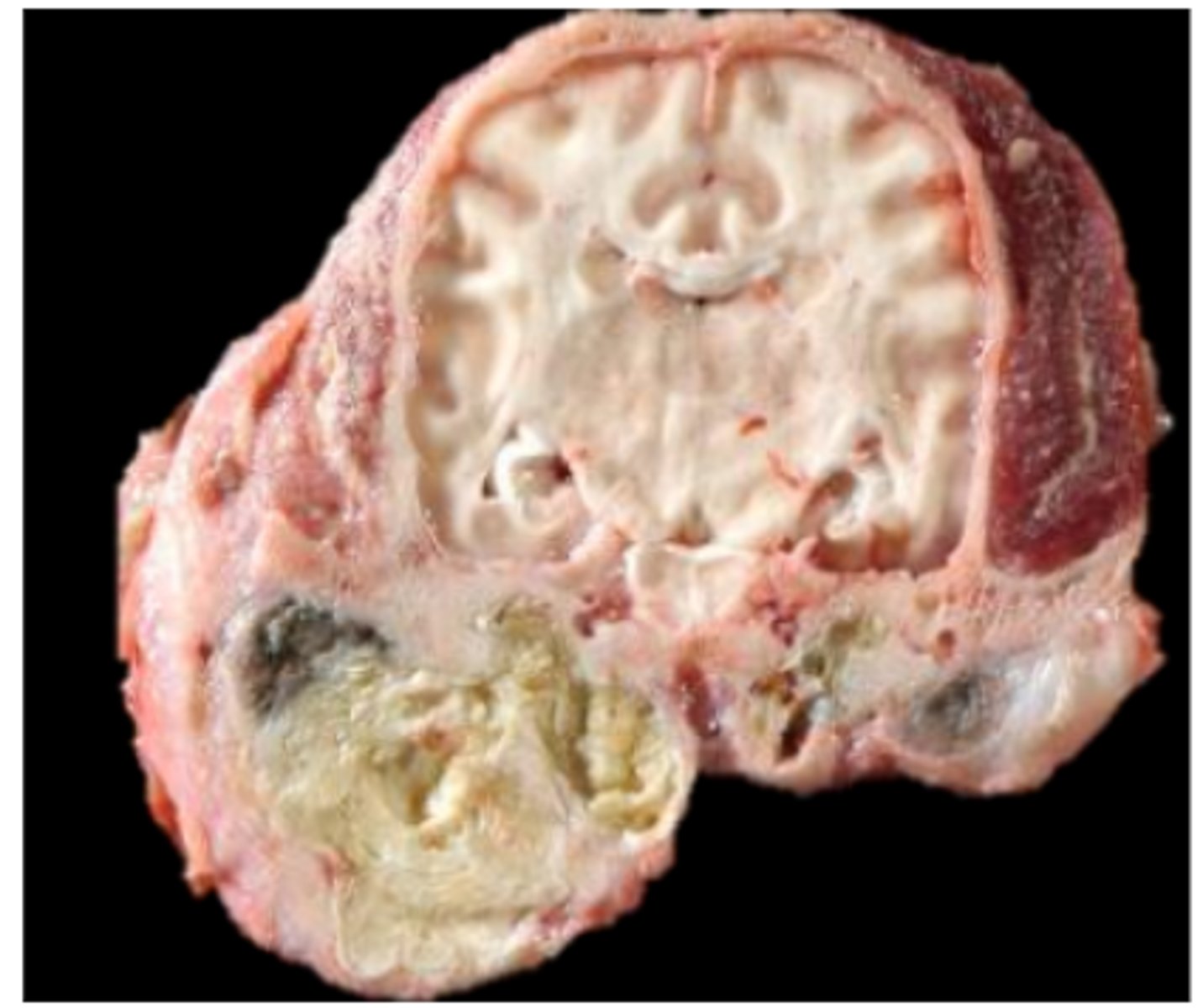
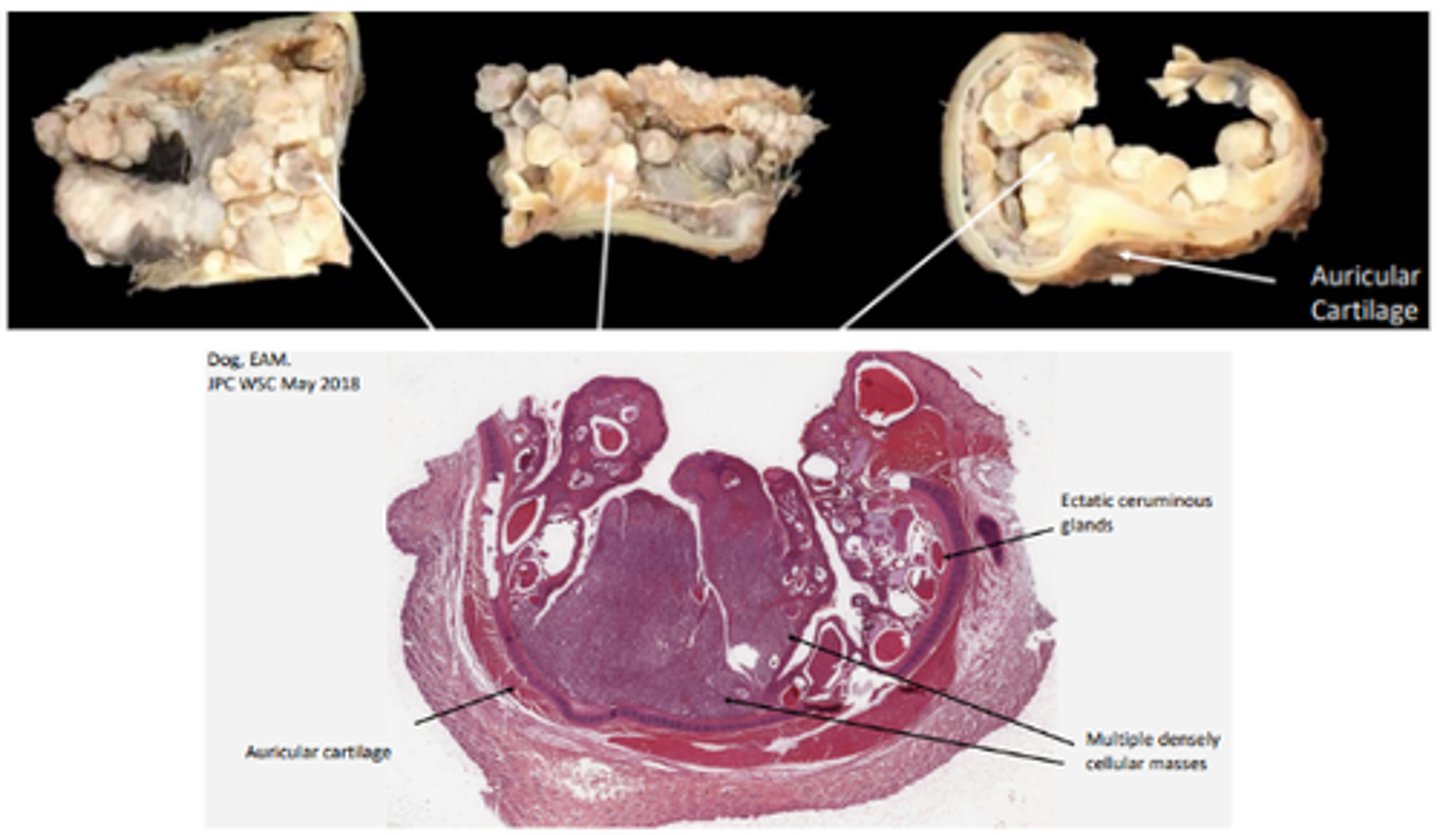
Ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma
Multifocal to coalescing nodules; firm, pale tan; EAM obstruction (perpetuates otitis externa!)
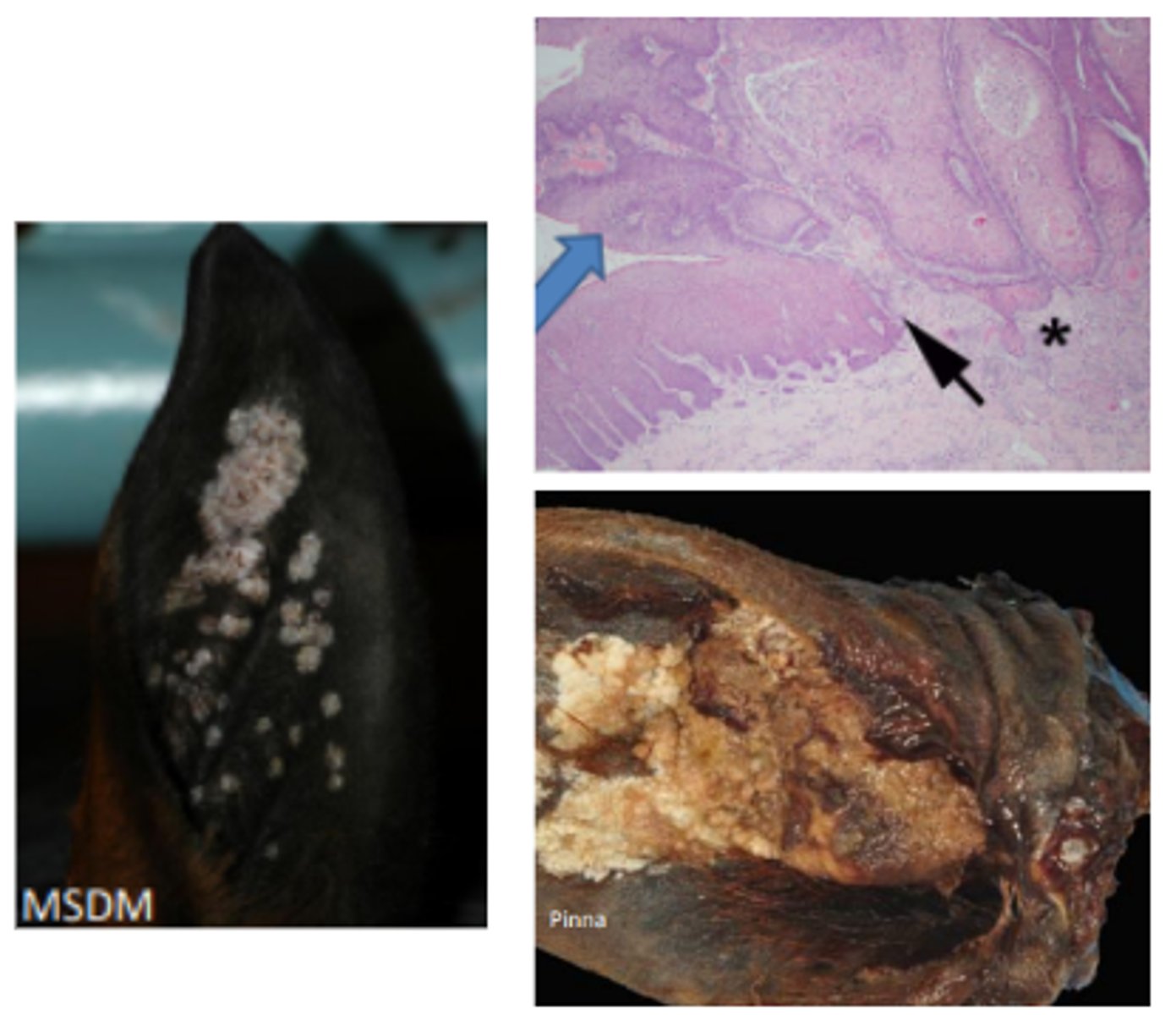
Equine aural plaques (papillomatosis)
Transition of viral plaque (black arrow) into SCC. Note the proliferative mass with disorganization of the keratinocyte layers and the invasive islands of neoplastic epithelium (*)
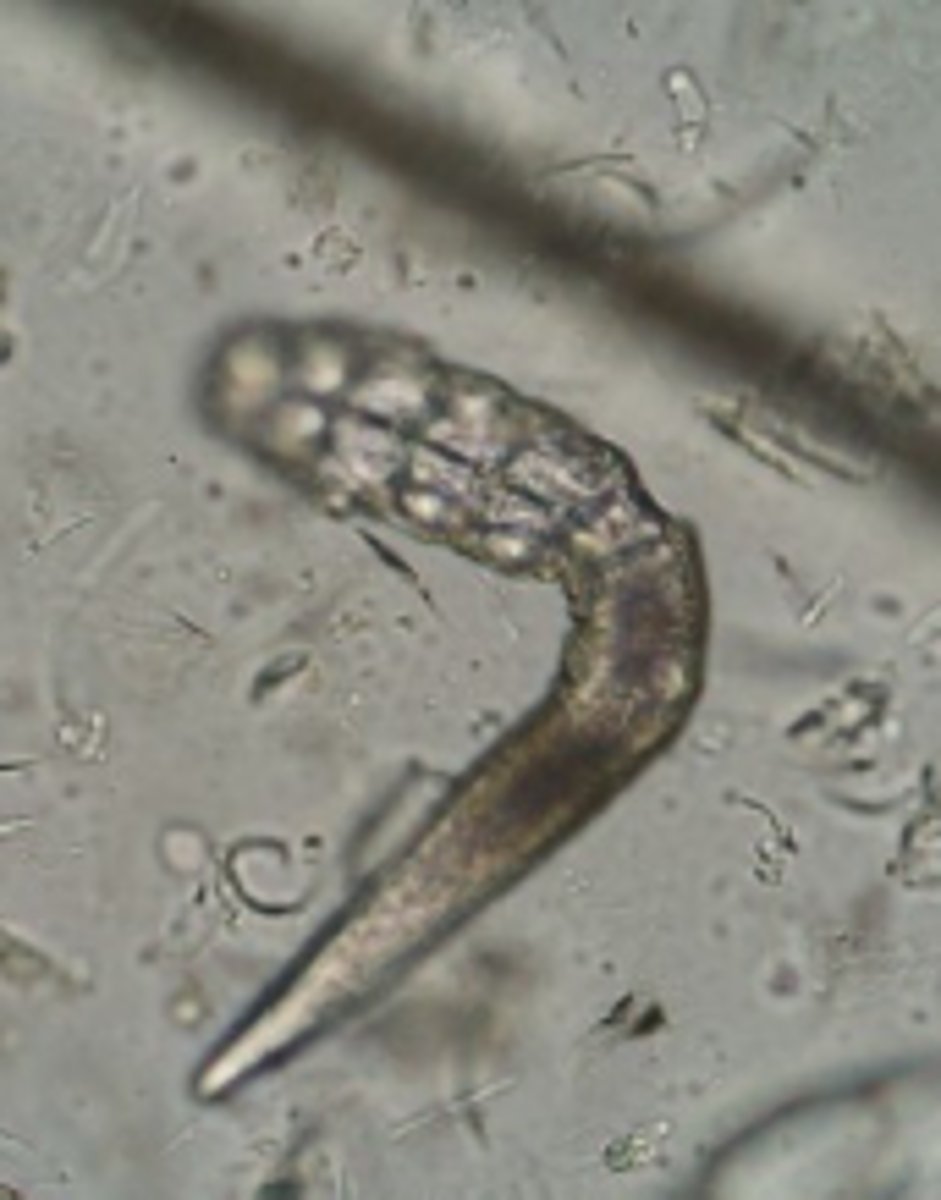
Demodex
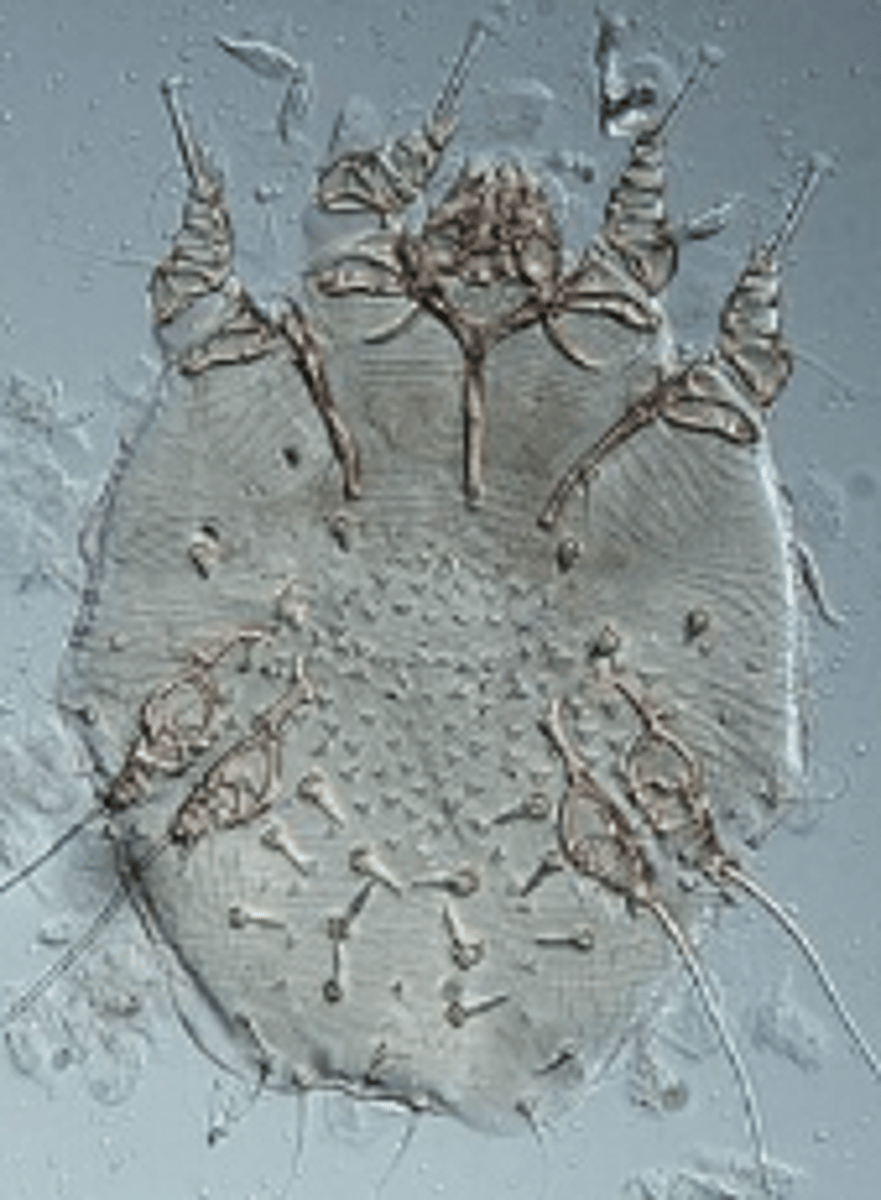
Sarcoptes scabiei
Otodectes
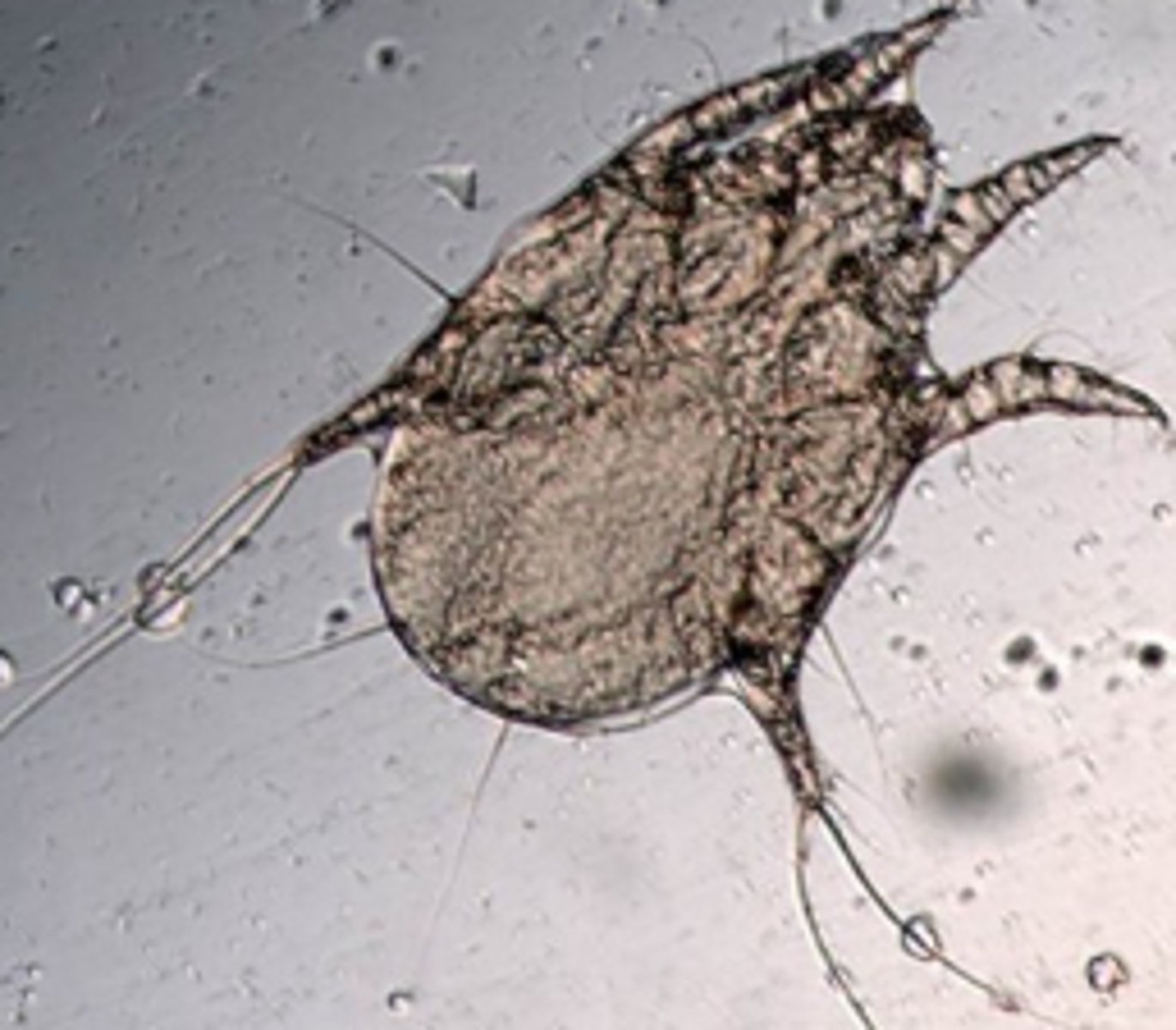
Dermatophytosis
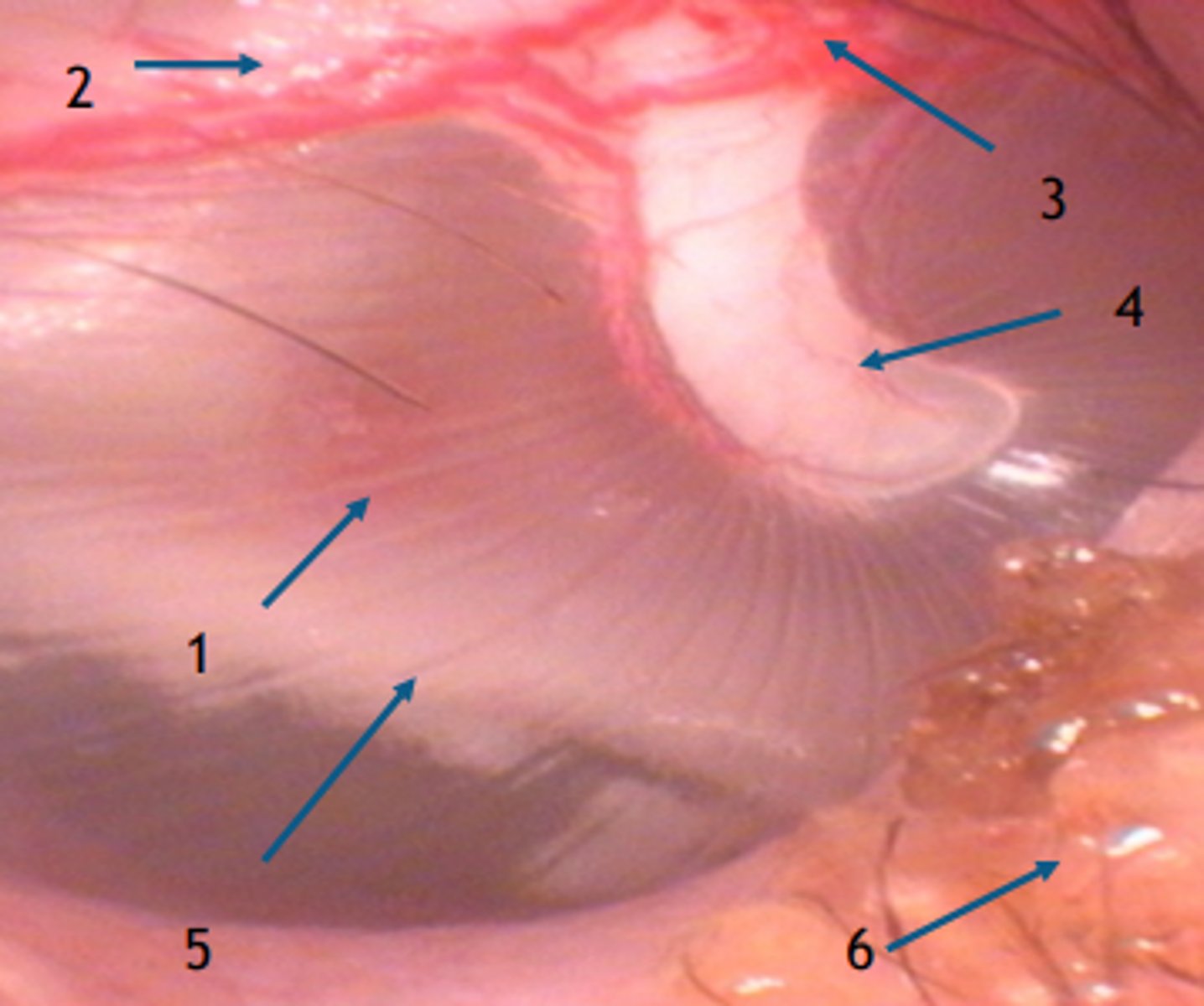
Tympanic membrane (normal)
1. Pars tensa
2. Edge of the pars flaccida
3. Blood vessel
4. Head of Malleus
5. Promontory
6. Cerumen and hair
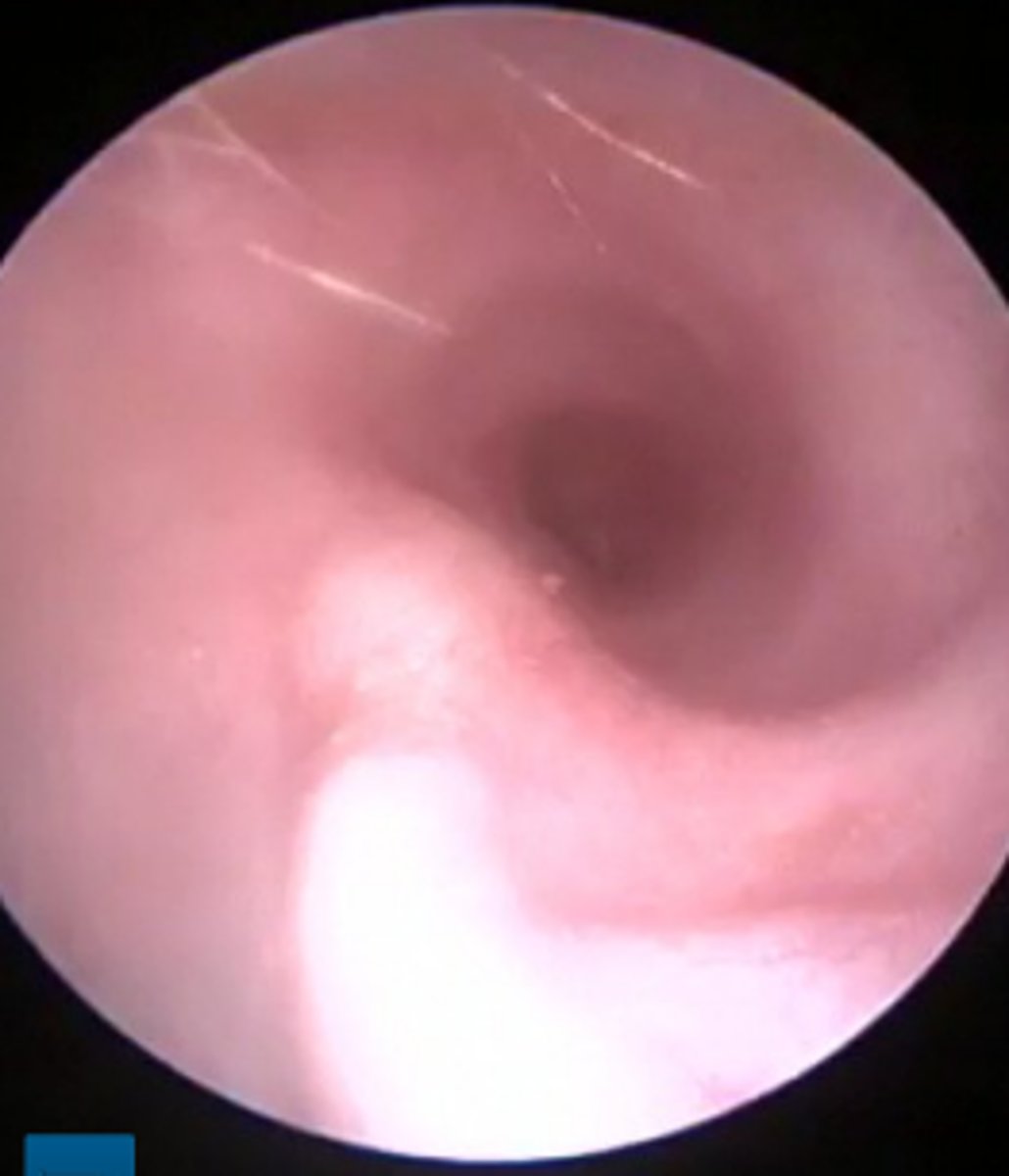
Tympanic membrane
Small amount of cerumen and hair adjacent
Ear canal
Epithelial fold formation, stenosis, ceruminous gland hyperplasia causing polypoid appearance, ulceration (bleeding)
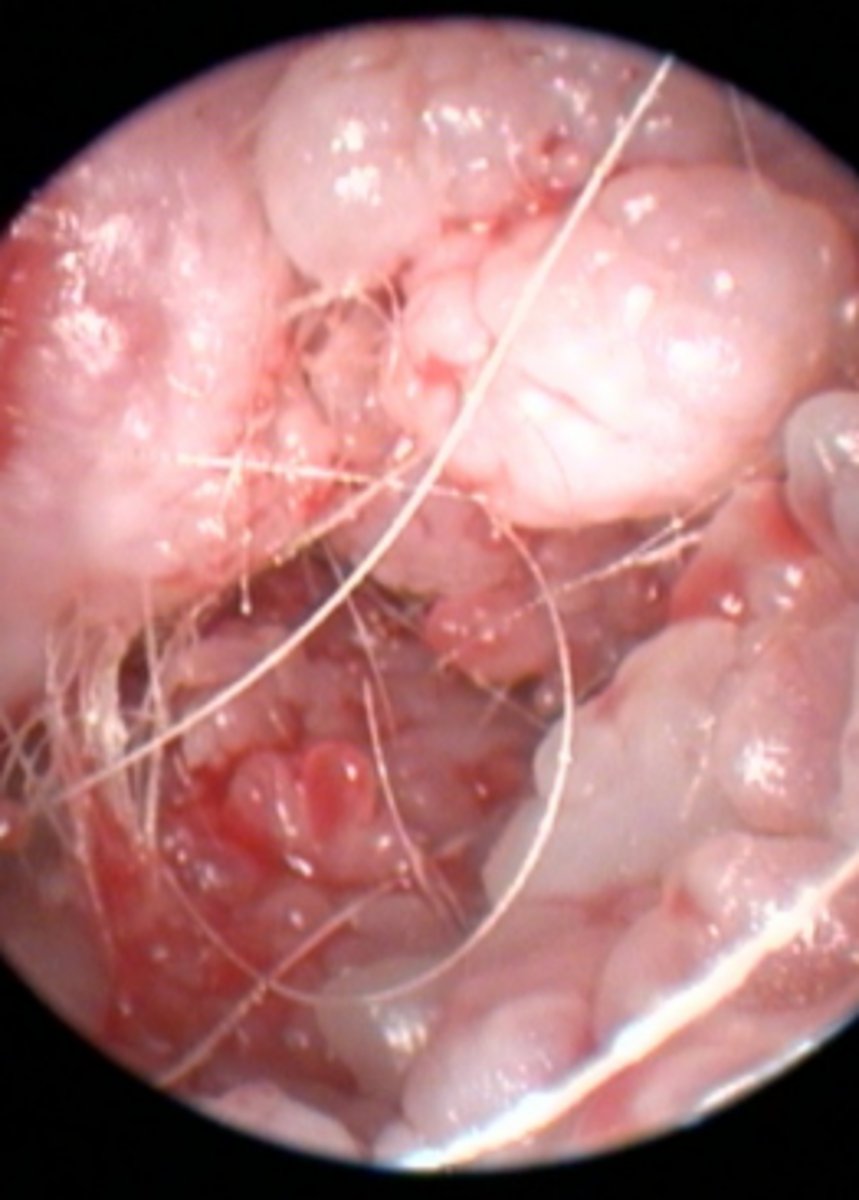
Ear canal
Erythema and mild ulceration of horizontal canal, abnormal opaque tympanic membrane
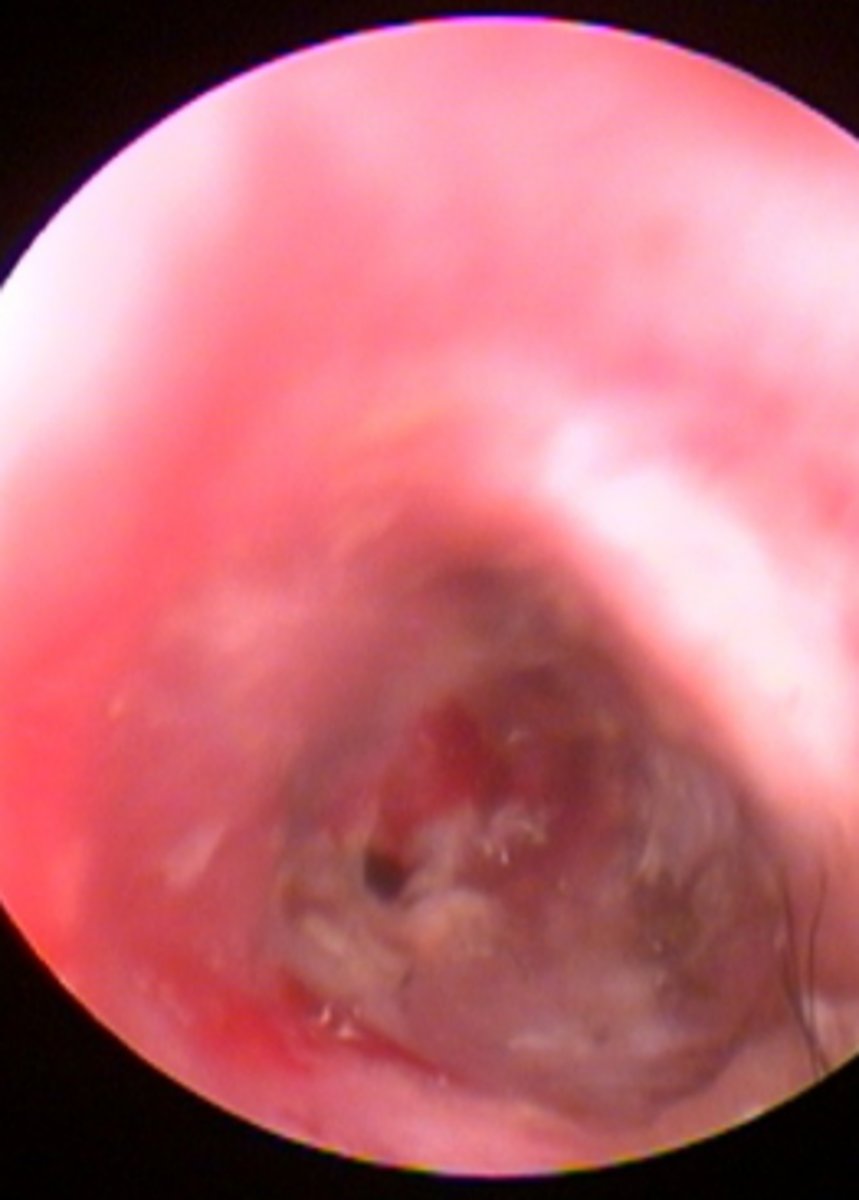
Ear canal
Opaque tympanic membrane, erythema and ulceration, purulent discharge
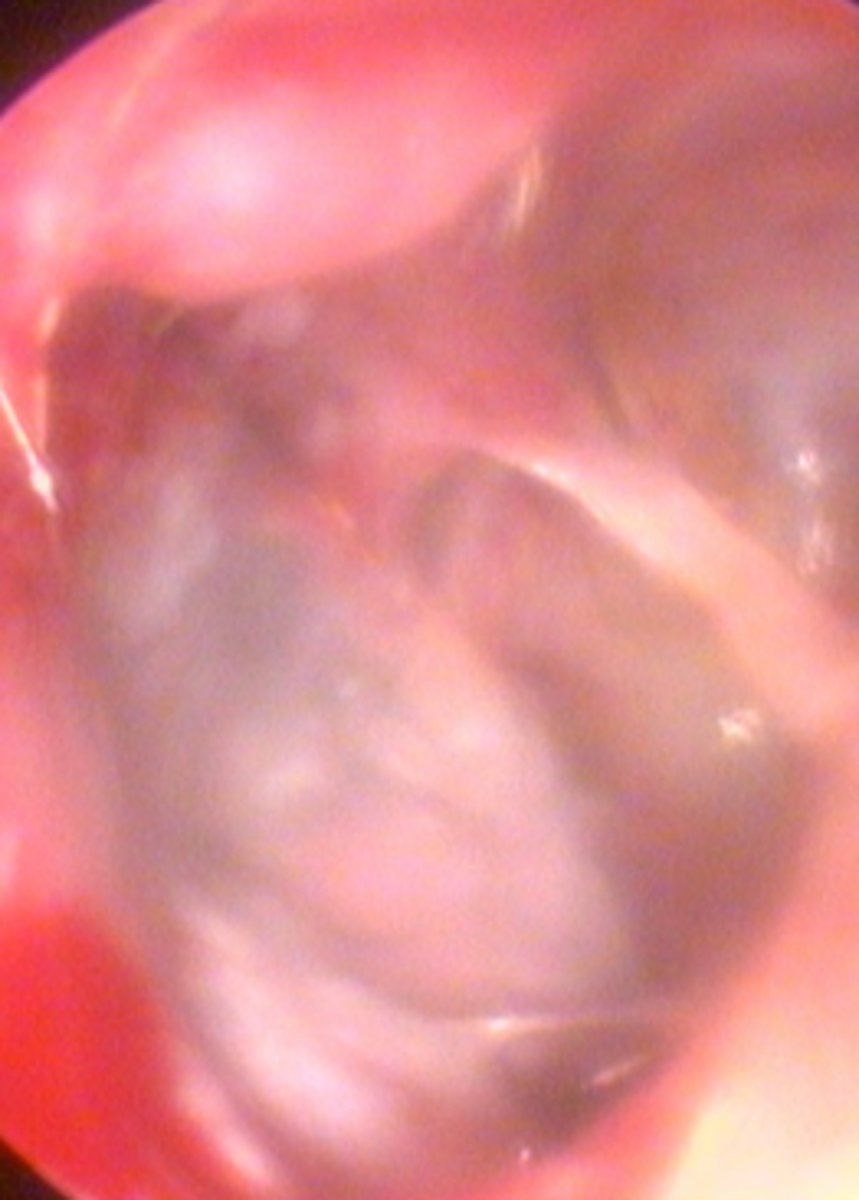
Ear canal
Erythema, ulceration, macerated epithelium (white areas), brown mucopurulent discharge
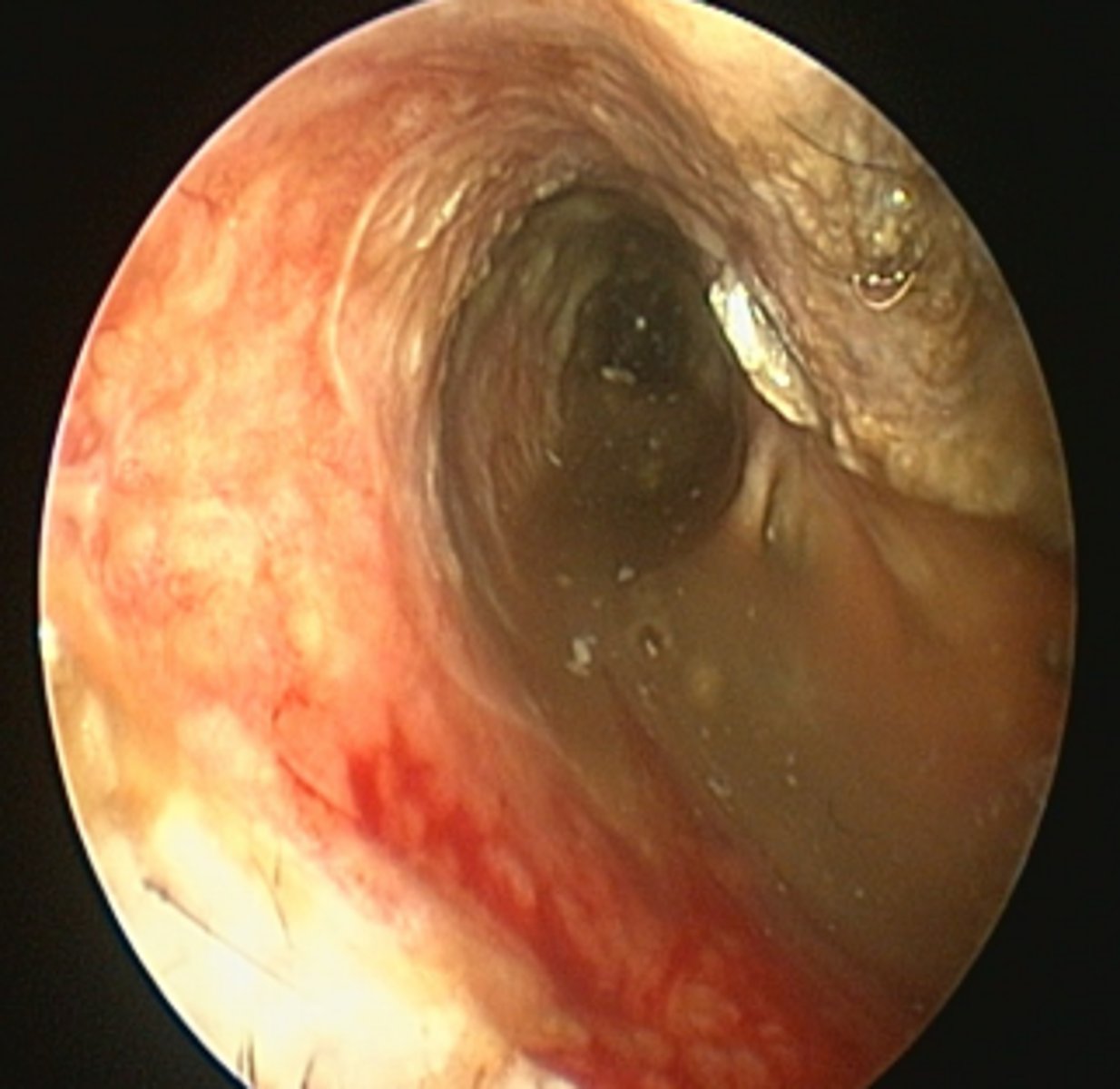
Ear canal
Erythema, stenosis, ulceration, sebaceous gland hyperplasia (small white spots)
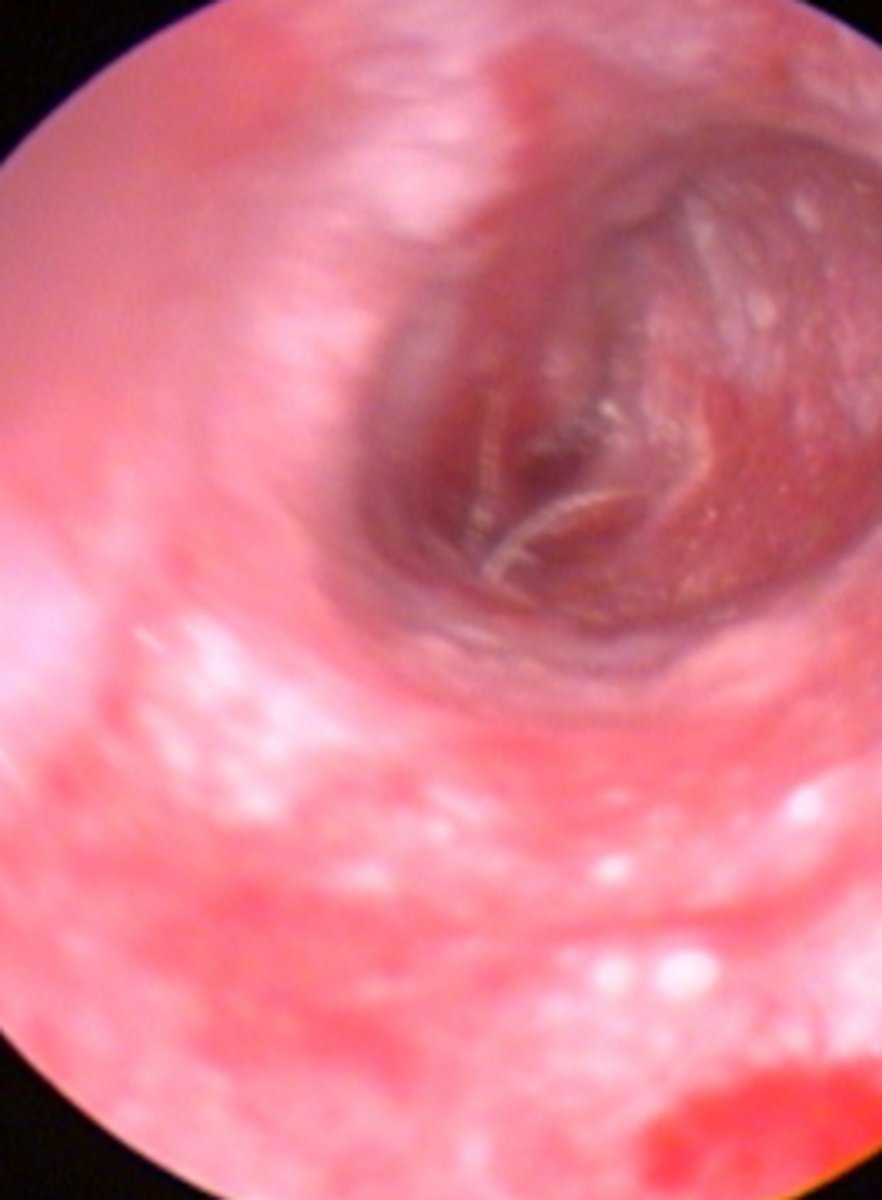
Severe stenosis of the ear canal
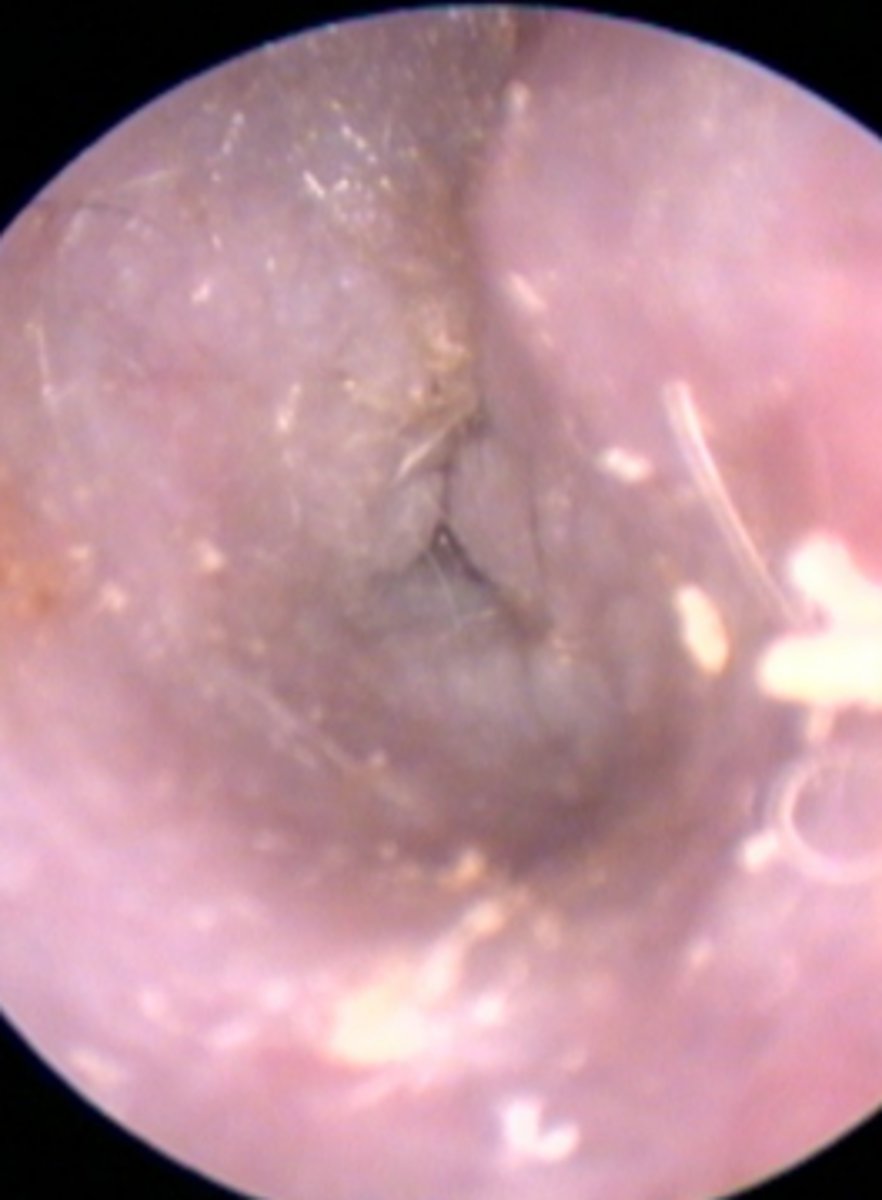
Ear canal
Brown ceruminous discharge caused by Malassezia pachydermatis
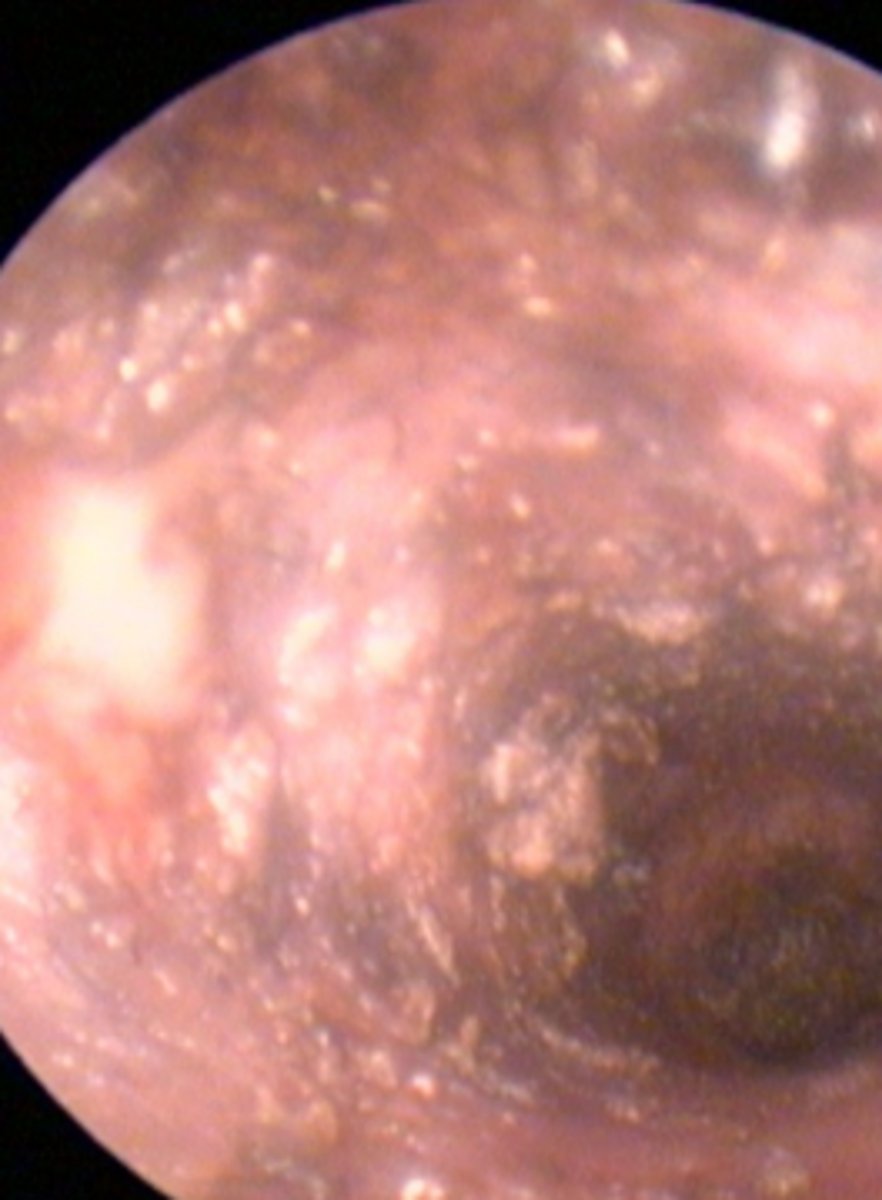
Ear canal
Purulent discharge due to bacterial infection
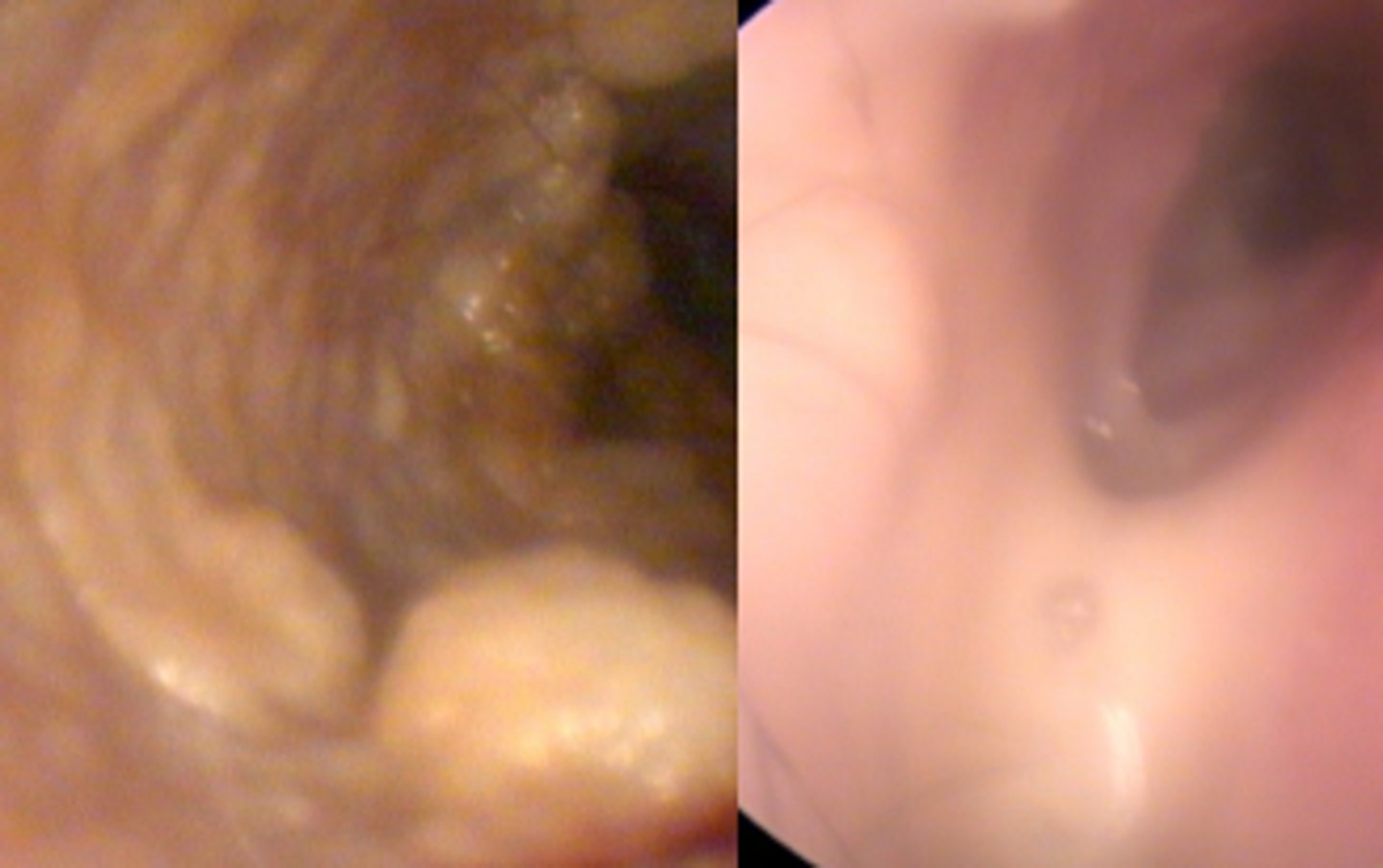
Ear canal macerated epithelium
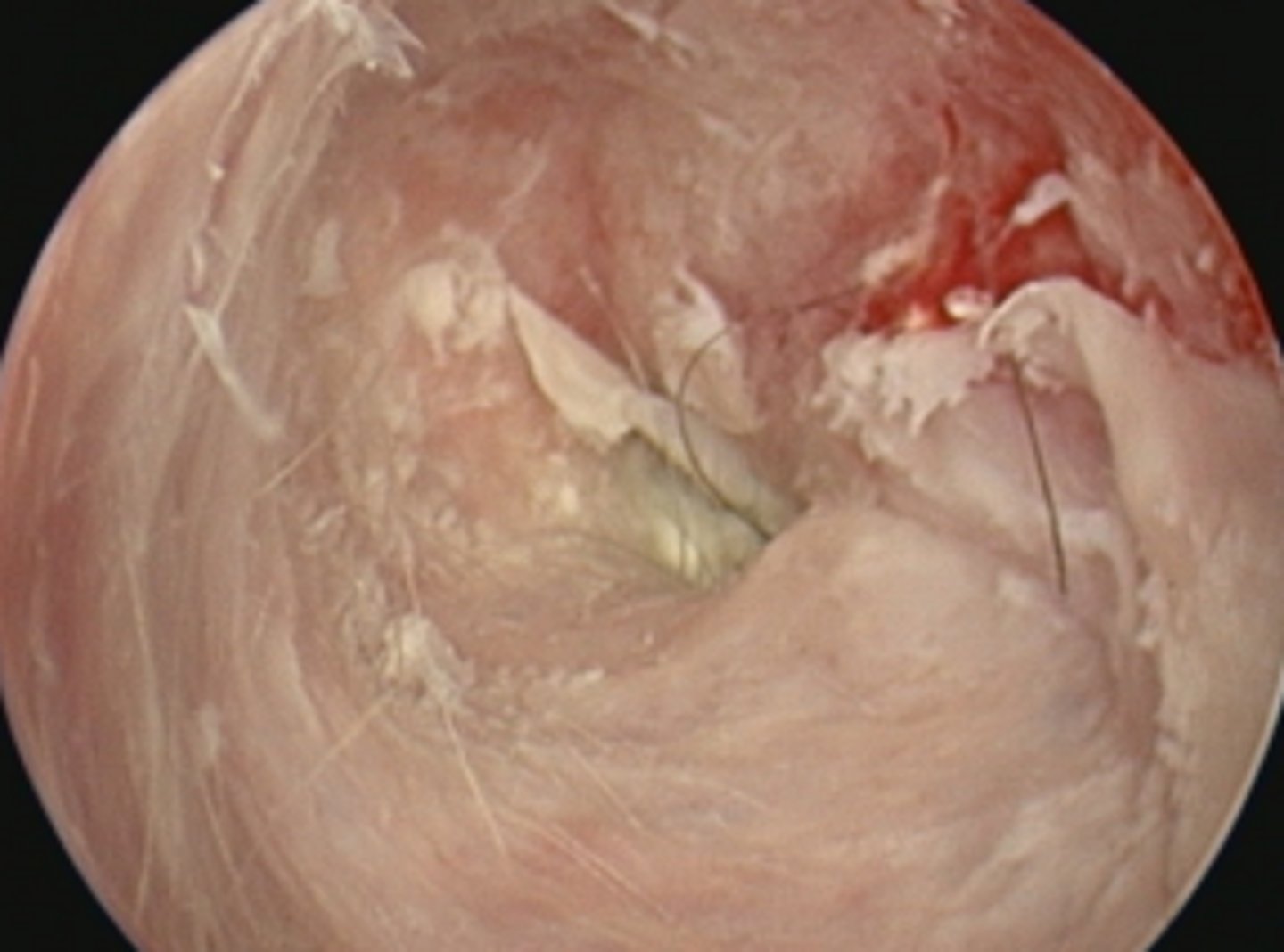
Ear canal - hirsuitism (excess hair)
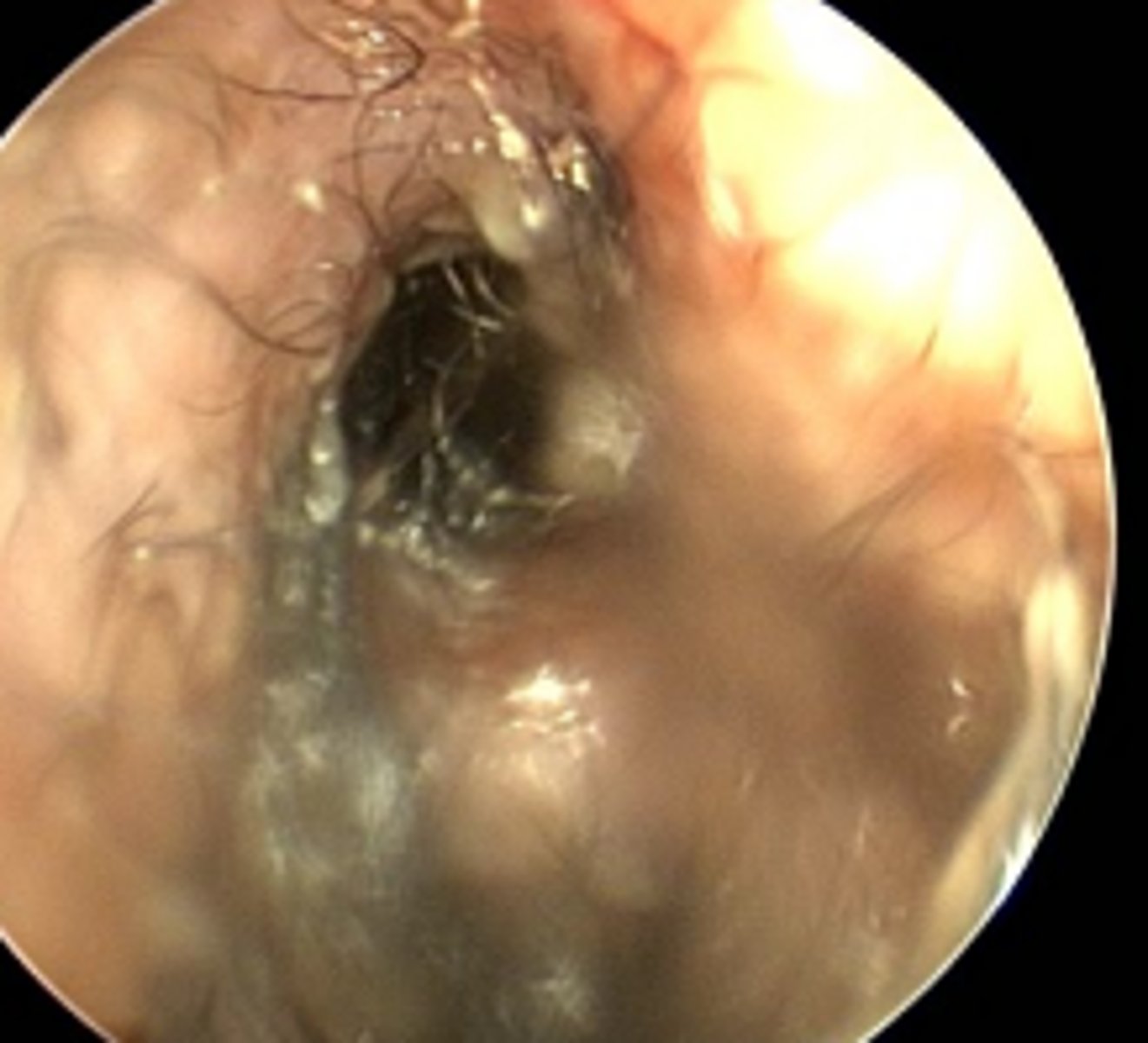
Mucopurulent discharge from the middle ear
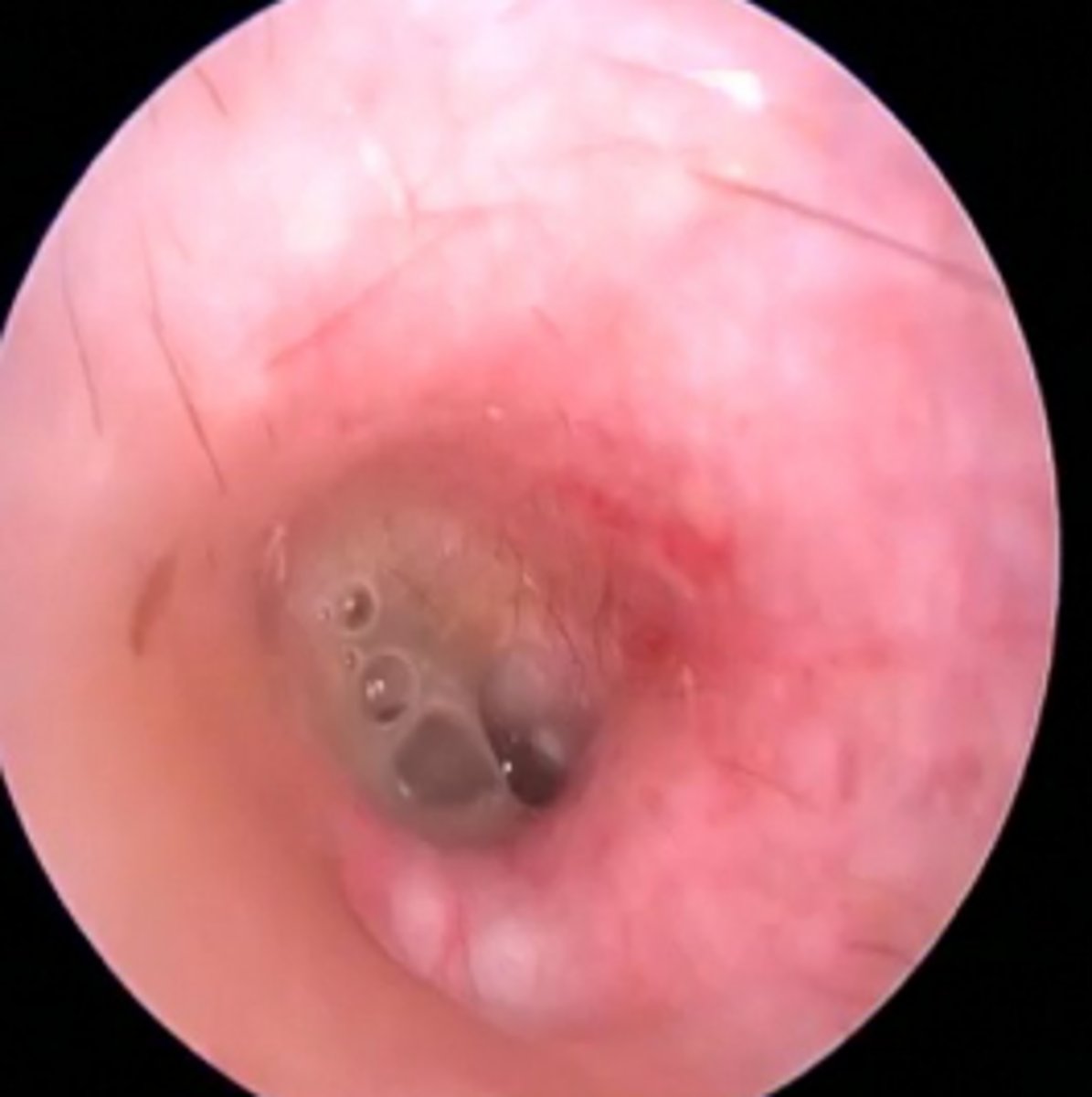
Ear canal - profuse slimy purulent discharge due to biofilm production
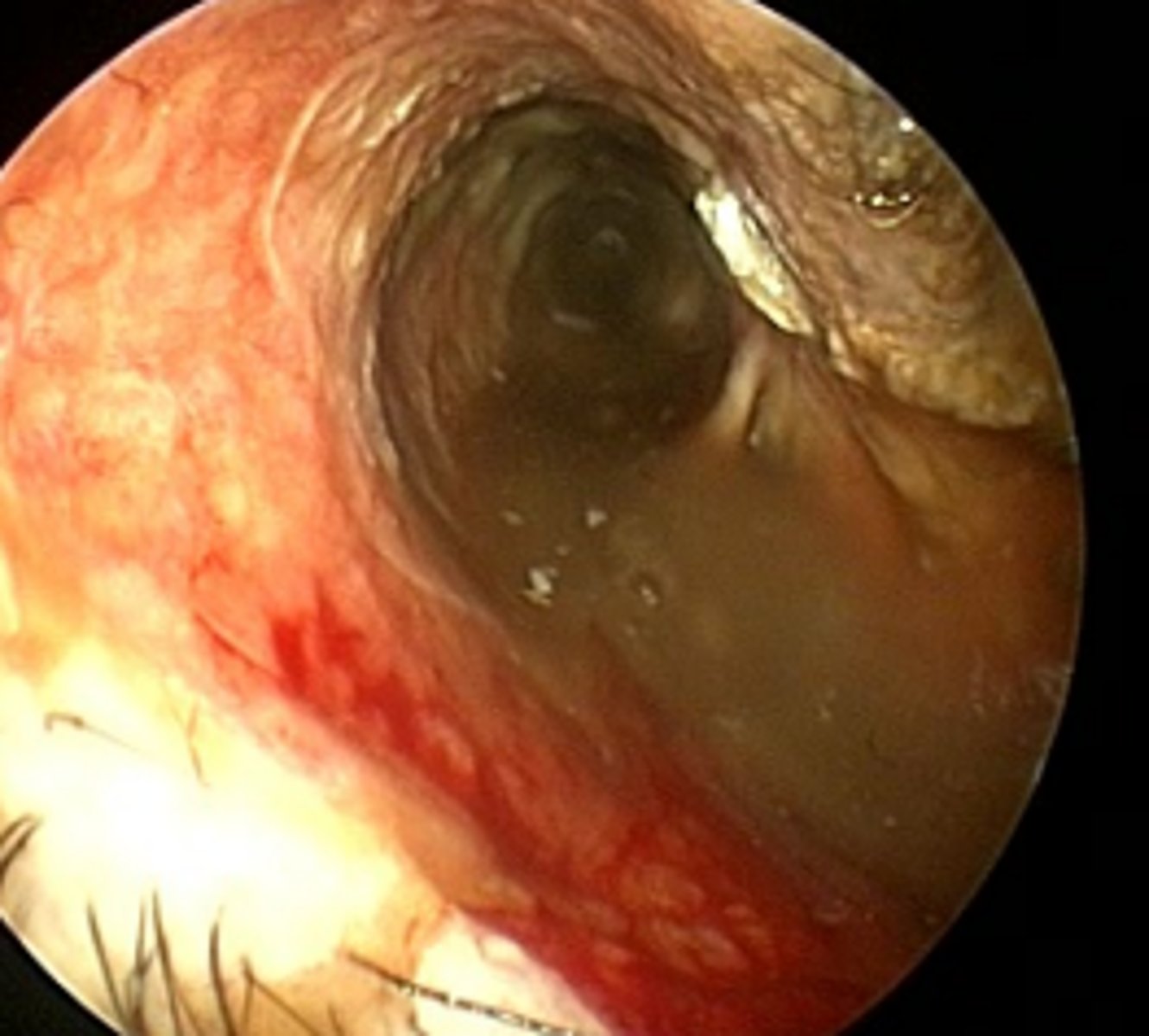
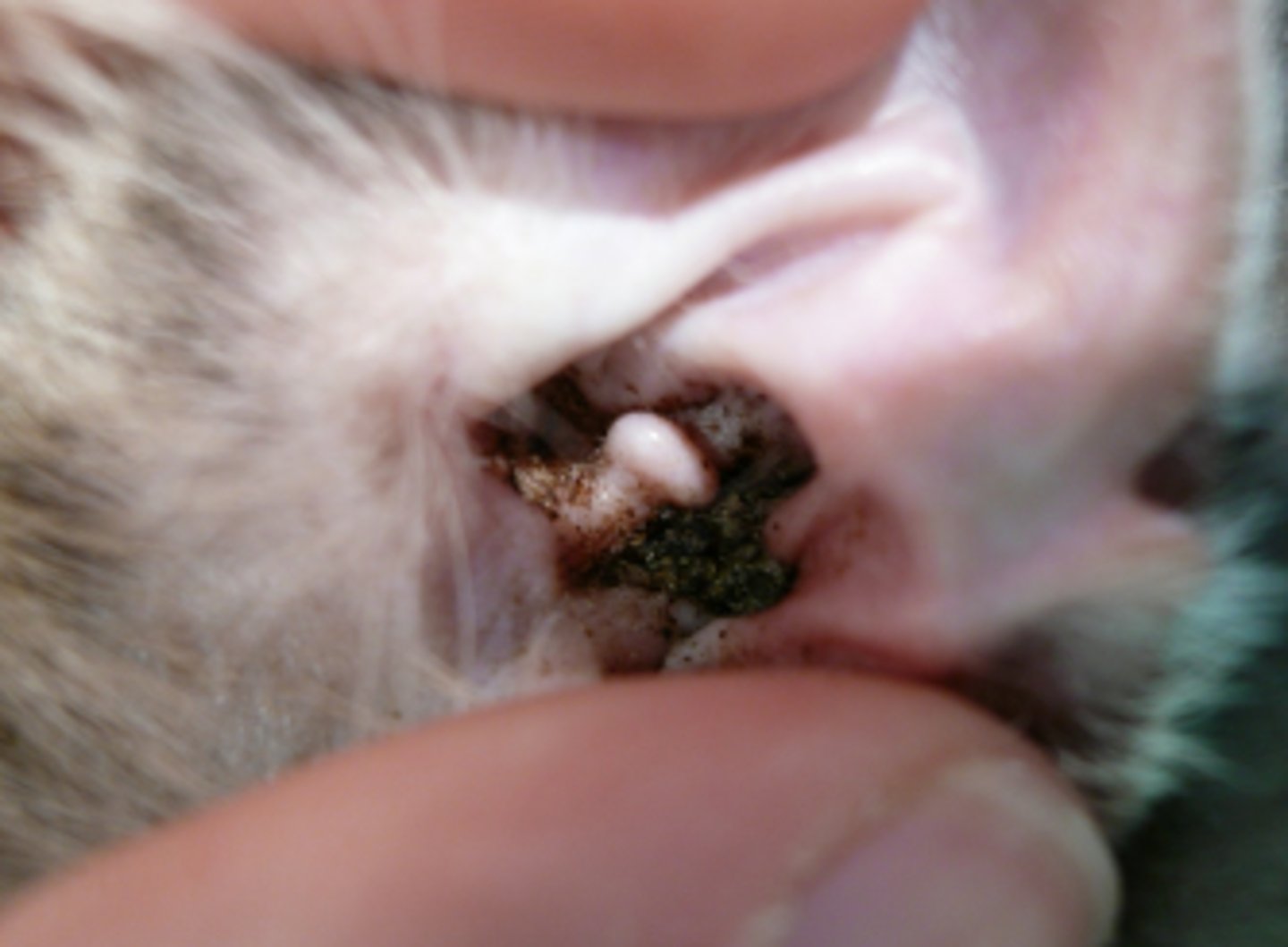
Grass seed adjacent to the tympanic membrane
Tan colour otic discharge and otitis
Many neutrophils (hypersegmented nuclei)
Phagocytosed bacteria (cocci) --> Staphylococcus or Streptococcus

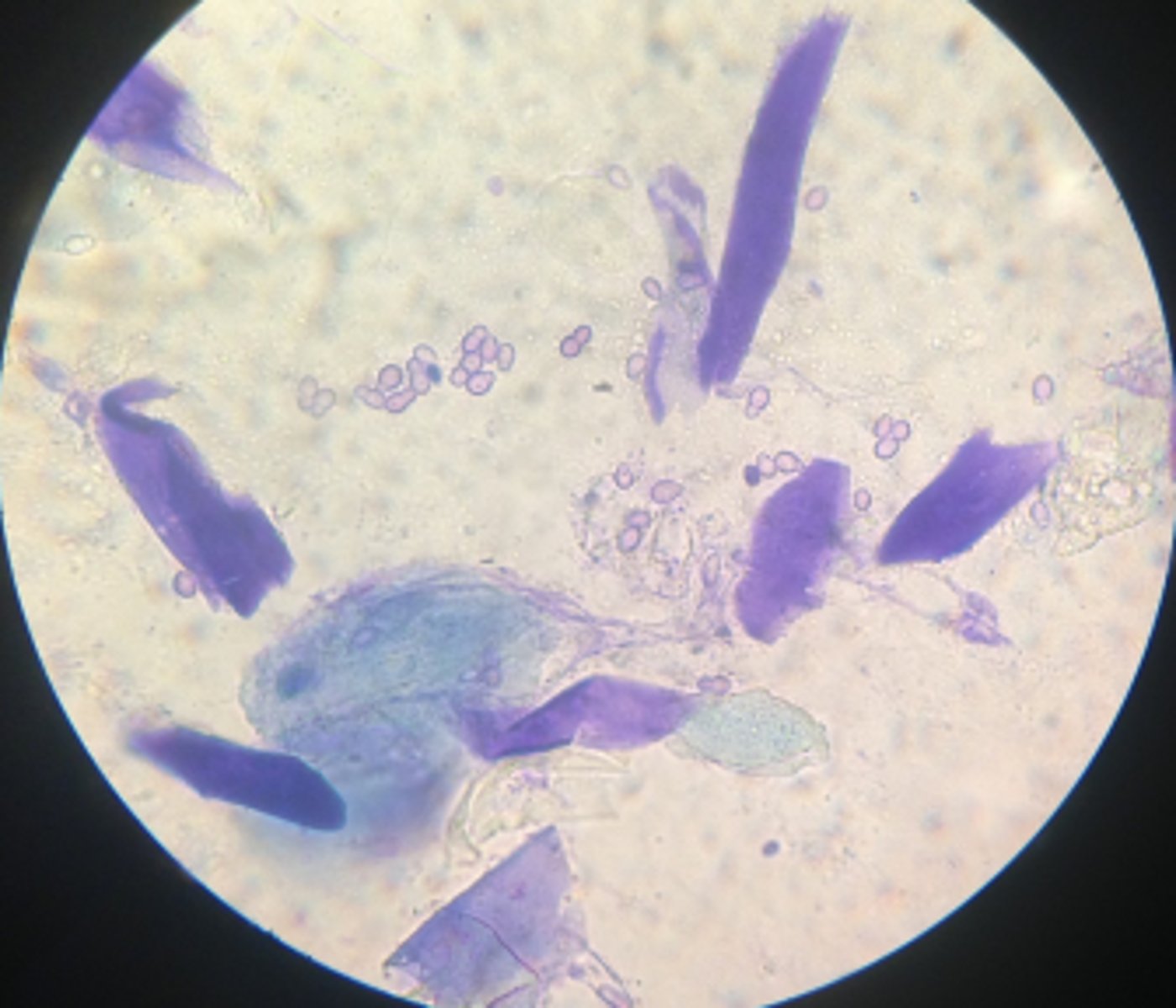
Ceruminous otitis
Unipolar budding yeat --> Malassezia pachydermatis
Purulent, painful and ulcerated malodourous otitis
Small numbers of neutrophuls (hypersegmented nuclei)
Rod shaped bacteria --> Pseudomonas, Proteus, E.coli, Klebsiella
Small number of cocci also present
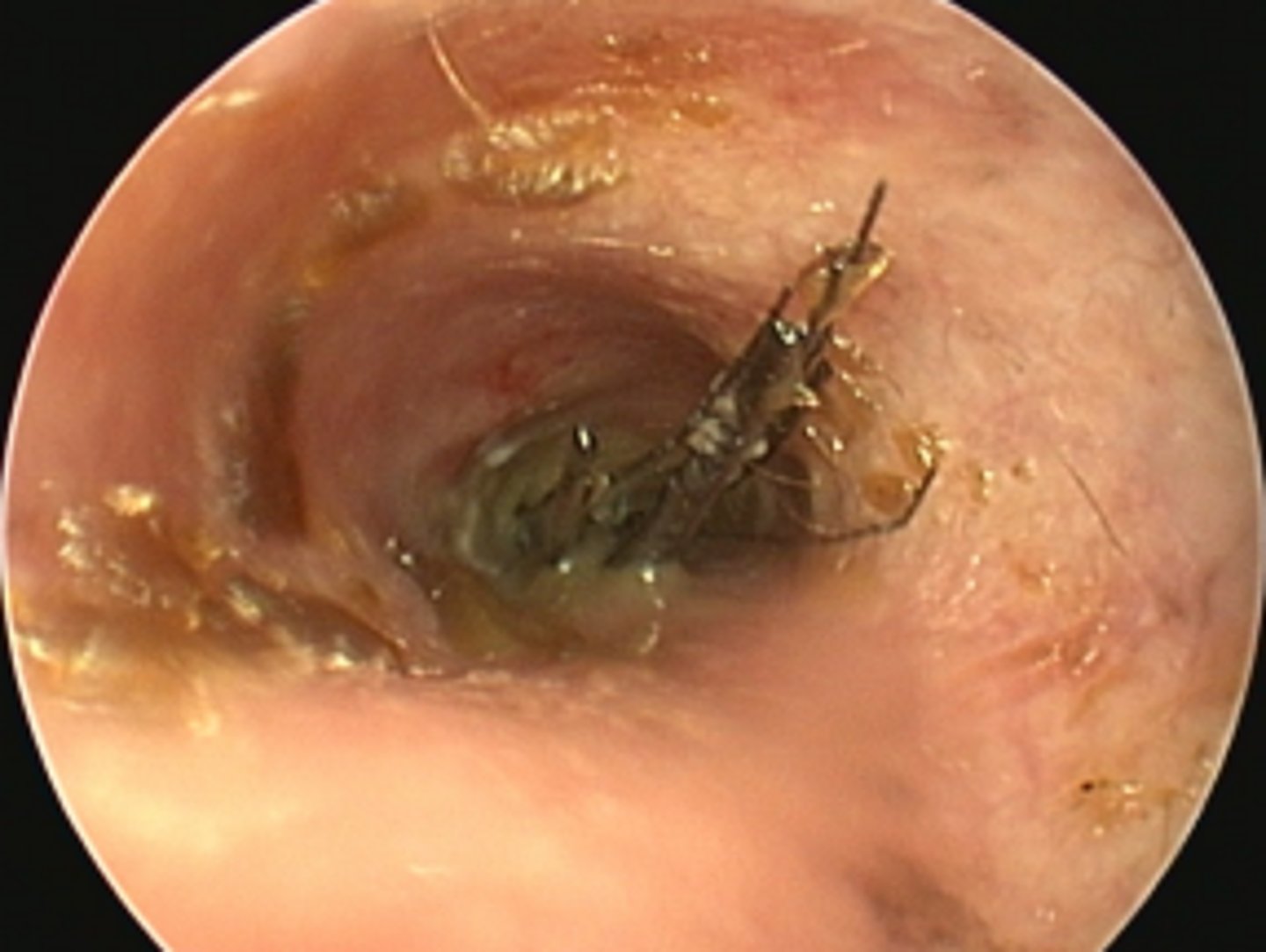
6 month old F cat with pruritic waxy ears - ear mites (otodectes cynotis)
Mild erthema of the pinna and ear canal entrance, dark brown coffee grounds like ceruminous discharge, white specks within cerumen
6 year old dog with severely painful and smelly unilateral otitis of 5 months duration
Purulent discharge, small ulcerations on the concave pinna and horizontal canal, tumour on the cranial lateral pinna - covered in crust, cobblestone appearance to the ear canal suggestive of ceruminous gland hyperplasia , inflammed and opaque tympanic membrane
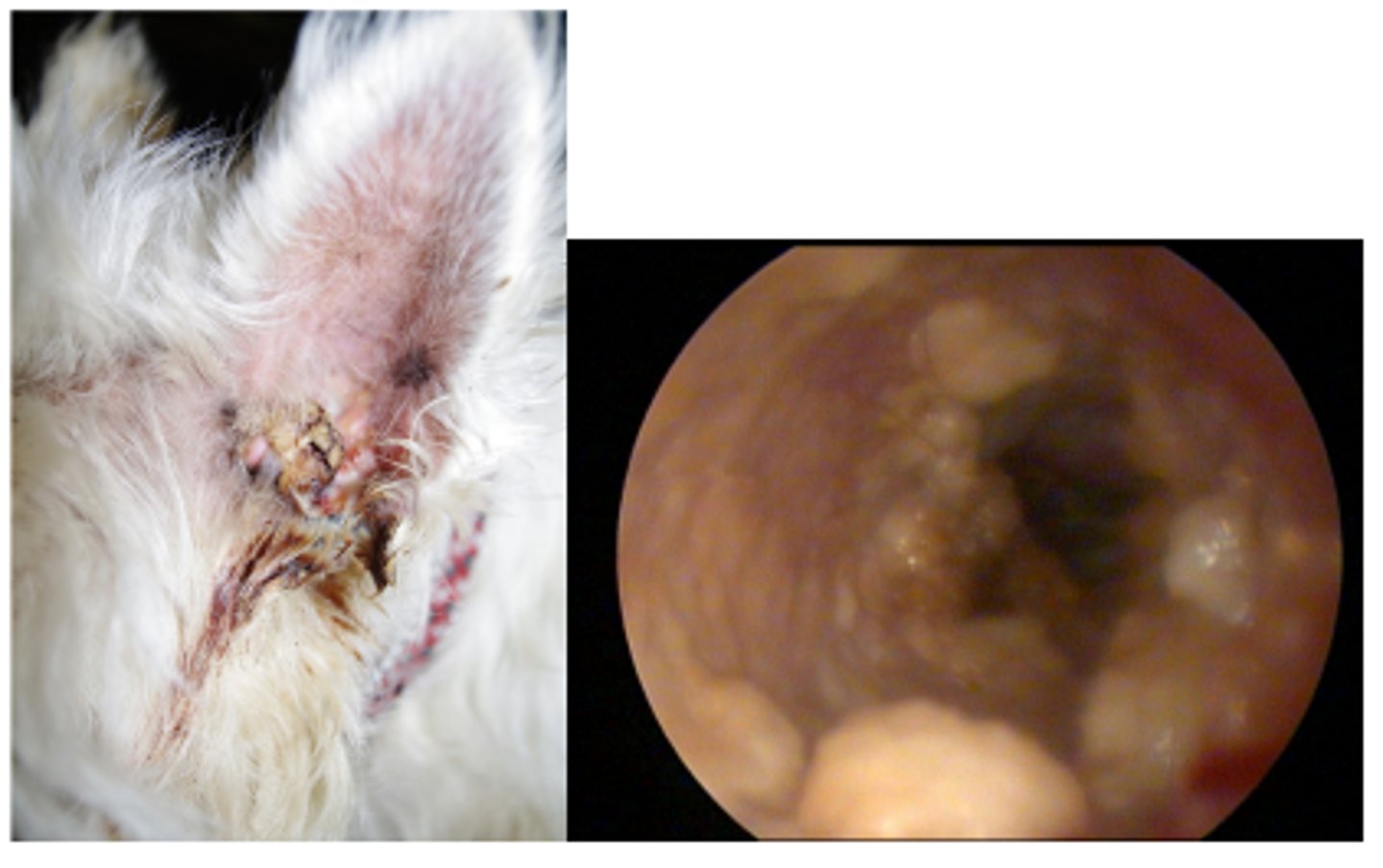
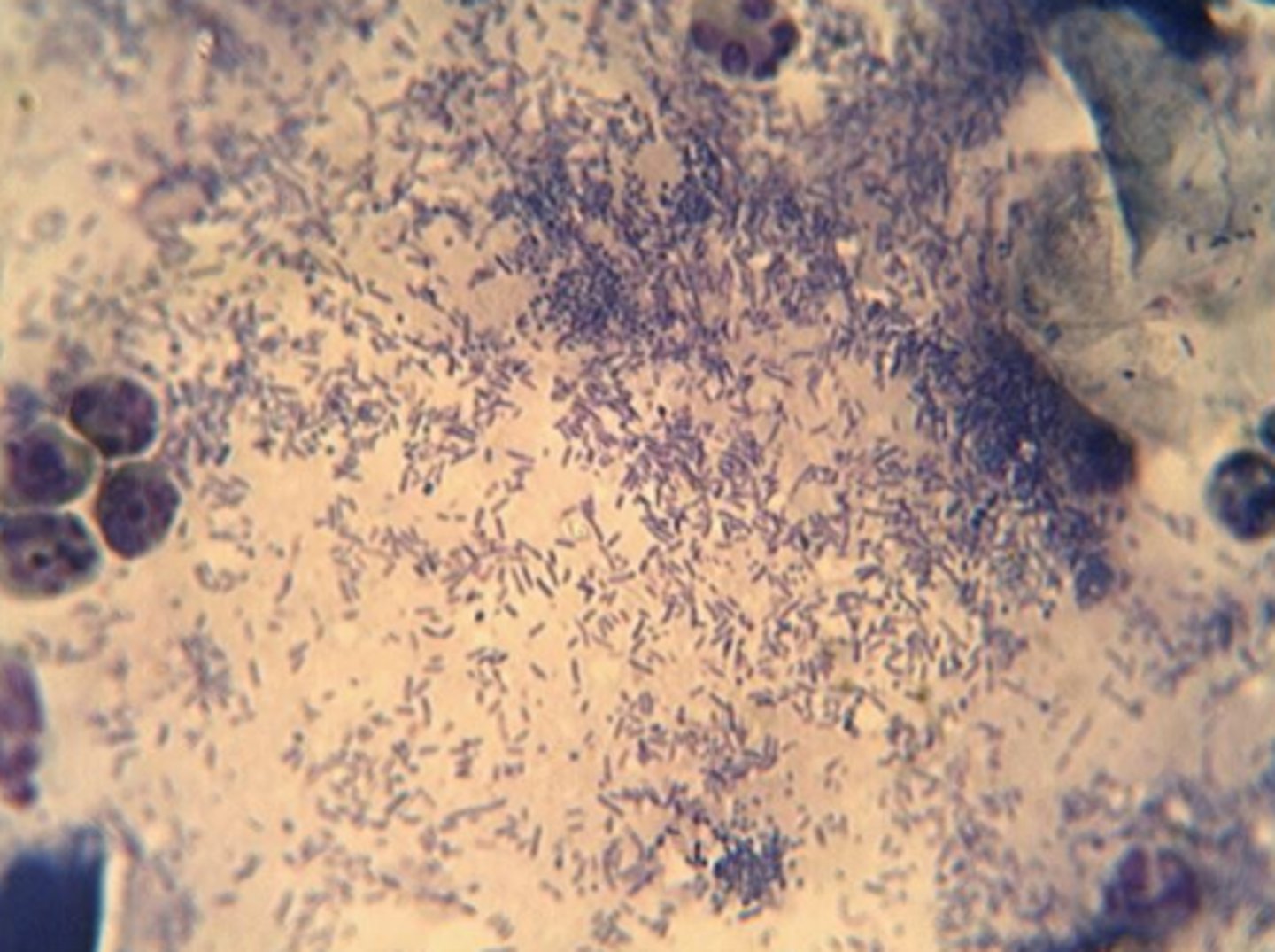
6 year old dog with severely painful and smelly unilateral otitis of 5 months duration - cytology - bacterial infection
Numerous rod bacteria and squames - gram negative --> e Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, E.coli
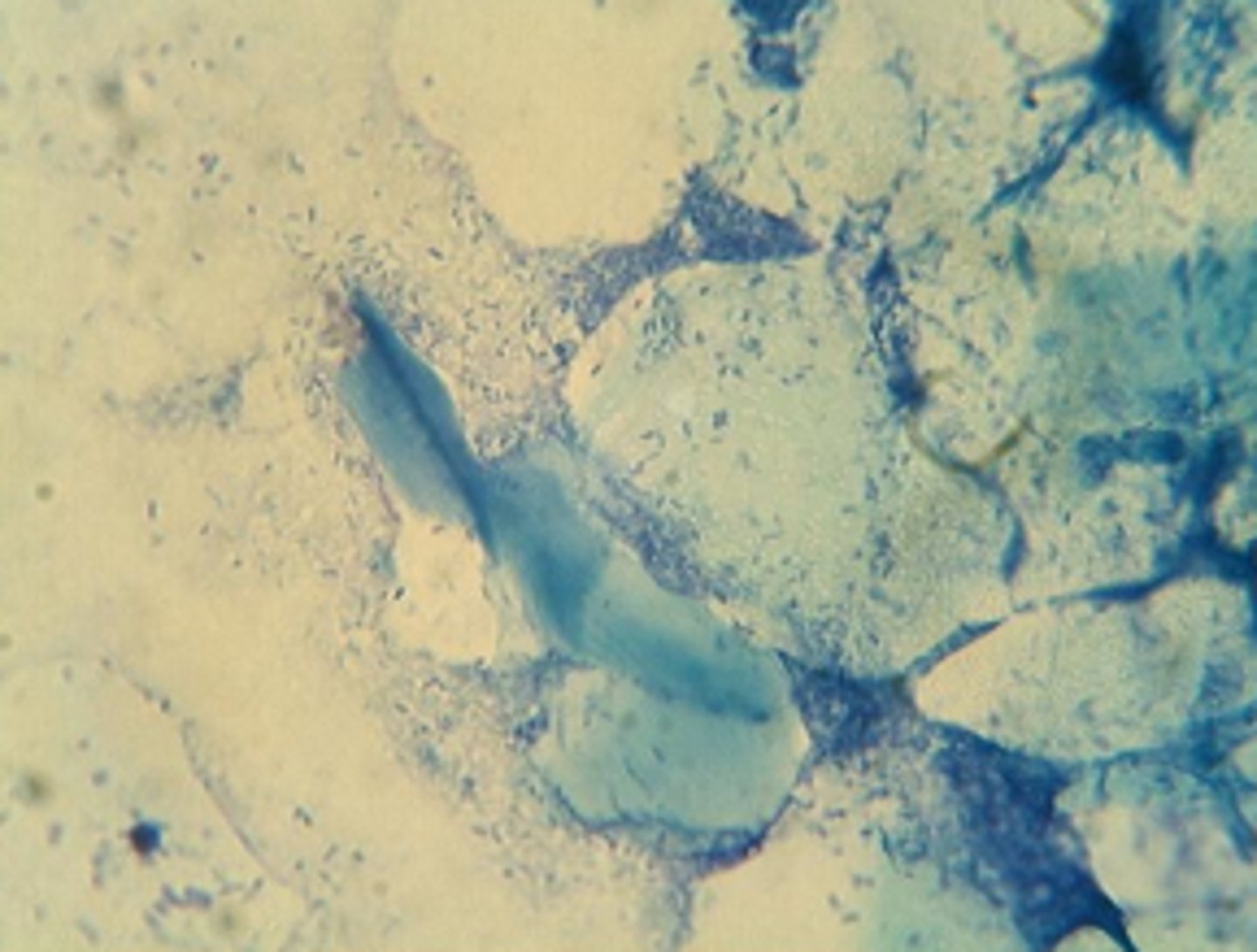

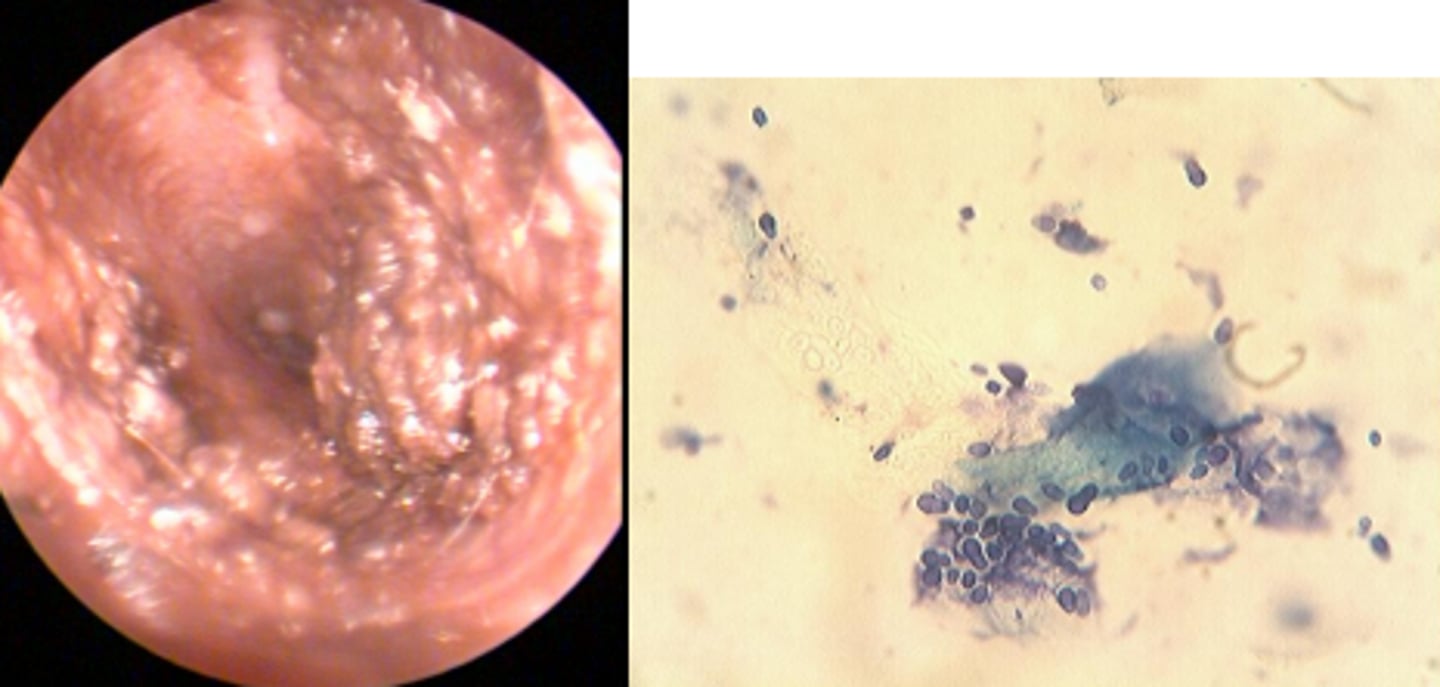
Ceruminous otitis
Head shaking, malodour, ceruminous discharge, erythema and oedema of the ear canal, ceruminous gland hyperplasia (cobblestone appearance), stenosis of the distal horizontal ear canal, numerous yeasts --> Malassezia pachydermatis and squame
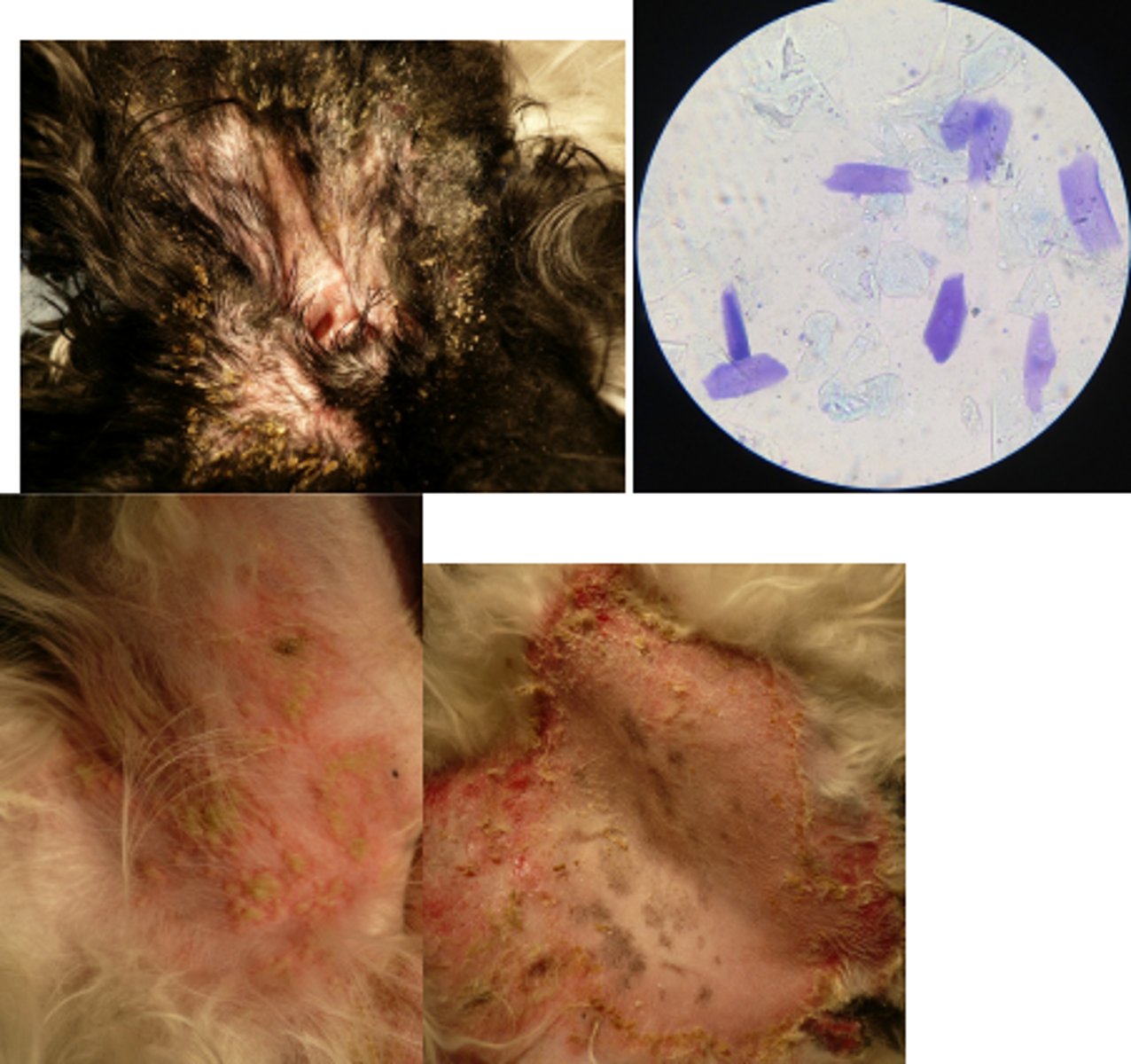
Pemphigus foliaceus
Scaling and crusting along the ear pinnal margins that is matting the coat, large pustules in the groin with erythematous margina, axilla is alopecic with a large peripheral epidermal collarette and erosions, hyperpigmented macules, squames on cytology, acanthocytes
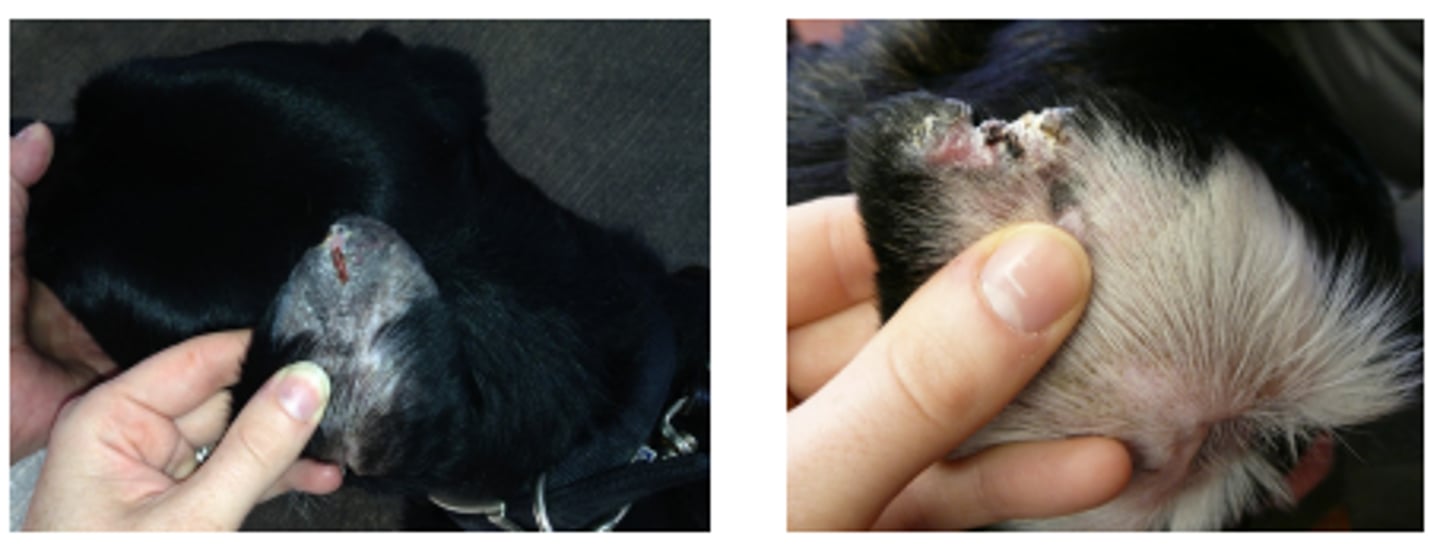
Vasculitis/ vasculopathy
Left pinna - alopecia, hyperpigmentation, linear ulceration covered with crust and eroded pinnal edge
Right pinna - extensive erosion, alopecia, crusting
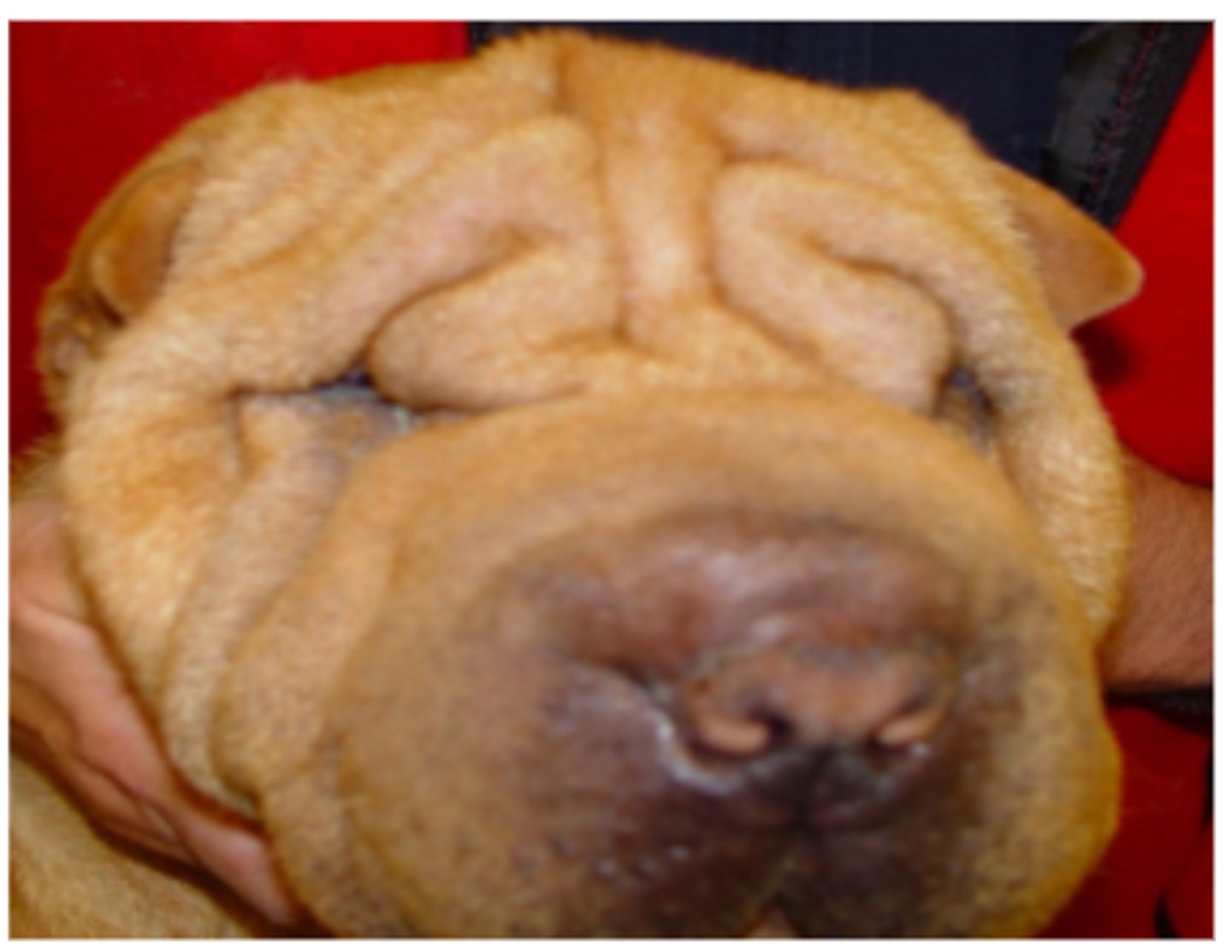
Macropalpebral fissure syndrome
Dogs with a prominent fold of skin over the nose
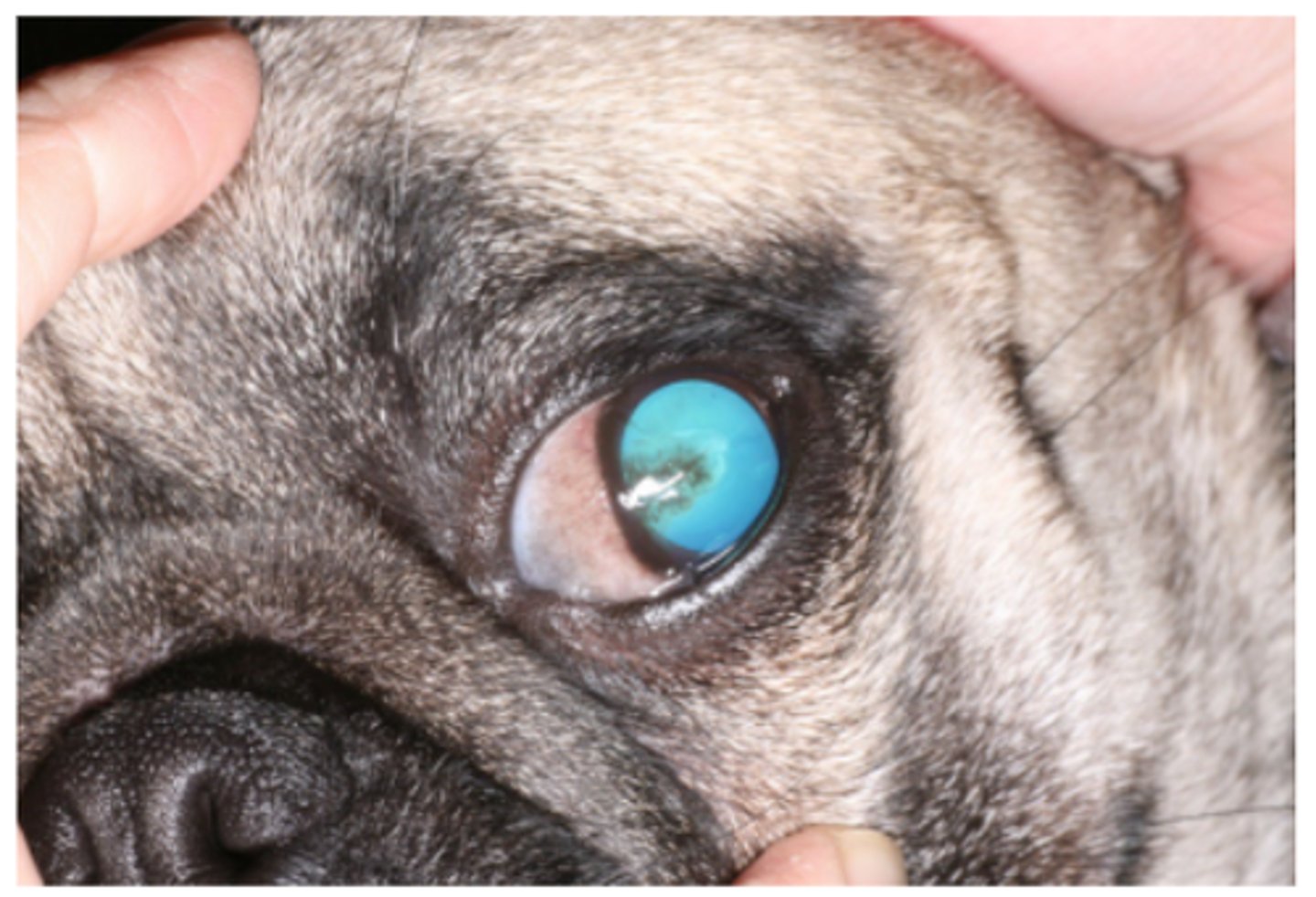
Corneal ulcer and entropion
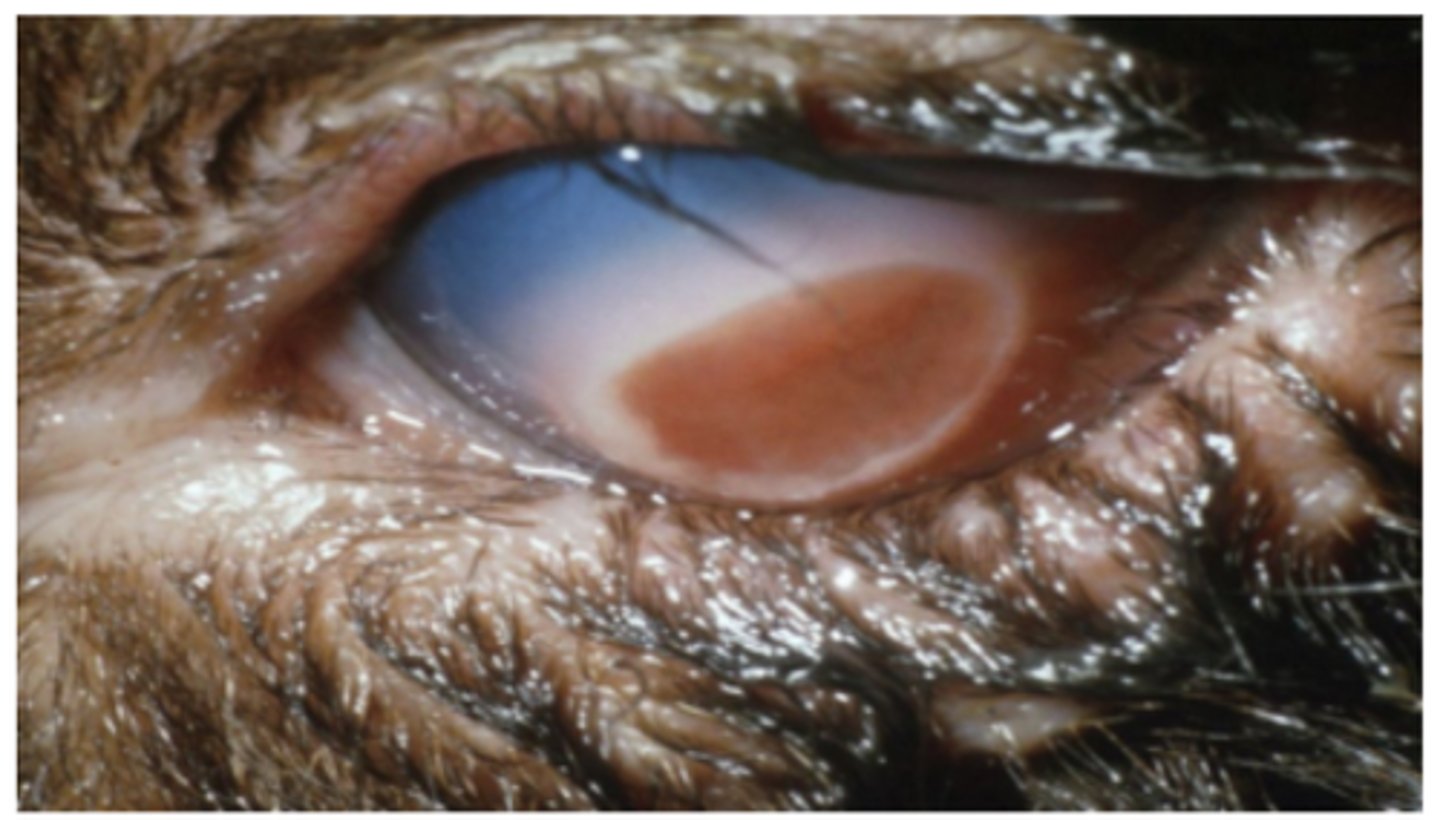
Entropion - Shar Pei
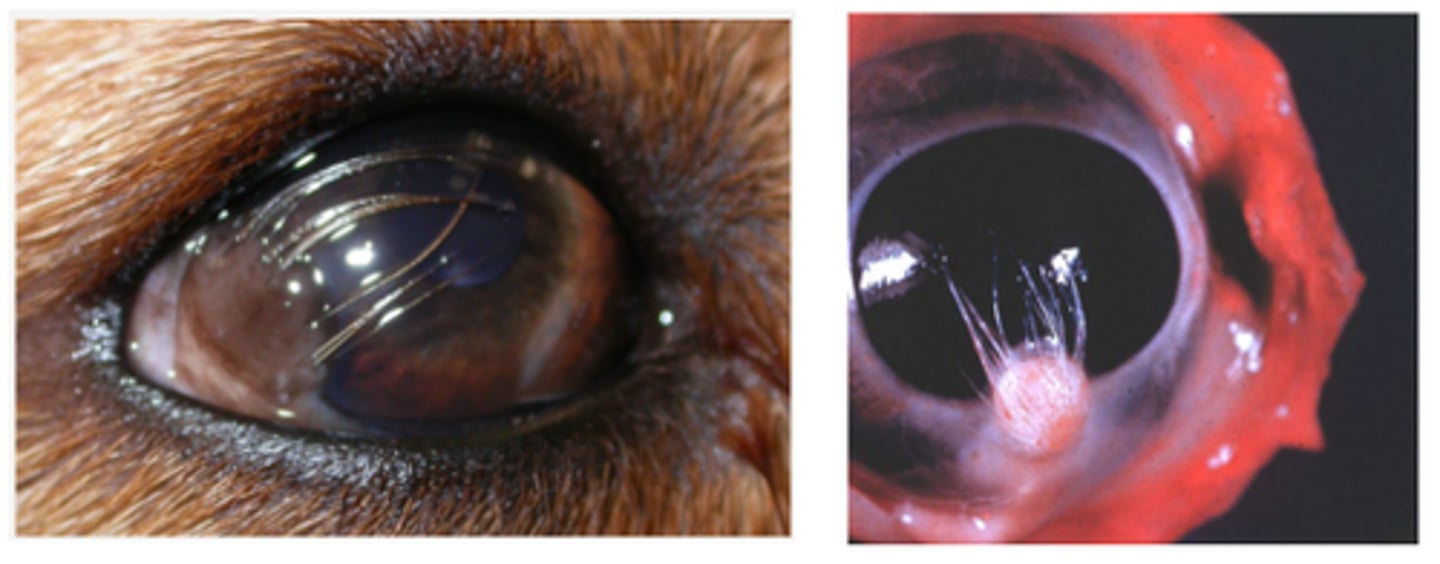
Nasal fold trichiasis (rubbing on the cornea)
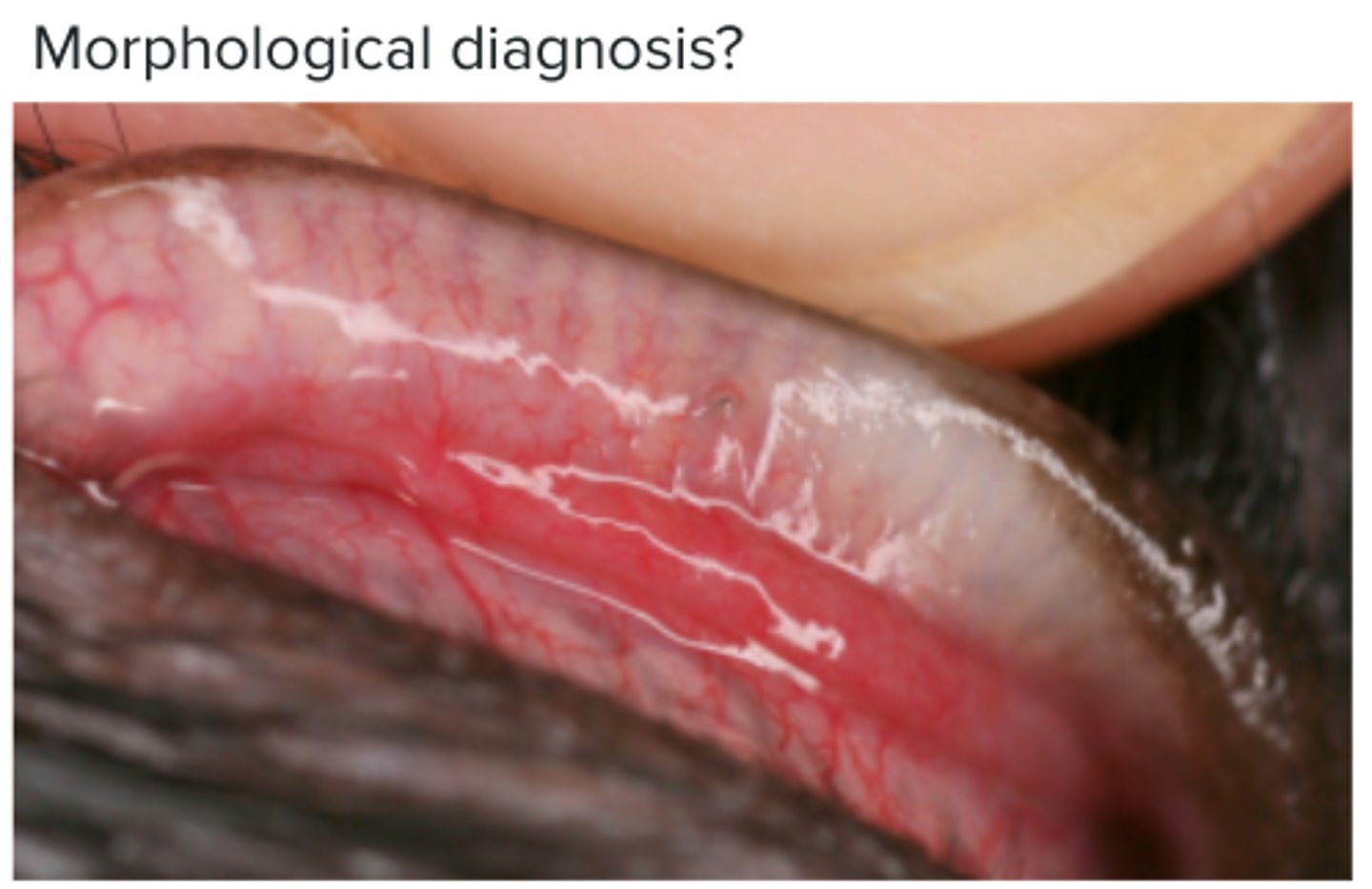
Bulbar conjunctiva of labrador - ectopic cilia
Blepharitis with thickened and calcified Meibomian glands
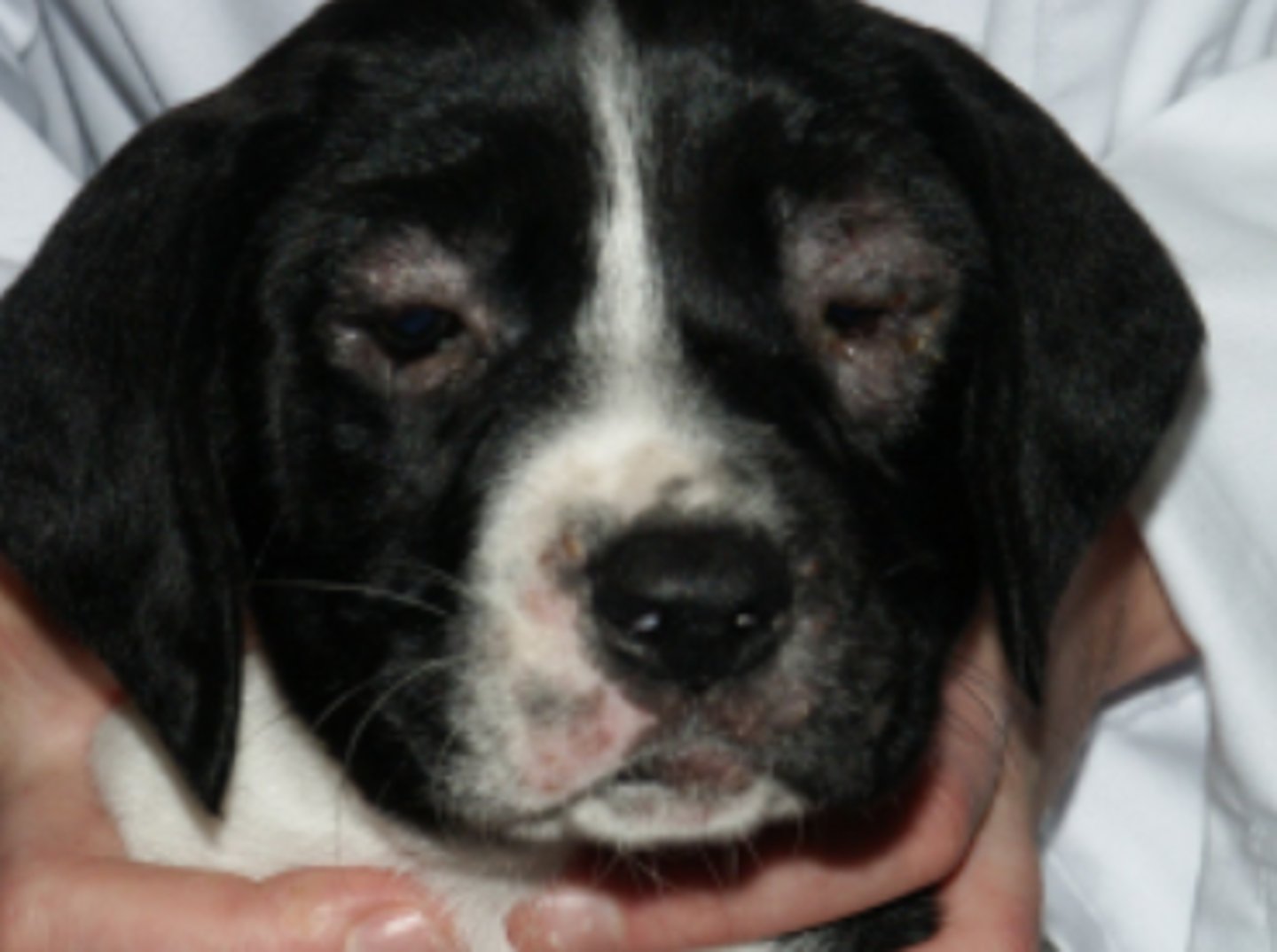
Puppy strangles - Blepharitis

Local blepharitis (inflammation of the meibomian gland)
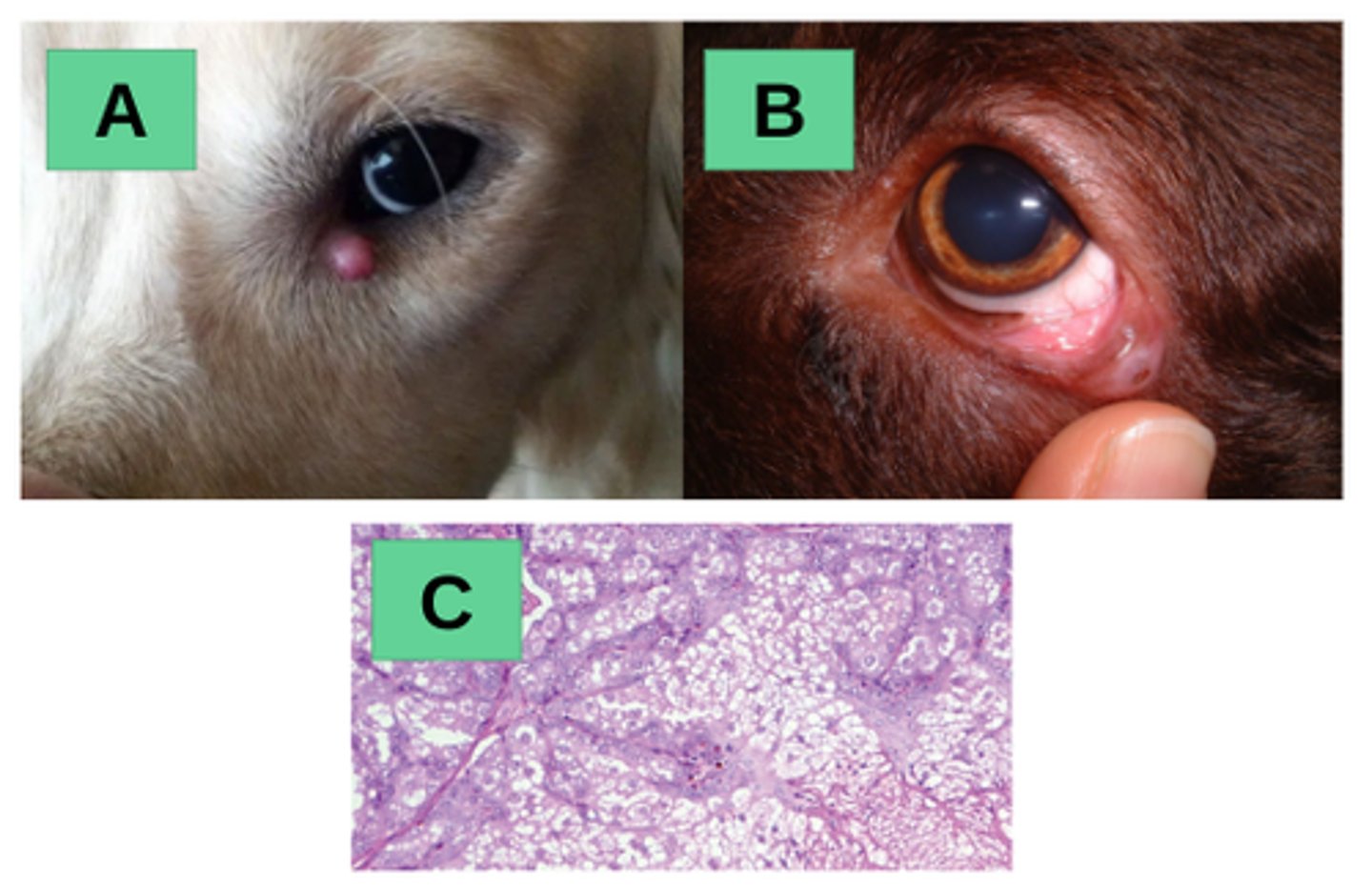
A - chalazion or meibomianitis
B - Chalazion on the left lower eyelid of a 9-year-old male dog. This consists in an inflammatory lesion of the meibomian gland, associated with secretion accumulation
C - Adenoma
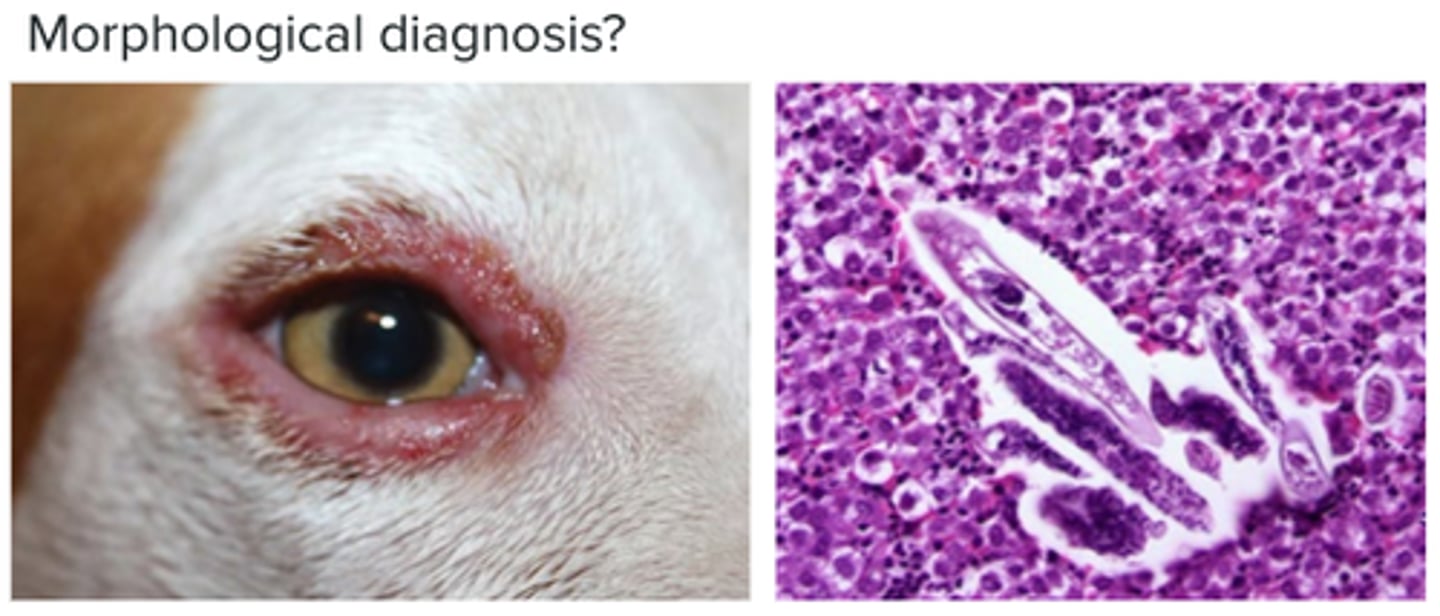
Parasitic blepharitis (Demodex species)
Circumferential alopecia, crusting, discharge and erythema
Protrusion of the nictitans gland (cherry eye)
Common in Bulldogs
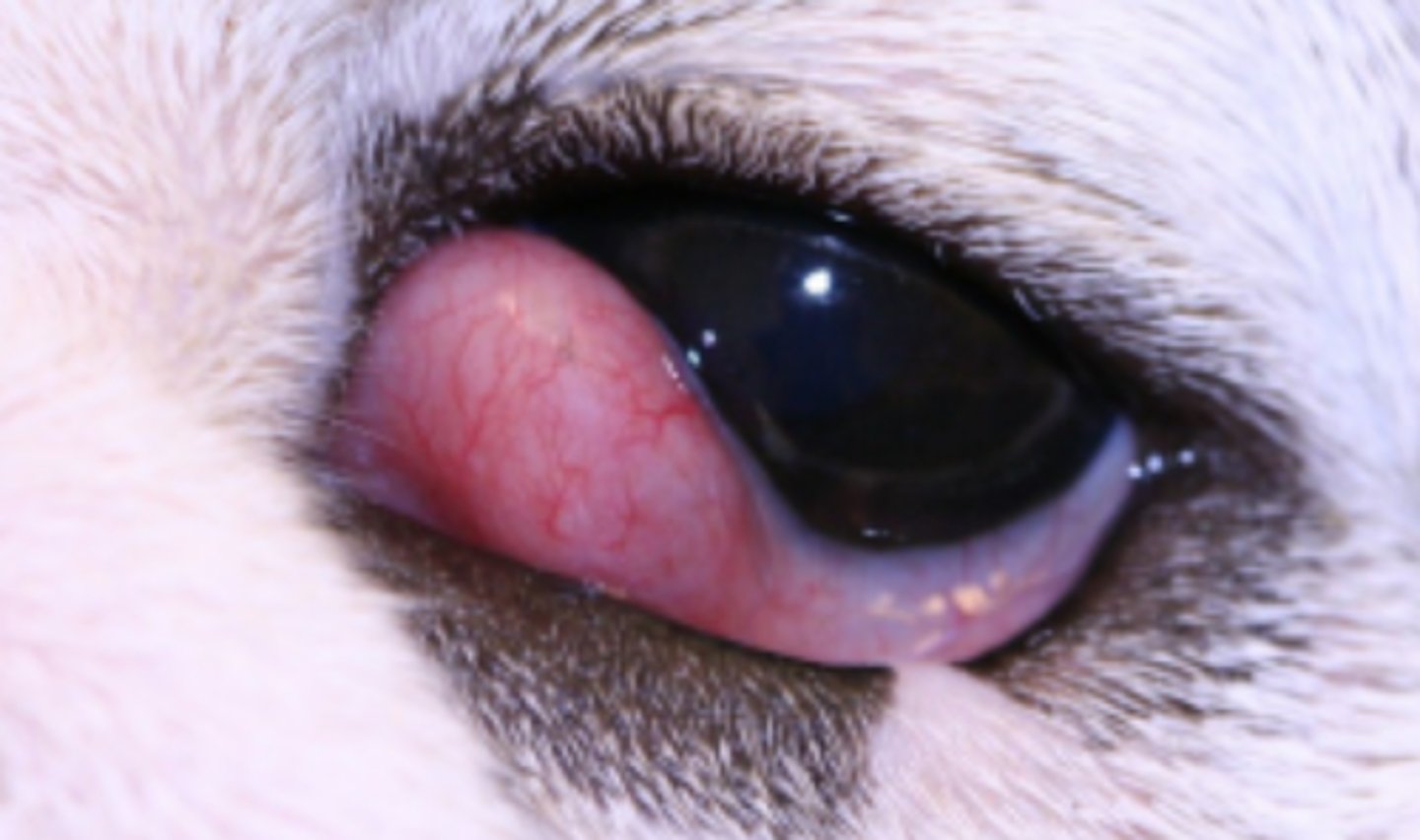
Conjunctivitis
Hyperaemic and oedematous conjunctiva, vasodilation, increased blood flow, lymphoid follicles, ulceration, fibrosis
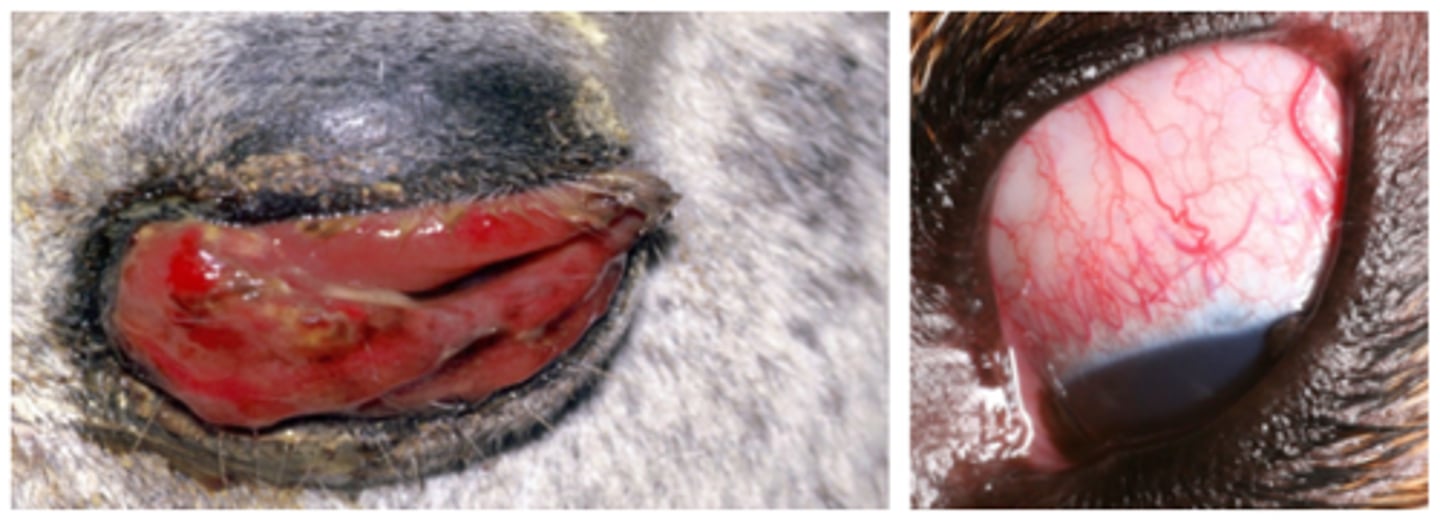
Habronemia conjunctivitis
Conjunctival hyperemia and thick mucopurulent ocular discharge
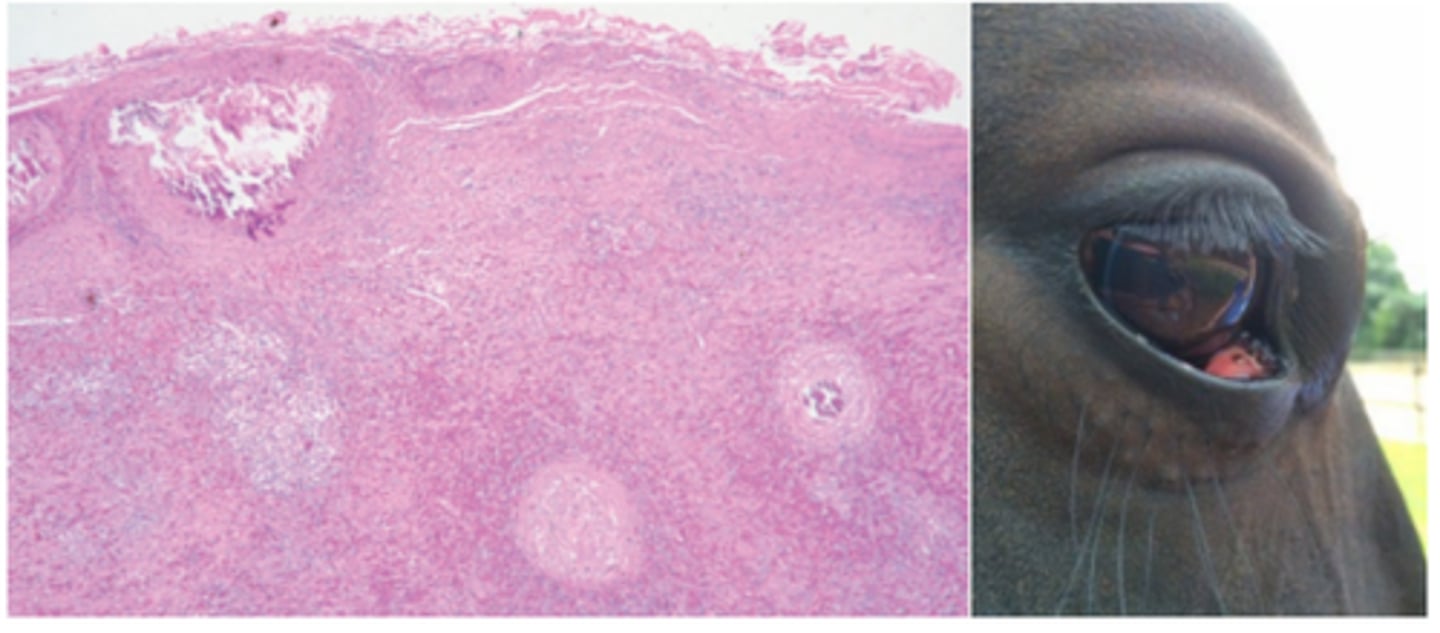
Chlamydophila felis - unilateral conjunctivitis (infection)
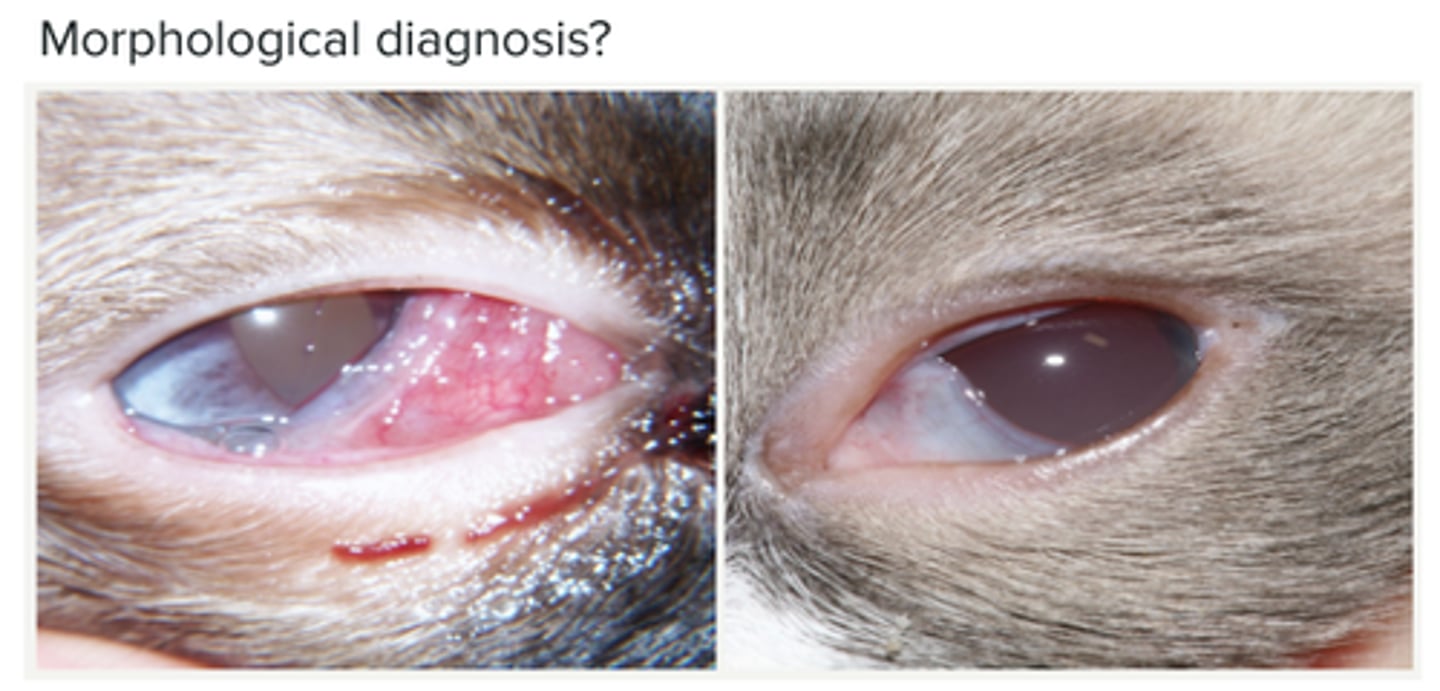
Conjunctivitis in cats associated with feline herpesvirus 1
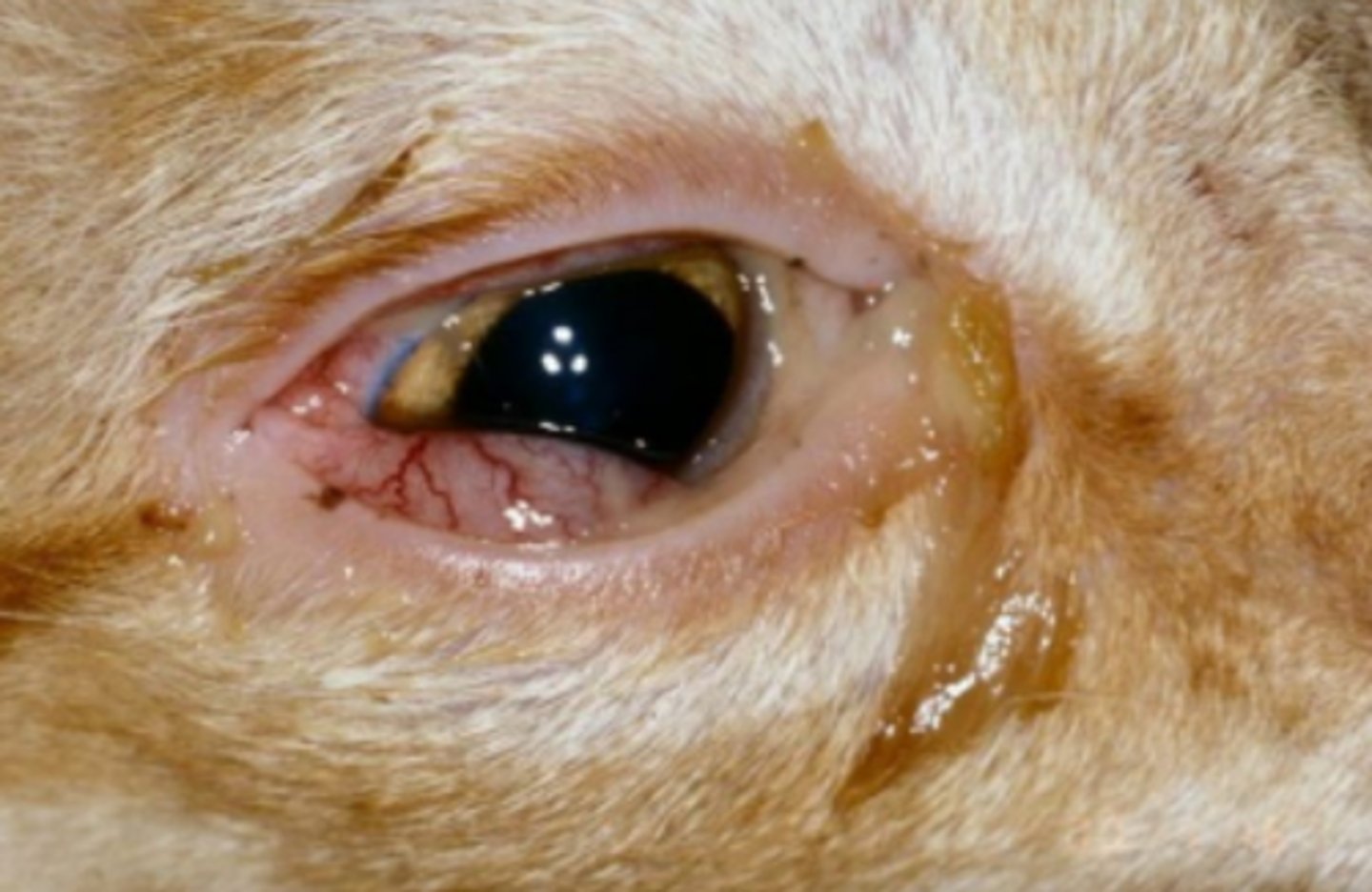
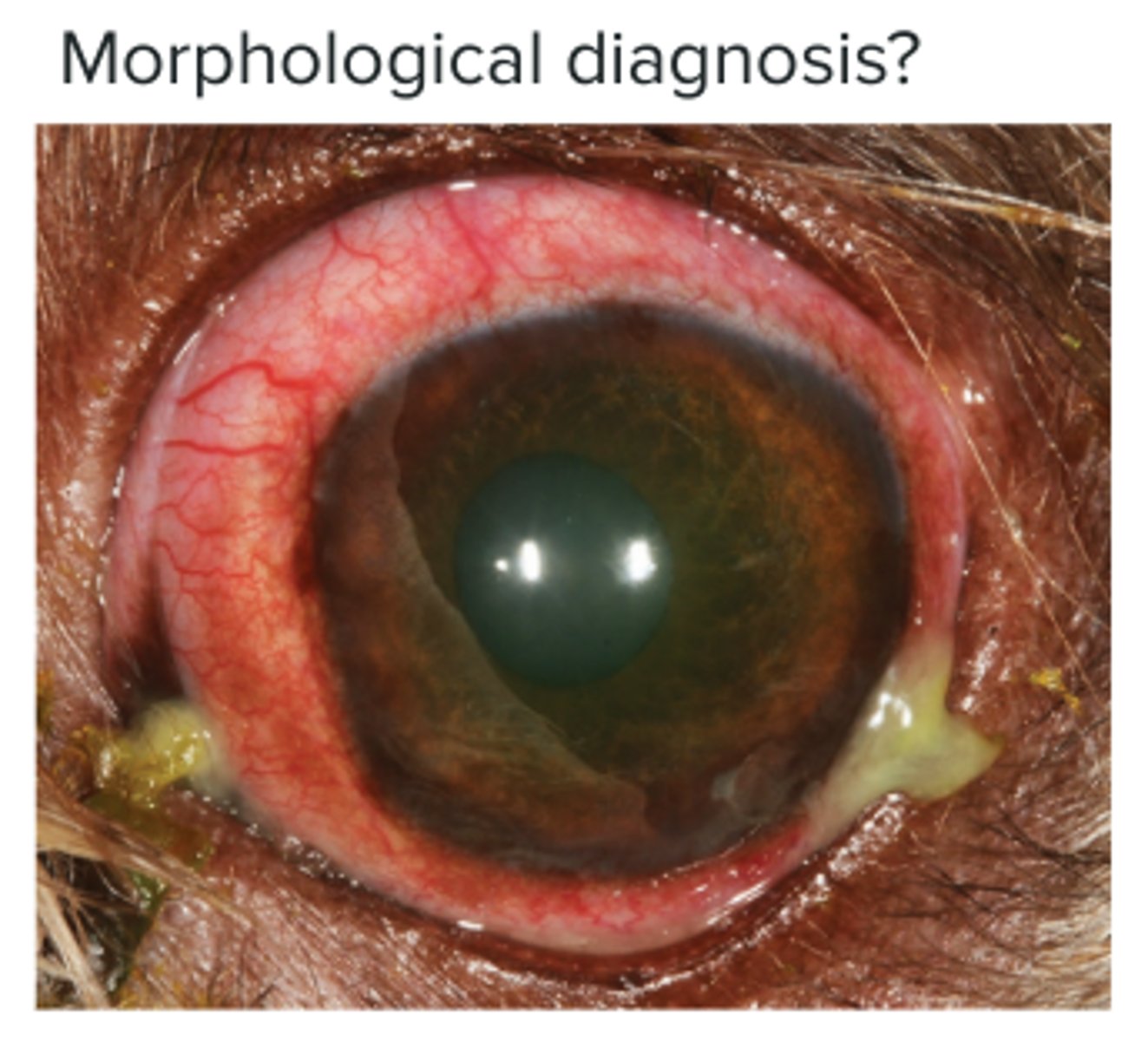
Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis (Pink eye) - Moraxella bovis
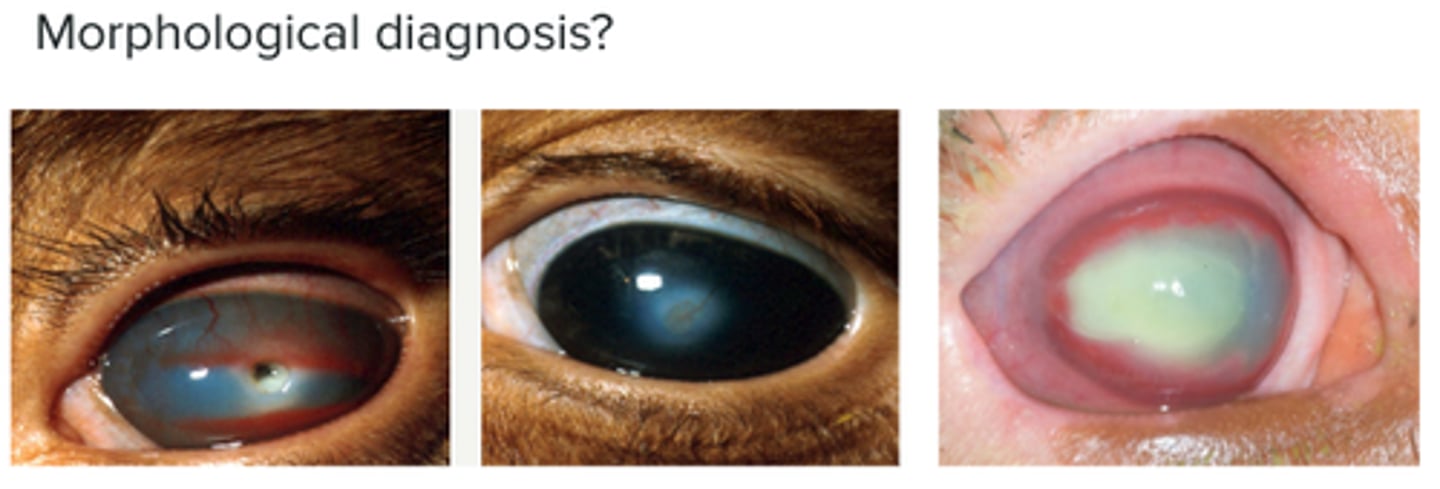
Immune-Mediated Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca (KCS)
Decreased tear film quantity and quality > dry eye
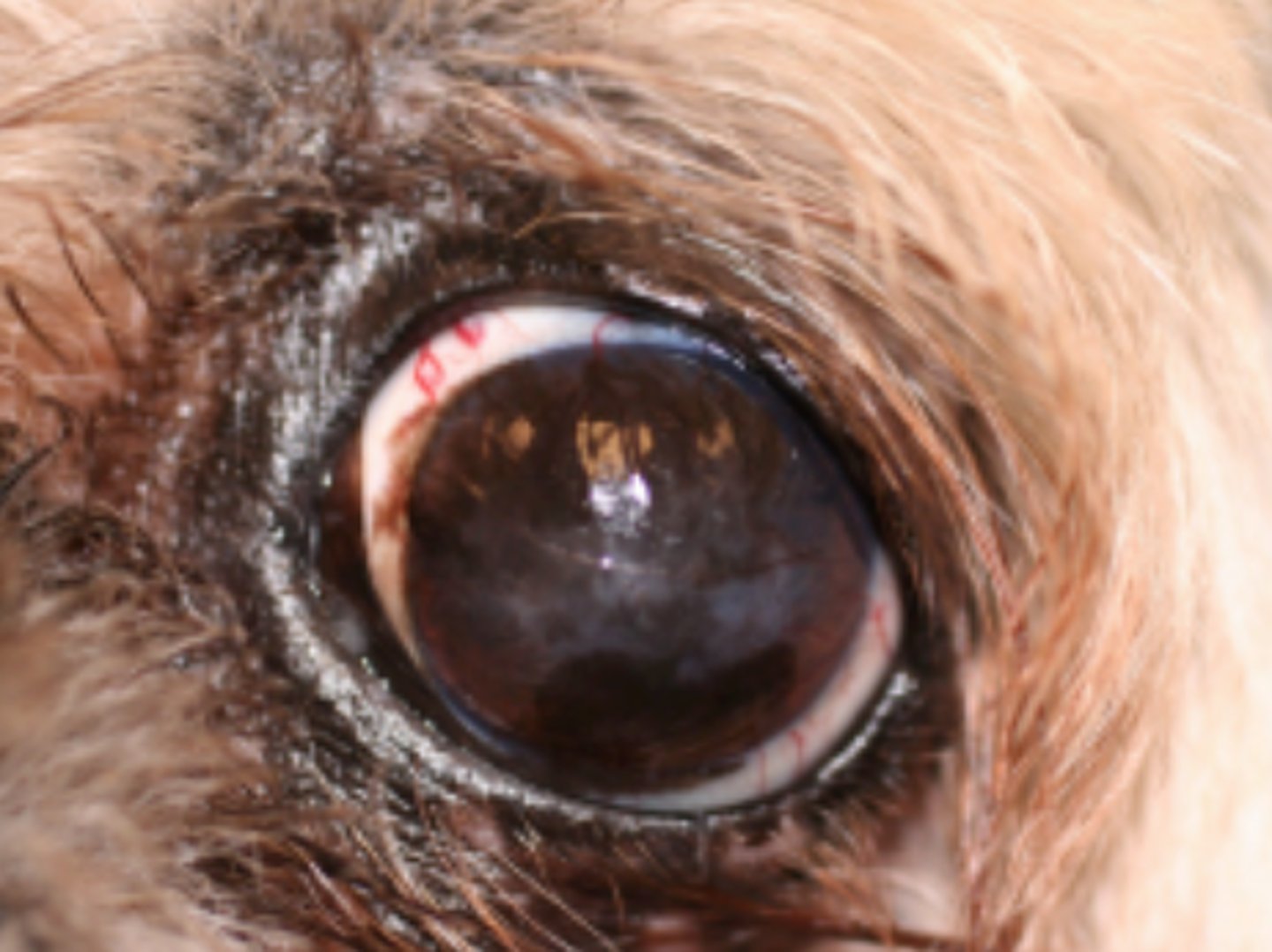
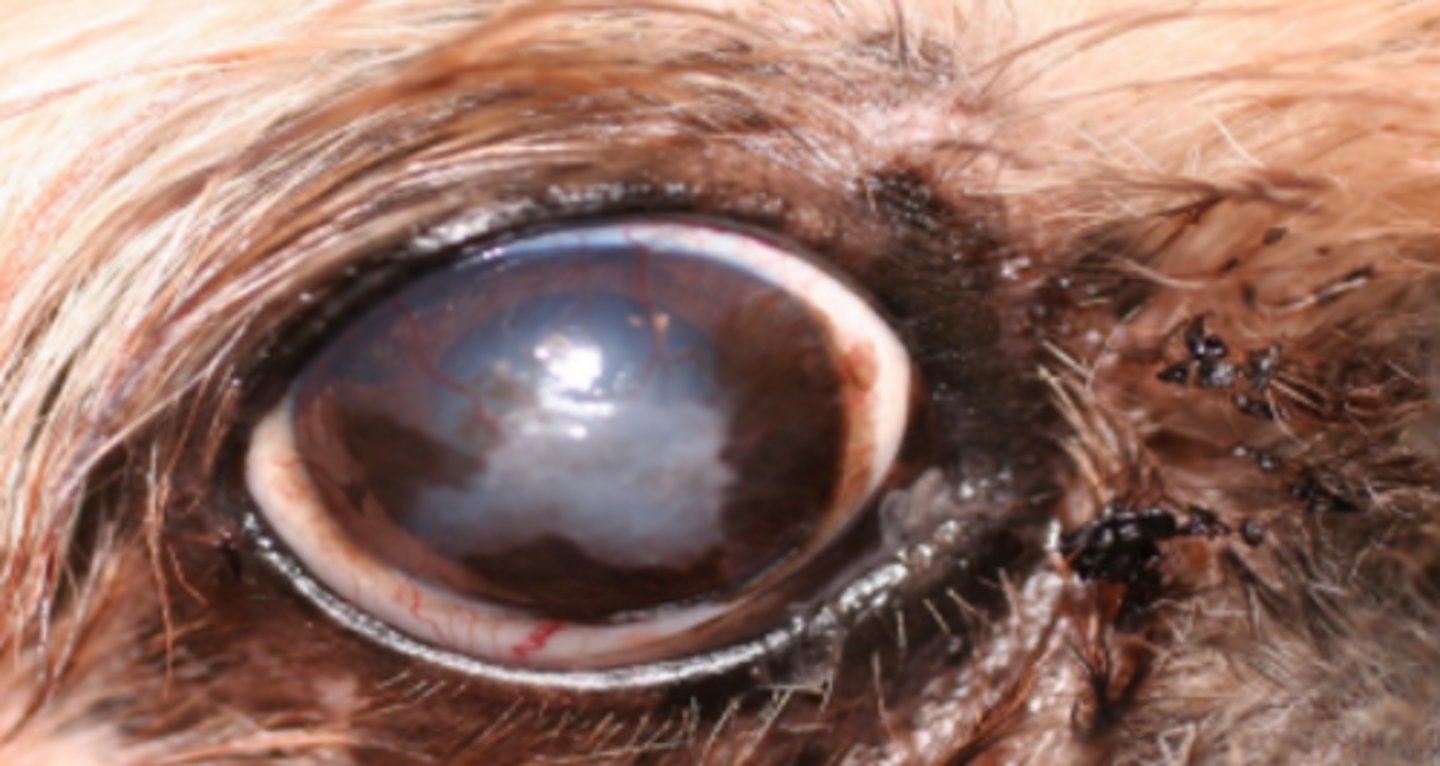
Keratoconjunctivitis
Corneal fibrosis, pigmentation and neovascularisation
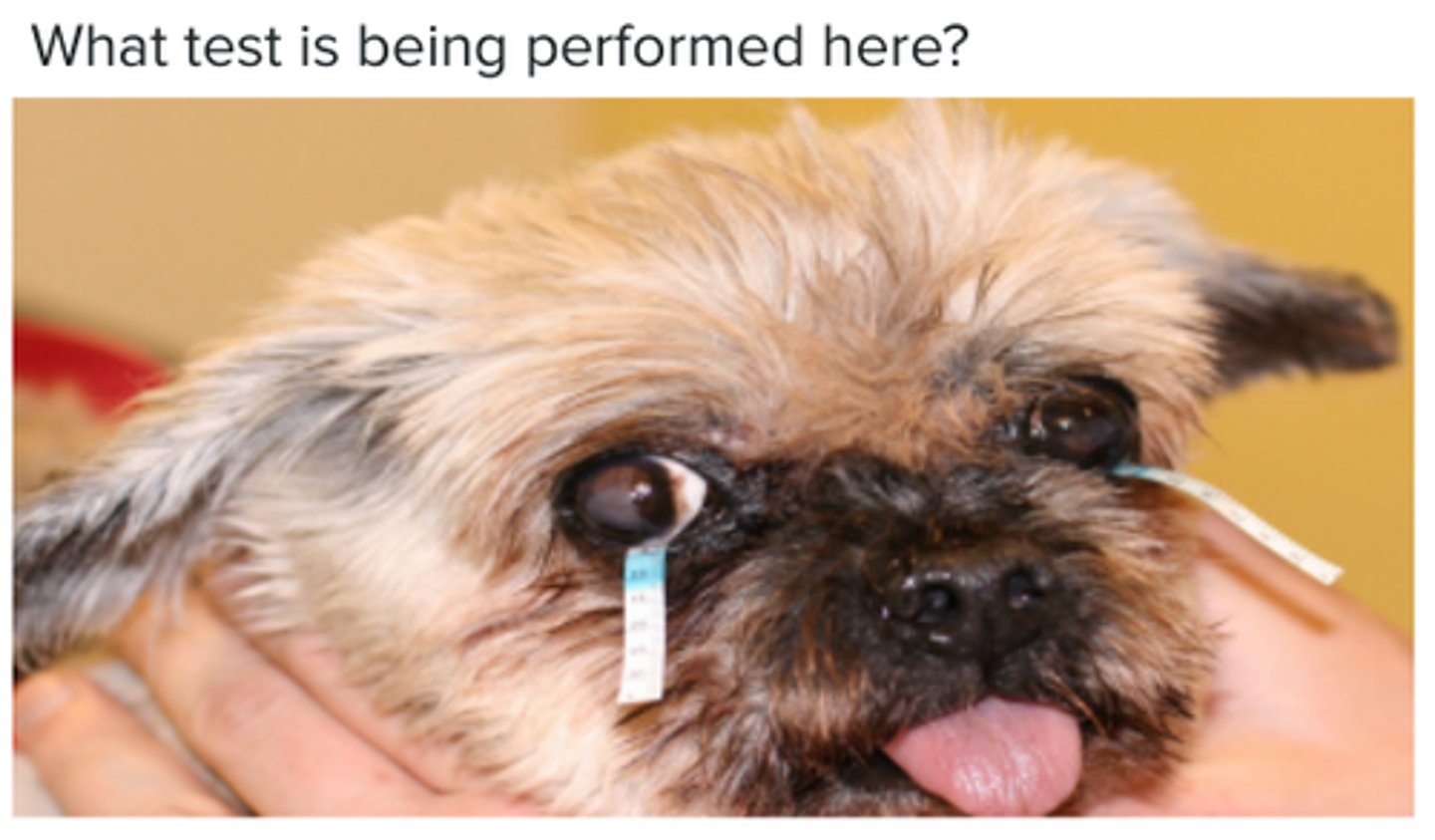
Schirmer Tear Test (STT)

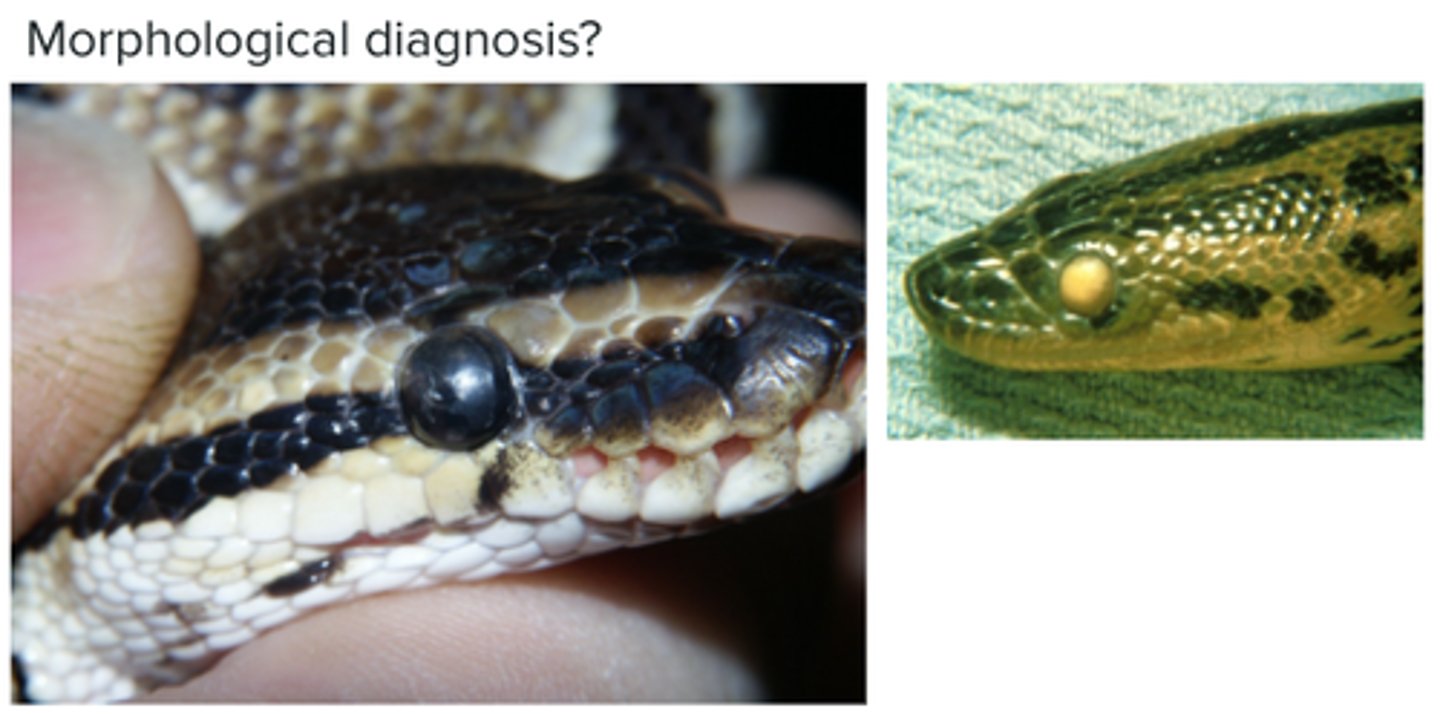
Retained spectacles > leads to abscess formation
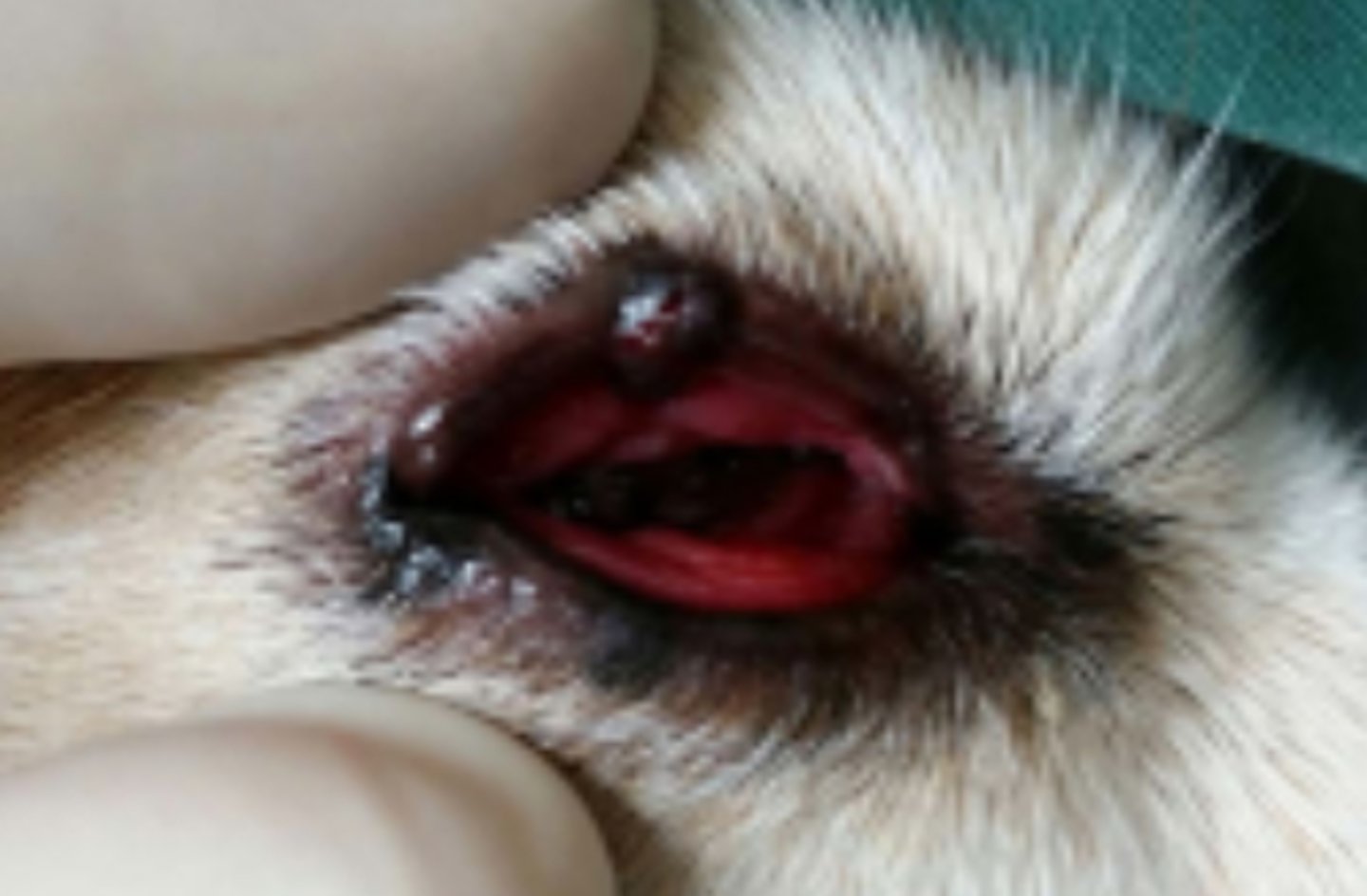
Meibomian adenoma (neoplasm of the eyelid)
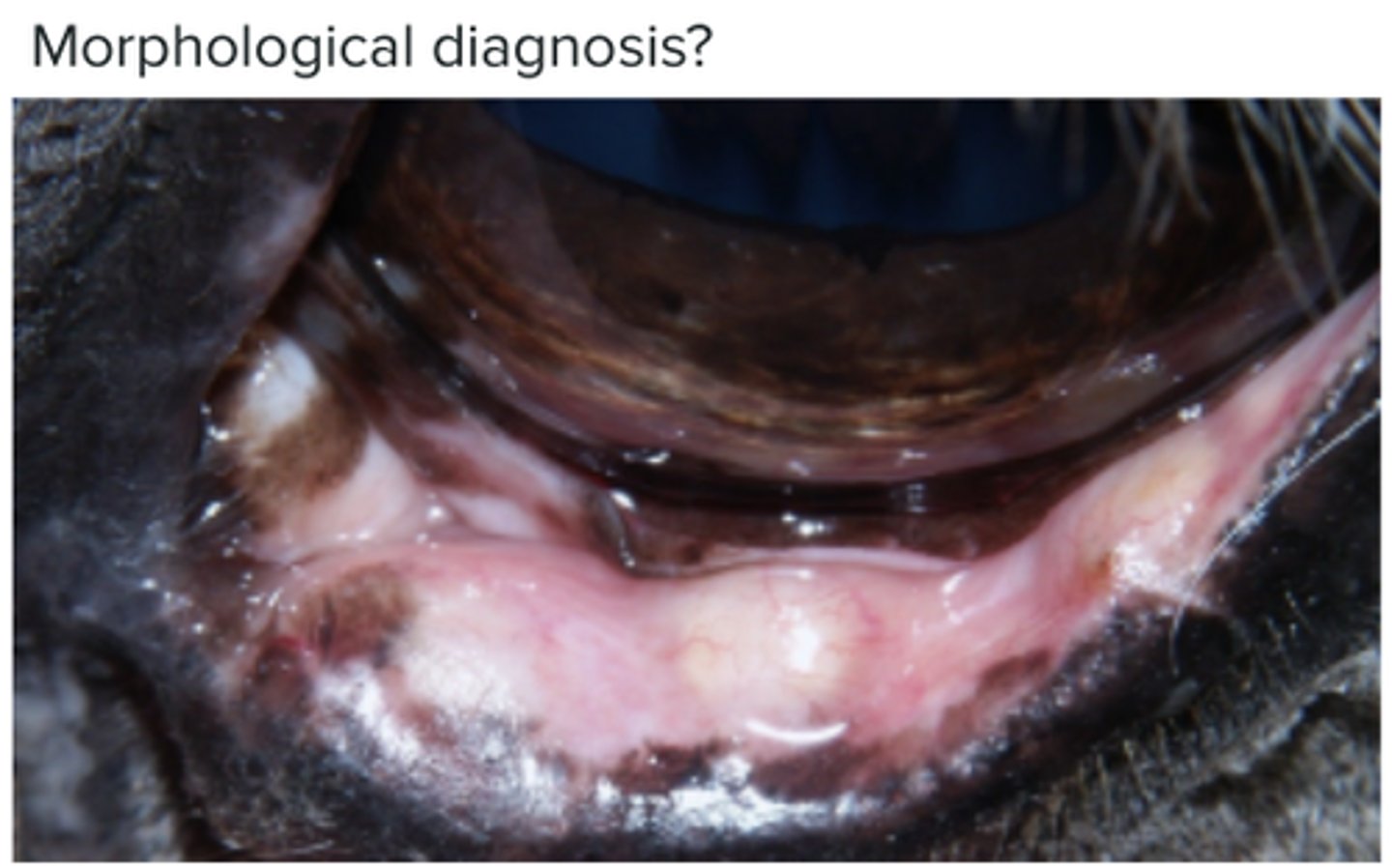
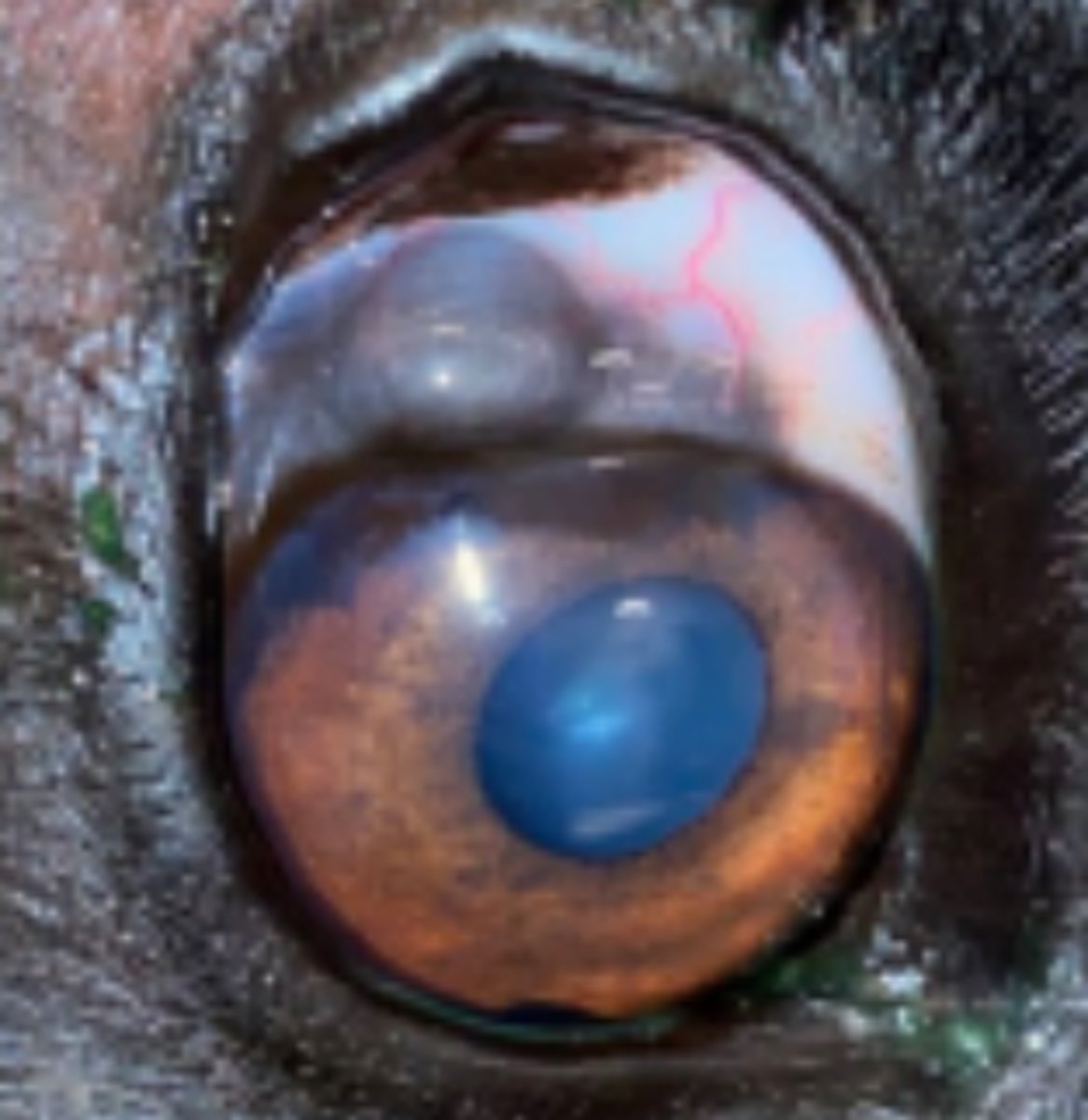
Limbal melanocytoma (neoplasm of the eyelid)
Squamous cell carcinoma of the eyelid
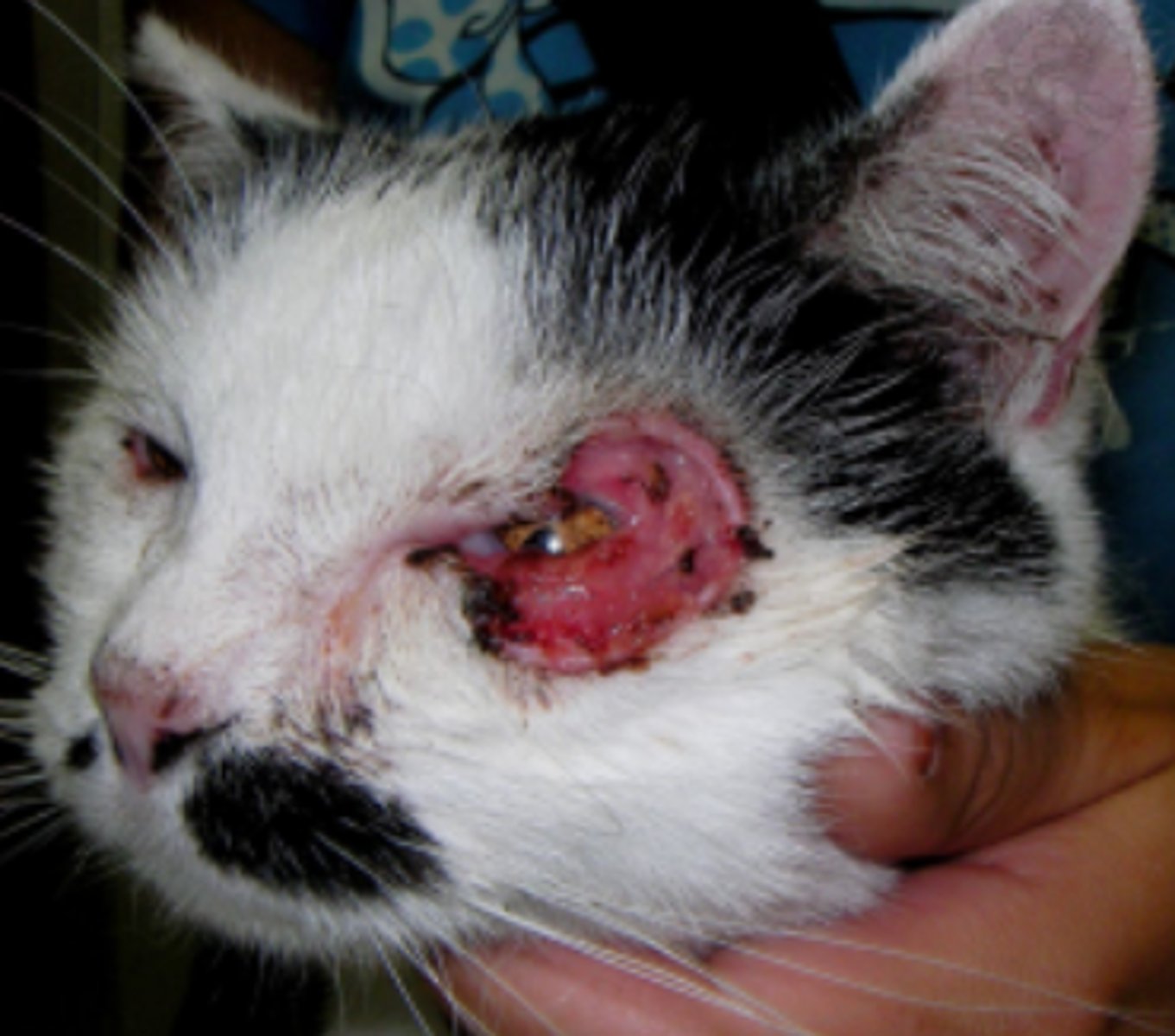
Mastocytoma of the eyelid
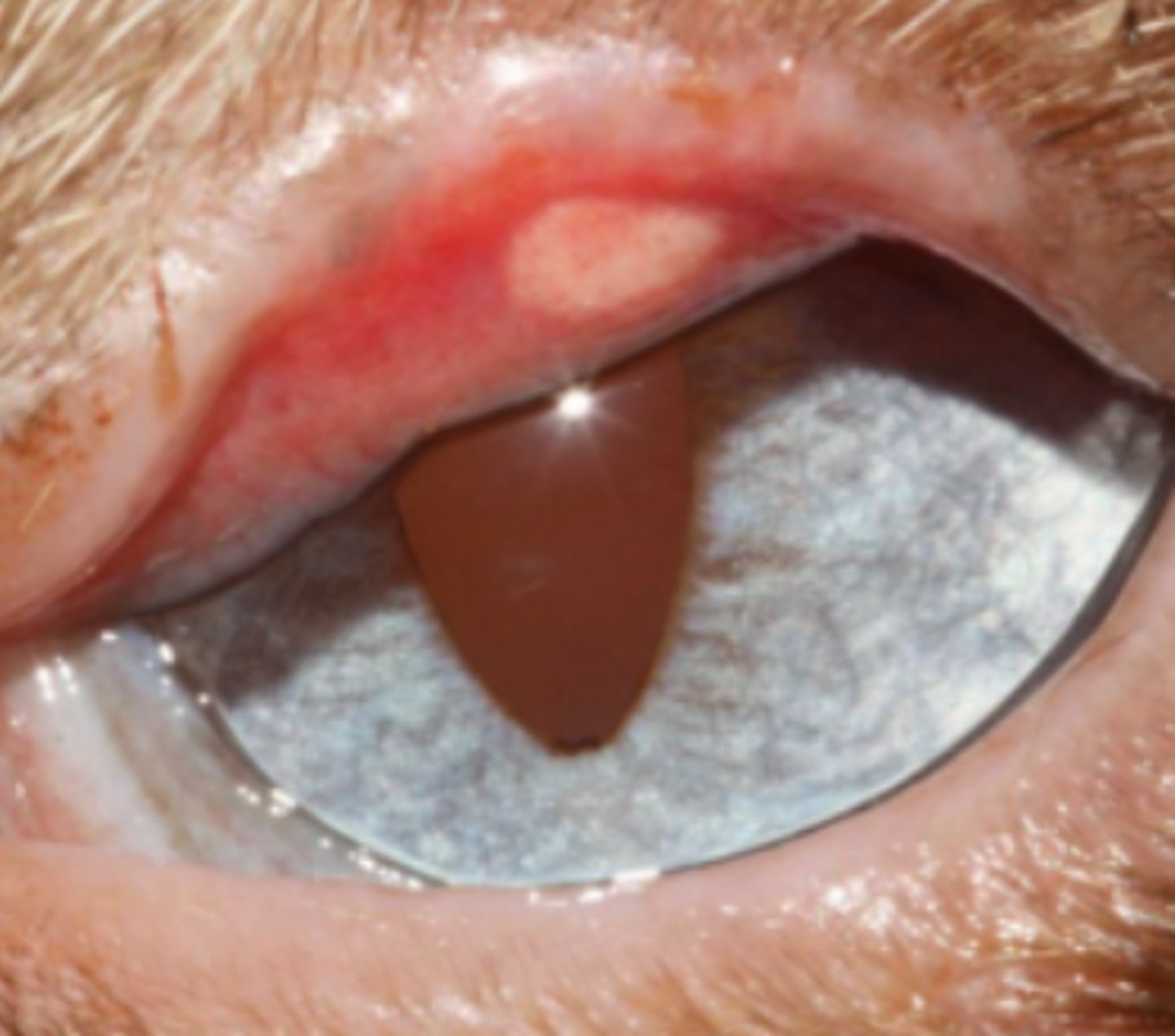
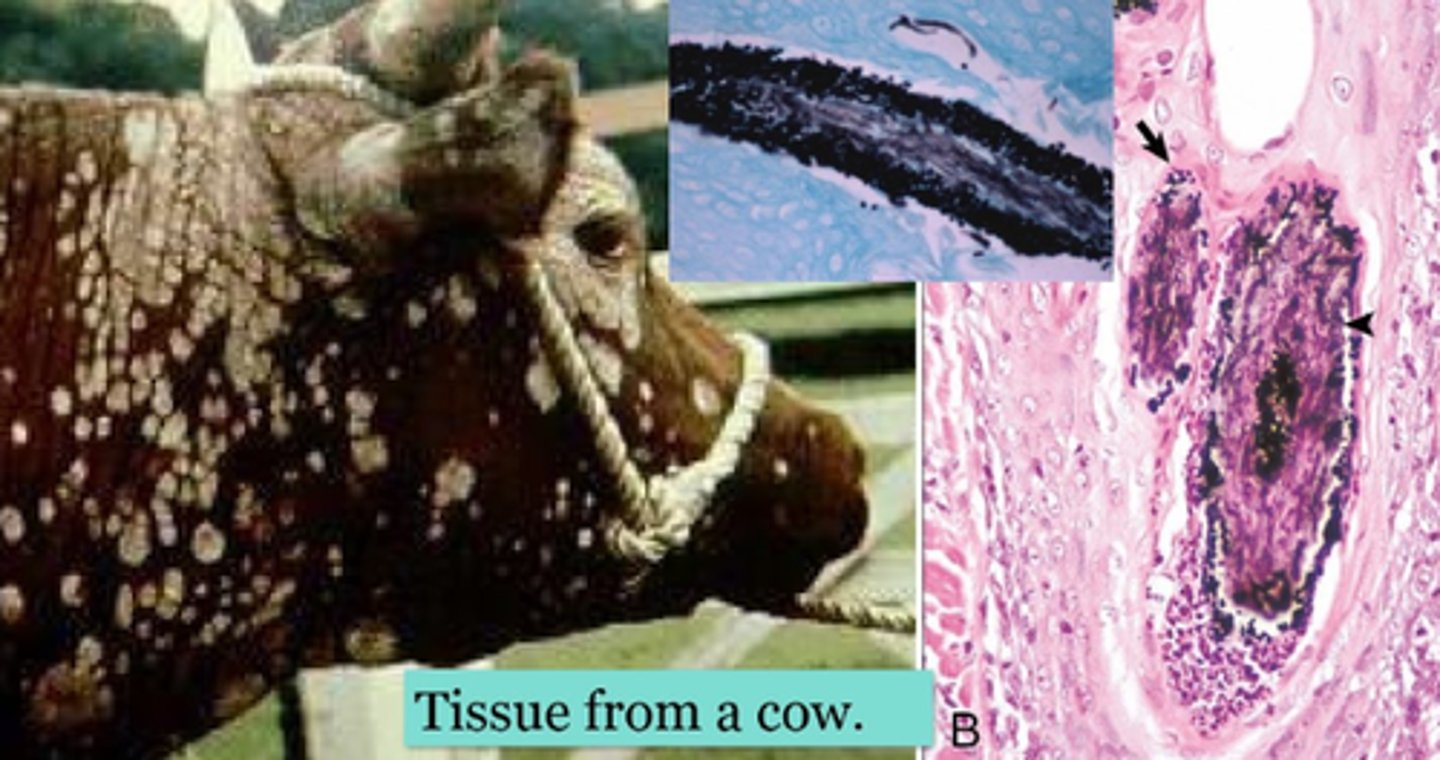
Squamous cell carcinoma, bovine
Polygonal neoplastic cells with scant to moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm, whorls of lamellar keratin (keratin pearls) within the centers of trabeculae and islands.
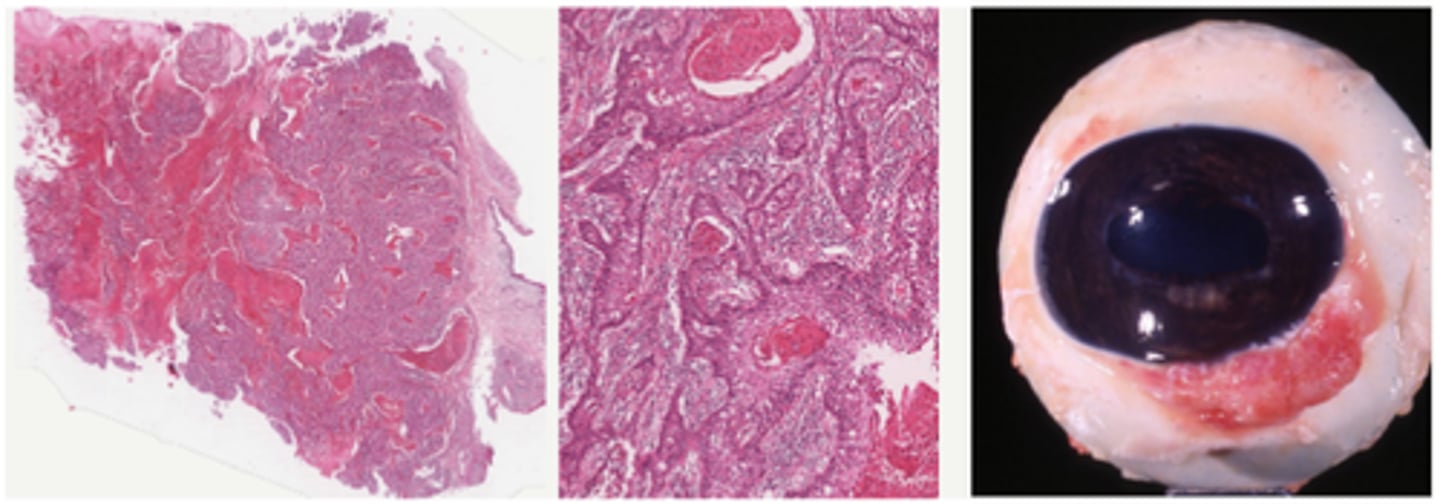
Ocular dermoid congenital condition