Lab 8 The Lymphatic System A&P2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
recycles lymph and immunity
What are the primary lymphoid organs and their function?
red bone marrow and thymus; to make/mature lymphocytes that defend the body
What are secondary lymphoid organs and their function?
lymph nodes, spleen, MALT, tonsils (three parts), and nodules; to protect/defend the body
thymus gland (function and location)
located in the mediastinal cavity, site of T-cell maturation, gets smaller with age, has 2 lobes
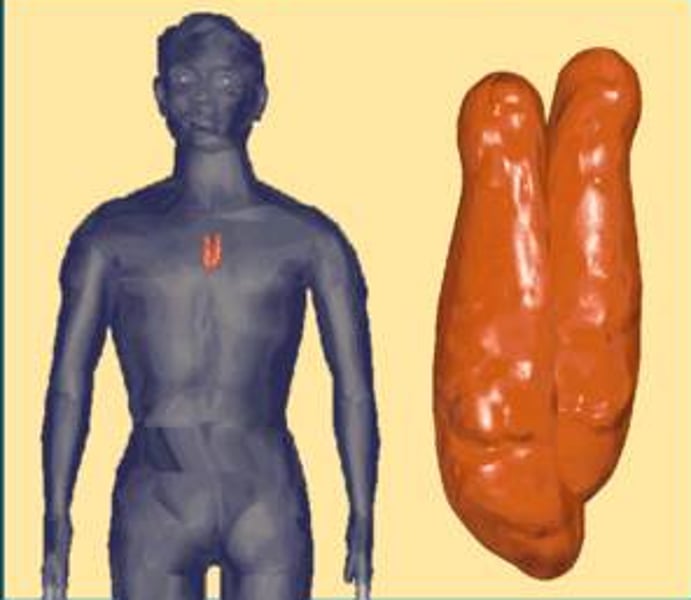
Where are the tonsils located and what are the three tonsils?
Located in the pharynx
the pharyngeal tonsil in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx
the palatine tonsils in the posterior oral cavity wall
the lingual tonsils at the root of the tongue
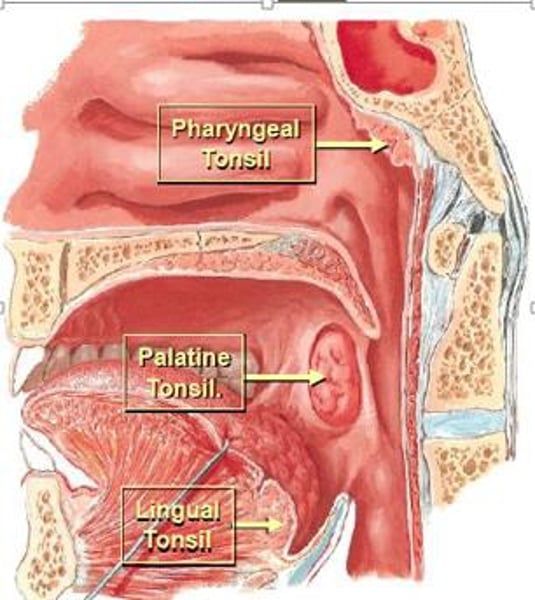
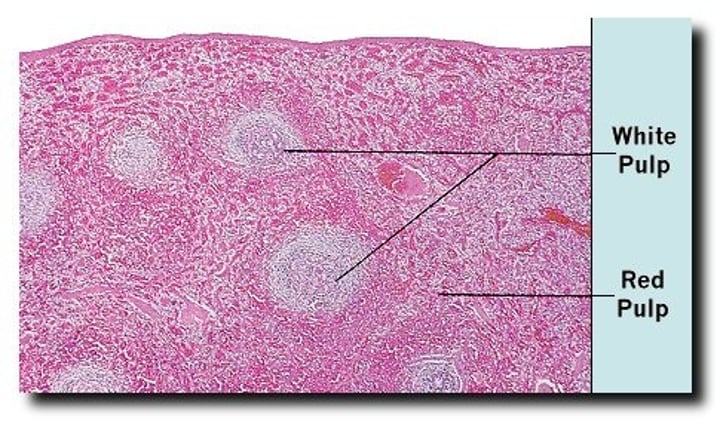
spleen
located in the abdominal cavity
blood reservoir and filters blood
has red and white pulp
red pulp
RBCs, looks light and is not nucleated
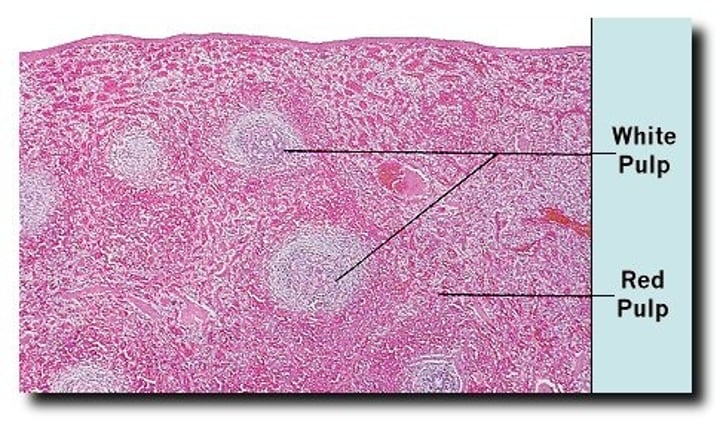
white pulp
lymphocytes, looks nucleated and purple
afferent lymphatic vessels
carry lymph to the lymph nodes, where it is filtered
efferent lymphatic vessels
transport filtered lymph away from the lymph node/spleen
MALT
Peyer's patches (an example) located within the walls of the small intestine, between the inner lining (mucosa) and muscle layers
Hassall's corpuscles
defining feature of the thymus, located in the medulla
looks like a ball/asteroid on the thymus cs
What are the hallmarks of inflammation?
redness, swelling, heat, pain, sometimes loss of function
The lymphatic vessel network, from smallest to largest, consists of:
Lymph capillaries→ lymph vessels→ lymph trunks → lymph ducts
inflammation response
damaged cells release chemicals into the interstitial fluid and produce cell debris
macrophages remove cell debris and/or pathogens by phagocytosis, also release chemicals signals that attract more phagocytic cells into the area
Mast cells release histamine
Histamine causes capillaries to vasodilate and be more permeable
Blood flow increases, bringing more WBCs and antibodies to fight infection and remove cell debris
localized tissue changes produce redness, swelling, heat, and pain
Pus is usually formed of dead WBCs, dead bacteria, cell debris, etc
cortex of lymph node
outer region of lymph node
medulla of lymph node
core of the lymph node
capsule of lymph node
connective tissue cover of lymph node
trabeculae of lymph node
internal extensions of the capsule that create divisions of the lymph node
What do valves do?
prevent back flow of blood
right lymphatic duct drains
right side of head, thorax, and right arm
thoracic duct drains and is the ___ duct
largest duct
lymph from the left side of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, left arm, and lower extremities
axillary lymph nodes
concentrated in armpit, receive lymph from upper limb (arms) and breast
cervical lymph nodes
drain and cleanse lymph coming from the head and neck areas
Inguial Lymph Nodes
purify lymph from legs
bronchomediastinal trunks
drain lymph from the thoracic cavity
cysterna chyli
an expanded sac; receives lymph from lumbar trunks and intestinal trunk; delivers lymph to thoracic duct