Microbial ecology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Essential nutrients
those that must be supplied by the environment
that includes macronutrients and micronutrients
Macronutrients needed for microbial growth
needed in large concentrations
Carbon
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Sulfer
we need a series of ions at high concentration, they function as coenzymes and used to generate an equilibrium within the cell
Mg2+
Fe2+
K+
Ca2+
Micronutrients needed for microbial growth
Micronutrients needed at smaller concentrations but they are still essential
Cobalt
Cu+
Mn2+
Mo2+
Ni2+
Zn2+
components of cofactors or enzymes
Where does the energy come from to build cells?
chemical reactions including anabolic and catabolic reactions
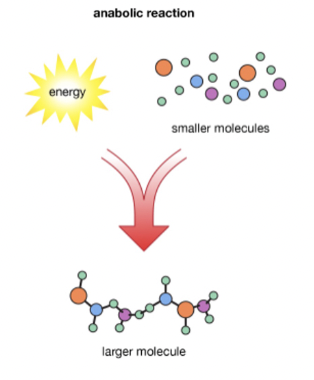
Anabolism
build molecules
endergonic: requires energy
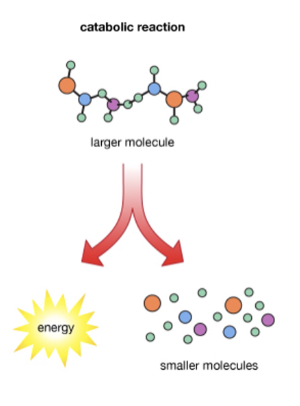
Catabolism
Breakdown of molecules
exergonic ; releases energy
Primary Producers
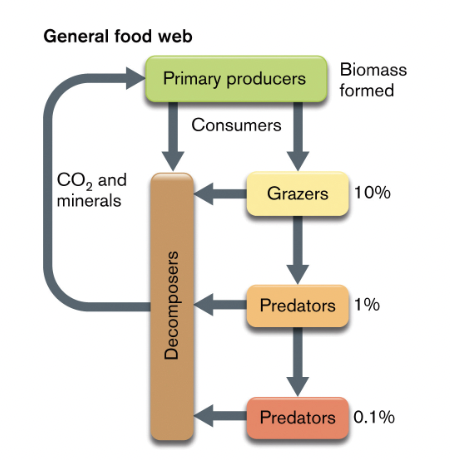
Primary producers make biomass by converting inorganic matter or light energy into organic compounds (e.g., plants, algae, photosynthetic bacteria).
Grazers
Grazers (e.g., herbivores) consume primary producers (e.g., grass, plants).
They rely on the organic energy produced by primary producers to fuel their own metabolism.
Consumers
Consumers are organisms that obtain their energy from primary producers or other consumers.
They eat organic matter created by primary producers and are part of higher trophic levels in the food web.
Decomposers
When consumers die, their nutrients are trapped within their bodies.
Decomposers (mainly microbes) break down dead organisms to release nutrients back into the ecosystem.
This process is vital for recycling minerals and nutrients in the food web.
Classification based on metabolism
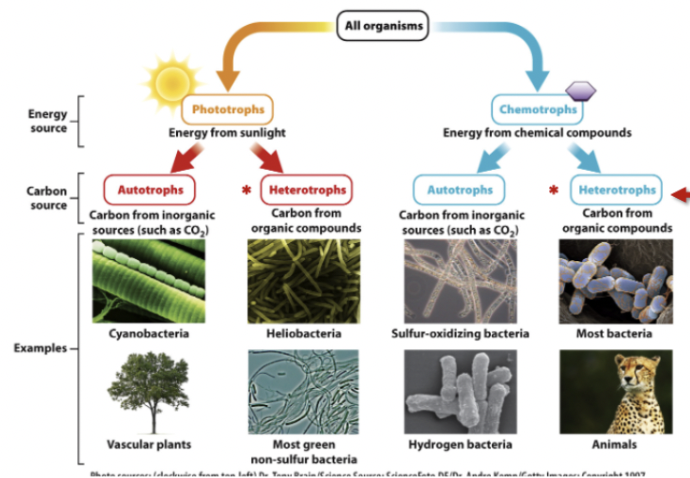
Phototrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from light.
Autotrophs
Heterotrophs
PhotoAutotroph
Organisms that produce their own compounds using light energy and inorganic substances like carbon dioxide.
Examples
Cyanobacteria
Vascular plants

PhotoHeterotrophs
Organisms that use light energy to produce ATP, but require organic compounds (rather than carbon dioxide) for their carbon source.
examples:
Heliobacteria
Most green non-sulfer bacteria
Chemotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from chemical reactions, typically by oxidizing compounds.
ChemoAutotroph aka chemolithotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from chemical reactions and use inorganic compounds (such as carbon dioxide) as their carbon source.
EXAMPLES)
Sulfer-oxidizinf bacteria
hydrogen bacteria
Chemoheterotrophs aka Chemoorganotrophs
Organisms that obtain both energy and carbon from organic compounds.
includes, mammals, funghi, most bacteria
organotrophic
Organotrophic
using organic compounds as source of electrons and carbon
Role of Microbes in Carbon Cycling
Microbes play a key role in carbon fixation, decomposition, and respiration, facilitating the movement of carbon through the ecosystem.
Autotrophic microbes (e.g., cyanobacteria, green algae, photosynthetic bacteria) capture carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis and convert it into organic carbon (e.g., glucose).
Role of microbes in nitrogen cycling
because most of the nitrogen in the atmosphere is unusable for most organisms, microbes can fix it and turn it into a usable form
nitrogen fixers: called diazotrophs have nitrogenase enzyme which converts inorganic N2 to Ammonium Ion
Example of nitrogen fixer
Rhizobium bacteria