bio (E-H)
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
diffusion is a consequence of
random movement of individual particles.
-movement of substances down a conc gradient
why do living organisms require diffusion
diff. doesnt require energy and only certain substances pass through the cell membrane this way e.g. water, co2, o2
Purpose of leaf having large SA
For diffusion of co2 and absorption of light
osmosis=
diffusion of water molecules from an area of higher w.p to an area of lower w.p across a s.p.m
osmosis -gradient
goes down a water potential gradient
turgid=
in plants or animals
swollen and pushed against the cell wall
plants
plasmolysed=
in plants or animals
shrunk and pulled away from the cell wall
plants (plas.. plant)
lysis=
in plants or animals
the cell bursts because it cant resist the pressure
animals
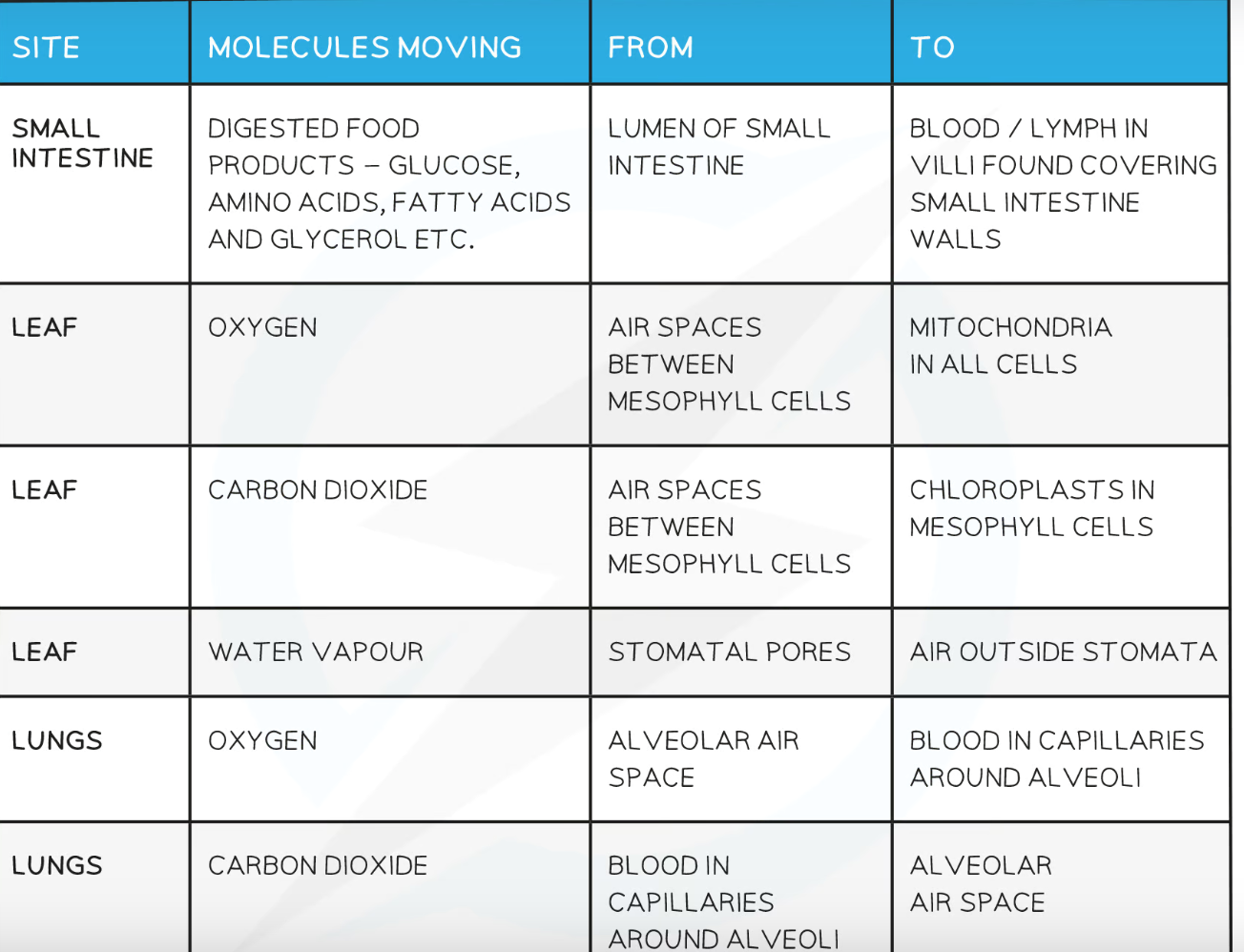
diffusion examples
yes
crenation example
in plants or animals
cell shrivels and shrinks.
animal
why plants wilt when not enough water
water moves in and out of plant cell through the cell wall + membrane by osmosis
when the cell vacuole is full of water, water pressure pushes against the cell wall and the cell is turgid.
the cell wall is inelastic so it supports the cell + plant
when the vacuole doesnt contain enough water bcus its losing more water then its absorbing, it becomes flaccid. theres not enough water pressure so it begins to wilt
if it loses so much water that the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall then it is plasmolysed.
flaccid vs plasmolysed
Flaccid refers to a wilted or limp state of a plant cell due to water loss and reduced turgor pressure, while plasmolysed describes a cell that has lost water to the point where the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall, resulting in cell shrinkage.
what factors effect rate of diff
conc gradient,
SA-vol ratio,
temp,
distance
active transport=
the movement of particles from an area of low conc to an area of high conc against a concentration gradient. thisrequires energy from respiration (ATp)
-needs a carrier protein in membrane
at transports what kind of stuff
large or charged particles
small obj have a smaller or larger SA:vol ratio
large
respiration in cell is
diffusion
Equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water --(chlorophyll/ light energy)→ oxygen + glucose
How photosynthesis work
It transfers light energy into chemical energy in the bonds in glucose
why do animals not do photosynthesis
They get their chemical energy in the food they eat (they’re heterotrophs not autotrophs)
Why glucose stored as starch
It’s insoluble so can be stored in cells without affecting the water movement in and out of cells by osmosis
Why some glucose converted to sucrose
Soluble but not as reactive as glucose so can easily be carried around the plant in solution
Why do you need glucose
To make energy and cellular structure
Factors affecting photosynthesis
(What they lack- LACCT)
-light intensity
-availability of water
-chlorophyll concentration (leaf size)
-carbon dioxide concentration
-temperature
How to inc physis
-artificial lighting (plants continue growing at night)
-adding co2 to atmosphere around plants by burning coal on oil stoves
-heating inc temp/ ventilated to dec temp
What absorbs co2
Potassium hydroxide
What’s a hydroponic
Grow plants without soil
do plants grow from water alone?
no as the plant is reliant on the roots for water + mineral uptake. the soil provides support from the stem
why leaves green
chlorophyll absorbs green wave lengths from the sun
how sugar made in leaf
water, co2 and sunlight combine
where is excess sugar stored in plant and in what form
-in roots as starch
aquatic plant
pondweed
what is a limiting factor
prevents r.o.r increasing
component of a reaction that is in shortest supply
why leaves have veins
to support and transport of water, minerals + sugar
what happens at night for plant
respiration takes place and co2 will diffuse out, also happens in day but o2 produced is more and there is light energy
why stomata on underside of leaf
to reduce water loss by transpiration
-not directly exposed to sun and more protected from the breeze.
explain why farmers add fertilisers to their fields to inc the yield but a wild area doesnt need for plants to grow well
the minerals r taken away w the crop when its harvested.
plants in wild areas do not need fertilisers cus the minerals in them return to the soil when they die and are decomposed so they r not removed from the soil
eg of inorganic fertiliser (chemical)
ammonium nitrate
eg of organic fertiliser
farmyard manure + straw
pros and cons of inorganic fertiliser
pros:-mineral content is known- minerals r soluble and available for immediate uptake so can be applied j as the crop needs them.
cons:-needs reapplying during the growing season -soluble minerals easily washed out of the soil polluting rivers and lakes
pros and cons of organic fertiliser
pros:-doesn’t need reapplying during the growing season -improves the soil structure
cons:-minerals not available immediately as the organic matter needs to decay -mineral content is not known and is variable
eutrophication-
is the adding of nutrients to water
( can be adv unless its excess)
eutrophication due to excess nutrients us caused by
fertiliser leaching and sewage pollution
explain process of eutrophication + water pollution
-fertiliser dissolves in rainwater and washes into lakes and rivers (leaching)
-the nitrate and phosphate in the fertiliser cause the rapid growth of algae
-the blanket of algae reduces the light reaching the water plants which now can’t photosynthesis
-water plants die due to lack of photosynthesis and eventually algae die as the nutrients in the fertiliser are depleted
-bacteria multiply very quickly as they decompose the dead plants + algae
-sewage can also be released into the water and the bacteria in sewage multiply very quickly
—the conc of dissolved water falls due ti the aerobic respiration of decaying bacteria
-animals with high oxygen demands suffocate and die e.g. fish
pests=
organisms that reduce yield of crop plants
pros and cons of pesticides
pros:-immediate effect
-increases yield by reducing crop eaten/ reducing competitor weeds
cons:- non-biodegradable
-kill non-pests species
-pests/insects become resistant
-can enter non target organisms and move it up food chains
pros and cons of biological control
pros:- doesn’t affect food chain
-use of a natural enemy to kill a specific pest
cons:- doesn’t kill 100% of the pests
-can cause a new pest problem
-might not be a natural enemy at that climate/ wont work as well at that climate
bio-accumlation=
inc in conc of a pollutant in an organism
bio-magnification=
inc in conc of a pollutant in a food chain
biological control=
+ e.g.
use of a natural enemy to kill a specific pest and so protect the crops
-pathogens, predators, parasites
adv of polythene tunnels
-prevent the entry of pests that can damage plants or diseases that can kill plants
-protect from weather
-slightly inc temp
nucleus=
organelle containing the genetic materialg
genome=
the entire DNA of an organism
chromosome=
very long threads of DNA found in the nucleus. only visible when the cell prepares to divide.
gene=
a section of DNA that codes for a particular protein
protein=
molecule made from a chain of amino acids which are vital for a cell to function
when is dna visible
when the cell is dividing: dna twists and coils up to form visible chromosomes
what form is dna normally found in
dna is uncoiled so the genes are accessible for protein sunthesis
dna structure
made up of two strands coiled into a double helix. each strand has a series of organic bases on the inside. the bases from each side pair up in a specific way. the chain/strand is made up of smaller units called nucleotides
what nucleotides consist
phosphate, sugar and a base
bases for DNA
(AT City Ground) adenine + thymine, Cytosine + guanine
sugar is … in dna
deoxyribose
complementary pairing=
the bases always pair in the same way
DNA vs RNA
rna: single stranded, uracil instead of thymine, has ribose sugar, shorter
genes are the code to make …
proteins
protein synthesis process:
TRANSCRIPTION:
-occurs in nucleus
-the DNA double helix unwinds, and one strand is used as a template which allows single RNA bases to attach in order to create a strand of mRNA.
-once complete, the mRNA strand leaves the nucleus to enter the cytoplasm via the nuclear pore
TRANSLATION:
-occurs in cytoplasm
-the mRNA attaches to the ribosome. The ribosome moves along the mRNA strand decoding it into base triplets, codons.
-each codon codes for a particular amino acid
-tRNA found free in the cytoplasm
-each tRNA codon has an amino acid attached to it which they bring to the ribosome. the tRNA bonds r complementary to the mRNA.
-once the amino acids have linked up, the tRNA then leaves to collect another amino acid.
-once polypeptide chain is complete, it will fold and twist or join other polypeptide chains to form a protein
RNA bases
Are U The Angel God C’s (chocolate?)
Adenine + uracil,
Thymine + adenine,
Guanine + cytosine
codon=
mRNA bases are read in groups of 3
purpose of tRNA
carries the amino acids to the ribosomes, each tRNA has a anticodon which is complimentary to the mRNA codon
a codon is made of 3 bases. there r 4 diff bases. how many diff codons can be produced?
4³ = 64nuc
nucleus cell contains
chromosomes which carry the genes
mutation=
rare random changes in the DNA
what happens if dna code changes (mutates)
the mRNA base sequence will change
-so a diff amino acid may be coded for changing the amino acid sequence
-so the function/ appearance of the protein changes
OR
-the amino acid sequence is the same + so the protein would have the same shape
alleles=
diff forms of the same genes
humans have how many chromosomes
23 -haploid
what cells dont hv pairs of chromosomes
gametes
gamete=
contains only 1 copy of each chromosome from each pair
fertilisation=
fusion of the m+f gametes forming a zygote w 2 copies of each chromosome
locus=
the specific position of a gene on a specific chromosome
dominant=
allele expressed even when only 1 copy present
recessive=
allele expressed only if 2 copies are present
heterozygous=
an individual with 2 diff alleles for a gene
homozygous=
an idividula with 2 identical alleles for a gene
genotype=
the allele each cell has for a certain feature (genetic makeup)
phenotype=
a feature that results from the genotypes (physical feature)
co-dominance=
e.g.
when neither of the alleles are dominant or recessive + so both alleles (r expressed) contribute to the phenotype
-blood groups combine so u hv both
purpose of a test cross
allows you to find out if the organism showing a dominant characterstic is homo/hetero for the fominant allele.
polygenic inheritence=
when several genes can cause a single characteristic
→therefore sm variation in features of ppl
purpose of pedigree charts
used to trace family history + work out the genotypes + risks in the case of inherited gene-related disorders
→ looks for carriers
how many alleles found in a:
zygote
gamete
2
1
monohybrid=
inheritance of characteristics controlled by a single gene
purpose of punetts square
shows possible combination of alleles that could be produced in the offspring
variation=
differences between members of the same species due to diff alleles
species=
a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring
discontinuos variation
-a characteristic that has discrete categories with no intermediates
-monogenic: one gene controls the characteristic
-the gene may also have 2 or more alleles
e.g. blood groups
continuous variation
-a characteristic with a range of values from the smallest to the largest
-polygenic: several genes control the same characteristic
-each gene contributes a little towards the overall pheno.
e.g. height
what factors is variation due to
genes, environment, combination of both
mutations are a source of variation due to the formation of new alleles
yes
when will a mutation be passed on in a sexually reproducing organism
if it occurs in a gamete
mutagens=
e.g.
increase the rate of mutation
ionising radiation (gamma rays), some chemical mutagens (tobacco)