PKG 221 Test #1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Is glass a solid or liquid?
No - it is its own state of matter
What is the molecular structure of glass?
Amorphous, random
What is the melting point of glass?
As glass cools/heats, it gets “stiffer” or “more viscous” W
What are the main raw materials used in glass?
Silica (sand), limestone, soda ash
What is the purpose of limestone in glass?
Improves chemical durability
What is the purpose of soda ash in glass?
Reduces melting temperature
What would happen if sand was the only component in glass?
It would be harder to melt, harder to fine (get rid of bubbles), and more difficult to mold (high viscosity)
Why is cullet used?
It reduced energy usage
What is added to make yellow glass?
Iron Oxide
What is added to make green glass?
Chromium Oxide
What is added to make blue glass?
Cobalt oxide
What is added to make brown glass?
Carbon + sulfur + iron
Why would you make brown glass?
To protect the product from light
How do you make Flint (clear) glass?
Iron content imparts green color while selenium metal imparts pink or salmon color to create a gray color that appears clear to the human eye.
What does adding lead oxide do?
Very clear but soft glass
What does adding aluminum oxide do?
Adds hardness, durability & resistance to chemical attack
What does adding boron oxide do?
Thermal shock resistance (won’t crack bottle when you go from hot to cold)
What is natural glass?
Glass created by high heat events (like obsidian)
How has glass progressed throughout history?
Handblowing to semi-automatic to automatic
What does it mean to marver glass?
The “gather” of hot glass on the end of the blowpipe and blow small puffs to begin the formation of the “parison”.
What is annealing?
The process of heating a glass object to release the strain introduced in the forming process.
What is “cracking off"?
The technique of breaking off the blowpipe that has been used as a handle during the forming process.
What is a gob?
A specific amount of molten glass, which is eventually formed into a glass container.
What is the shoulder, neck, and finish of a bottle?
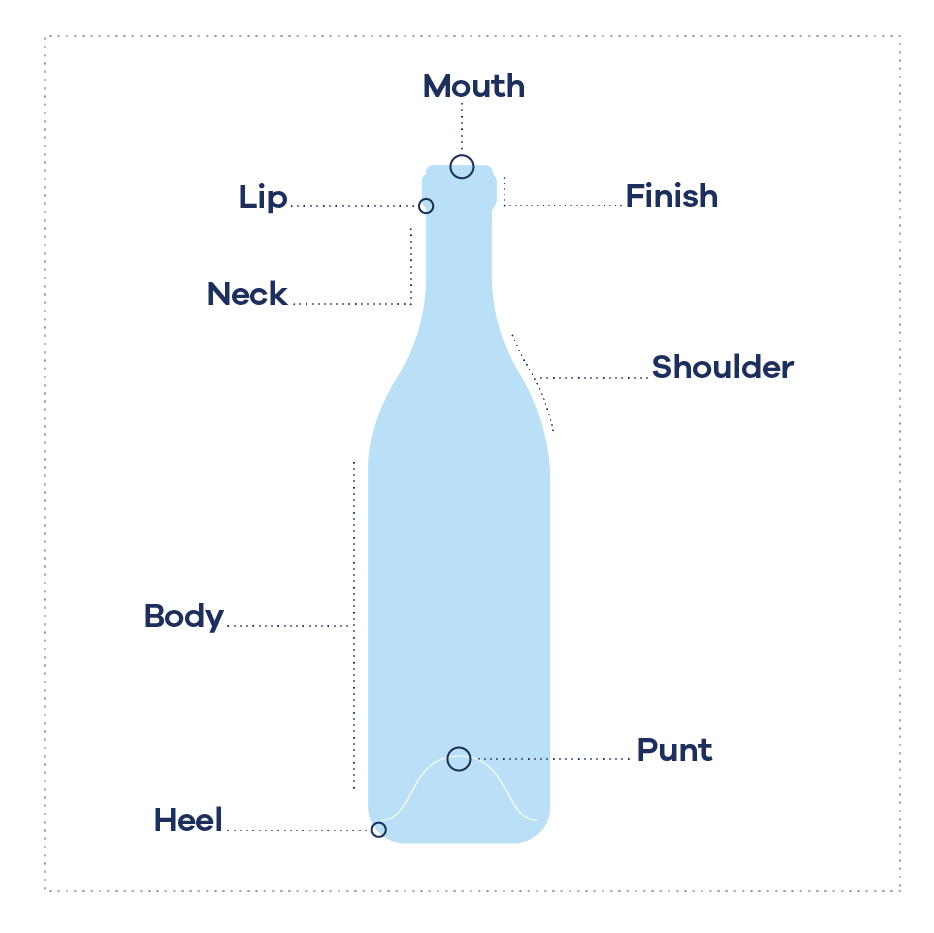
What is the process for making a glass container?
Batch house > melting chamber > forehearth > feeder > forming machine > annealing lehr > inspection > load building
What happens in the batch house?
Raw materials storage, weigh material, mix material in batches
What happens in the melting chamber?
Melts raw material
What happens in the forehearth?
Channels glass & cools glass
What happens in the feeder?
Mixes glass, controls glass flow, shears/drops gob
What happens in the forming machine?
Creates containers
What happens in the annealing lehr?
Removes stress, reheats/slowly cools
What happens during inspection?
optically scans & automatically rejects
What happens during load building?
Pack for shipment
What is the difference between bottles & jars
Size
What is leaching?
When certain chemicals come out of the glass over time
What kind of product do we need to be concerned about leaching?
Medicine
What type of glass is used for pharmaceuticals?
USP Glass
What are vials?
Multi-use, small, round bottles, oversized rubber septum, syringe penetrates septum
What are ampoules?
Single use, extruded tubes, pinched on one end
What is the primary problem of the furnace?
Refractory materials are needed, zircon most common (most commonly run by natural gas)
What are the 3 stages of the melting process?
Melting, fining, and conditioning (reduces temp to make it consistent all the way through)
What is the goal of the melting process?
Convert batch materials into homogenous mixture suitable for forming
What is blow and blow process used for?
Large vessels >9.5” & heavy containers
What is the press and blow process used for?
9.5” or less & wide mouth jars
What is the narrow neck press and blow used for?
Less than or equal to 9.5” & 1.5” or less finish
What are the goals of surface treatments (hot & cool end coating)?
Preserve the strength of the glass containers & facilitate flow through glass manufacturer/customer filling line
What is striking?
When glass is reheated after the inspection process to make black glass
What are considerations for vertical pallet load?
Must design shoulder and heel for proper vertical loading (flat shoulder angles & large heel radii)
What are considerations for shipping cases?
Label indent, partition cells need to be large enough for insertion, corrugated needs to be designed with the right height and weight
What might a marketing group require?
An aesthetically pleasing packaging, unique shape, quality image, good size impression, adequate label area
What might a production group require?
A design that can be handled by automated/mechanical equipment, provides enough volume to meet specified label claim, and sufficient head space to allow product expansion due to temp changes
Why is bottle shape important?
Influences container strength: sphere is the strongest, cylinder is next strongest, rectangular is poorest
What is a critical defect?
Hazardous. to the user and makes the container unusable
What is a major defect?
reduces the usability of the container
What is a minor defect?
Do not affect the usability of the container but detract from its appearance or acceptability