OPRE 3330 - Cost Managemen
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is a common cause of project failure?
Cost
What do PMs need to consider in order to determine the overall cost of a project?
Time, Resources, Scope
Project Cost Management:
Planning, budgeting, financing, funding, and controlling costs so that the project can be completed within the APPROVED budget
Project Cost Management Challenges) Lack of resources
The PM will have a hard time securing the resources(people, technology, materials) necessary to complete the project on-time
Project Cost Management Challenges) Poor Cost Estimation
Most common issue in failing projects. Poor estimation/forecasting can occur when a PM isn’t experienced enough(Ex. cost, scope, schedule). Poor cost estimation can often lead to cost overruns.
Project Cost Management) What DO you need for an accurate cost estimate?
A well-defined scope, robust WBS, a complete project schedule with activities and their durations and resource estimates, etc.
Fixed Cost:
This type of cost doesn’t change as production changes throughout the project
Variable Cost:
This type of cost will vary with the amount of work or production and changes month to month
Direct Cost:
Only occurs because of the project and can be DIRECTLY attributed to it(Ex. Salaries/wages, purchased parts, manufacturing supplies)
Indirect Cost:
Cost incurred for the benefit of MORE than one project. Not incurred for one specific project.(Ex. Heating, lighting, taxes, renting out an office space)
Plan Cost Management(Planning Phase):
Define how the project costs will be estimated, controlled, and monitored through the project lifecycle.
Estimate Costs(Planning Phase):
Approximate the costs of all resources that are needed to complete project work(Ex. Labor, materials, equipment, services)
Determine Budget(Planning Phase):
Add the estimated costs of individual activities or work packages in order to establish a baseline
Control Cost(Monitoring & Control):
Monitor the project status in order to update project costs and MANAGE changes to the cost baseline
Estimate Costs) Types of Costs for Estimation
Cost of quality efforts and risk efforts
Cost of the PM’s time.
Cost of project management activities
Expenses for physical office spaces, and overhead costs
Salaries and general office expenses.
Estimate Costs) Use following inputs to estimate costs
Cost management plan, risk register and previous projects, scope baseline and project schedule
Analogues Estimating:
Your neighbor made a perimeter fence and it cost them $100, THEREFORE, you can estimate that it will take around $100 dollars for you to make YOUR fence.
Parametric Estimating:
Uses a mathematical model based on historical records from other projects.
Parametric Estimating: Example
It costs you $100 to build 5 feet of fence. To build 10 feet of fence, it can be estimated that it will cost $200(100 × 2)
Bottom-Up Estimating:
Rollup the cost for individual activities, with each schedule activity being calculated and then aggregated
3-point Estimating:
Takes a weighted average of the optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates.
3-Point Estimating(Formula):
(0 + 4M + P)/6
Reserve Cost:
The extra money in the project budget that’s to be used if necessary
Reserve Cost) Contingency Reserve:
The money held in order to pay predictable but unspecified extra costs(Ex. a breakdown in the manufacturing line)
Reserve Cost) Management Reserve:
Money assigned to the project for unknown costs, it’s money that senior management controls.(Ex. If something happens during the project that changes the scope, the money would be used then)
Estimated Cost:
The TOTAL project cost estimate that the PM makes
Budgeted Cost:
A budget that the manager has prepared and allocated to the project
Determine Budget:
You aggregate the estimated costs of individual activities/individual costs to come up with an authorized cost baseline
Cost Baseline:
Time-phased budget used to measure, monitor, and control cost performance during the project(Includes contingency reserve but NOT management reserve)

Q: What is the project estimate?
$100 + $200 + $400 +$100 = $800

What’s the cost baseline?
The project estimate + contingency reserve = $800(project estimate) + $80(Contingency Reserve) = $880

What’s the Project Budget?
Cost Baseline + Management Reserve = $880(cost baseline) + $50(Management Reserve) = $930
Earned Value Management)Control Costs
Monitor the project status in order to update project costs and manage changes to the cost baseline
Earned Value Management(EVM):
Method of project performance and progress measurement through the project lifecycle regarding schedule control and cost control
Earned Value Management(EVM):Part 1
Integrates project schedule, costs, and scope in order to measure overall performance
Earned Value Management(EVM): Part 2
Compares the BUDGETED and ACTUAL costs of a project
When do PMs use EVM?
When there is a risk to on-time and on-budget project delivery
When cost and schedule need to be managed
What questions do EVMs answer?
Are we AHEAD or BEHIND of schedule?
Are currently UNDER or OVER budget?
When is the project LIKELY to be complete?
What’s the remaining work LIKELY to cost?
Planned Value:
How FAR ALONG the project work is supposed to be at any point in the schedule.
Budget at Completion(BAC):
The total Planned Value for the project
Earned Value:
Shows the work that’s been performed until now(represents the COST of the work completed until now)
Actual Cost(AC):
Amount of resources used to perform the work thus far(sum of $ used so far)(represents the ACTUAL money spent to-date on a project)
EV< PV:
Project is BEHIND SCHEDULE(earned less than planned)
EV>AC:
Project is UNDER BUDGET(spent less than the value earned)
EV<AC:
Project is OVER BUDGET(earned value less than money spent)
EV = AC
Project is on-budget
EV>PV:
Indicates a project is AHEAD Of schedule
Schedule Variance(SV): A measure of schedule performance. How is it calculated?
EV - PV(it’s the difference betweeen the work DONE and the work PLANNED to be done)
Positive SV:
Project is AHEAD of schedule
Negative SV:
Project is BEHIND schedule
Cost Variance(CV):
The amount of budget deficit or surplus at a given time
Cost Variance Calculation:
EV(Earned Value) - AC(Actual Cost)
Positive CV:
A project is UNDER budget
Negative CV:
A project is OVER budget
Schedule Performance Indicator(SPI):
Shows how efficient a project team is in utilizing time during a project
SP > 1
Project team is VERY EFFICIENT in using time during the project.
SP < 1
Project team is NOT EFFICIENT in using time during the project
CPI:
Shows how efficient a project team is in utilizing resources(money) for the project
CPI > 1
GOOD efficiency in using the resources allocated to the project
CPI < 1
BAD efficiency in using the resources allocated to the project

What is the SV for the project?
EV - PV = $70,000 - $60,000 = $10,000
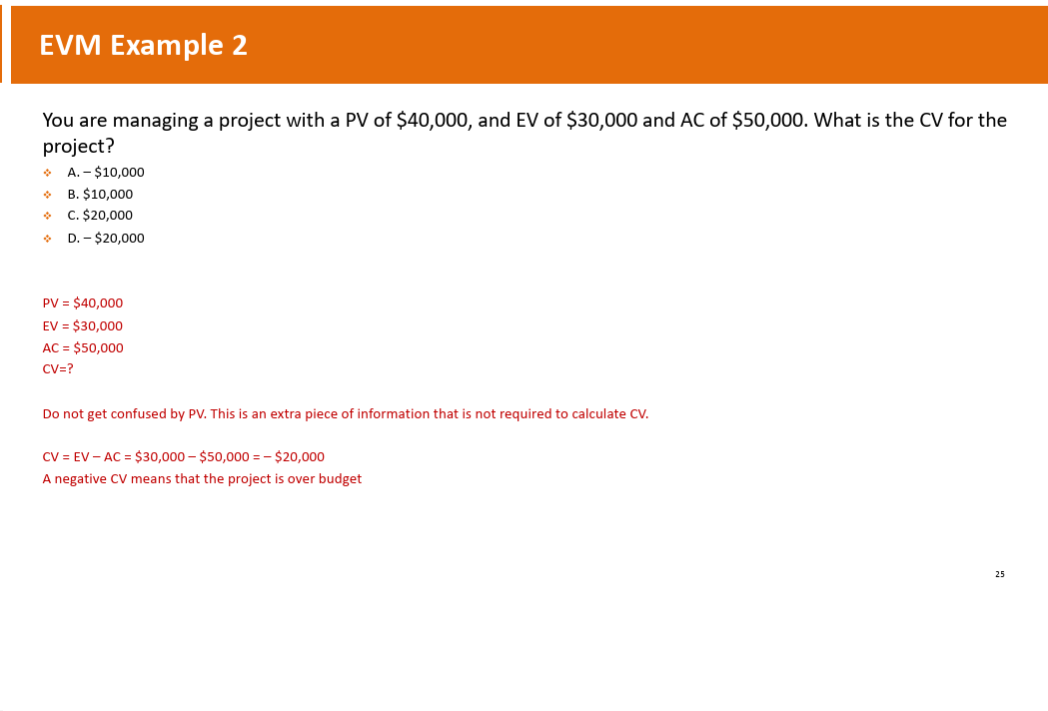
What is the CV for the project?
EV - AC = $30,000 - $50,000 = -$20,000(OVER BUDGET)

What is the SPI?
EV/PV = 30,000/15,000 = 2(ahead of schedule)

What is the CPI?
EV/AC = 30,000/60,000 = 0.5

You have a project you’re managing with an SPI of 1.1. What’s the best way of describing this project?
C. The project is progressing at 110% of the rate originally planned for the schedule.
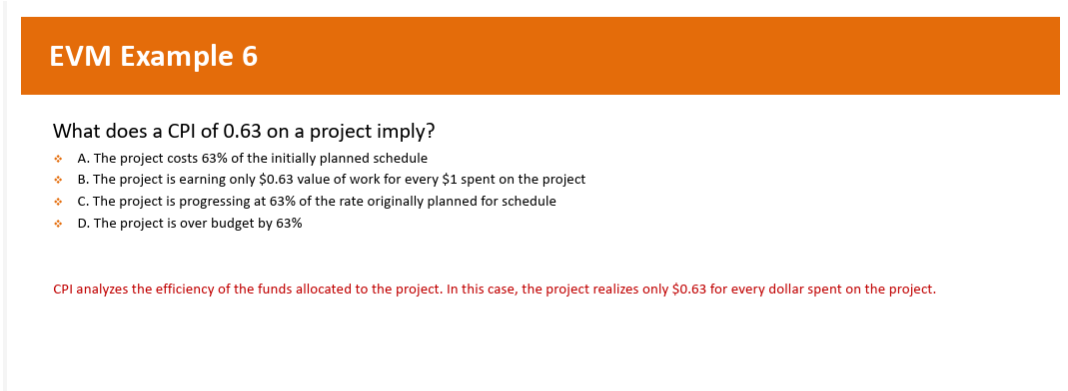
What does a CPI of 0.63 on a project imply?
The project only EARNS $0.63 value of work for every $1 spent
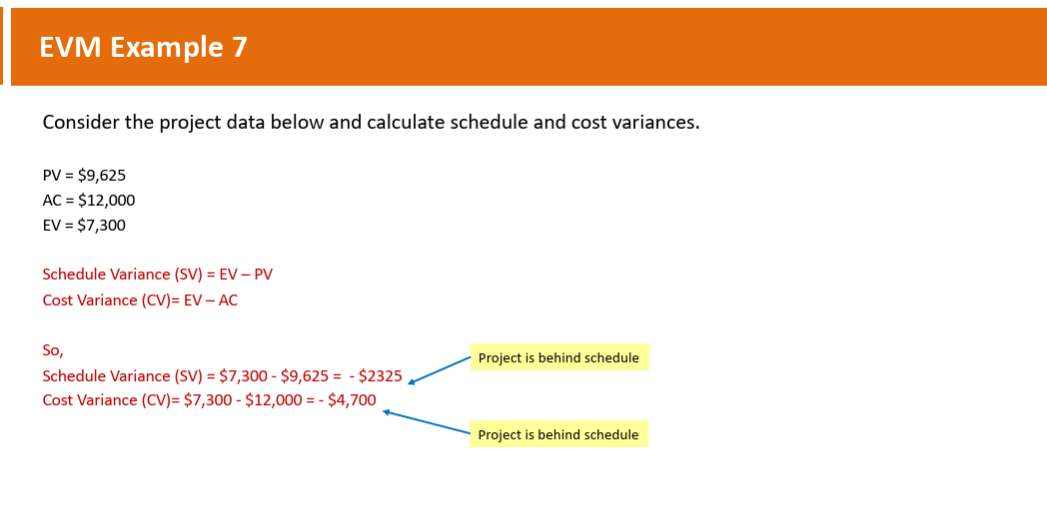
What are the schedule variances and cost variances?
SV: $7,300 - $9625 = -$2325(behind schedule)
CV: $7300 - $12000 = -$4,700(behind schedule)