Chemistry EOY revision Wednseday
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is an atom made mostly of
empty space
What is the relative mass and charge for a proton
Mass 1
Charge +1
What is the relative mass and charge for a neutron
Mass 1
charge 0
What is the relative mass and charge for an electron
Mass-1/2000
Charge -1
What does the mass number represent
the number of protons and neutrons in an atom
What does the atomic number represent
Number of protons/electrons
Who made the solid spheres model of the atom
John Dalton
What model did JJ. Thompson make
The plum pudding model
What did rutherford discover about the atom
He discovered the nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space and have a cloud of electrons
What did Niels Bohr discover
that electron exist on shells, fixed distances apart
What experiment did Rutherford do to find out that atoms are mostly empty space
He shot alpha particles at gold foil and most of the atoms passed through but some reflected
What are isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of a certain element that have the same atomic number but a different mass number. They have more or less neutrons so the charge doesn’t change
What is the relative atomic mass
The weighted mean mass of the isotopes of an element compared with 1/12 of a carbon 12 atom
What equation is used to calculate the relative atomic mass
Relative atomic mass=(MassX%abundance)+(MassX%abundance
Total abundance(usually 100)
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be on shell 1
2
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be on shells 2+
8
What is another name for an electron shell
energy level
How would you show that and element had 2 electrons on the first shell, 8 on the second, and 4 on the third
2.8.4
What is an ion
an electrically charged particle formed when atoms lose or gain electrons
Do non-metals usually lose or gain electrons
They usually gain electrons to form negative ions
Elements in the same group all have what
The same number of electrons on the outer shell. Group number=number of electrons in the outer most shell.
What happens when you are writing complex ions
The number on the top right of the 2 ions cross over and go to the bottom of the other atom
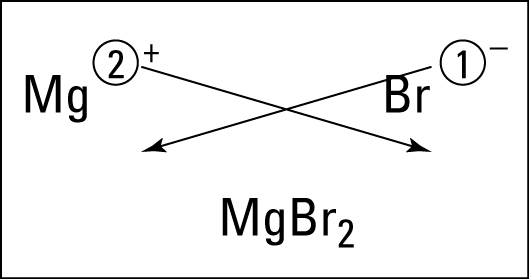
What is the complex ion formula for ammonium

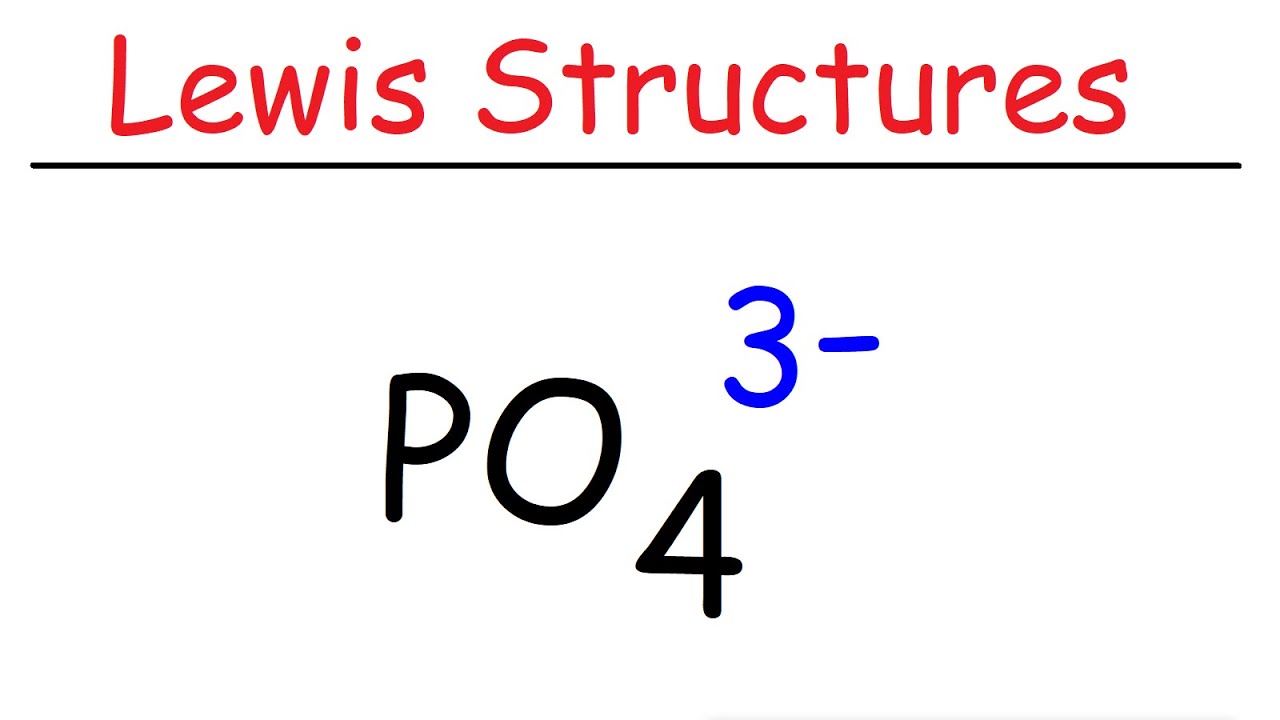
What is the complex ion formula for Phosphate
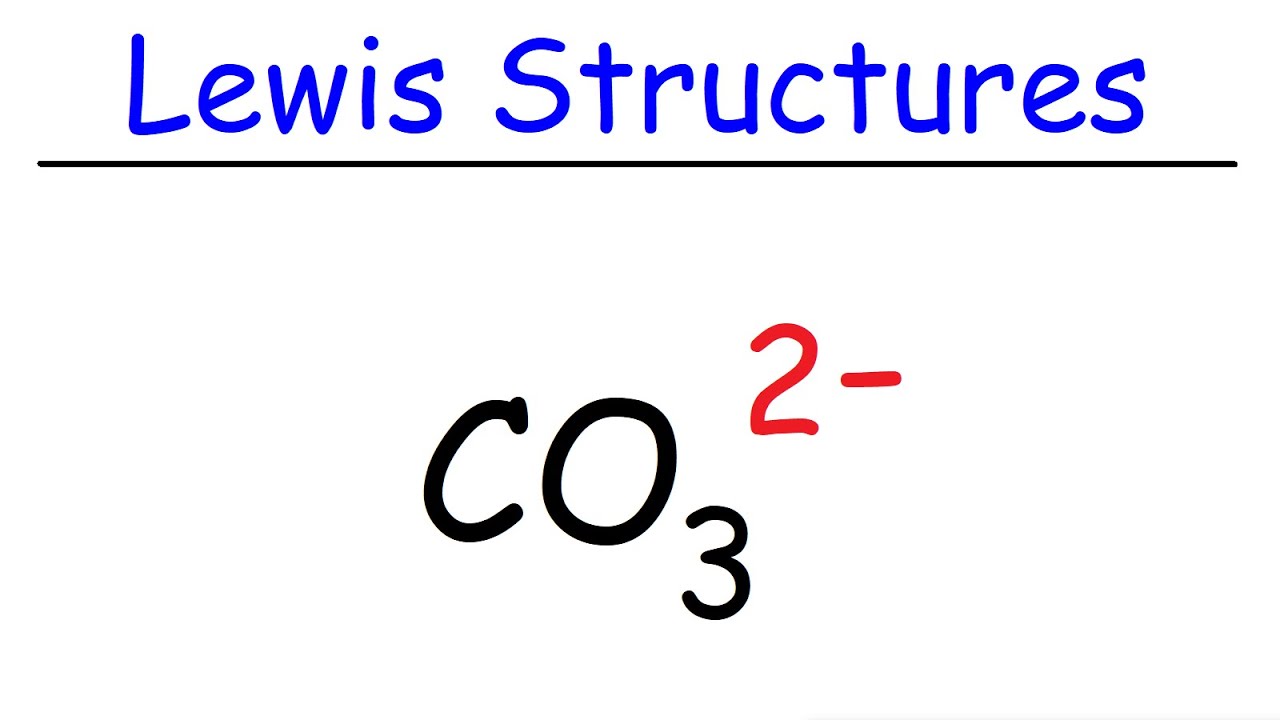
what is the complex ion formula for Carbonate
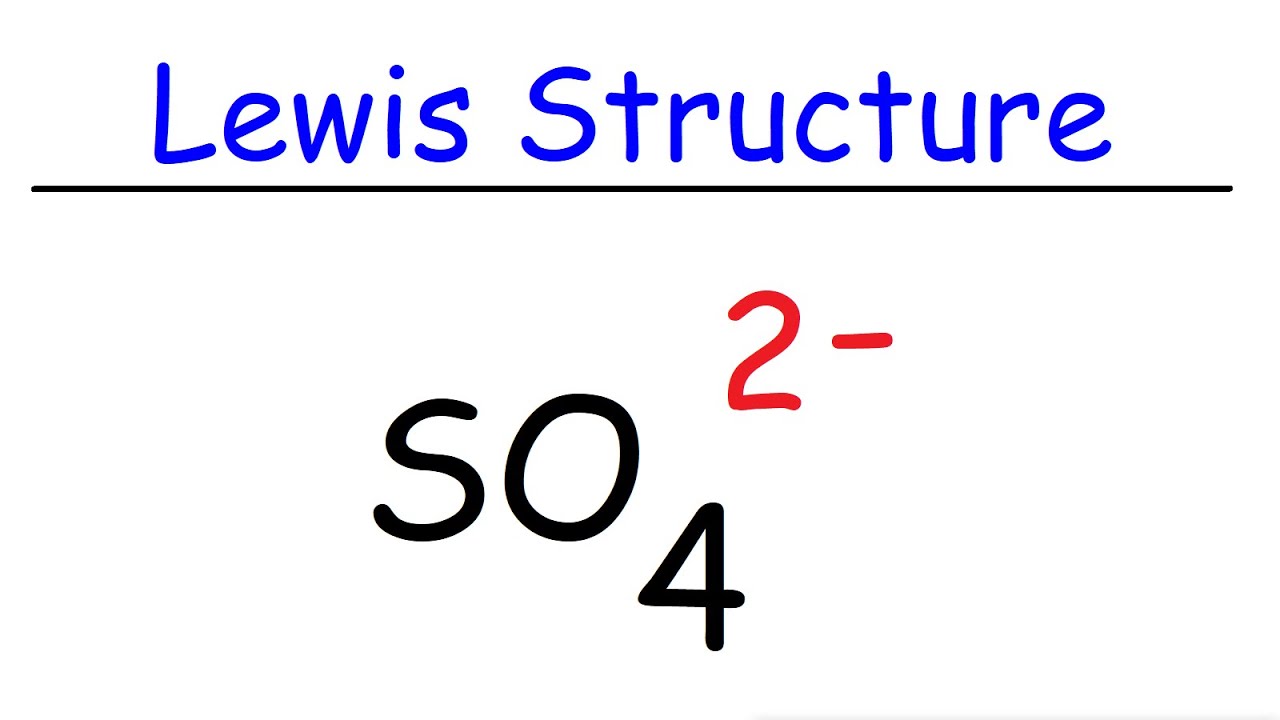
What is the complex ion formula for sulphate
What is the complex ion formula for Hydrogen-carbonate
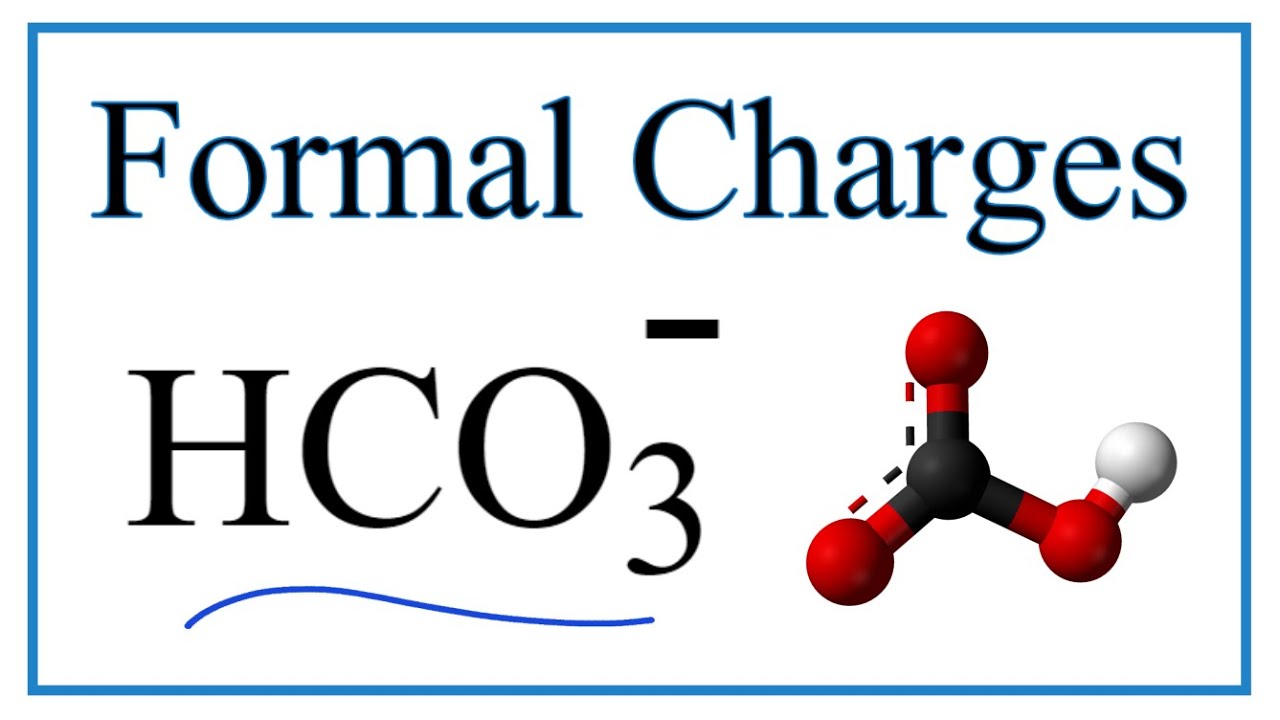
What is the complex ion formula for nitrate
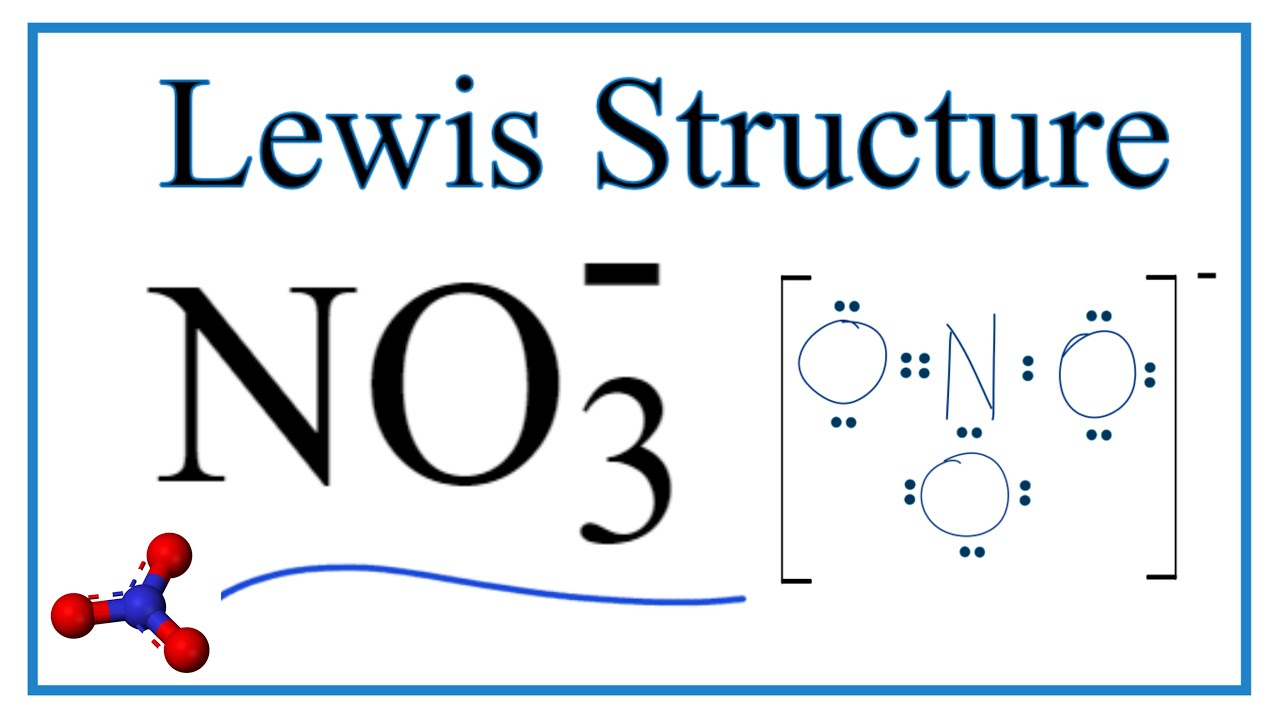
What is the complex ion formula for Hydroxide

What is the complex ion formula for Ethanoate
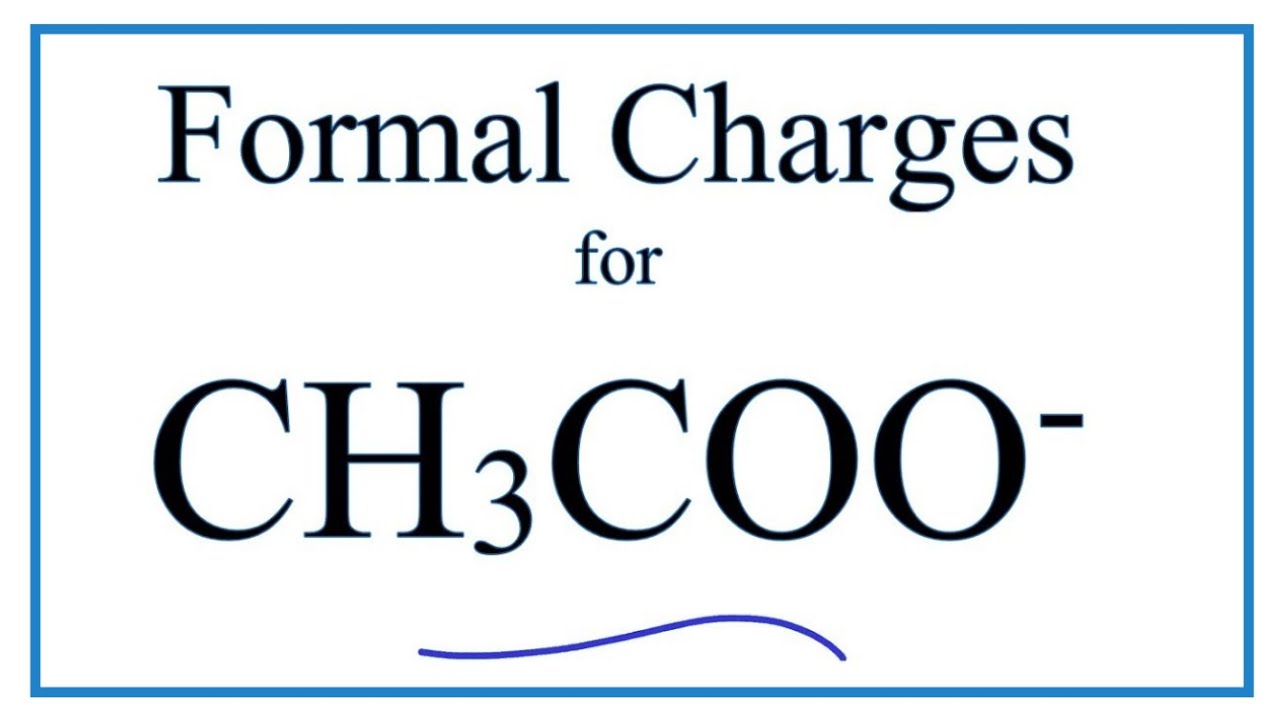
What is a complex ion
an ion containing more than one type of element
What charge will an ion of an element from group 5 have
-3
What charge will an ion of an element from group 3 have
+3
What charge will an ion of an element from group 1 have
+1
what charge will and ion of an element from group 7 have
-1
What is a cation
A positive ion that is formed when an atom loses an electron
What is an Anion
A negative ion that is formed when an atom gains an electron
What are the proportions of gas in the air
78% hydrogen
21% oxygen
1% trace gases
What is test for hydrogen
Put a lit splint in and if hydrogen is present it will make a squeaky pop
What is the test for oxygen
out a glowing splint in and if it relights then oxygen is present
What is the test for carbon dioxide
Pump through limewater and if there is carbon dioxide it will go cloudy
What is the test for chlorine gas
It will bleach damp blue litmus paper white
What are the 2 way of testing for cations
Flame tests, precipitate reactions
What colour does lithium burn in a flame test
red
What colour does sodium burn in a flame test
Yellow
What colour does potassium burn in a flame test
Lilac
What colour does copper burn in a flame test
Green
What colour does calcium burn in a flame test
Brick red
What is the colour of iron 2 solution and what precipitate is formed when it reacts with sodium hydroxide
The solution is pale green and the precipitate is green/grey
What is the colour of iron 3 solution and what precipitate is formed when it reacts with sodium hydroxide
The solution is yellow and the precipitate is orange/brown
What is the colour of copper solution and what precipitate is formed when it reacts with sodium hydroxide
The solution is blue and the precipitate is blue
What is the colour of magnesium solution and what precipitate is formed when it reacts with sodium hydroxide
The solution is colourless and the precipitate is white
What colour is aluminium solution and what precipitate is formed when it reacts what sodium hydroxide
The solution is colourless and the precipitate is white
What colour is calcium solution ad what precipitate is formed when it reacts with sodium hydroxide
The solution is colourless and the precipitate is white
What is the test and result for the anion of chloride
Add silver nitrate and it will produce milky white precipitate
What is the test and result for the anion of bromide
Add silver nitrate and it will produce a cream precipitate
What is the test and result for the anion of iodide
Add silver nitrate and a yellow precipitate will be produced
What is the test and result for the anion of sulfate
Add Barium chloride and a white precipitate will form
What is the test and result for the anion of carbonate
Add hydrochloric acid and it will create effervesence
What is the difference between evaporation and boiling
Evaporation will only occur on the surface of the liquid whereas boiling occurs over a large mass of the liquid. Evaporation can happen at any temperature but boiling only occurs at the liquids boiling point.
What is diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
How does chromatography work
it is used to separate and identify liquids base on there solubility. The water is drawn up by capillary action. When the solvent reaches the ink spots they are dissolved and carried up the paper.
Diagram for chromatography
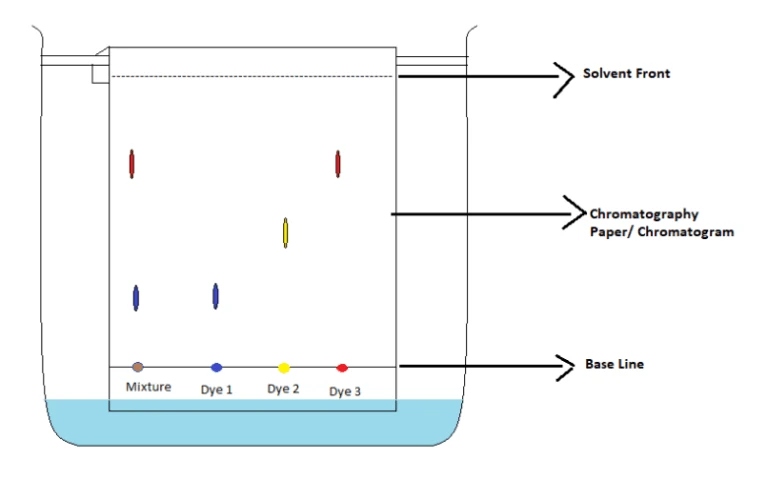
What is an rf value and how can it be calculated
It is a ratio of the distance travelled by sample to the distance travelled by the solvent.
RF = distance moved by sample/distance moved by solvent
What is qualitative data
Qualitative data is subjective therefor is more likely to cause errors or anomalies. e.g. colours
What is quantitative data
Quantitative data is more accurate and less subjective .e.g .Rf value
What is a formulation
A formulation is a mixture which has been designed as a useful product. This includes fuel, cleaning products and fertilisers
Give a simplified method for separating salt from rock salt
Grind the rock salt with a pecil and mortar for 2 minutes to that the salt will dissolve easier.
Pour the mixture into a beaker of water and mix it to dissolve smaller salt particles.
Then put a filter funnel into a conical flask and fold the filter paper and put it in the funnel.
Then pour the salty water, a bit at a time until the liquid has passed through.
Then use a Bunsen burner with a heat proof mat and a tripod and gauze. Then pour the liquid into an evaporating basin and place it on the heat proof mat until the water has evaporating leaving salt behind.
What is simple distillation
It is used to separate a liquid from a mixture.
Diagram for simple distillation
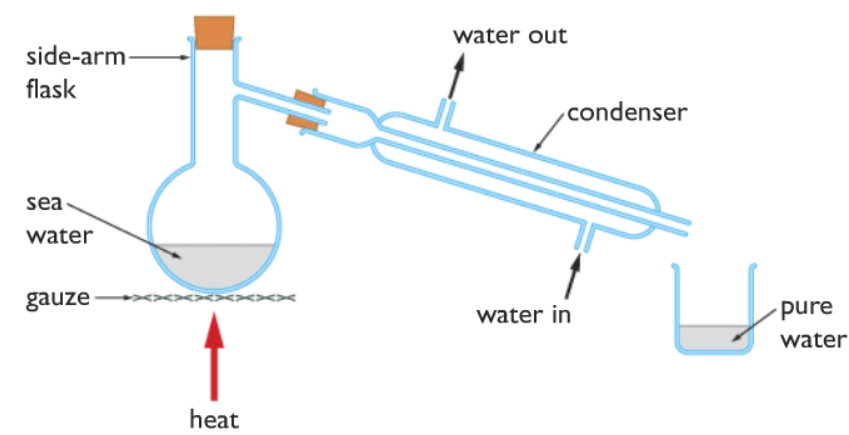
What is fractional distillation
Can be used to separate and individually collect liquids from a mixture.
What is pure water
A substance that only contains h2o molecules
What is potable water
Water that is safe to drink
What is fresh water
Water from lakes, rivers, and reservoirs
What is the method for making potable water
Choose a source of fresh water
Sedimentation allows heavy particles to settle at the bottom. These are removed using wire meshes
Passing it through filter beds removes solid particles
Sterilize/kill microbes using disingectants.
What does saline mean
contains salt
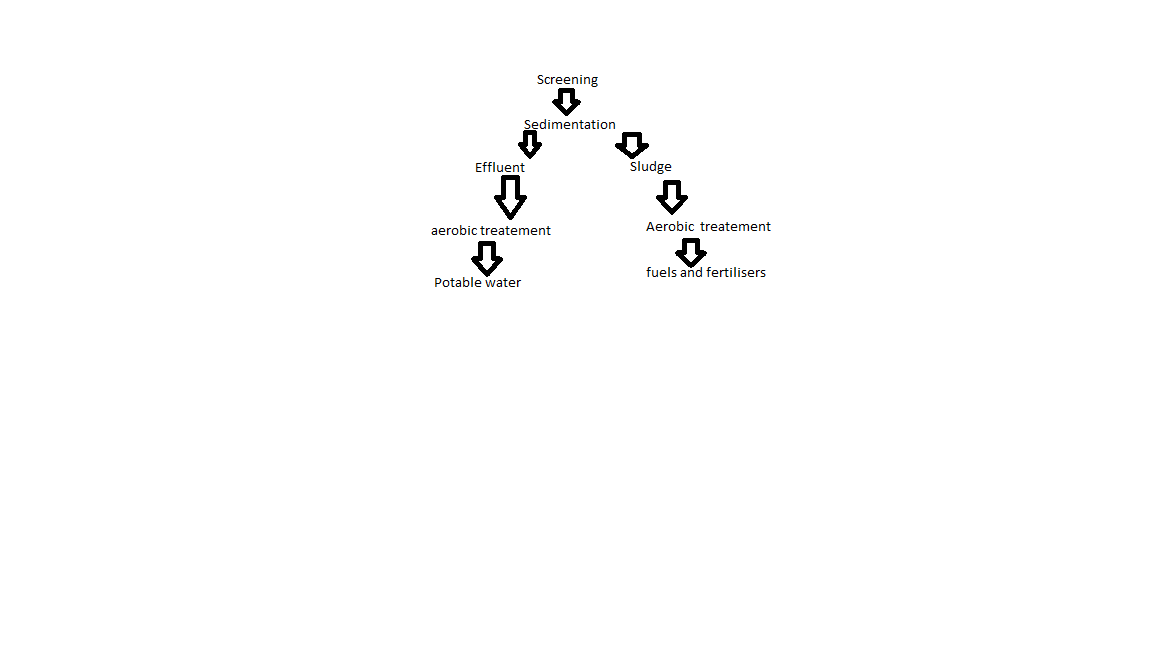
Process of potable water
What are the benefits and key facts for fresh and ground water
It is the easiest and cheapest of the 3 main methods of making potable water.
It requires filtration and sterilisation.
What are the benefits and key facts of desalination
It is the hardest and most expensive method
It involves distillation or using membranes. for example reverse osmosis
Both require lots of energy
What are the benefits and key facts of Waste water treatement
It is moderately cheap and uses less energy
It involves screening, sedimentation, digestion.
Several steps, requires large treatment plant
What was the composition of the early earth atmosphere
4% water vapour
95% carbon dioxide
1% trace gases e.g. nitrogen, ammonia, methane
What is the greenhouse effect
It is a necessary process that maintains a temperature high enough for life.
This is how it works
Short wavelength radiation from the sun is absorbed by the planets surface.
The surface re-radiates long wavelength radiation back into the atmosphere. This is absorbed by greenhouse gasses, preventing it from escaping.
This process traps heat at the surface of the Earth, rising the average surface temperature.
What are 5 human impacts on the greenhouse effect
Combustion of fossil fuels releases CO2, increasing carbon emissions
Deforestation- clearing land, releasing CO2, reducing global photosynthesis
Mass farming- Use of fuels releasing CO2, cattle farms release methane
Rice farming- flooded rice paddies released methane from decomposition of organic matter.
Landfill-anaerobic fermentation releases methane
What are effects of climate change
rising average global temperatures
Melting polar ice caps
More extreme weather variations in seasonal temperatures
More extreme weather
More frequent natural disasters
What is a carbon footprint
The sum of all greenhouse gases emitted by a person, product or industry.
What are natural resources
Resources produced without any human influence and instead grow or form naturally. e.g. water, coal, crude oil, metal ores, wood, agricultural crops, cotton, wool.
What are renewable resources
Resources that can be reformed or replenished over an short time. e.g. wood, cotton, wool. IF used responsibly, we wont run out of these.
What are non-renewable resources
Resources that are used up quicker than they are reformed. e.g. crude oil takes millions of years to be created. At current rates, the will run out soon.
What is sustainability
Using resources to meet our current needs without jeopardizing the needs of the future.
What is an LCA
Life Cycle Assessments assess environmental impacts of products and services that people use in their everyday lives
What are the 5 stages of a life cycle assessment
Extraction of raw materials. Mining, drilling, deforestation.
Manufacturing and packaging
distribution and transport
useable lifetime
Disposal. Recycling? Reuse?
What are some limitations of LCAs
Some impacts are easy to see, such as environmental destruction from mining or carbon emissions. Some however are more difficult to assess. e.g. when impacts become indirect, it becomes difficult to assess where to draw the line.
It is also difficult to numerically assess some environmental impacts. People will need to make value judgement on the scale and severity of an impact, and this will always be subjective