Year 13 weakpoints
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
How are chloroplasts adapted to carry out photosynthesis?
The thylakoid membrane provides a large surface area
Proteins hold grana for maximum light absorption.
ATP synthase and selectively permeable membrane and for ATP synthesis.
DNA and ribosomes for synthesis of required proteins.
Describe the stages of the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis?
Firstly it takes place on the thylakoid membrane between the stroma and the thylakoid membrane and light energy causes a pair of electrons to enter an excited state and gain in energy exiting the cell this is called photoionisation.
Then due to this light energy splits water into electrons which replace these electrons, protons helping to establish a concentration gradient and oxygen which can be used for aerobic respiration this is called photolysis.
After this the initial electrons move along the electron transport chain a series of transport proteins via a series of oxidation and reduction reactions which provides energy to the transport proteins to actively transport proteins across the thylakoid membrane into the stroma.
This means that a protein gradient was established so protons move through ATP synthase into the stroma which provides the energy for ATP synthase to combine ADP and a phosphate ion to form ATP.
Meanwhile when the electrons reach the end of the electron transport chain they combine with NADP and a proton to form NADPH.
Describe the stages of the light independent reaction of photosynthesis?
It takes place in the stroma
Firstly, RuBP a 5C compound combines with a CO2 molecule through carbon fixation catalysed by rubisco to form two molecules of the 3C compound GP.
Next the 2 GP molecules are reduced by NADPH which is oxidized to NADP and ATP is hydrolysed to ADP+Pi to provide energy to convert these 2 GP compounds to 2 triose phosphates.
Then 20% of triose phosphates are used to form organic substances such as hexose sugars and amino acids.
Meanwhile 80% is used to regenerate RuBP by the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP+Pi and then the cycle repeats.
ADP+Pi and NADP return to the light dependent reaction.
Describe the steps of glycolysis?
Firstly this occurs in the cytoplasm and glucose is converted to glucose phosphate by the break down of two ATP to two ADP molecules and this is called phosphorylation.
Then glucose phosphate is split into two molecules of triose phosphate.
Then each triose phosphate is oxidised by reducing NAD to NADH and the loss of a phosphate by the conversion of two ADP molecules to ATP leading to a net yield of two ATP molecules.
Describe anaerobic pathway in animals?
Pyruvate in animals is reduced by the oxidation of NADH into NAD and this converts ethanol to lactate and means glycolysis can repeat allowing ATP to be formed.
Describe anaerobic pathway for yeast?
Pyruvate is decarboxylated to form ethanal and then reduced by NADH to NAD to form ethanol allowing glycolysis to repeat.
Describe the steps of the link reaction?
In the link reaction pyruvate is decarboxylase as a carbon dioxide molecule is released and NAD is reduced to form NADH by oxidising pyruvate to form acetate which combines with co-enzyme a to form acetyl co-A.
Where does each step of aerobic respiration take place in Biology?
Glycolysis in the cytoplasm
Link reaction and Krebs cycle in the mitochondrial matrix
Oxidative phosphorylation in the intermembrane space.
Describe the steps of the krebs cycle?
Firstly in the mitochondrial matrix a 4 carbon compound intermediate combines with acetyl coA to form a 6 carbon compound and then coenzyme A is released and it returns to the link reaction.
After this NAD is reduced to NADH and the carbon is decarboxylated as a carbon dioxide molecule is released to form a 5 carbon compound.
Then another carbon is released in the form of carbon dioxide, 2 NAD’s are reduced to NADH, FAD is reduced to FADH2 and ADP is phosphorylated to form ATP. This forms a 4 carbon compound which can return to the start of the process and repeat it.
How many ATP molecules are produced by each step of aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis yields 2 ATP
The link reaction yields none
The krebs cycle yields 2 as 1 is yielded for 1 acetyl coA and glucose forms two.
Oxidative phosphorylation can yield more than 30.
Describe the steps of oxidative phosphorylation?
Firstly NADH and FADH2 travel to the inner mitochondrial membrane and donate their electrons to transport proteins in the membrane reducing these proteins and oxidising NADH into NAD and FADH2 into FAD and they release protons.
These co-enzymes then return to earlier stages of aerobic respiration and the electrons travel along the proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane known as the electron transfer chain via a series of oxidation-reduction reactions.
This provides energy to these proteins to actively transport proteins out of the mitochondrial matrix into the inter-membrane space establishing a proton gradient.
Due to this protons move down a proton gradient through ATP synthase which provides ATP synthase with the energy to form ATP by comping ADP and a phosphate ion.
Meanwhile when electrons reach the end of the electron transfer chain they combined with oxygen known as the final electron acceptor and a proton to form water.
How are triglycerides used in respiration?
Triglycerides are broken down into three fatty acids and glycerol.
The three fatty acids are converted into acetyl-CoA which is used in the krebs cycle
The glycerol is converted into triose phosphate which is used in glycolysis.
How are amino acids used in aerobic respiration?
Amino acids with three carbons are converted into pyruvate which is used in the link reaction.
Meanwhile amino acids with 4 and 5 carbons are converted into molecules used in the krebs cycle.
Define GPP?
All the chemical energy which is converted from light energy into biomass by producers through photosynthesis in a specific area and time representing all the energy captured by an area.
Define NPP?
All the chemical energy converted from light energy into biomass by producers through photosynthesis in a specific area and time take away the energy losses to respiration.
NPP equation?
GPP-Respiratory losses=NPP
What is the equation for the net production of consumers?
N = I - (F + R)
Where:
I = the chemical energy store in ingested food
F = the chemical energy lost to the environment in faeces and urine
R = the respiratory losses to the environment
How to calculate the percentage efficiency of energy transfer?
Percentage efficiency= productivity of trophic level divided by energy available from the trophic level below times 100.
Define net production of consumers?
Net production of consumers is the energy stored as new biomass by consumers when ingesting energy.
How can biomass be measured?
Measuring the mass of carbon of a given area.
Using a bomb calorimetry. Where you take a known dry biomass sample and burn the sample in a bomb calorimeter.
Then the heat released from this warms a known value of water and measuring the temperature change of the water allows the energy released to be calculated using a specific heat capacity equation.
Different bacteria for steps of nitrogen cycle?
Nitrobacter convert nitrite to nitrate whilst nitrosomonas convert ammonium ions into nitrite.
Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle?
Firstly nitrogen gas is converted into ammonia by mutualistic nitrogen fixing bacteria in plants which take up ammonia and free living nitrogen fixing bacteria which release ammonia into the soil this is called nitrogen fixation.
Then ammonia is converted into ammonium ions when released into the soil and it is also released into the soil when saprobionts break down organic matter through ammonification.
The ammonium ions are converted into nitrite by nitrifying bacteria (nitrosomonas) through nitrification and then nitrifying bacteria (nitrobacter) convert nitrite into nitrate and this process is known as nitrification.
After this nitrate is taken up by plants and denitrifying bacteria convert nitrate into nitrogen gas which is released into the atmosphere when anaerobic conditions are present.
Describe the process of eutrophication
Firstly fertilisers leak into bodies of water causing algae to grow rapidly in an algal bloom.
This causes the light to be blocked for other marine plants so they die and are broken down by saprobionts who use up oxygen.
This leads to there being too little oxygen in the ecosystem leading to organisms dying which breaks down the ecosystem.
What is the role of mycorrhizae?
Mycorrhizae is a fungus which is present in the roots of plants and increases the surface area to volume ration enabling the plant to increase uptake of inorganic ions and water in return for sugars.
What are phosphate containing compounds?
ATP and DNA and RNA.
Describe the steps of the phosphate cycle?
Phosphate is present in the soil due to the weathering of rocks by rainfall.
This phosphate is taken up by plants to form phosphate containing compounds such as DNA and ATP.
When plants die and consumers which consume phosphate from plants to form their own phosphate containing compounds die their organic material with phosphate containing compounds are broken down by saprobionts and released into the soil.
This phosphate can then be taken up by plants again.
Also phosphate enters bodies of water and over thousands of years it is used to form new rocks containing phosphates.
What are nitrogen containing compounds?
DNA
RNA
Amino acids
What does IAA do differently?
Inhibits cell elongation in roots and induces cell elongation in shoots.
How does positive phototropism work?
IAA moves away from light so more elongation occurs on this side so a bend towards light occurs.
How does positive gravitropism occur?
IAA moves towards gravity downwards so this side of the root has cell elongation inhibited to a larger extent so a bend towards the forces of gravity occurs.
Difference between taxis and kinesis?
Taxis is a directional movement of part of a plant in response to a stimulus where kinesis is a non-directional movement where speed and rate of turning change in response to environmental conditions where the severity of the conditions influences the rate of movement.
What is the advantage of a simple reflex arc?
The main advantage of simple reflexes is rapid, automatic protection from harm, allowing the body to react instantly to dangerous stimuli like heat or sharp objects before the brain consciously processes the danger.
This is the three-neuron reflex enabling response to a stimulus?
A three-neuron reflex arc involves a receptor, a sensory neuron, an interneuron (relay neuron), a motor neuron, and an effector, forming a rapid pathway for involuntary actions like pulling your hand from a hot surface
Where does the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis occur?
On the thylakoid membrane
Role of chlorophyll in light dependent reaction?
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy causing electrons (from water) to become excited.
When temperature is discussed as a limiting factor what is the main purpose of this?
The enzyme activity of rubisco.
Where are protons released?
Protons are pumped into the intermembrane space, not released generally.
Difference between taxis and kinesis?
Taxis is a directional movement in response to a stimulus
Kinesis is a non-directional response to environmental conditions which influences rate of turning and speed of movement.
What is depolarization peak?
+40Mv
What are the differences between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres?
Fast muscle fibres rely on anaerobic respiration for ATP AND slow muscle fibres rely on aerobic respiration for ATP;
Fast muscle fibres have fewer mitochondria AND slow muscle fibres have many mitochondria;
Fast muscle fibres have large concentrations / stores of phosphocreatine AND slow muscle fibres have small concentrations / stores of phosphocreatine;
Fast muscles fibres fatigue faster AND slow muscles fibres fatigue slower;
More lactate is produced in fast muscle fibres AND less lactate is produced in slow muscle fibres;
What are phosphocreatine stores used for in muscles?
To provide phosphate ions for the production of ATP to be used in muscles for muscle contraction
Why is phosphocreatine reformation slower in older animals?
This is because fast twitch muscle fibres through fast and high energy providing contractions rapidly use up phosphocreatine stores. These stores are regenerated slower as older animals have a slower metabolic rate so less ATP is converted to phosphocreatine.
How is ATP converted to phosphocreatine?
When muscles are at rest during low activity of muscles excess ATP is used to convert creatine back into phosphocreatine which restores stores.
What is the sequence for the digestion of proteins?
Firstly proteins than polypeptides than dipeptides and than amino acids.
The enzyme endopeptidase hydrolyse central peptide bonds converting proteins to polypeptides.
Exopeptidase hydrolyses peptide binds at the ends of polypeptide chains converting them to dipeptides.
Dipeptidases an enzyme converts dipeptides to amino acids.
What is the formula to work out the number of possible chromosome combinations after random fertilization?
2 to the power of the number of homologous pairs and this number is squared.
How does independent segregation cause genetic variation?
Randomly arranging and separating homologous chromosome pairs during meiosis ensures that daughter cells have a random mix of paternal and maternal genetic material.
What are the steps of the cardiac cycle?
Diastole- the phase of the heartbeat where the muscles relax allowing the heart to fill with blood
Atrial systole where the atria contract pumping blood into the ventricles.
Ventricular systole where the ventricles contract pumping blood into the relaxed atria.
What does myogenic mean?
The muscle initiates its own contraction.
What initiates atrial systole?
The sinoatrial node generates electrical impulses which travel across the atria. These are sometimes called a wave of depolarization.
What happens whist the atria contract with electrical impulses?
The impulses released by the sinoatrial node travel to the atrioventricular node.
Then there is a brief delay allowing the ventricles to fill with blood and then the atrioventricular node sends electrical impulses to the bundle of his.
The bundle of his is made up of purkyne tissue which the electrical impulses follow to the bottom of the heart and trigger ventricular contraction from the bottom upwards ensuring max blood is pumped by ventricles.
How is resting heart rate controlled?
The sinoatrial node (SAN) generates electrical impulses, which trigger the atria to contract.
While the atria are contracted, the electrical impulses reach the atrioventricular node (AVN).
There is a brief delay of approximately 1/10th of a second, and this allows time for the ventricles to fill up.
After the delay, the atrioventricular node sends the electrical impulses along the bundle of His, which is made up of Purkyne tissue.
The electrical impulses reach the Purkyne tissue at the base of the ventricles. This triggers the ventricles to contract from the base upwards.
Why don’t the atria and ventricles contract at the same time?
There is a wall of non-conductive tissue between the atria and ventricles to prevent electrical impulses released by the sinoatrial node causing both to contract.
What causes high and low blood glucose concentration and what are issues?
Exercise will decrease blood glucose concentration. Low blood glucose concentration means that cells cant carry out respiration.
Eating food will increase blood glucose concentration which means that the water potential of the blood drops and water moves out of cells.
What detects blood glucose concentration?
Islets of langerhans in the pancreas.
What is released when blood glucose is high and low?
Glucagon is released when blood glucose is low and insulin is released when blood glucose is high.
What detects a decrease in blood glucose concentration?
Alpha cells which are located in islet of langerhans which release glucagon.
What detects an increase in blood glucose concentration?
Beta cells and they release insulin in response
How does insulin decrease blood glucose concentration?
Insulin binds to complementary insulin receptors on the cell
This causes vesicles to move to the membrane which contain additional glucose channel proteins.
These fuse with the membrane and add the glucose channel proteins to it allowing more glucose to enter the cell.
How else does insulin decrease blood glucose concentration?
It binds to complementary insulin receptors on liver cells.
This activates enzymes inside the cell which catalyse the conversion of glucose into glycogen.
This is because glycogen is larger and easier to store and can be converted easily back to glucose. Also, it decreases blood glucose concentration in the cell meaning more glucose enters the cell.
What is converting glucose to glycogen called?
Glycogenesis
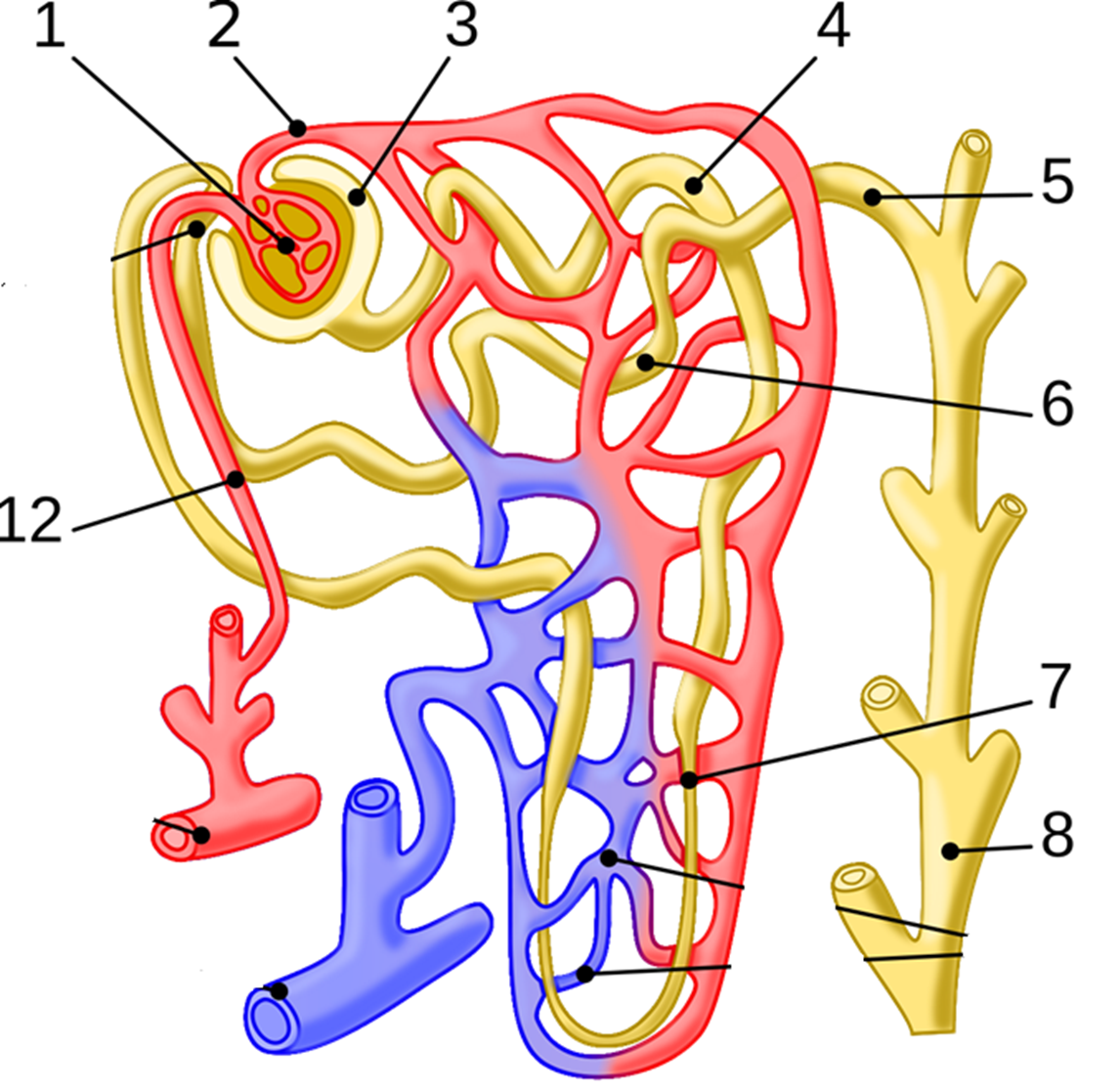
Label each structure?
•1. Glomerulus,
•2. Efferent arteriole,
•3. Bowman’s capsule,
•4. Proximal convoluted tubule,
•5. Cortical collecting duct,
•6. Distal convoluted tubule,
•7. Loop of Henle,
•8. Collecting duct,
•12. Afferent arteriole
How does adrenaline impact blood glucose concentration?
Adrenaline binds to complementary adrenaline receptors on the outside of liver cells
This activates the enzyme adenlyate cyclase which converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP binds to protein kinase to convert glycogen to glucose through glycogenesis
What is the enzyme which is stimulated by adrenaline and glucagon and how to rememeber?
Adenylate cyclase
Aden Why Late - Cycle lanes
What does glucagon and adrenaline do?
Stimulates the conversion of glycogen to glucose through glycogenolysis which raises blood glucose concentration. Whilst only neoglycogenesis only occurs for glucagon.
What does insullin do?
It converts glucose to glycogen through glucogenesis and neoglucogenesis involing the conversion of useful molecules such as amino acids to glucose
What are the different messangers in how glucose and adrenalin impact blood glucose concentration?
The first messanger is adrenalin for adrenalin and glucagon for glucagon
The second messanger is cAMP for both which adenylate cyclase converts ATP into and this stimulates protein kinase
What does glucagon do?
Glycogenolysis as it converts glycogen to glucose increasing the blood glucose concentration
Glyconeogenesis as it converts other organic substances into glucose as well.
How can type 2 diabetes occur?
The beta cells lose their sensitivity to insulin for instance
This causes the pancreas to not be able to secrete insulin
Thus resulting in the blood glucose concentration not being regulated
Define homeostasis
The maintaince of a stable internal environment within a designated range.
What produces ADH?
Osmoreceptors in hypothamalus
What detects a change in water potential?
Osmoreceptors in hypothamalus
Where is ADH secreted?
Posterior pituraity gland
What does ADH do?
Regulates the water potential of the blood through negative feedback.
Other than ADH how does the body increase water potential?
Osmoreceptors in the hypothamalus stimulate feelings of thrist
This causes the body to want to take in more water