Adrenergic antagonists
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
alpha receptors: CV systems
alpha 1 receptors are located on arterial and venous smooth muscle
endogenous NT is NE and Epi (SNS)
normally there is underlying sympathetic tone at arteries and veins that control BP
so blockade of alpha receptors in normal and hypertensive patients will cause vasodilation and decrease BP
alpha receptors: Urinary system
urination is controlled by a PSNS/SNS balance
M3 receptors cause contraction of detrusor and relaxation of the sphincters to cause micturition (PSNS)
beta 2 receptors cause relaxation of the detrusor and alpha 1 receptors cause contraction of the sphincters to prevent micturition (SNS)
Blockade of alpha 1 receptors reduces the constriction and sphincter tone allowing urine to flow more freely
BPH (Benign Prostatic hyperplasia)
a condition in which the prostate grows in size
this places pressure on the urethra and bladder neck making urination difficult and incomplete
non-selective alpha antagonists
Phentolamine and Phenoxybenzamine
both block alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors
alpha 2 receptors are located presynaptically and their role when activated is to decrease the amount of NE release. Blockade of alpha 2 will cause an increase in NE release
Non-selective alpha antagonists: clinical limitations
vasodilation can cause activation of the baroreceptor reflex resulting in reflex tachycardia
phentolamine and phenoxybenzamine exaggerate the reflex tachycardia because they block alpha 2 receptors causing more NE to be released in the synaptic cleft
Prazosin: MOA/kinetics
selective alpha 1 antagonist (1000x more potent at alpha 1)
vasodilates venous blood vessels which decreases venous return to the heart to reduce CO
may have a CNS effect to inhibit SNS outflow and inhibit baroreceptor reflex
DOA = 10h (BID dosing)
Tx HTN (also effective in BPH)
Prazosin: counseling points
First dose phenomenon: up to 50% of patients experience syncope and/or orthostatic hypotension with the first dose
Take first dose at bedtime or remain recumbent for a few hours
dosing started low and is slowly titrated up
large dose changes/addition of antihypertensive agent can cause reoccurrence of syncope
nasal stuffiness is common
Terazosin/Doxazosin
selective alpha 1 antagonist
both have similar profiles as prazosin
BPH: may be an advantage, both appear to cause induction of apoptosis of prostate cells
Tx BPH
Alfuzosin
- selective alpha 1 antagonist (not approved for HTN Tx)
Tamsulosin/Silodosin
- alpha 1A selective, which appears to be located on the smooth muscle of prostate cells and bladder neck and trigone sphincter
- effect on urine flow is seen within the first few doses
- minimal effects on BP and syncope
Yohimbine
alpha 2 antagonist
increases SNS outflow and potentiates the actions of NE by blocking negative feedback on release
Not really used clinically
Beta-blocker characteristics
Selectivity (can reduce side effects)
Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (partial agonist)
Membrane stabilizing activity (local anesthetic-like effect, may be helpful in treating arrythmias)
alpha - blocking activity (another benefit to reducing BP)
lipid solubility (CNS penetration can be advantage or disadvantage)
isoproterenol
beta 1/beta 2 agonist
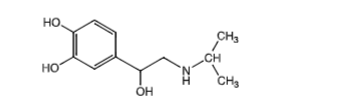
Propranolol
nonselective beta blocker
classic/standard beta blocker
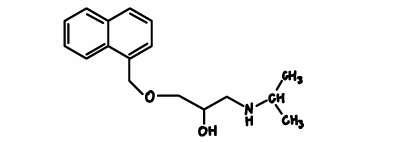
Atenolol
beta blocker
beta 1 selective
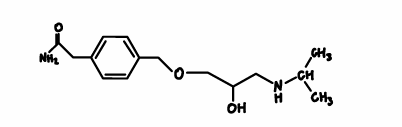
Metoprolol
beta blocker
beta 1 selective
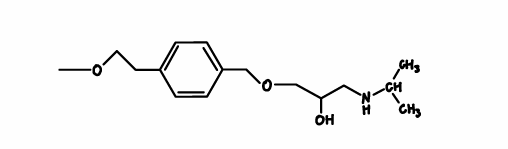
Pindolol
nonselective beta blocker
has ISA
beta 2 effects on the heart
Stimulation: increased chronotropy, ionotropy, and dromotropy (increased CO, HR/BP)
Blockade: decreased chronotropy, ionotropy, and dromotropy (decreased CO)
Beta 2 effects on the kidney
stimulation: increased renin secretion (increased fluid retention, BP)
blockade: decreased renin secretion (Decreased plasma volume and BP)
Beta 2 stimulation
vascular smooth muscle: vasodilation
bronchial smooth muscle: bronchodilation
liver: glycogenolysis
beta 2 blockade
vascular smooth muscle: small vasoconstriction
bronchial smooth muscle: bronchoconstriction
liver ???
not a big player in BP control
Effects of beta blockers: CV system
HR
- effect on resting HR is dependent on SNS tone
- typically have little effect on resting HR
- greatest effect seen during stress/exercise (less stamina, less endurance bc HR cannot rise)
BP
- initially rises then returns to baseline
Kidney
- tends to reduce renin secretion (beta 1 receptors)
beta blockers: metabolic effects
beta 2 receptors cause glycogenolysis and release of glucose
non-selective beta blockers can impair T1D patients’ ability to recover from hypoglycemia (can also mask the symptoms) - use with caution in patients with uncontrolled diabetes
nonselective beta blockers have an adverse effect on lipid profile
beta blockers: respiratory system effects
little effect on respiratory function on normal people
non selective beta blockers can produce life threatening bronchoconstriction in patients with asthma or COPD
beta 1 selective antagonists with ISA are safer but still carry risk
labetolol
nonselective beta blocker
alpha 1 antagonist
has additional CV effects
Carvedilol
nonselective beta blocker
alpha 1 antagonist
anti-inflammatory actions that may have cardioprotective actions