Organizational Psych
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:25 PM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
1
New cards
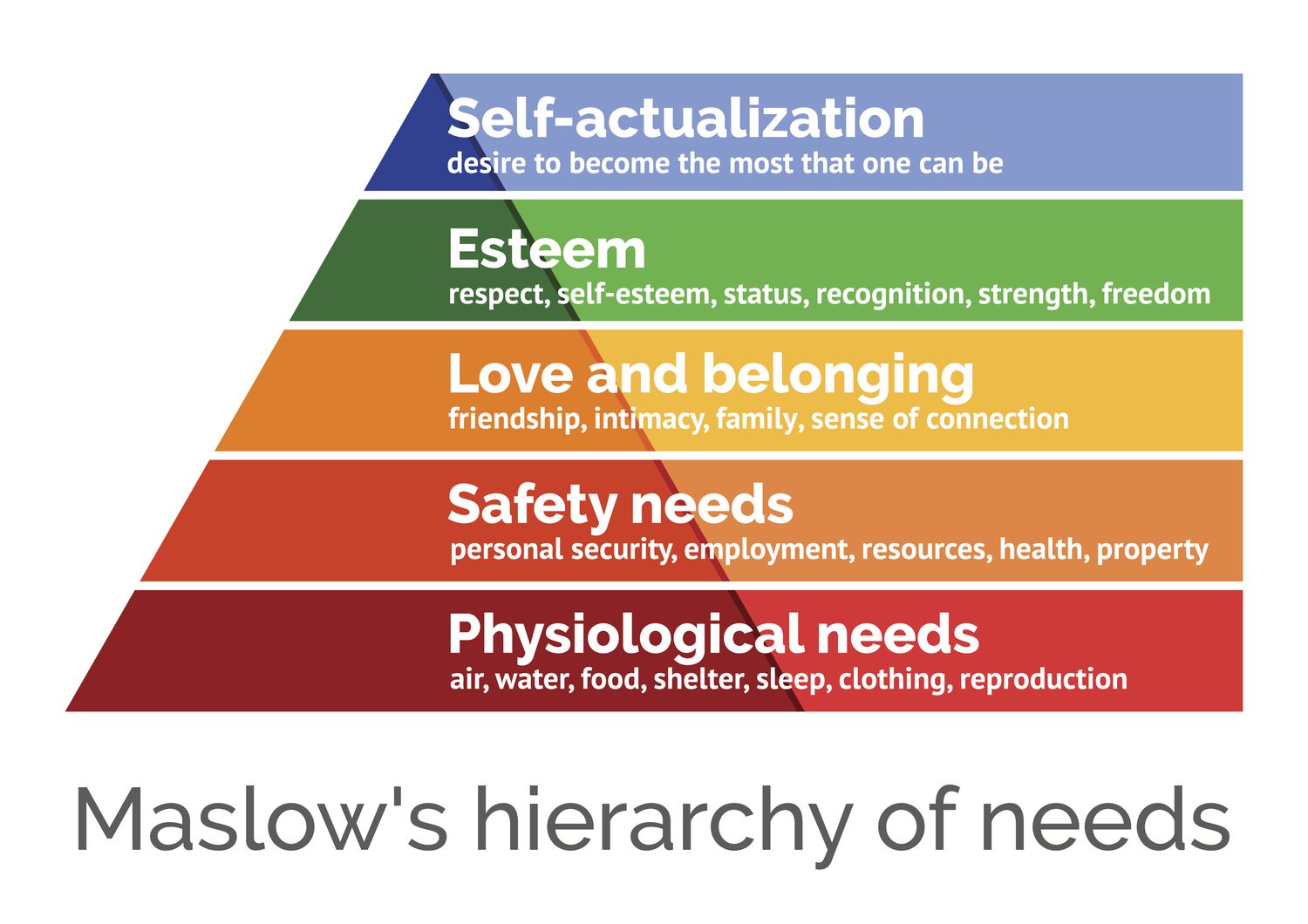
maslov’s need theory
* people are motivated by need
* arranged in hierarchy
* motivated by lowest-level unmet need
* arranged in hierarchy
* motivated by lowest-level unmet need
2
New cards
herzberg’s need theory
* simplified maslov’s theory
* hygiene needs and motivator needs
* provide motivation needs to motivate employees
* hygiene needs and motivator needs
* provide motivation needs to motivate employees
3
New cards
hygiene need
animal nature of humans, physiological needs
4
New cards
motivator need
psychological growth
5
New cards
alderfelder’s need theory
* ERG- existence, relatedness, growth needs
* development of maslov’s theory
* development of maslov’s theory
6
New cards
equity theory
* people compare their inputs and outputs, motivated to achieve fairness/equity
* compare their ratio with others’
* compare their ratio with others’
7
New cards
how to solve inequality
* decrease input
* change input of person being compared
* change results (ex. talk to boss)
* compare with others output
* rationalize inequality
* compare with another colleague
* leave job
* change input of person being compared
* change results (ex. talk to boss)
* compare with others output
* rationalize inequality
* compare with another colleague
* leave job
8
New cards
expectancy theory
* when/why reinforcement leads to behavior
* expecting a reward leads to increased effort
* expecting a reward leads to increased effort
9
New cards
vroom’s equation
force = expectancy × ∑ (valences × instrumentalities)
10
New cards
force
amount of motivation needed
11
New cards
expectancy
probability of performance
12
New cards
valence
value of outcome
13
New cards
instrumentality
probability that behavior leads to reward
14
New cards
self-efficacy theory
* motivation/performance determined by how effective individual believes they can be
* concerned with general feeling of capability
* concerned with general feeling of capability
15
New cards
galatea effect
confidence in skills leads to better performance
16
New cards
goal setting theory
* setting goals leads to motivation
* motivated by internal intentions, objectives, or goals
* motivated by internal intentions, objectives, or goals
17
New cards
learning oriented goal
internally motivated
18
New cards
performance oriented goal
externally motivated
19
New cards
job characteristics theory
* hackman and oldham
* people are motivated by nature of tasks
* jobs lead to satisfaction, motivation, and task performance
* people are motivated by nature of tasks
* jobs lead to satisfaction, motivation, and task performance
20
New cards
core characteristics of jobs and what they lead to
* skill variety, task identity, task significance → experienced meaningfulness
* autonomy → experienced responsibility
* feedback → knowledge of results
* autonomy → experienced responsibility
* feedback → knowledge of results
21
New cards
motivational potential score (MPS)
(Skill Variety + Task Significance + Task Identity) / 3 × Autonomy × Feedback
22
New cards
growth need strength
need for fulfillment of higher-order needs (high GNS fits high MPS jobs)
23
New cards
job analysis
trying to find out what an employee needs from a job
24
New cards
job-oriented procedure
focuses on work itself
25
New cards
worker-oriented procedure
focuses on describing psychological/behavioral requirements of the job
26
New cards
validity
does the test measure what it is intended to measure
27
New cards
criterion validity
measures whether there’s a relationship between test and what it’s meant to measure
28
New cards
predictive validity
measure that shows how much we can predict something in future
29
New cards
concurrent validity
prospects tested based on predictor data obtained from current employees
30
New cards
construct validity
how well test measures what its meant to measure
31
New cards
convergent validity
measures extent to which measurement is related to another
32
New cards
divergent validity
measures how 2 tests differentiate between each other
33
New cards
increment validity
when selection process combines 2+ predictors
34
New cards
faith validity
when organization believes their predictive is acceptable and valid
35
New cards
content validity
how fully a test represents what it needs to measure
36
New cards
face validity
measures whether test procedure looks good to interviewee
37
New cards
reliability
consistency under various circumstances
38
New cards
test-retest reliability
same results on same test on different occasions
39
New cards
parallel forms
strong correlation between 2 equivalent tests
40
New cards
internal reliability
different parts of the same measure produce similar, consistent results
41
New cards
selection instrument relaibility
whether instrument has consistent measurement under variant conditions
42
New cards
adverse impact
certain requirement difficult for certain minority to achieve
43
New cards
direct discimination
treating individual less favorably because of background
44
New cards
indirect discrimination
unintentional discrimination based on biological predispositions
45
New cards
structured interview
interview has same questions for each applicant
46
New cards
situational interview
interviewee presented with hypothetical situation
47
New cards
behavioral interview
interviewee asked to describe previous relevant behavior
48
New cards
unstructured interview
interviewer asks questions that come to mind
49
New cards
psychological tests used in job selection
* intelligence tests
* personality tests
* interest tests
* personality tests
* interest tests
50
New cards
personnel selection methods
* psychological tests
* biodata
* work samples
* assessment centres
* \
* biodata
* work samples
* assessment centres
* \
51
New cards
unstructured interview validity
* predictive validity: low
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: inconclusive
* adverse impact: high
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: inconclusive
* adverse impact: high
52
New cards
structured interview validity
* predictive validity: very high
* face validity: positive-moderate
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
* face validity: positive-moderate
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
53
New cards
cognitive testing validity
* predictive validity: high
* face validity: negative-moderate
* construct validity: clear
* adverse impact: high
* face validity: negative-moderate
* construct validity: clear
* adverse impact: high
54
New cards
personality testing validity
* predictive validity: moderate
* face validity: negative-moderate
* construct validity: clear
* adverse impact: low
* face validity: negative-moderate
* construct validity: clear
* adverse impact: low
55
New cards
biodata validity
* predictive validity: moderate
* face validity: moderate
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
* face validity: moderate
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
56
New cards
work sample validity
* predictive validity: high
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
57
New cards
assessment centre validity
* predictive validity: moderate
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
* face validity: positive
* construct validity: unclear
* adverse impact: low
58
New cards
great man theory
a trait approach, studied great men of past for their traits
59
New cards
trait approach leadership
people have intrinsic traits that make them better leaders
60
New cards
behavioral approach leadership
behavior of leader is more important than trait or situation
61
New cards
participative leadership style
asks for advice, has discussions
62
New cards
autocratic leadership style
makes a decision individually and announces it
63
New cards
consideration
amount of concern supervisor shows for welfare of subordinates
64
New cards
initiating structure
extent to which supervisor defines roles and expectations
65
New cards
Ohio State Leadership Studies
defined consideration and initiating structure as leadership dimensions
66
New cards
fielder’s contingency theory
* characteristics of people will make them good leaders, behaviors will be effective regardless of situation
* leadership is a function of person and situation
* leadership is a function of person and situation
67
New cards
situational control
amount of influence leader has over subordinates
68
New cards
3 characteristics that make up situational control
* leader-member relations
* task structure
* position power
* task structure
* position power
69
New cards
leadership grid
* situations call for different leadership styles
* 2 axes: concern for results (CR) and concern for people (CP)
* 2 axes: concern for results (CR) and concern for people (CP)
70
New cards
leadership grid leadership styles
* country club (high CP, low CR)
* impoverished (low CP, low CR)
* middle (middle CP, middle CR)
* team (high CP, high CR)
* authority compliance (low CP, high CR)
* impoverished (low CP, low CR)
* middle (middle CP, middle CR)
* team (high CP, high CR)
* authority compliance (low CP, high CR)
71
New cards
situational leadership theory
* 2 axes, ability and willingness/confidence of subordinate
* each combination requires different leadership style
* unable unwilling→ direct
* unable willing→ coach
* able unwilling→ support
* able willing→ delegate
* each combination requires different leadership style
* unable unwilling→ direct
* unable willing→ coach
* able unwilling→ support
* able willing→ delegate
72
New cards
path-goal theory
* job performance and satisfaction come from situational and subordinate characteristics
* 4 styles: supportive, directive, participative, achievement
* 4 styles: supportive, directive, participative, achievement
73
New cards
locus of control
extent to which subordinates believe they can control rewards in their lives
74
New cards
self-perceived ability
extent to which subordinate believes they’re capable of a specific task
75
New cards
full range leadership model
leadership styles can be understood by 2 axes: involvement of leader, and effectiveness of leader
76
New cards
leader-member exchange theory
* supervisors treat individual subordinates differently based on ingroup/outgroup
* ingroup is trusted, participative style
* outgroup has directive style
* ingroup is trusted, participative style
* outgroup has directive style
77
New cards
transactional leadership
utilizes punishment and reward for motivation of subordinates
78
New cards
laissez-faire leadership
absence of leadership
79
New cards
management by exception
transactions are primarily negative, responding only to mistakes
80
New cards
passive management
mostly ignore subordinates unless there is a mistake
81
New cards
active management
actively looks for and prevents mistakes before they happen
82
New cards
contingent reward
positive transaction, goals and contingent feedback based on behavior
83
New cards
transformational leadership
focuses on charismatic leaders
84
New cards
4 components of transformational leadership
* inspirational motivation: providing vision
* intellectual stimulation: encouraging followers to question things
* individualized consideration: paying attention to development and wellbeing of followers
* idealized influence: extent to which leaders encourage followers
* intellectual stimulation: encouraging followers to question things
* individualized consideration: paying attention to development and wellbeing of followers
* idealized influence: extent to which leaders encourage followers
85
New cards
vroom-yetton model
indicates best approach to decision making in particular situations
86
New cards
conflict
a process in which an individual or a group perceive another individual or group as hindering for their goal
87
New cards
4 types of conflict perspectives
* unitarian perspective
* pluralistic perspective
* interactionist perspective
* radical perspective
* pluralistic perspective
* interactionist perspective
* radical perspective
88
New cards
unitarian perspective
everyone drives for the same goal and conflict gets in the way of the goal
89
New cards
pluralistic perspective
view conflict as natural, conflict might be beneficial
90
New cards
interactionist perspective
conflict is necessary for improvement
91
New cards
radical perspective
conflict is seen as an inevitable part of capitalism
92
New cards
functional conflict
can stimulate a group (ex. devil’s advocate)
93
New cards
dysfunctional conflict
creates hostility and hinders group progress
94
New cards
cognitive conflict
can be solved on an intellectual
95
New cards
affective conflict
emotional investment in conflict
96
New cards
individual conflict
frustration when not achieving personal goals or when values clash with work task
97
New cards
group conflict
institutionalized conflict, groups fight. over resources
98
New cards
sources of conflict
* communication
* structure
* ambiguity
* interdependence
* sequential
* pooled
* reciprocal
* change to structure and processes
* rewards
* organization size and specialization
* leadership
* personal factors
* structure
* ambiguity
* interdependence
* sequential
* pooled
* reciprocal
* change to structure and processes
* rewards
* organization size and specialization
* leadership
* personal factors
99
New cards
selective perception
when someone says something, and you only process certain aspects and create your own understanding
100
New cards
structure conflict
the larger the group and stricter the specialization, the more prone to conflict