Chapter 9--Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, and Their Sulfur Analogs
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Naming Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
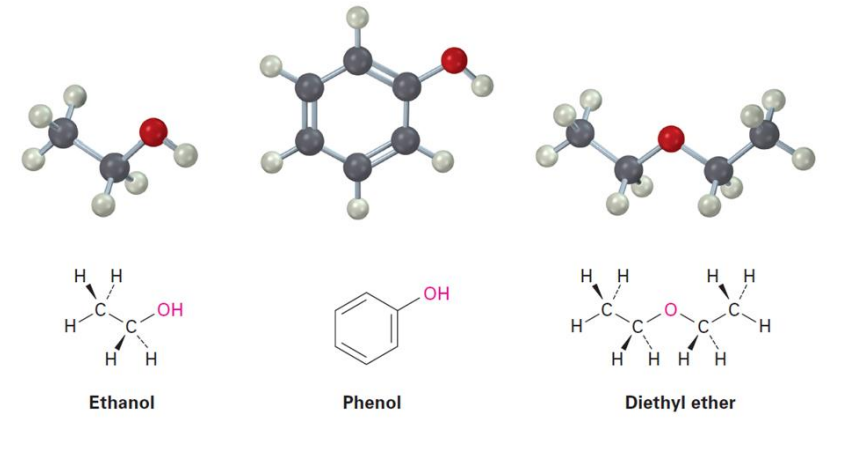
Alcohols
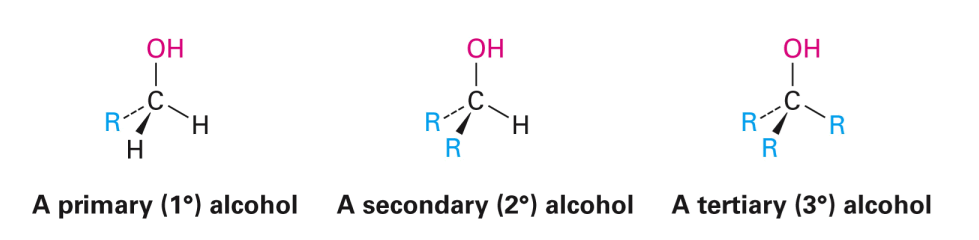
Naming Alcohols
1. Select the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group, and replace the -e ending of the corresponding alkane with -ol.
2. Number the carbons of the parent chain beginning at the end nearer the hydroxyl group.
3. Number all of substituents according to their position on the chain and write the name listing the substituents in alphabetical order and identifying the position to which the -OH is bonded. In diols, the -e is not removed (alkane-#, #-diol).
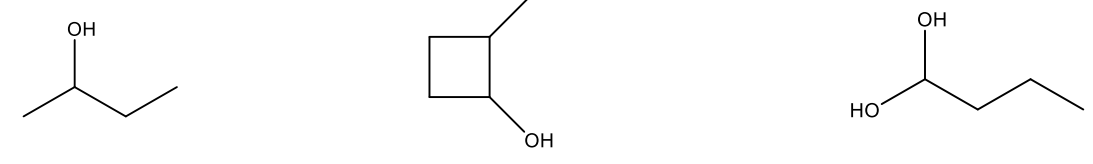
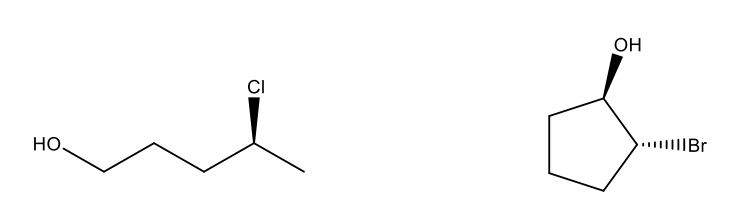
Give the IUPAC name for the following compounds, including stereochemistry.
(S)-4-chloropentan-1-ol
(1R,2R)-2-bromocyclopentan-1-ol
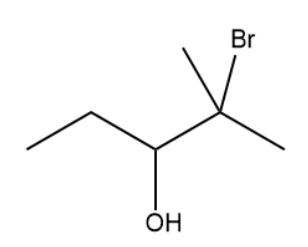
What is the IUPAC name of the following structure?
2-bromo-2-methylpentan-3-ol
Naming Phenols
Phenol gets names as parent, where the –OH group automatically gets the numbering of one.
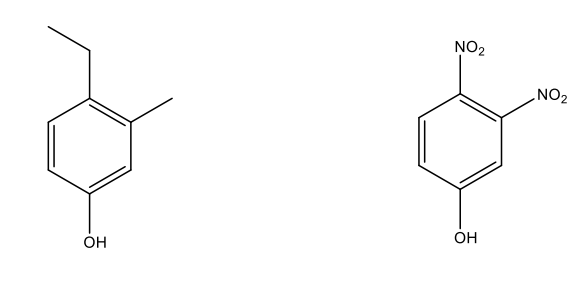
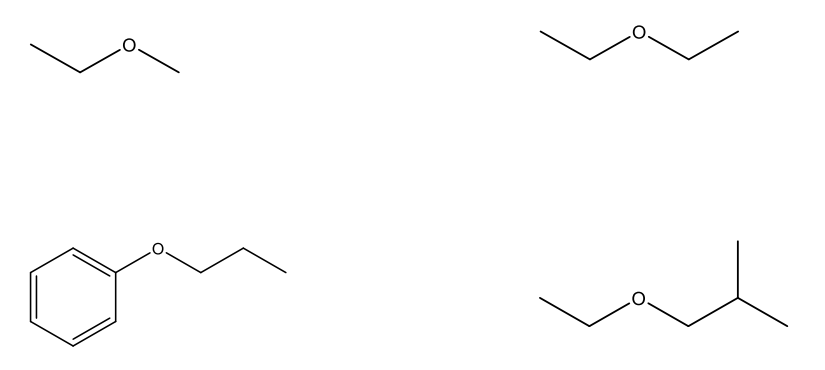
Naming Ethers
Identify the two alkyl groups bonded to the oxygen, list them alphabetically and follow with “ether”.
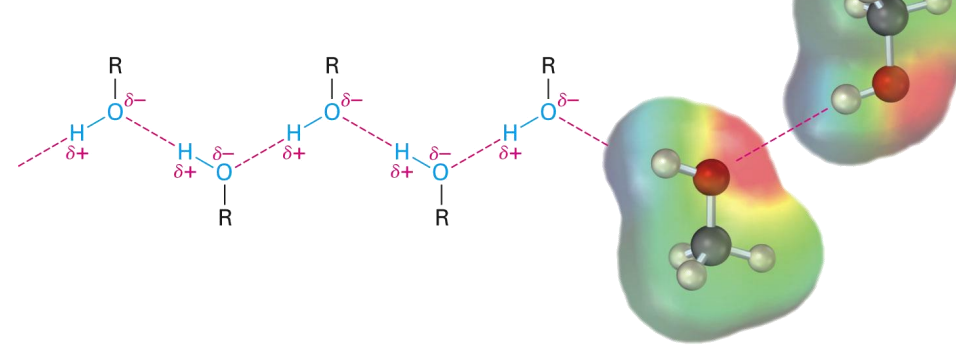
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols: Hydrogen Bonding
Alcohols and phenols can be thought of as derivatives of water
Higher boiling points than alkanes
Intermolecular forces H-Bonding!
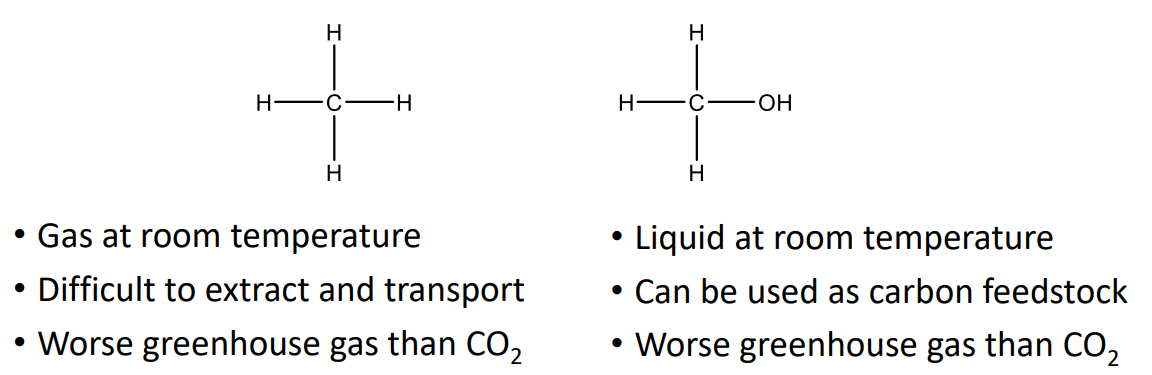
Science Big Challenges
“The holy grail of catalysis” – turning methane into methanol under ambient conditions using light. University of Manchester scientists developed MOF (metal-organic framework).
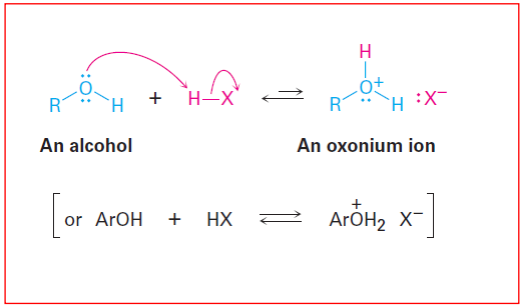
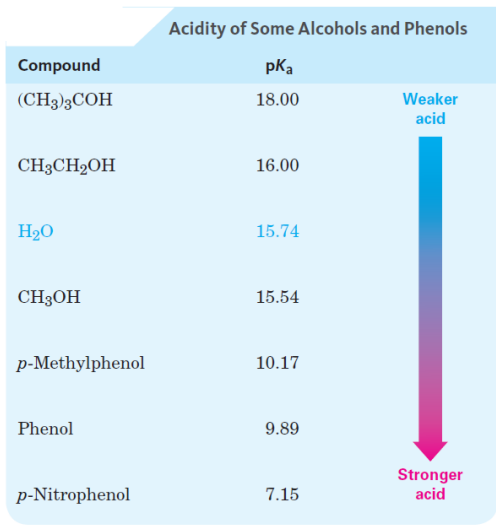
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols: Basicity: Weakly basic
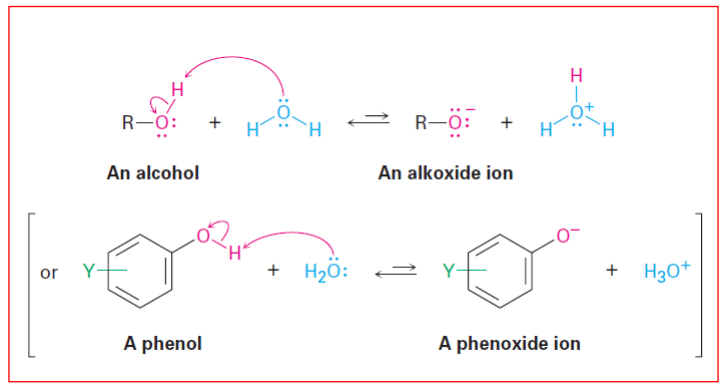
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols: Acidity 13: Weakly acidic
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols: Acidity chart
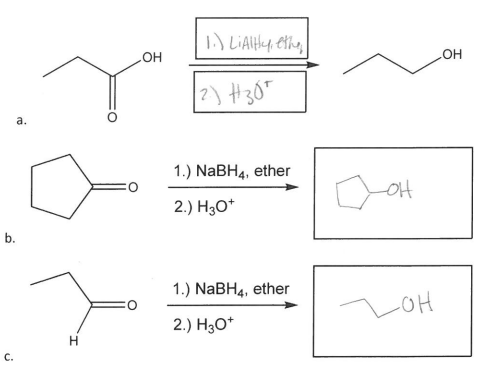
Synthesis of Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds
Reduction of carbonyl compounds
Aldehydes reduce to primary alcohols
Ketones reduce to secondary alcohols
Carboxylic acids and esters reduce to primary alcohols
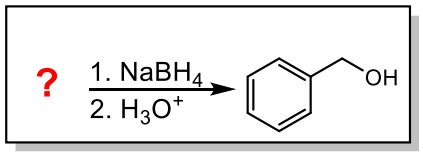
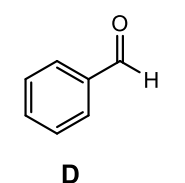
Which carbonyl compound would reduce to produce the following product?
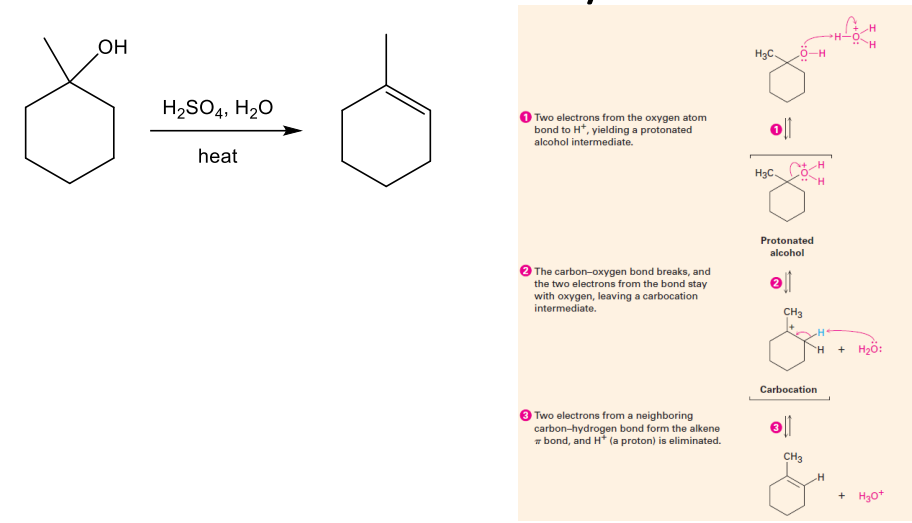
Reactions of Alcohols: Dehydration
Dehydration of Alcohols (elimination of water via –H and –OH from neighboring atoms)
Oxidation of Alcohols
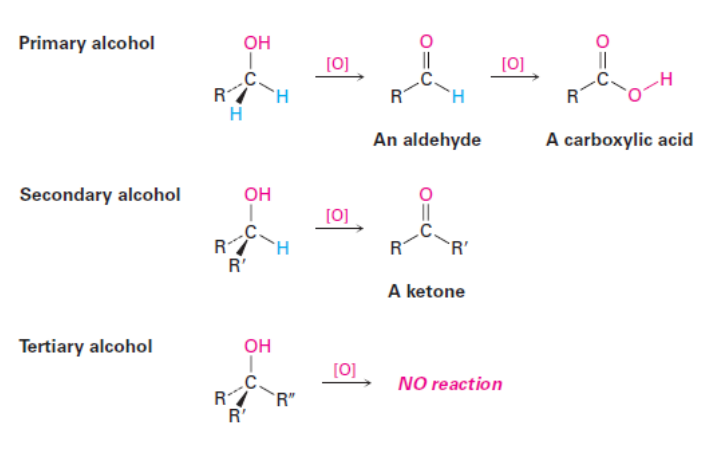
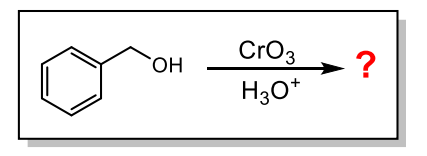
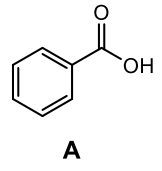
What is the product of the following reaction?
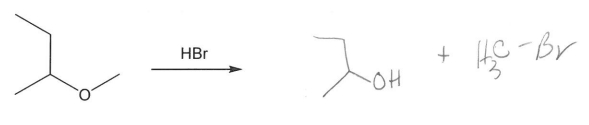
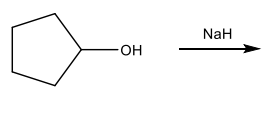
Conversion of Alcohols to Ethers
Synthesis of alkoxide salts from alcohols and NaH.
Williamson Ether synthesis:
Reactions of Phenols
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (previous chapter)
Substitutions using base and alkyl halide
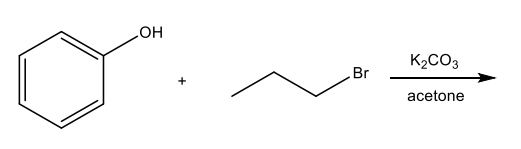
Reactions of Ethers
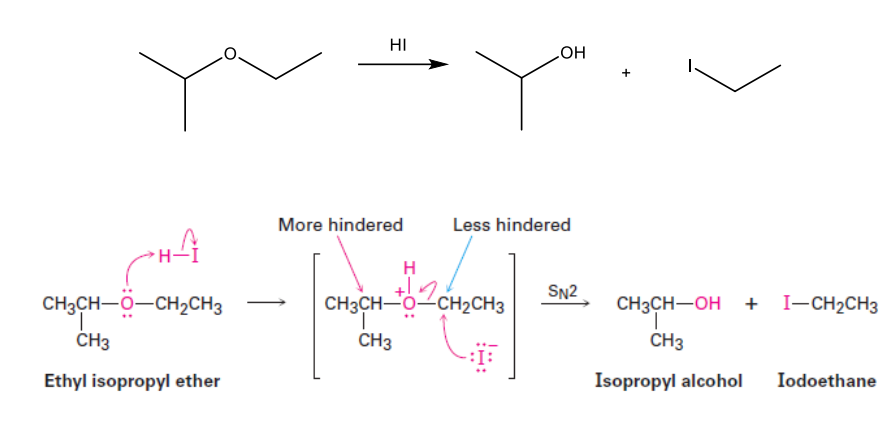
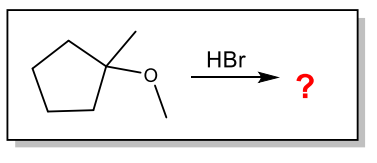
What are the products of the following reaction?
Cleave to make a more substituted alcohol
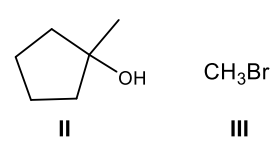
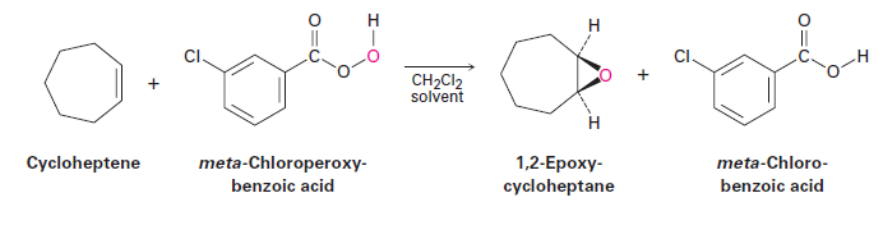
Epoxidation
Thiols and Sulfides Naming
Thiols are named like alcohols, except “-thiol” ending
Sulfides get named like ethers, except “sulfide at the ending

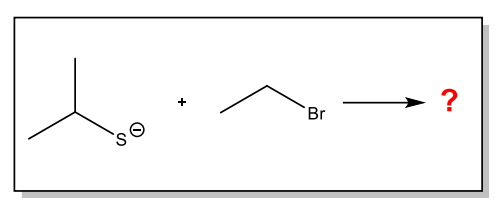
Give the IUPAC name of the product of the following reaction
Ethyl isopropyl sulfide
Naming Alcohols Rules
STEP 1: Name the parent compound. Find the longest chain that has the hydroxyl substituent attached (replace the -e ending with –ol).
STEP 2: Number the carbon atoms in the main chain. Begin at the end nearer the hydroxyl group, ignoring the location of other substituents. In a cyclic alcohol, the carbon that bears the –OH group is #1.
STEP 3: Write the name, placing the number that locates the hydroxyl group immediately before the parent compound name. In a cyclic alcohol the number “1” for the location of the –OH group is not needed.
Dialcohols, or diols, are often called glycols.
When the molecule has more than one alcohol group, the complete alkane name is used as you can see here (names in parenthesis).
Unsaturated alcohols Alcohol (hydroxyl) group takes precedence. Assign that carbon the lowest number.
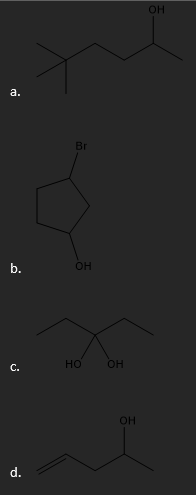
Give the IUPAC name for the following molecules.
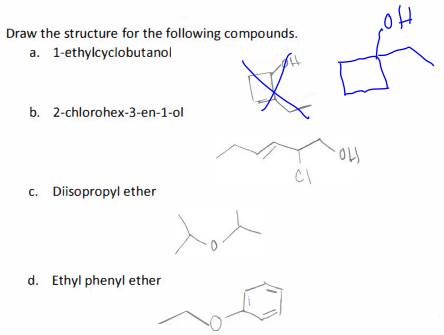
1. Draw the structure for the following compounds.
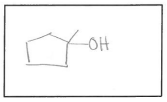
a. 1-ethylcyclobutanol
b. 2-chlorohex-3-en-1-ol
c. Diisopropyl ether
d. Ethyl phenyl ether
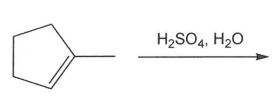
Draw the product for the following acid catalyzed addition of water to 1-methylcyclopentene.
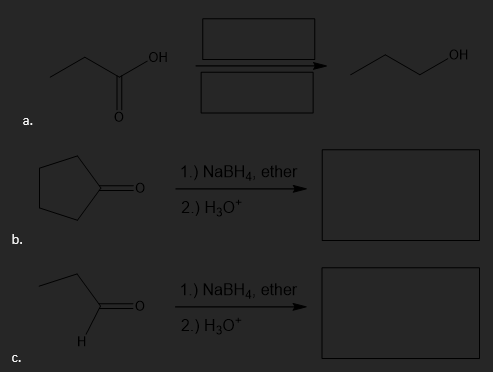
Fill in the indicated product or reagents for the following reduction reactions.
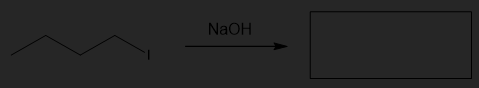
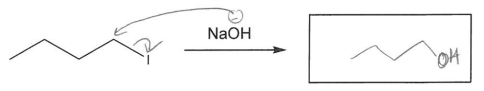
Predict the product for the following SN2 reaction.
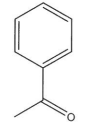
Draw the product for the reaction of the following ketone with CH3CH2MgBr.
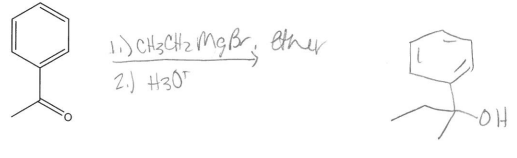
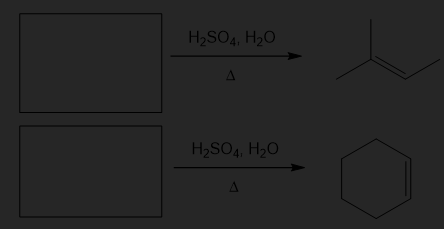
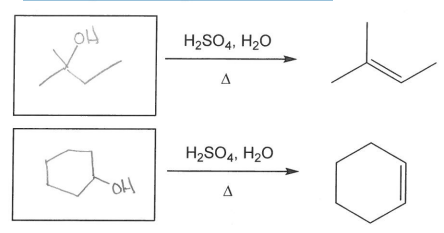
What alcohols might the following alkenes be made from?
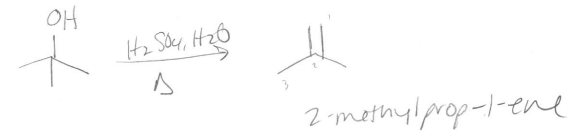
Give the IUPAC name for the product formed in the dehydration reaction of tert-butanol (2- methylpropan-2-ol).
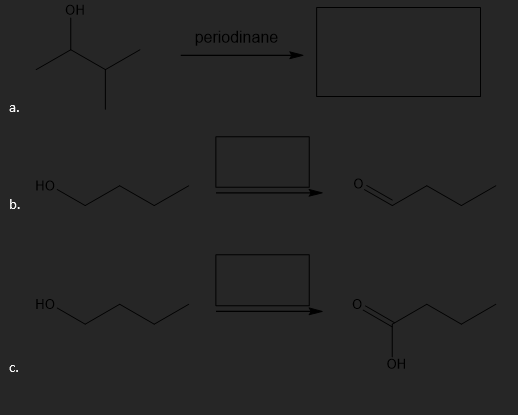
Fill in the missing reaction components (reactant, reagents, or product) for each of the following oxidation reactions.
What is the name of the product obtained with propan-1-ol reacts with sodium hydride (NaH), followed by 1-chloroethane?

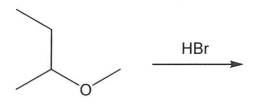
Draw and name the products for the following reaction.