PNB 2264 Lab Practical #2 Study Guide (mostly lab 8, brain +eye+ ear)
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
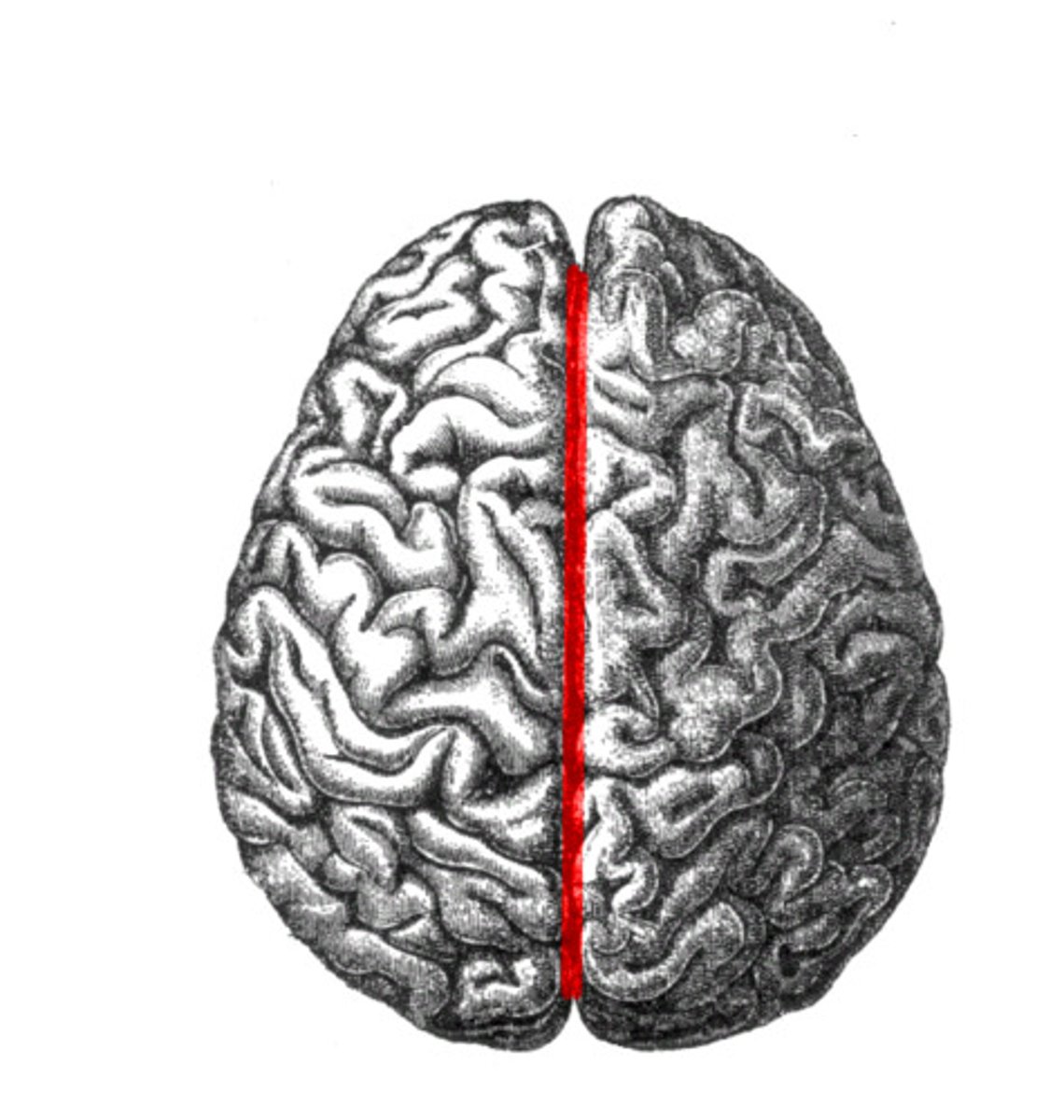
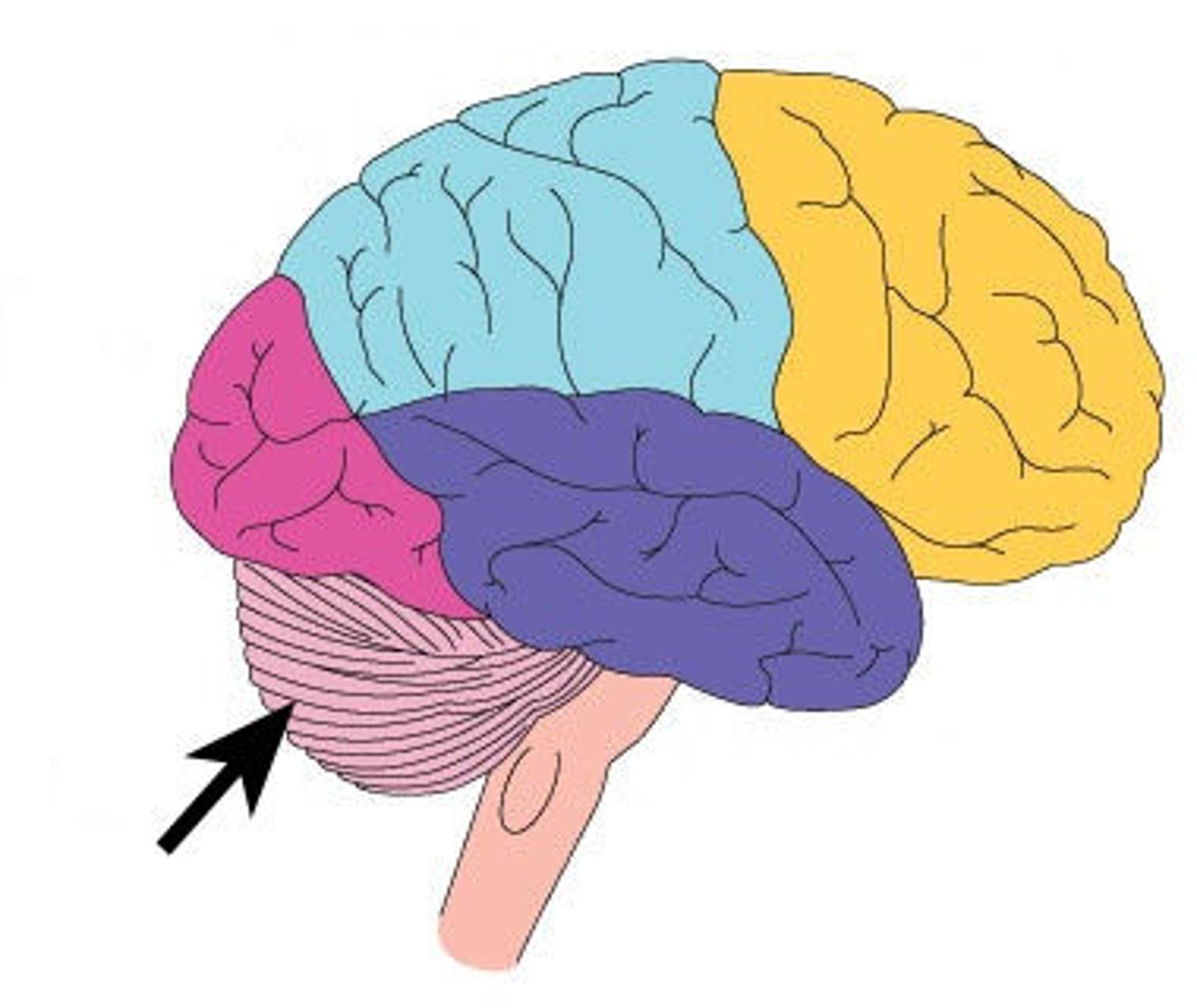
Superior Dorsal View of brain
Gyri
Sulci
Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure
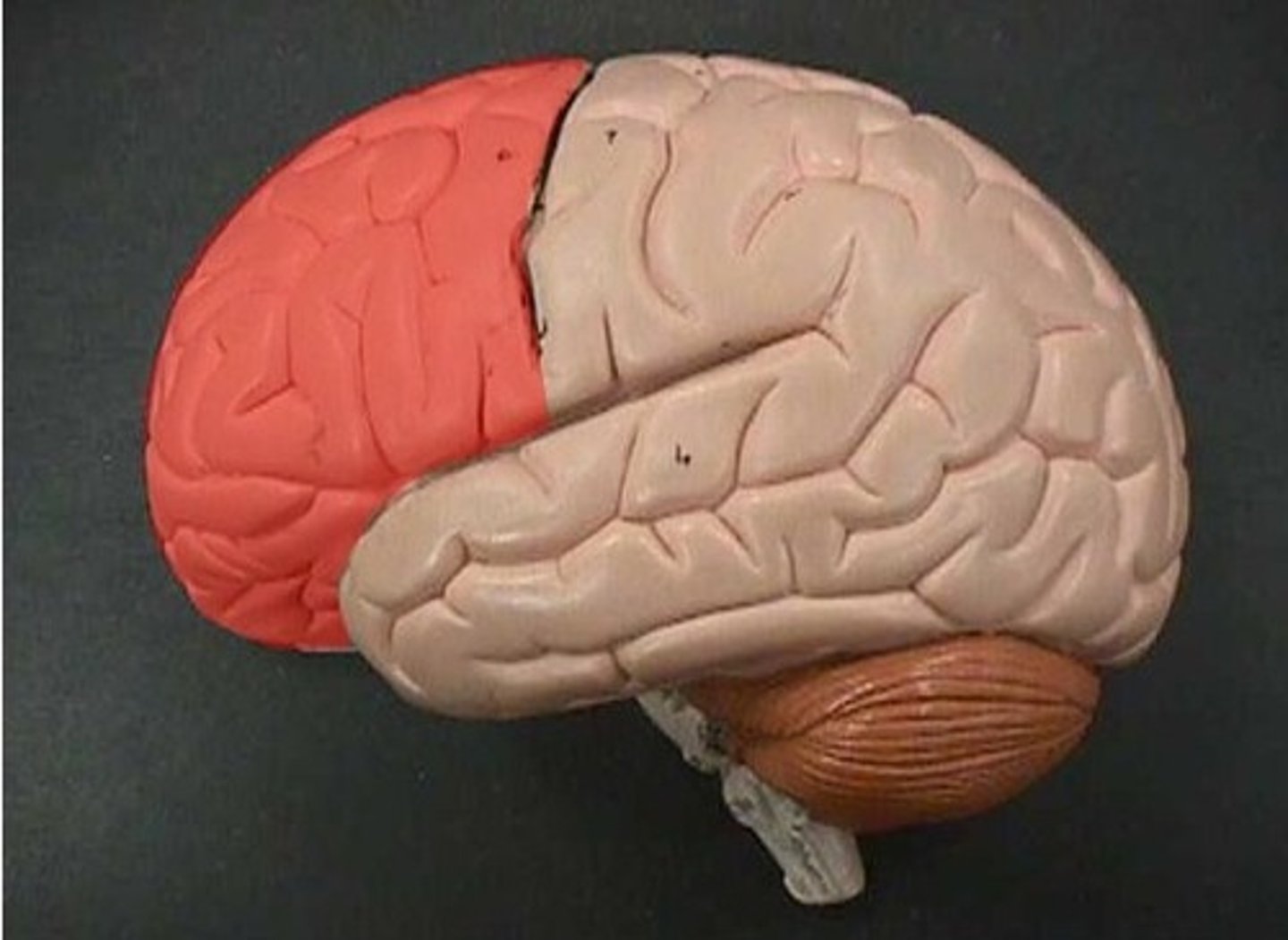
Frontal Lobe
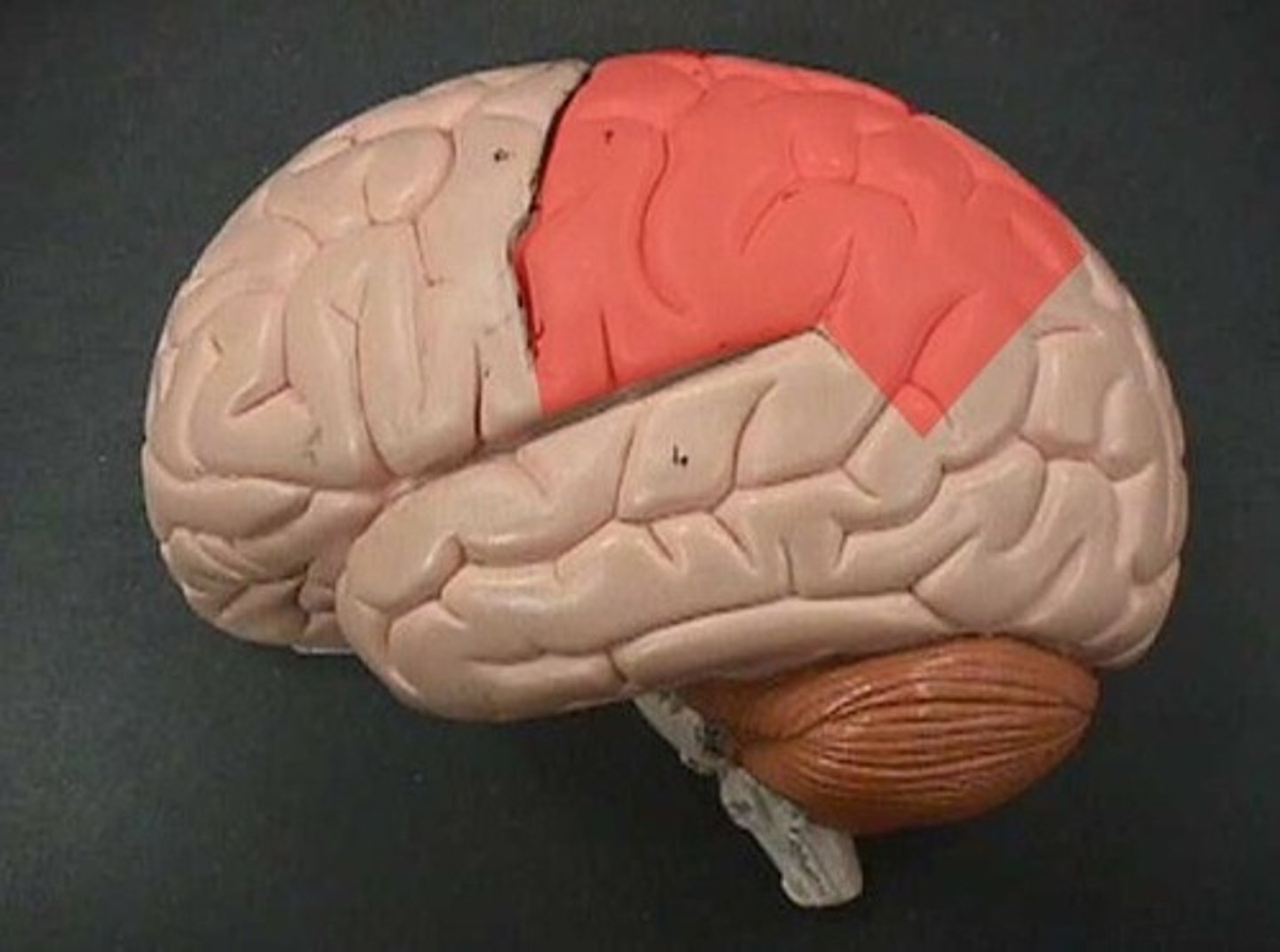
Parietal Lobe
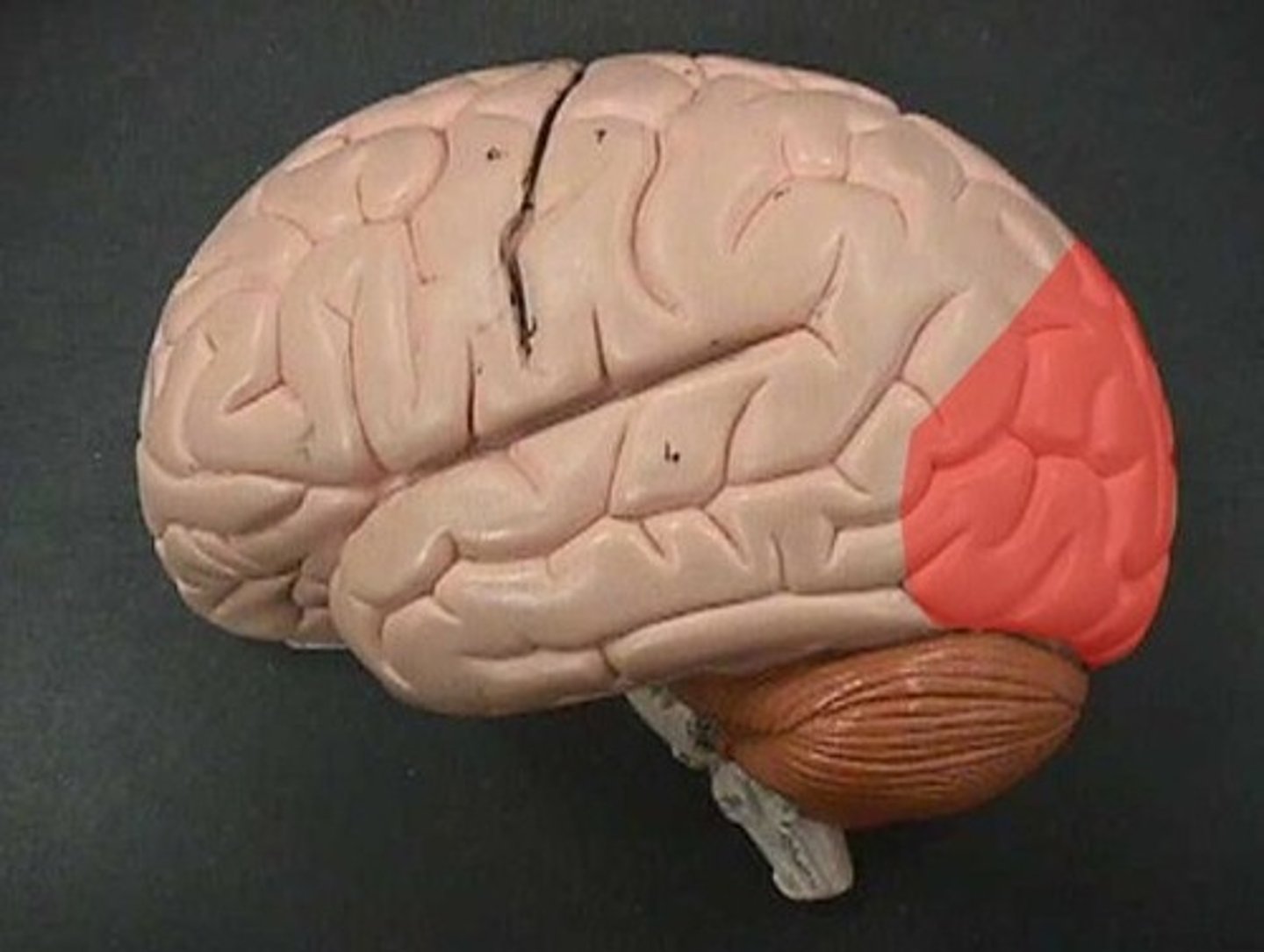
Occipital Lobe
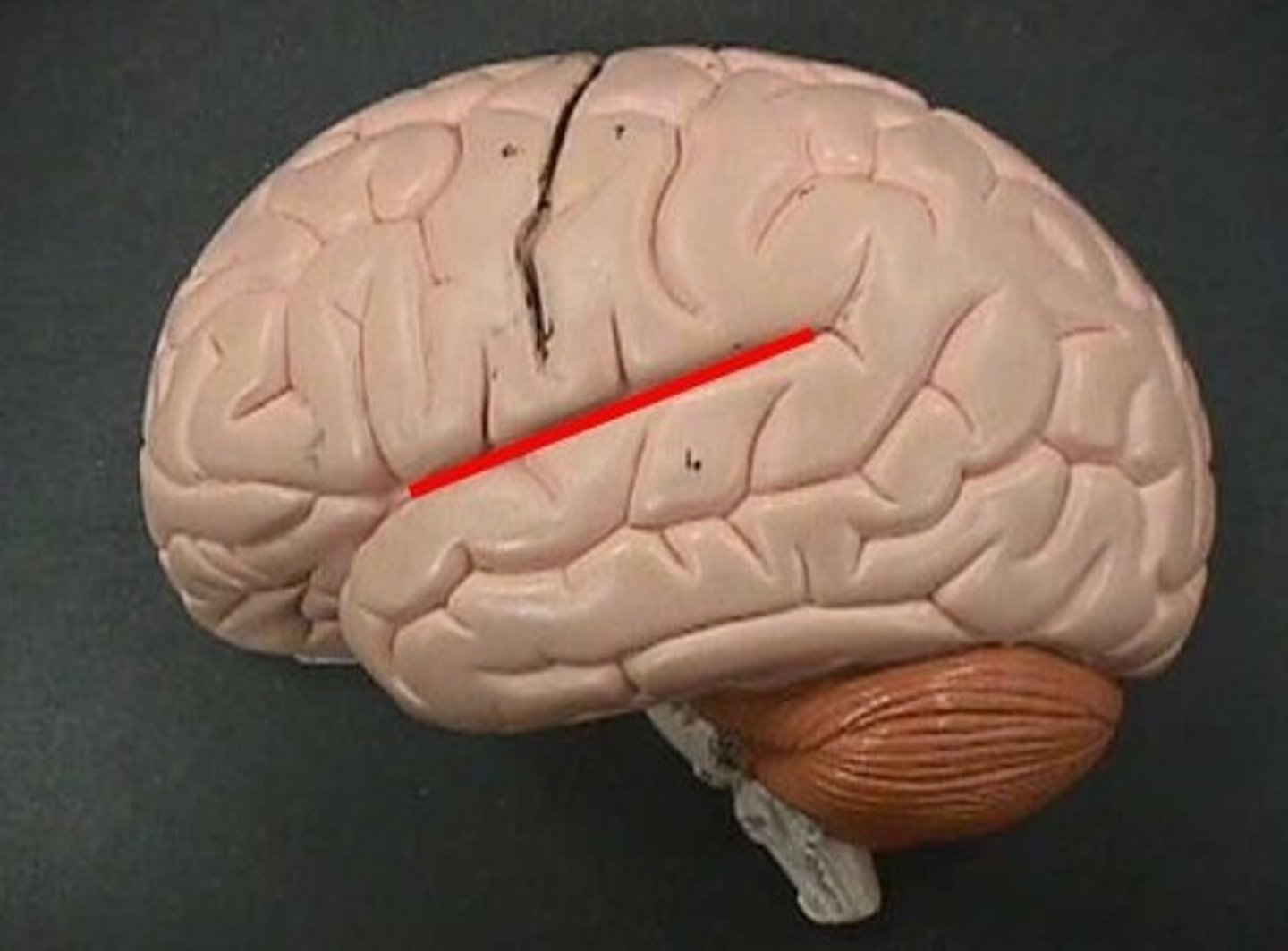
Central Sulcus
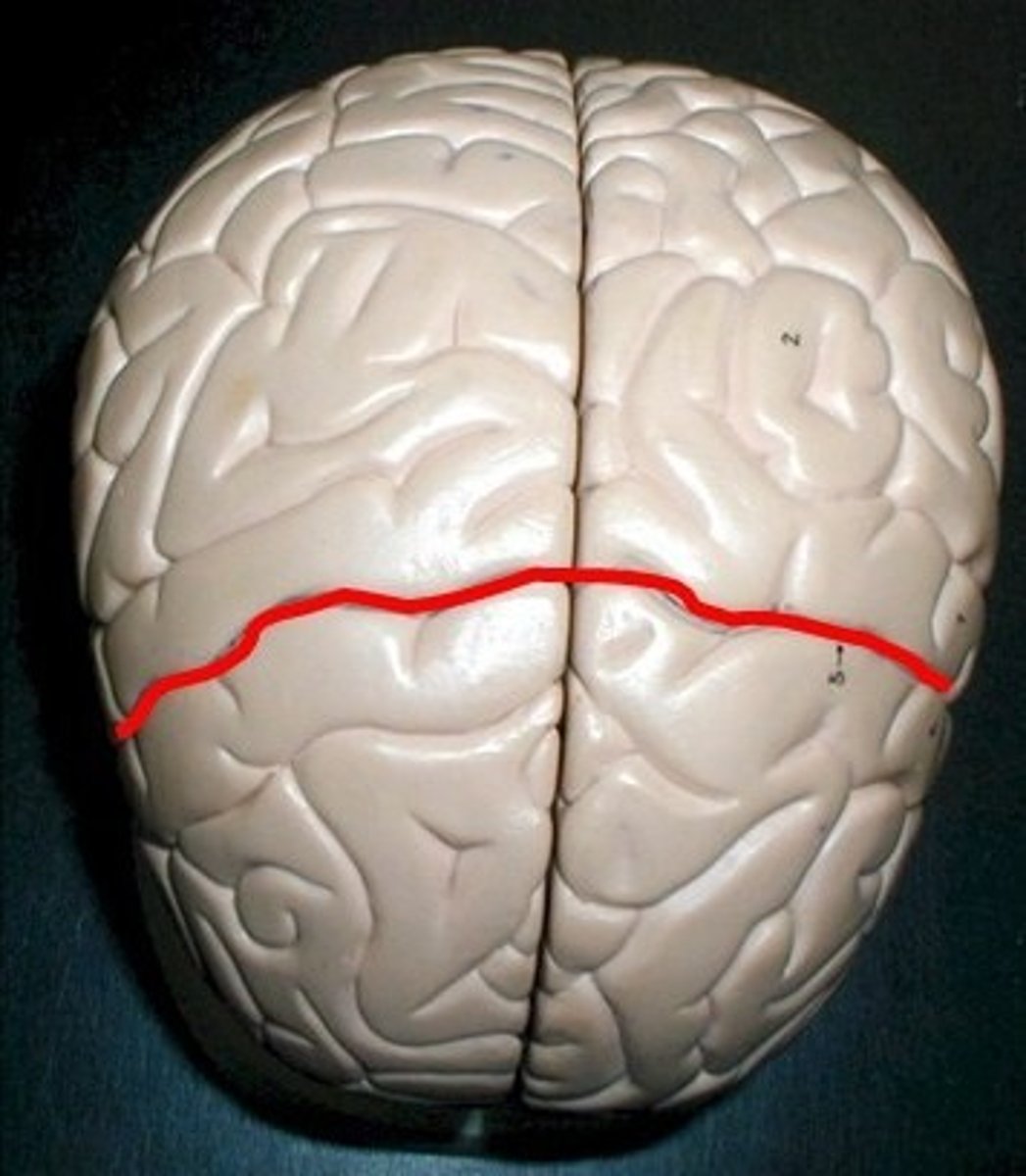
Lateral Sulcus
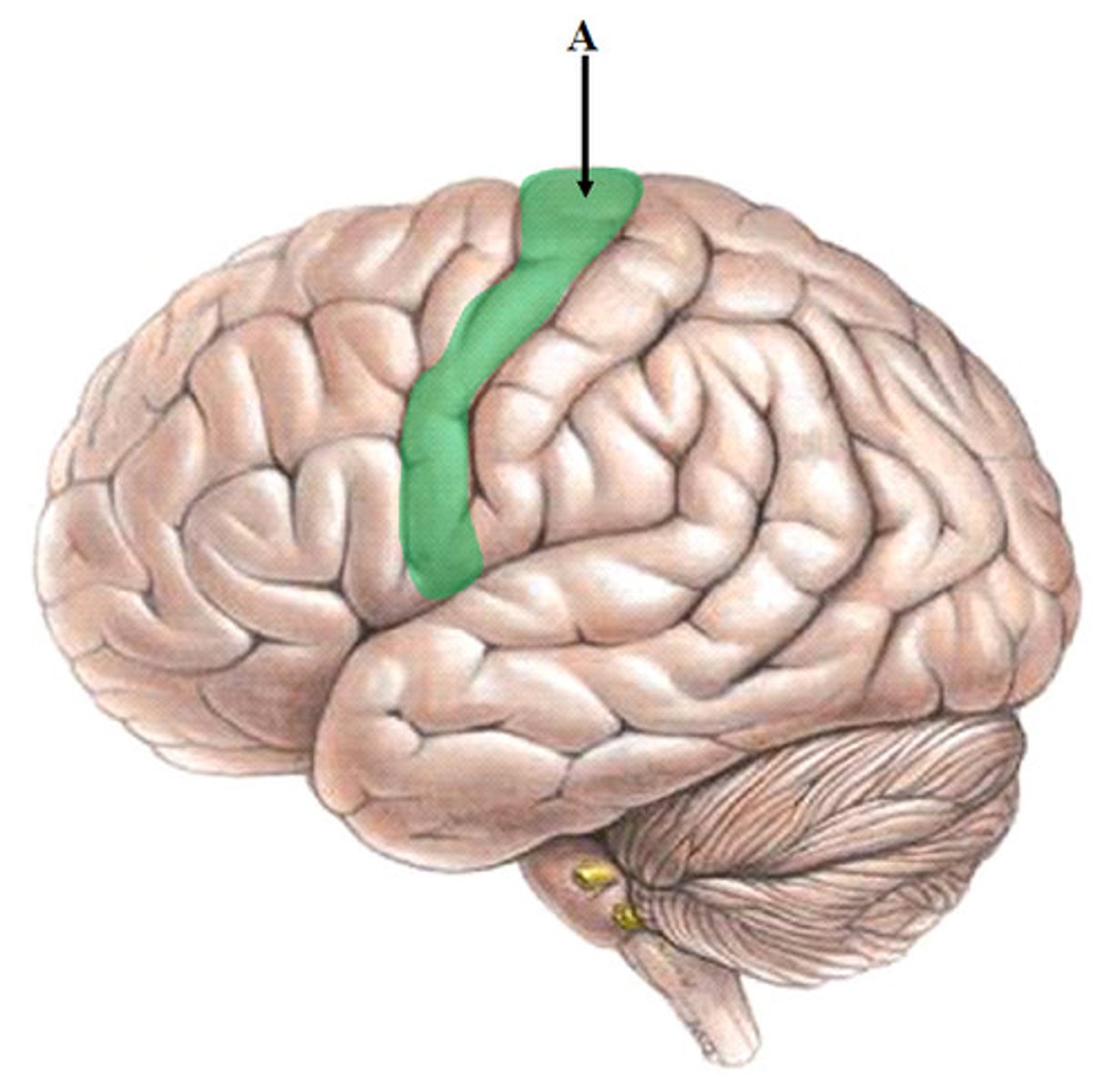
Somatomotor Area
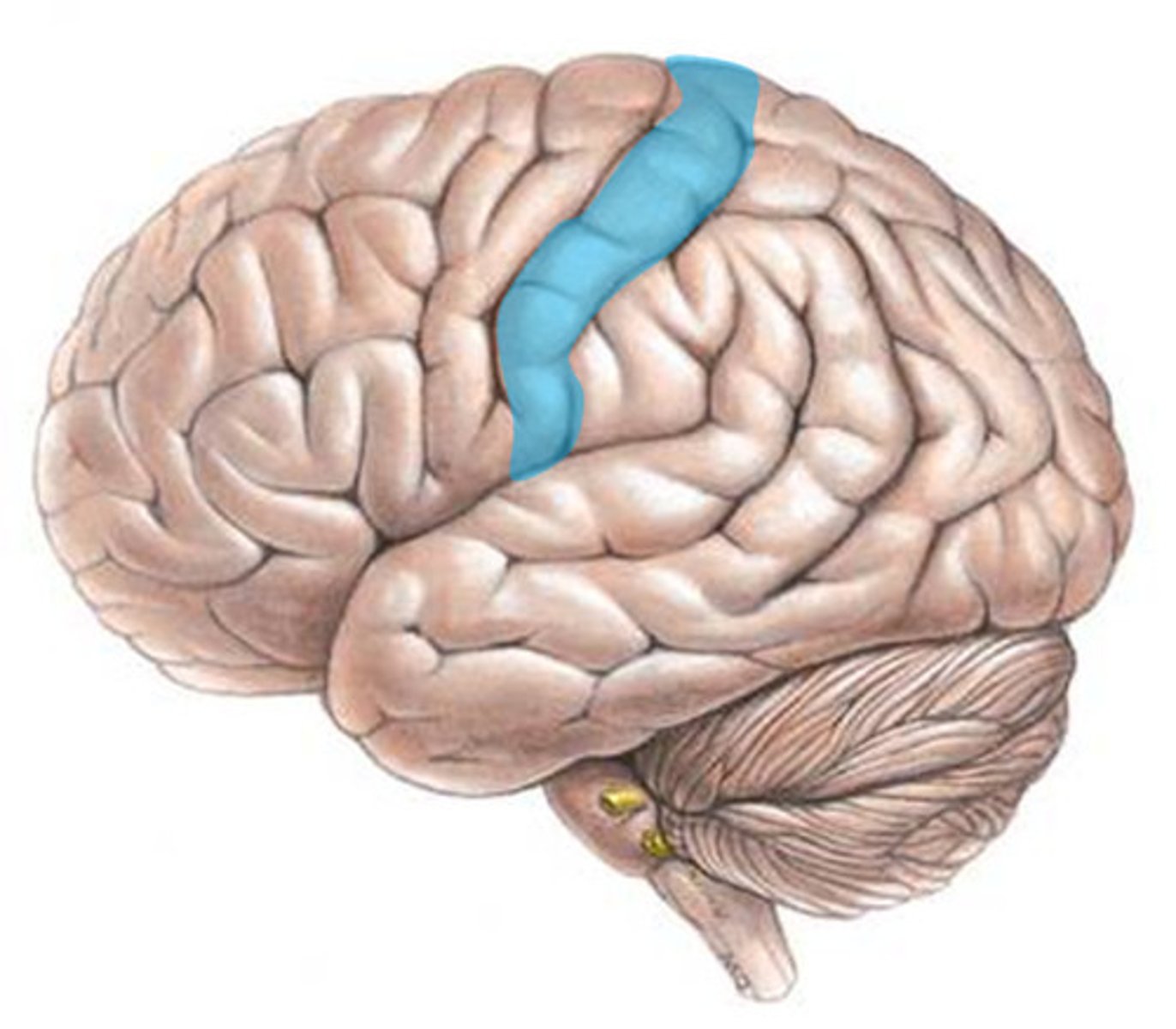
Somatosensory Area
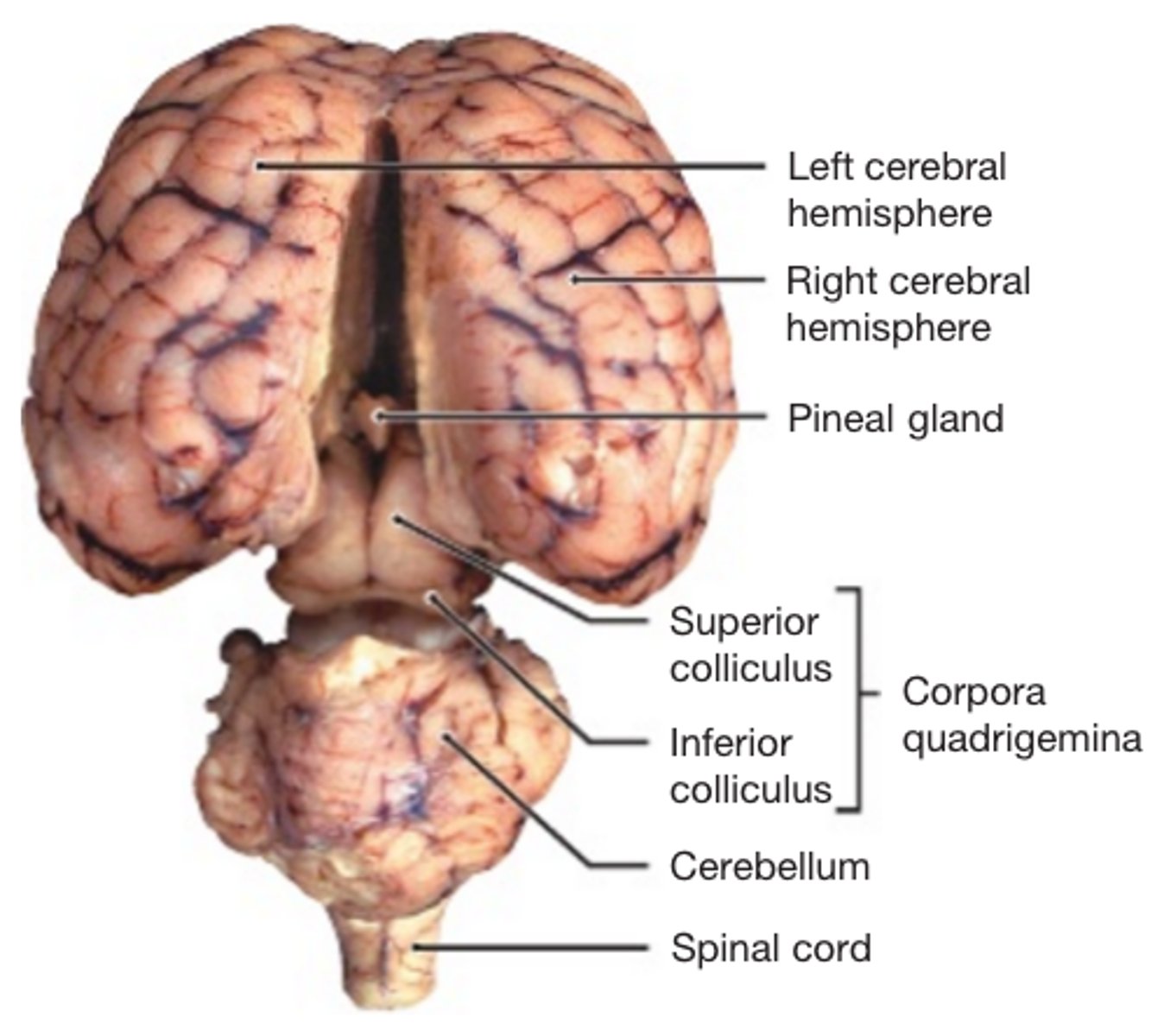
Cerebellum
Olfactory Bulb
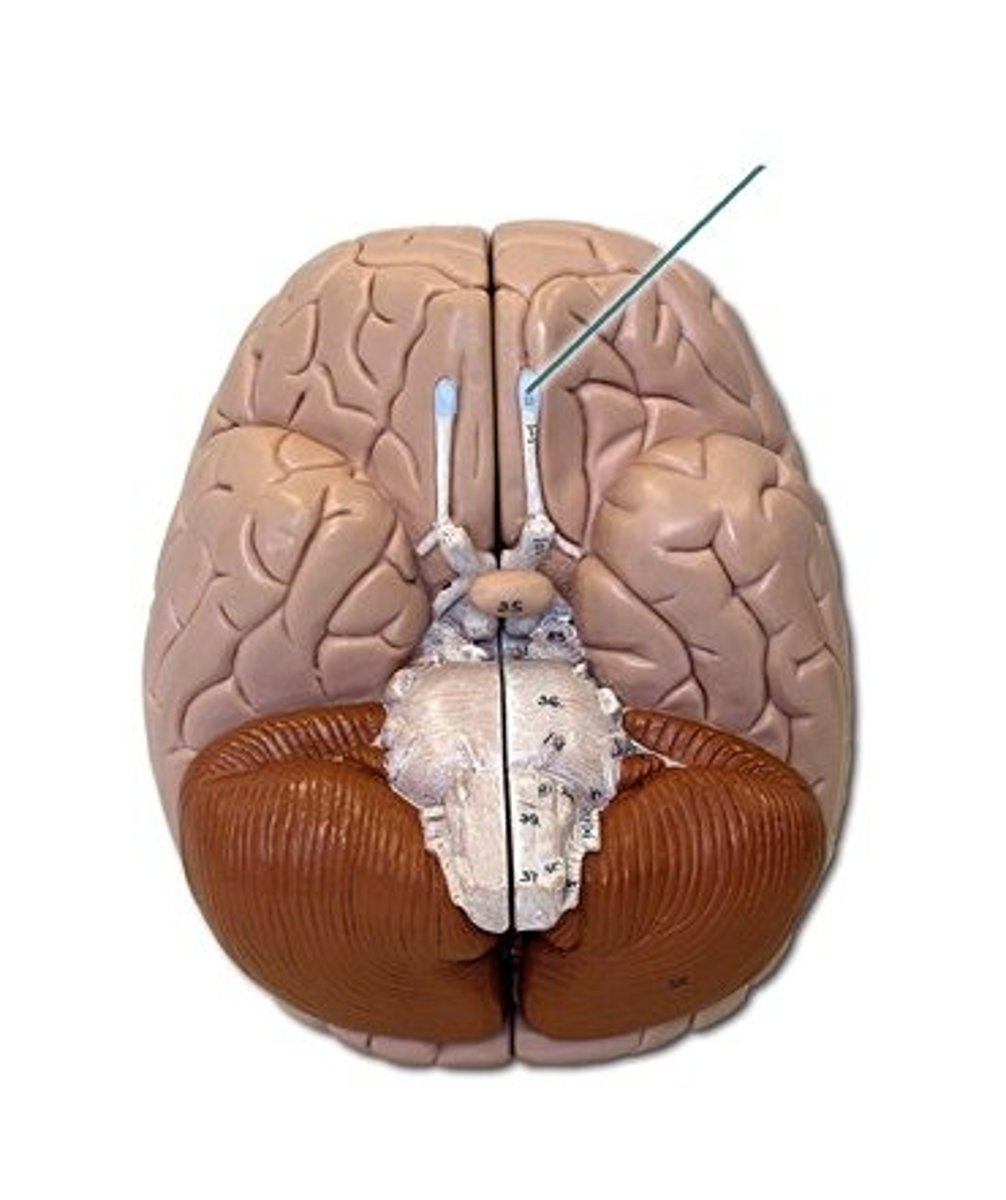
Optic Chiasm
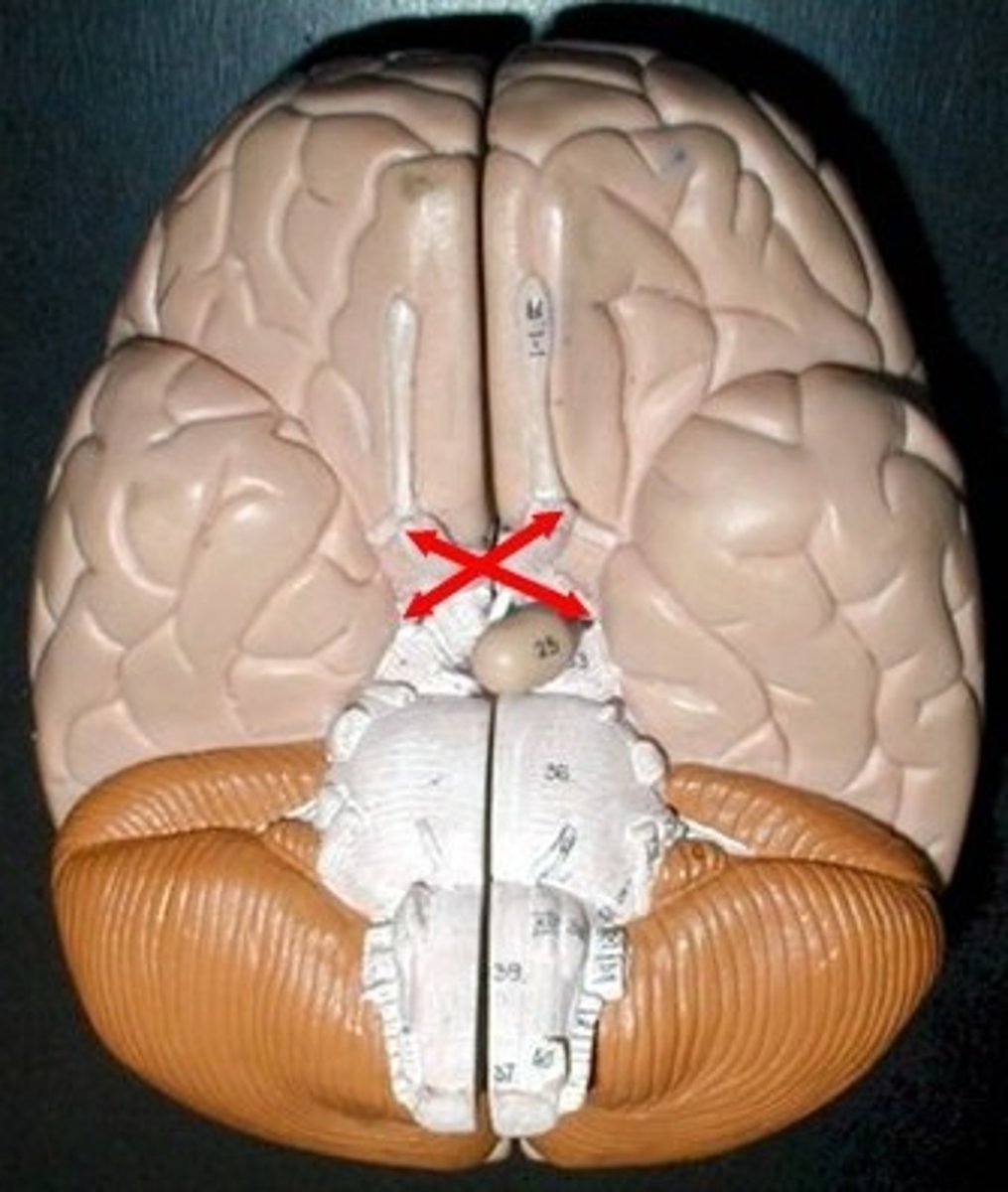
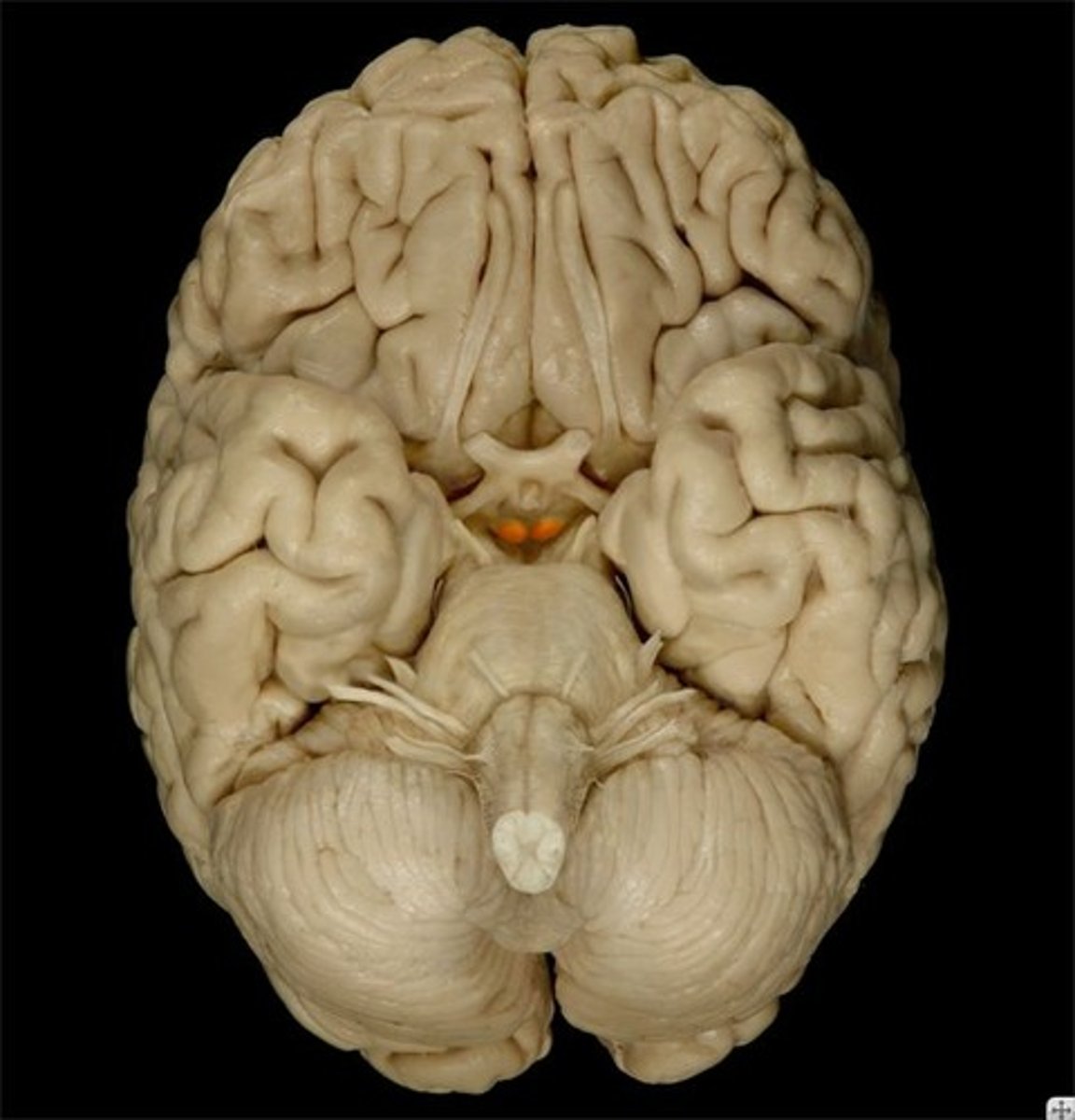
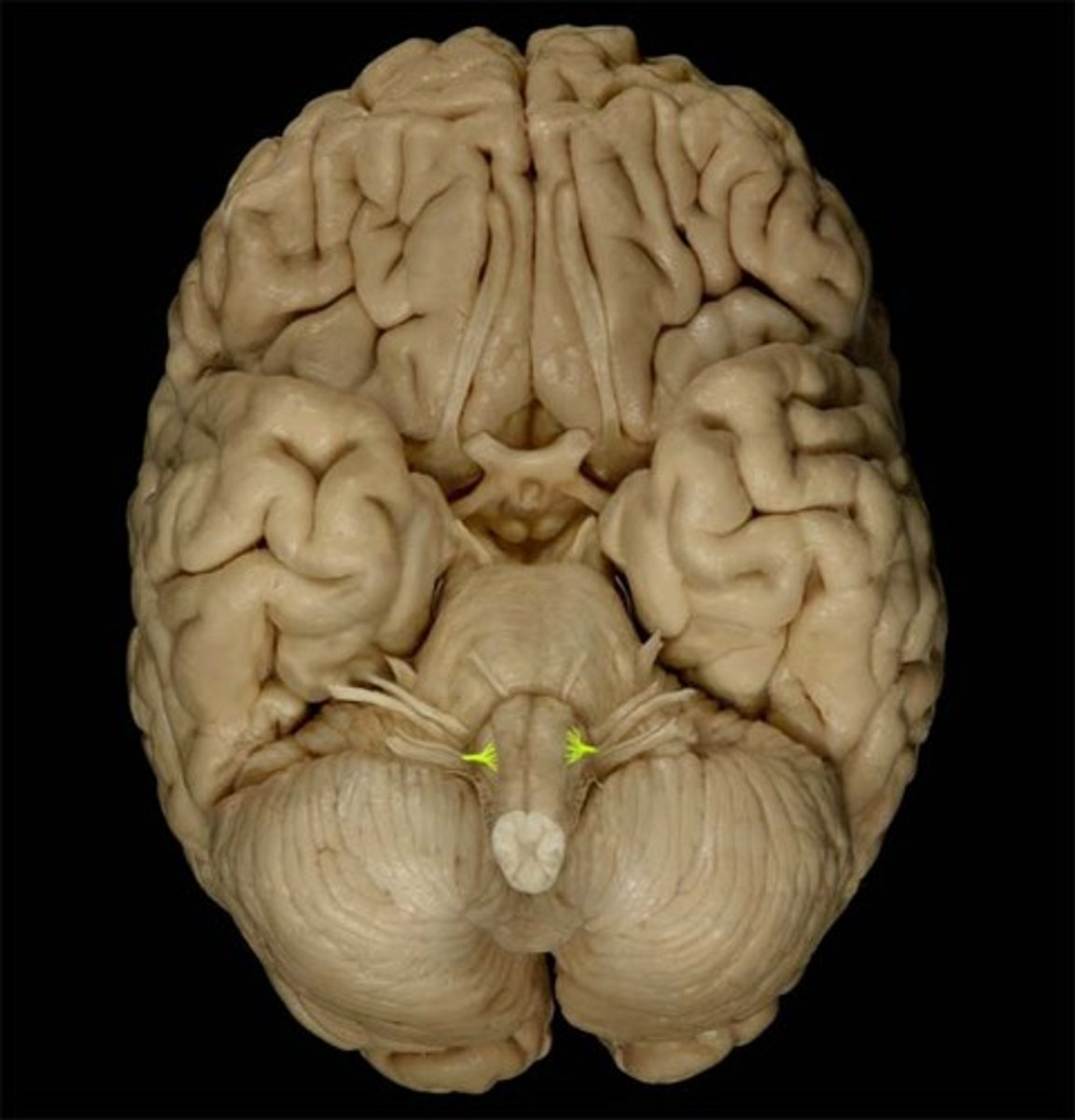
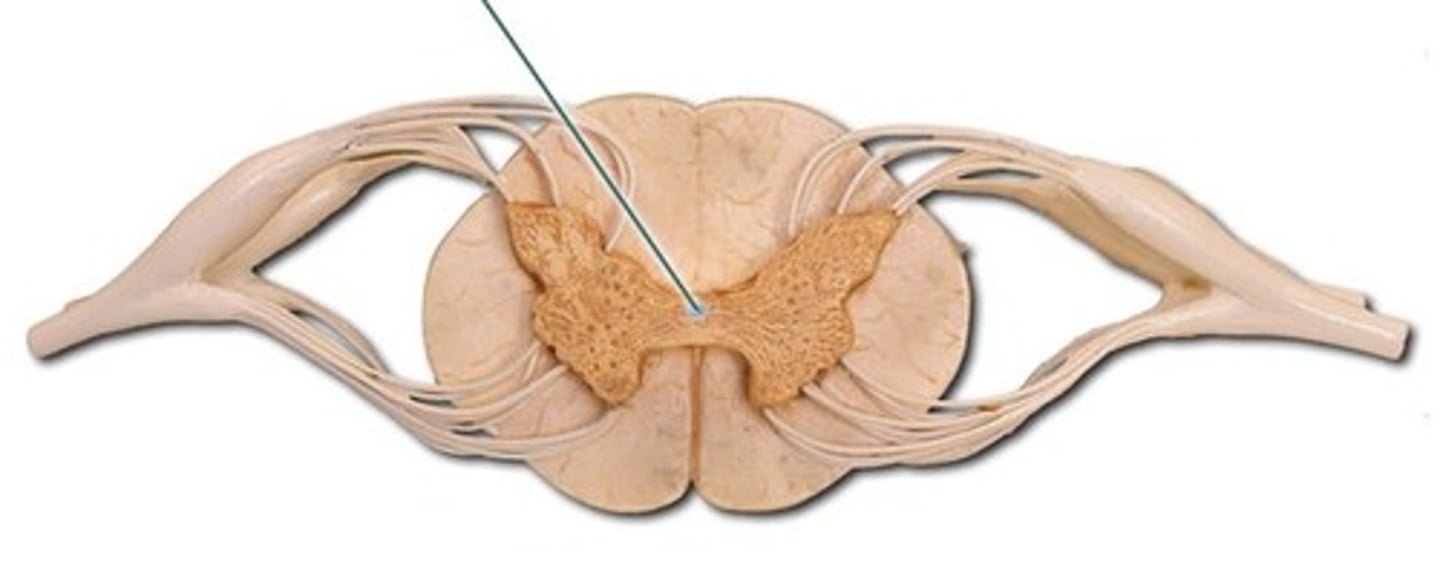
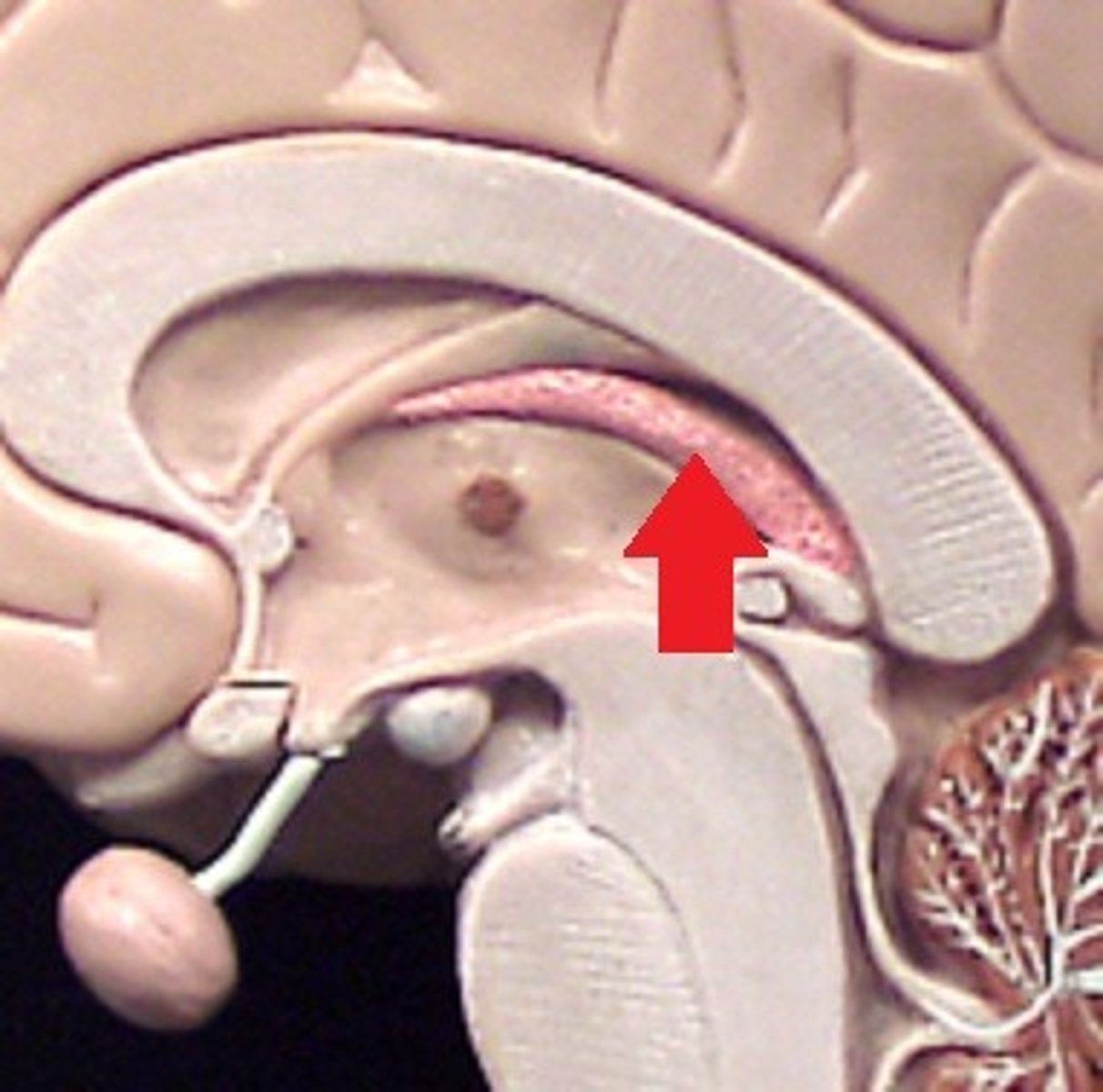
Mammillary Bodies
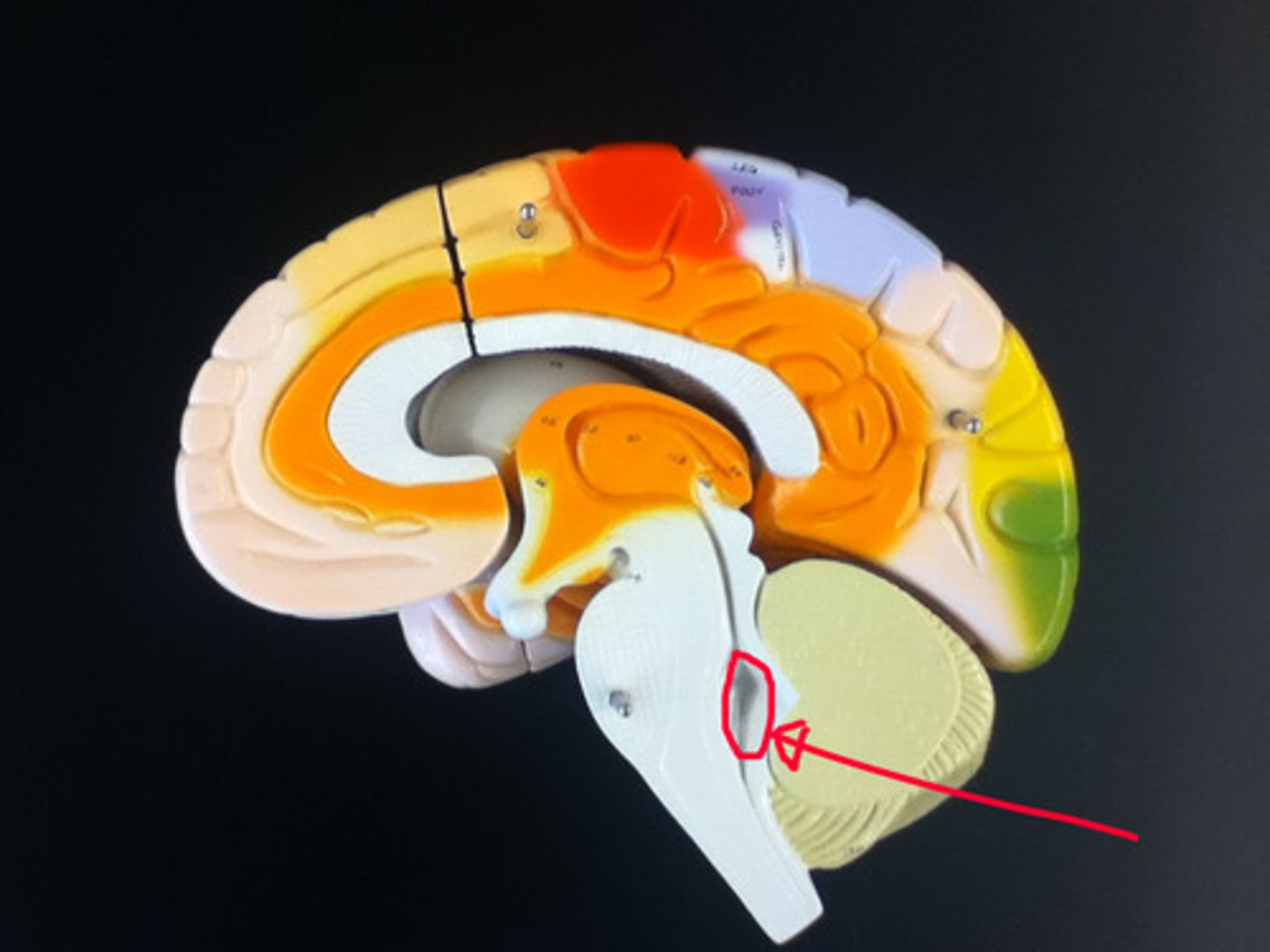
Pons
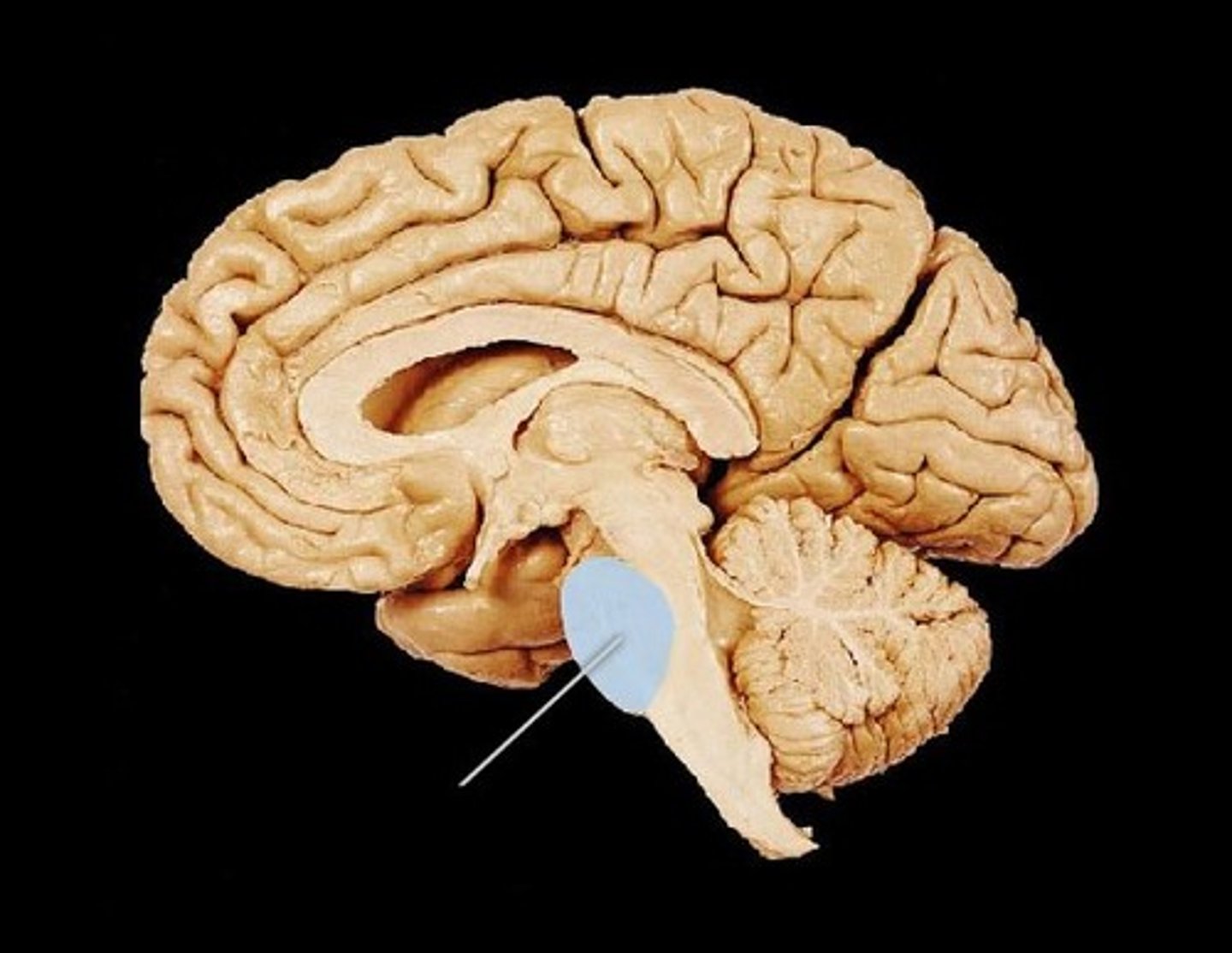
Medulla Oblongata
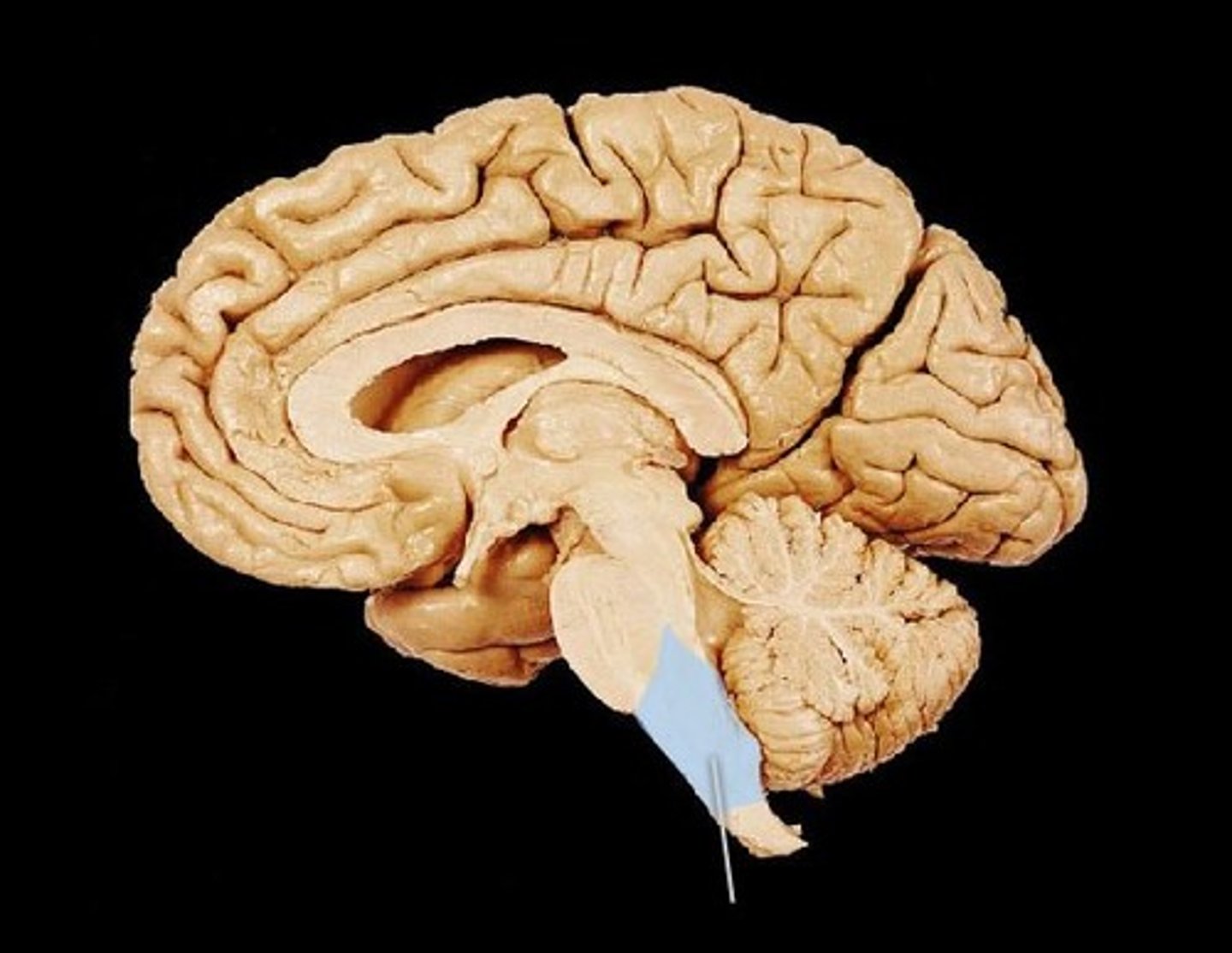
MIdsagittal View of brain
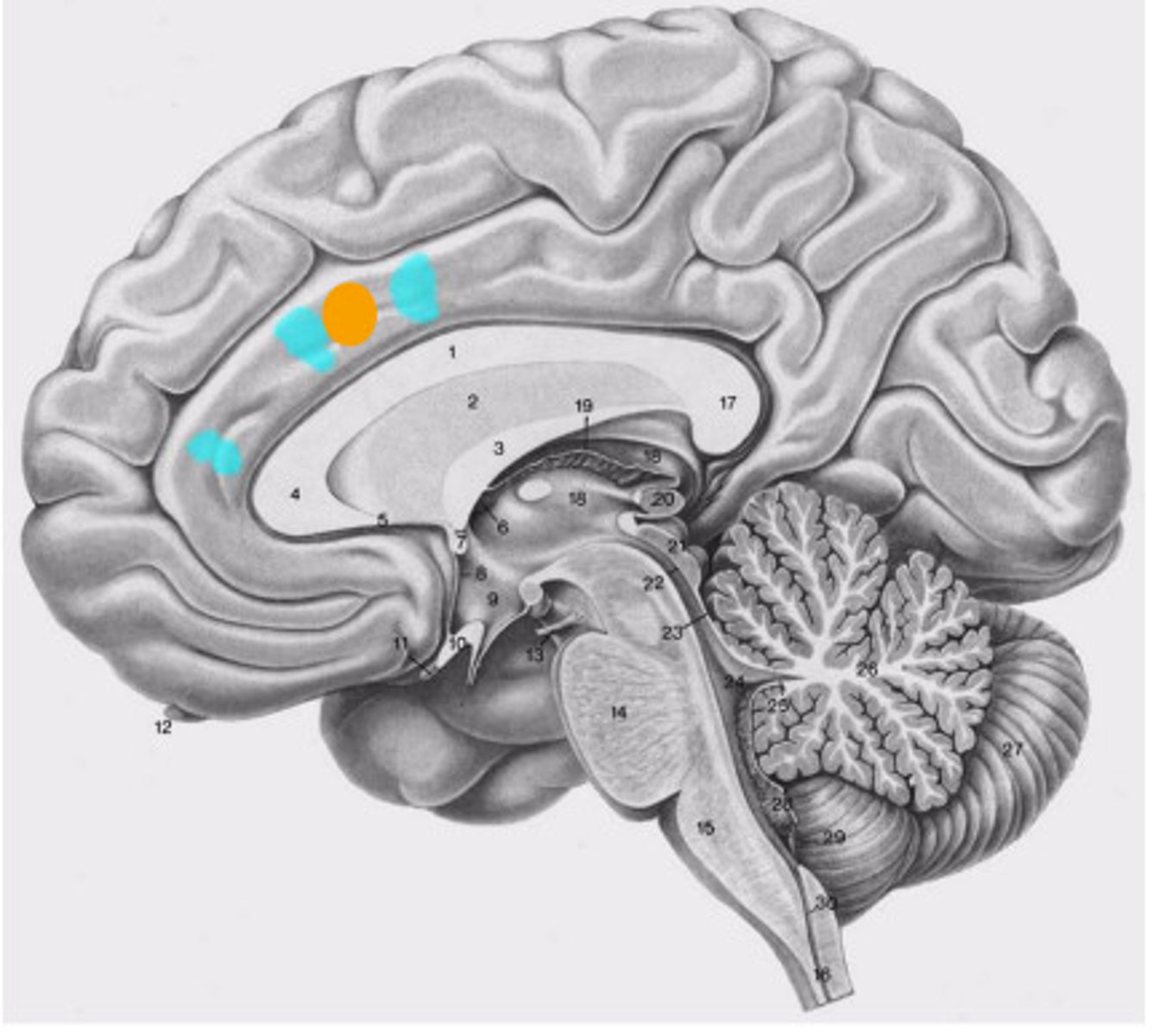
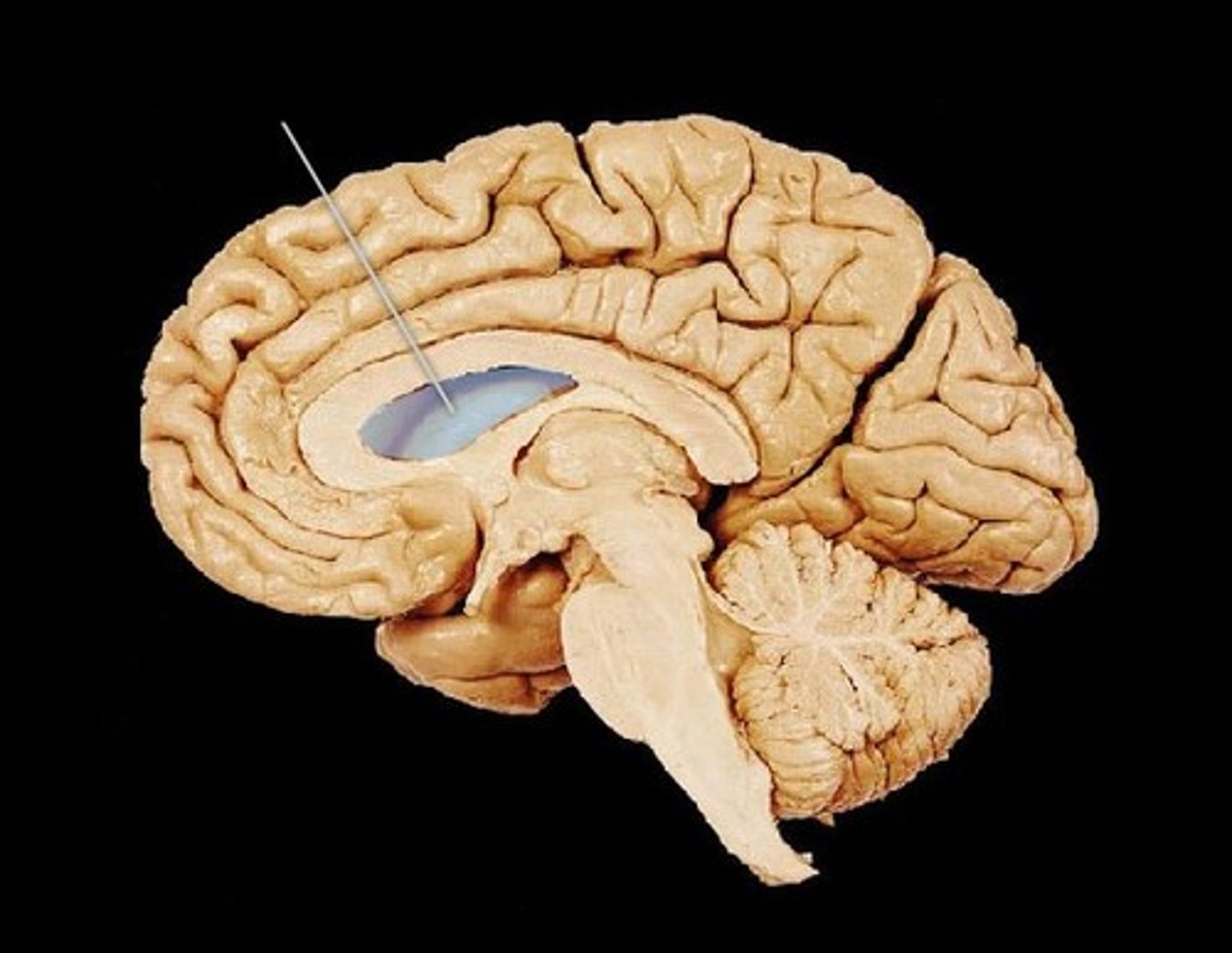
Lateral Ventricle
Third Ventricle
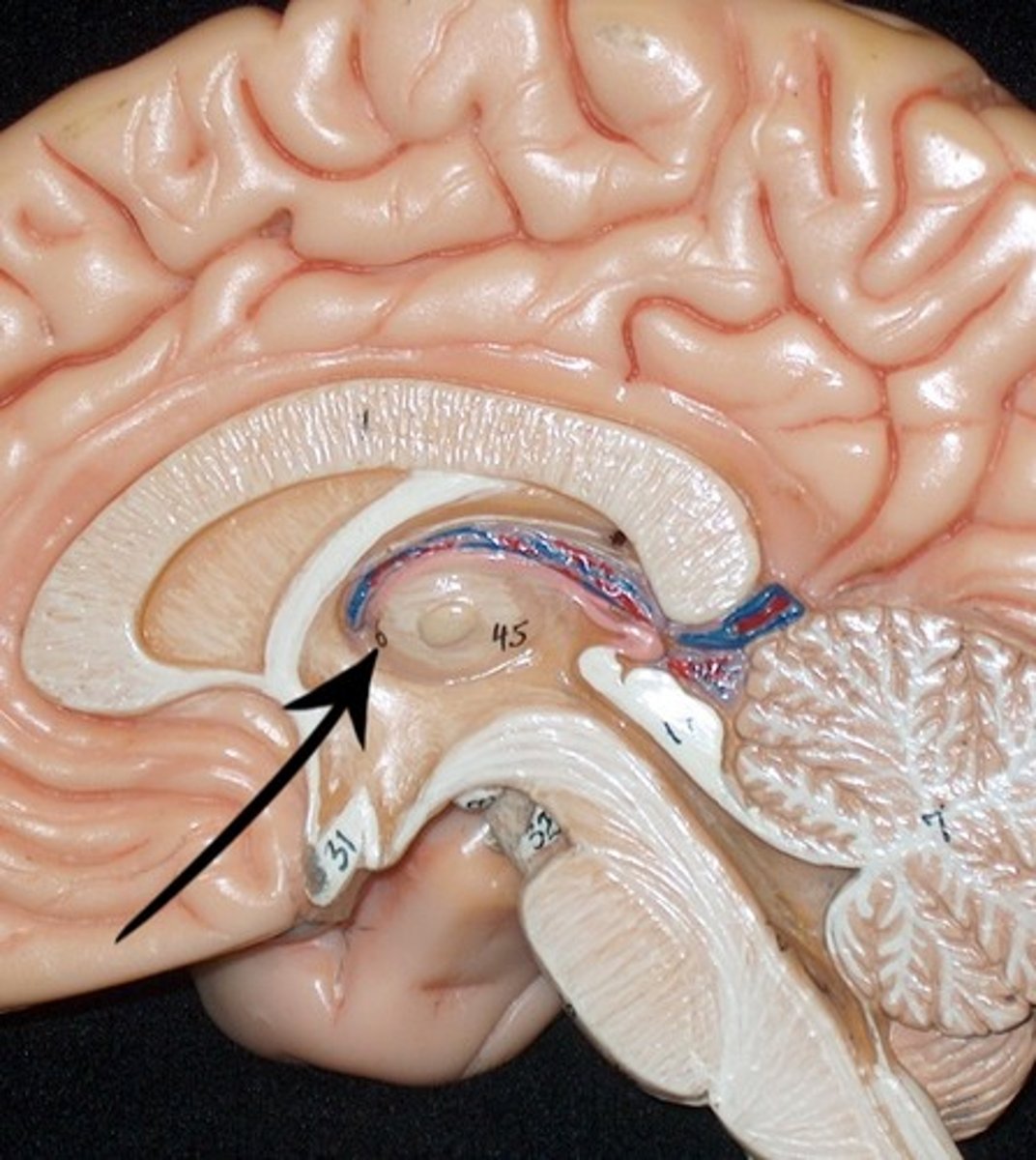
Cerebral Aqueduct
Forth Ventricle
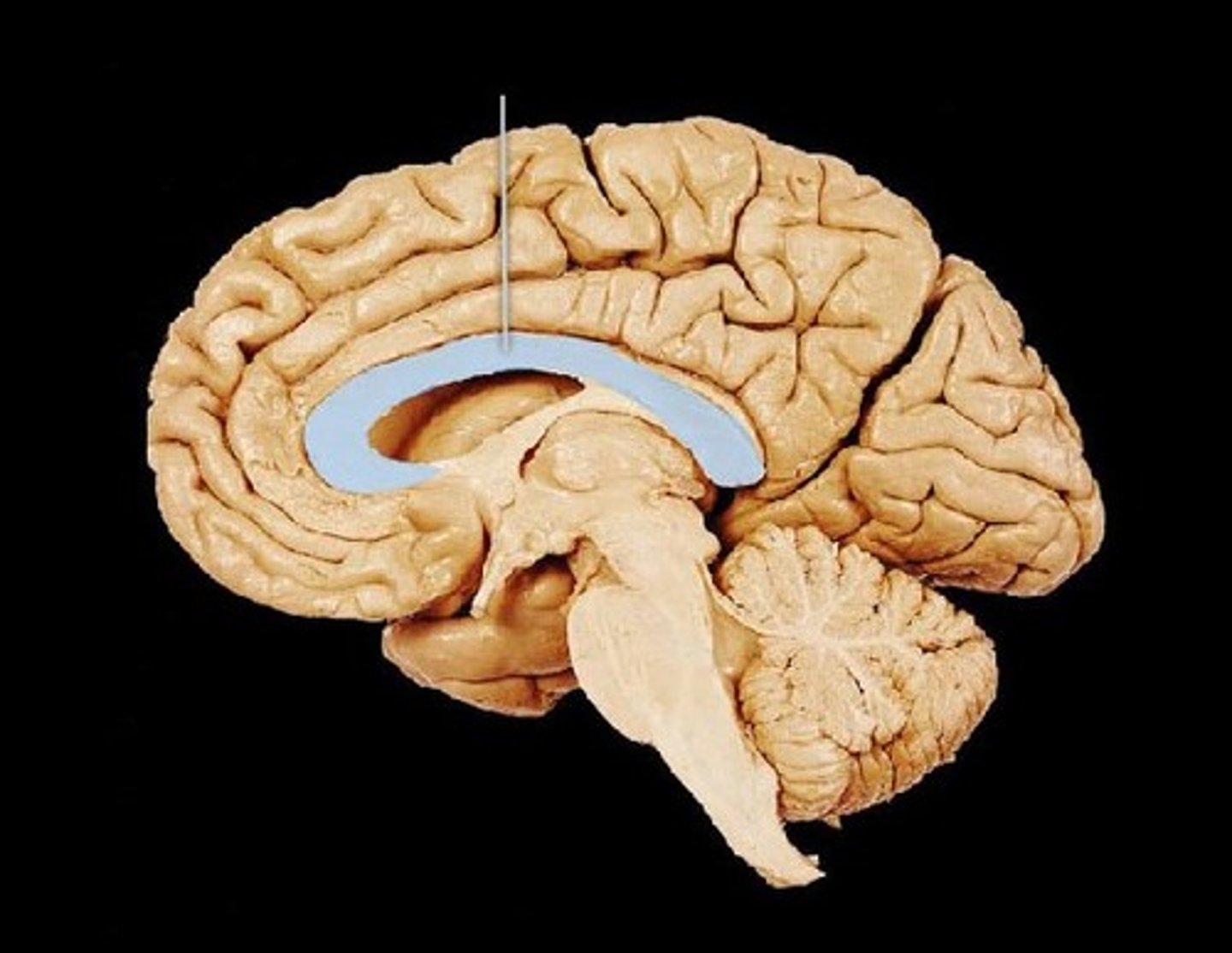
Corpus Callosum
Fornix
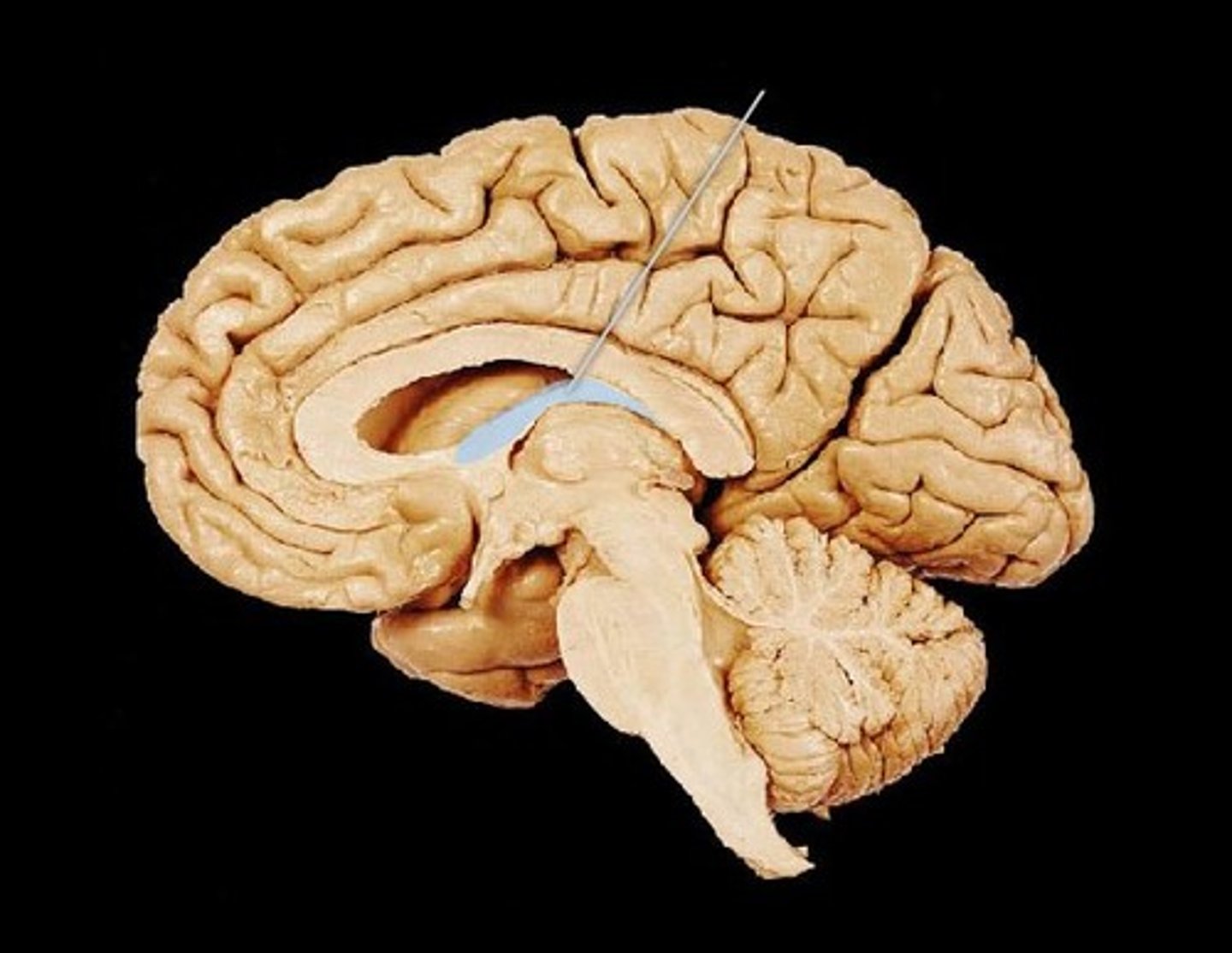
Thalamus
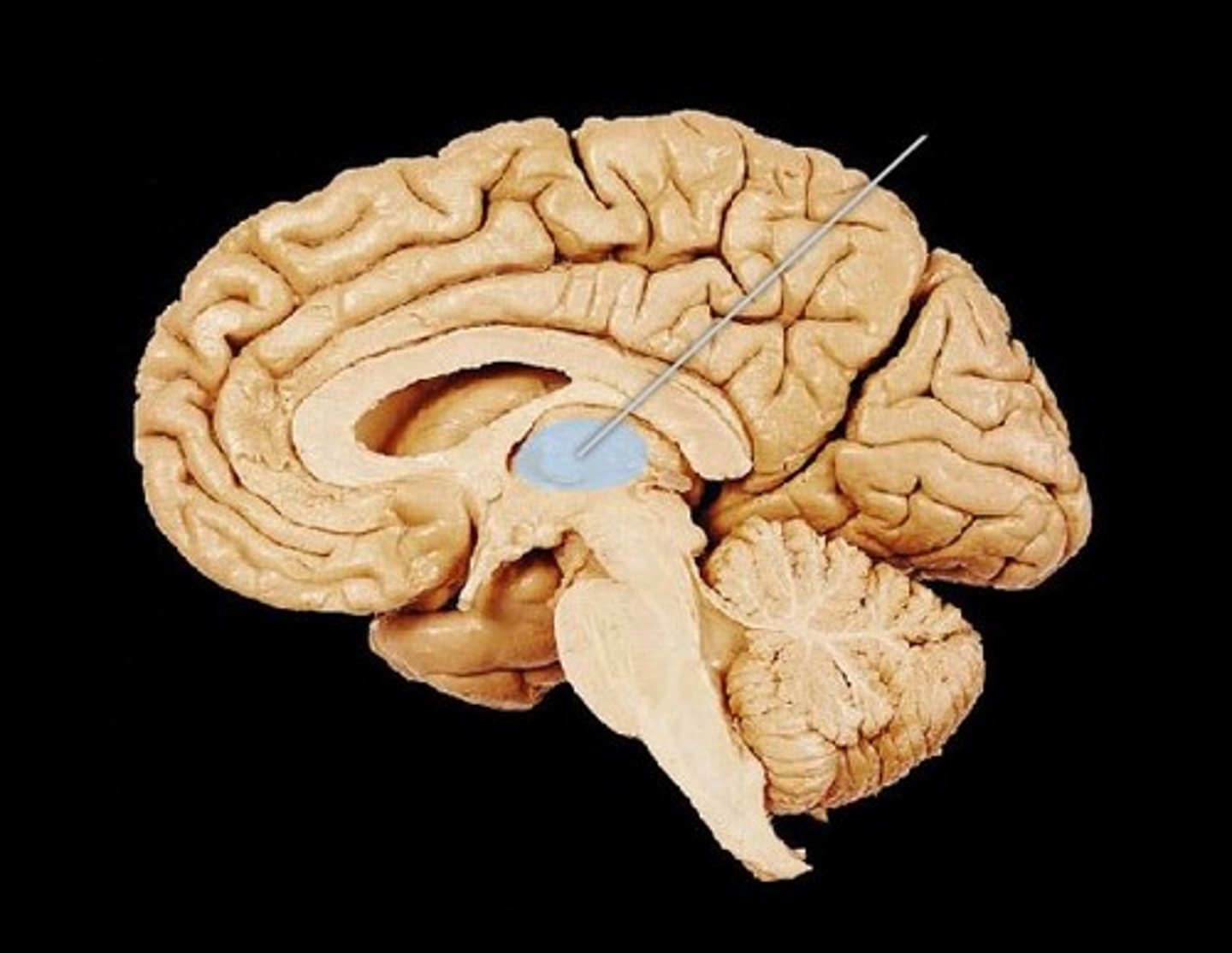
Pineal Gland
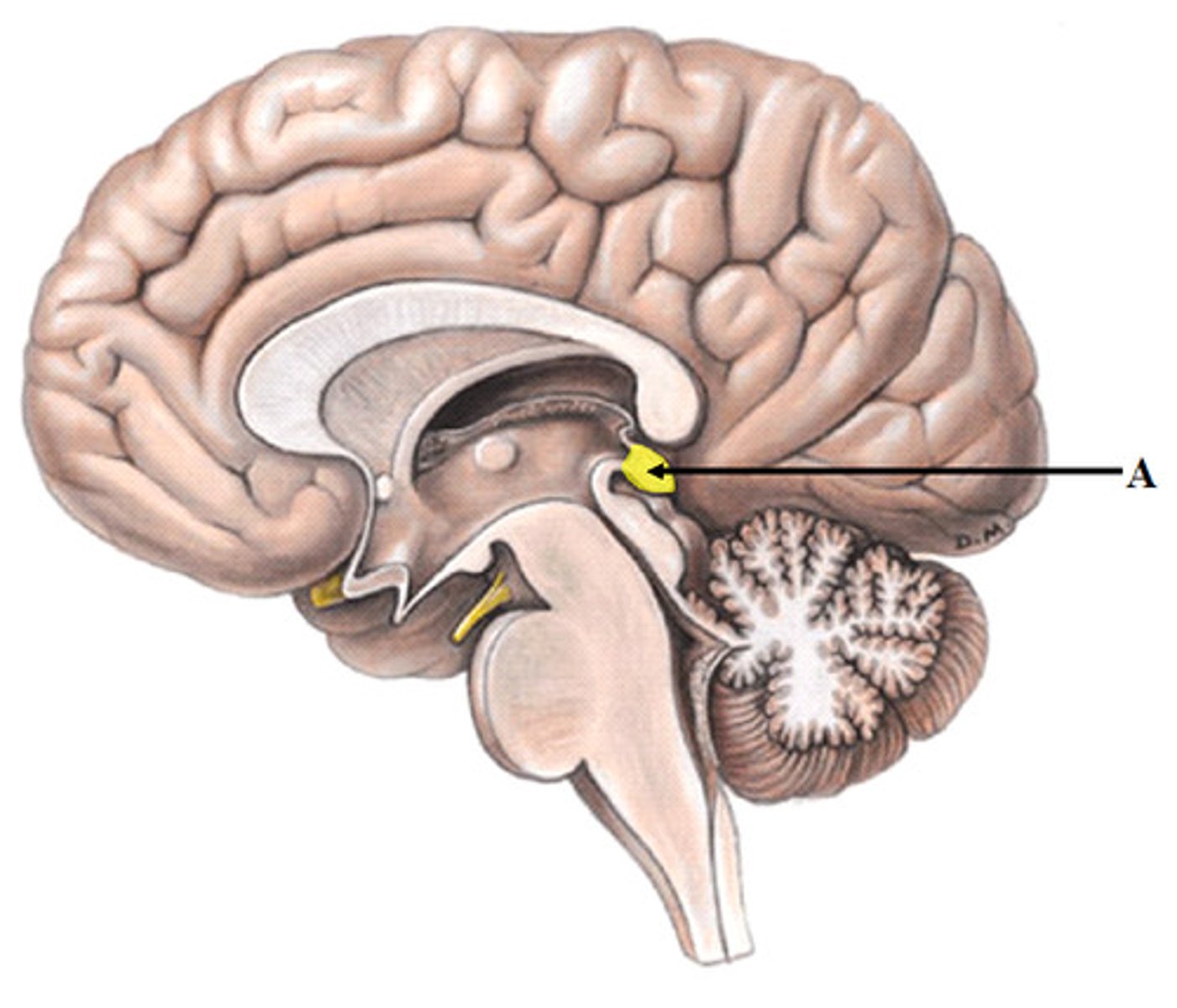
Superior Colliculi
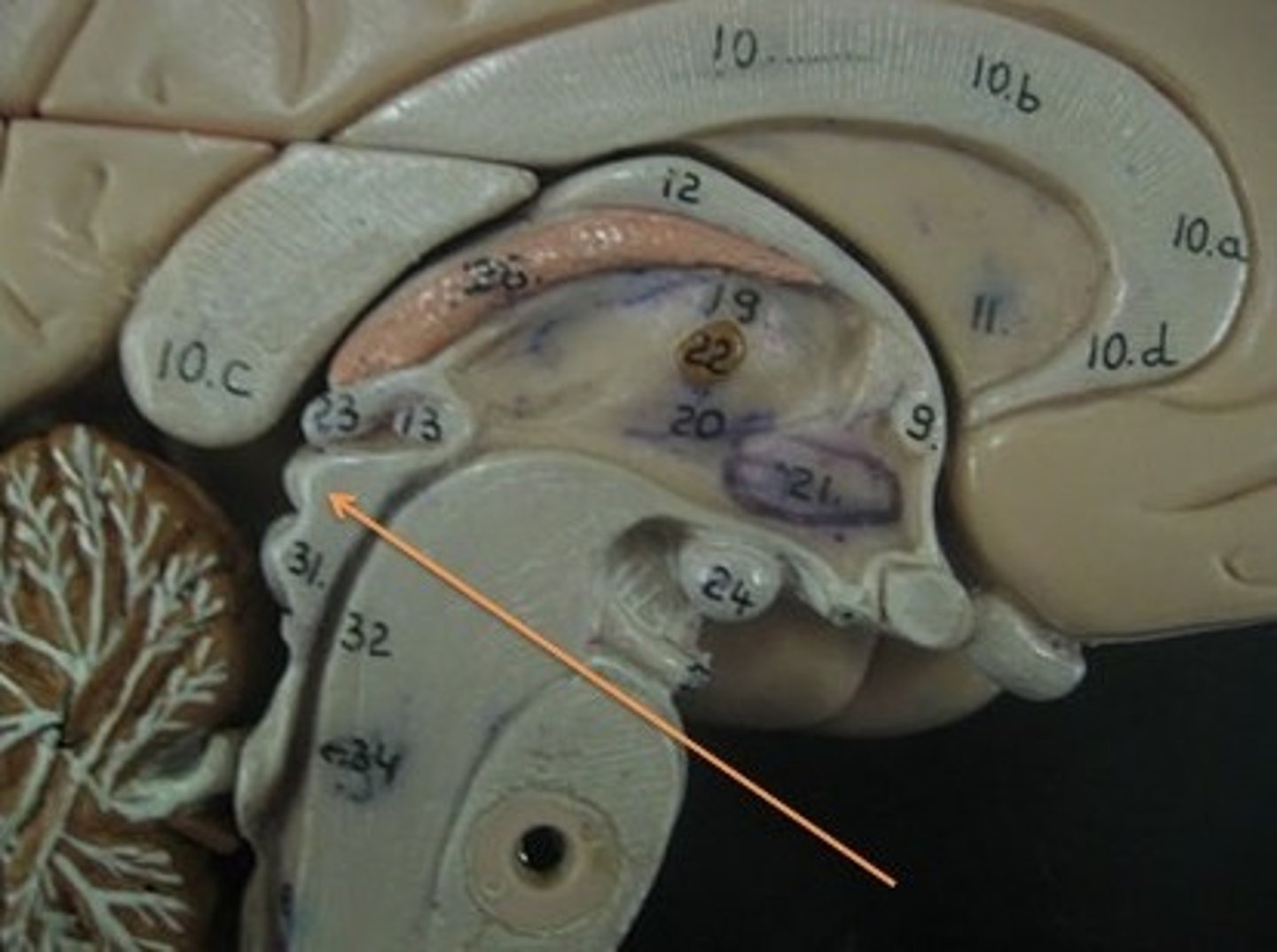
Inferior Colliculi
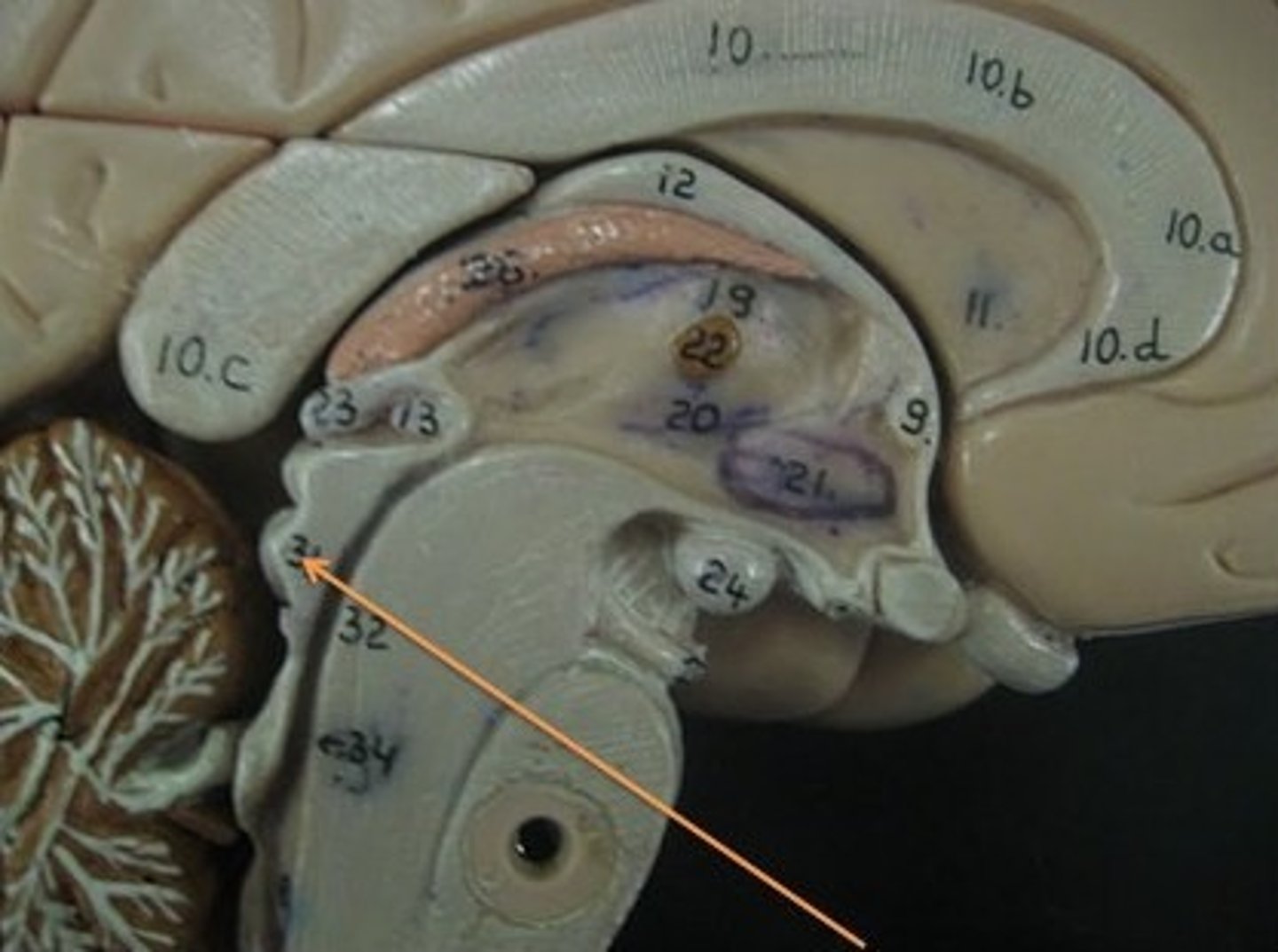
Midbrain
Hypothalamus
Cerebral Cortex Gray Matter (nerve cell bodies)
White Matter (myelinated nerve fibers)
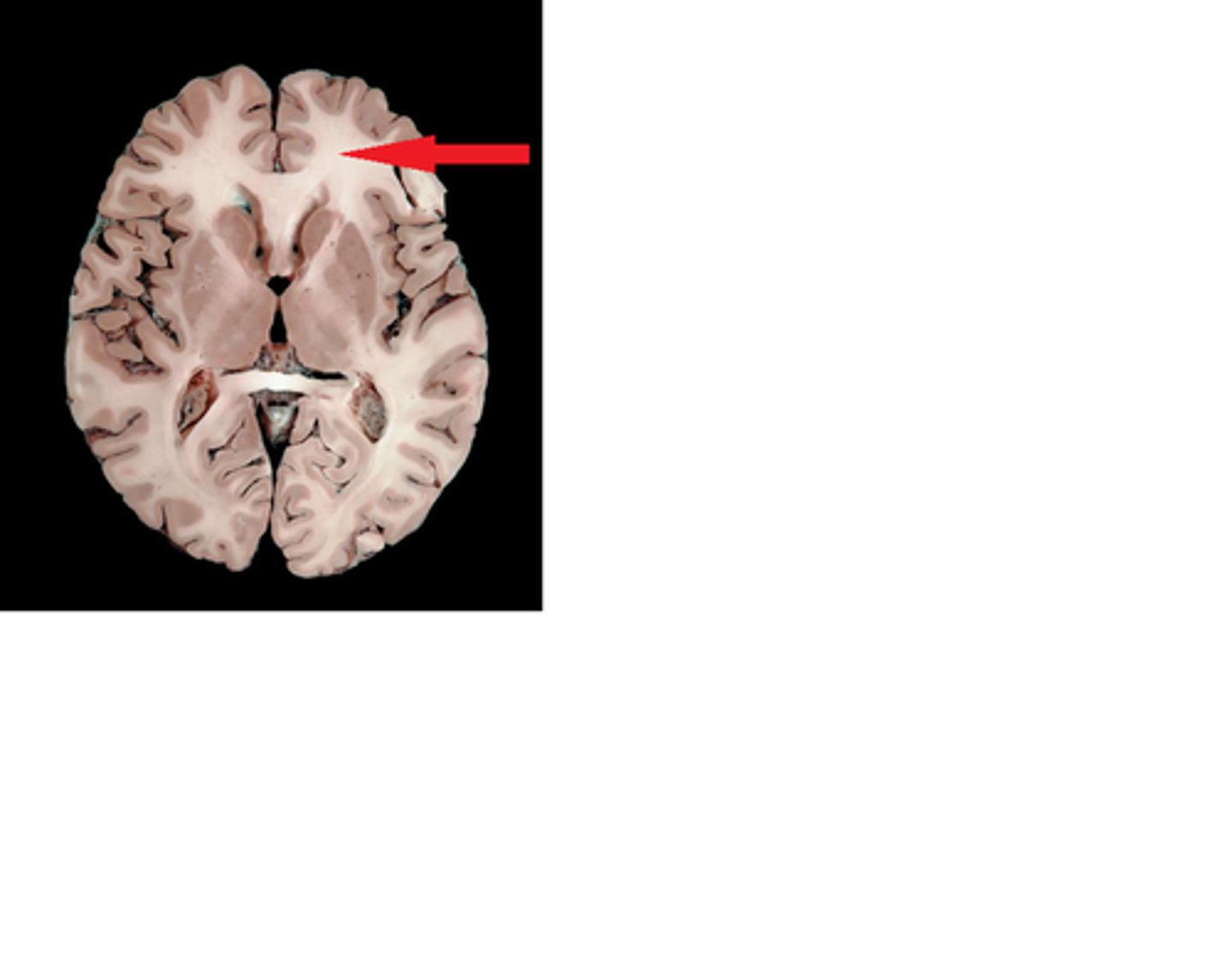
Olfactory Nerve
Function: special sensory- smell
Location: Telencephalon
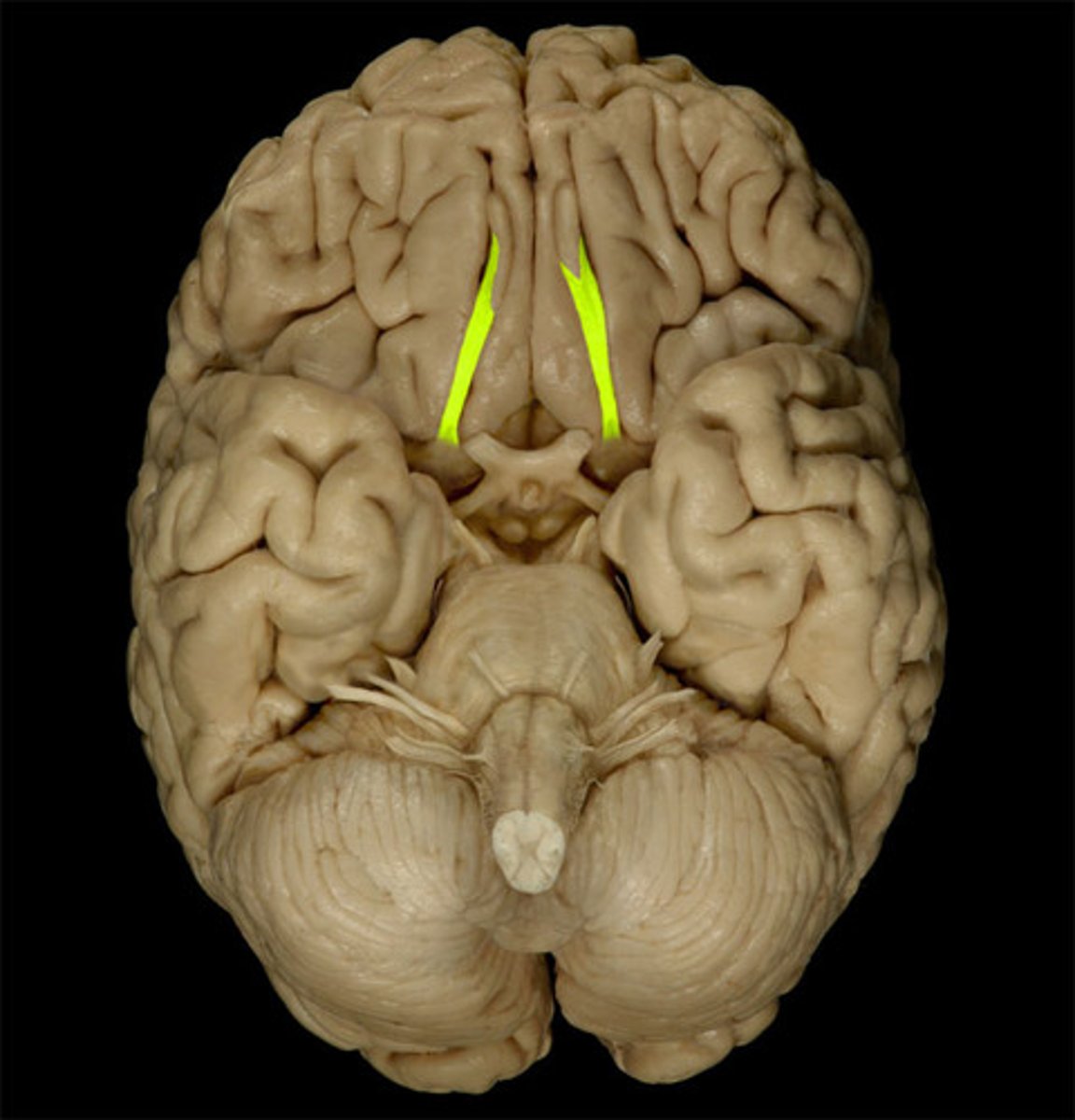
Optic Nerve
Function: special sensory- vision
Location: Diencephalon
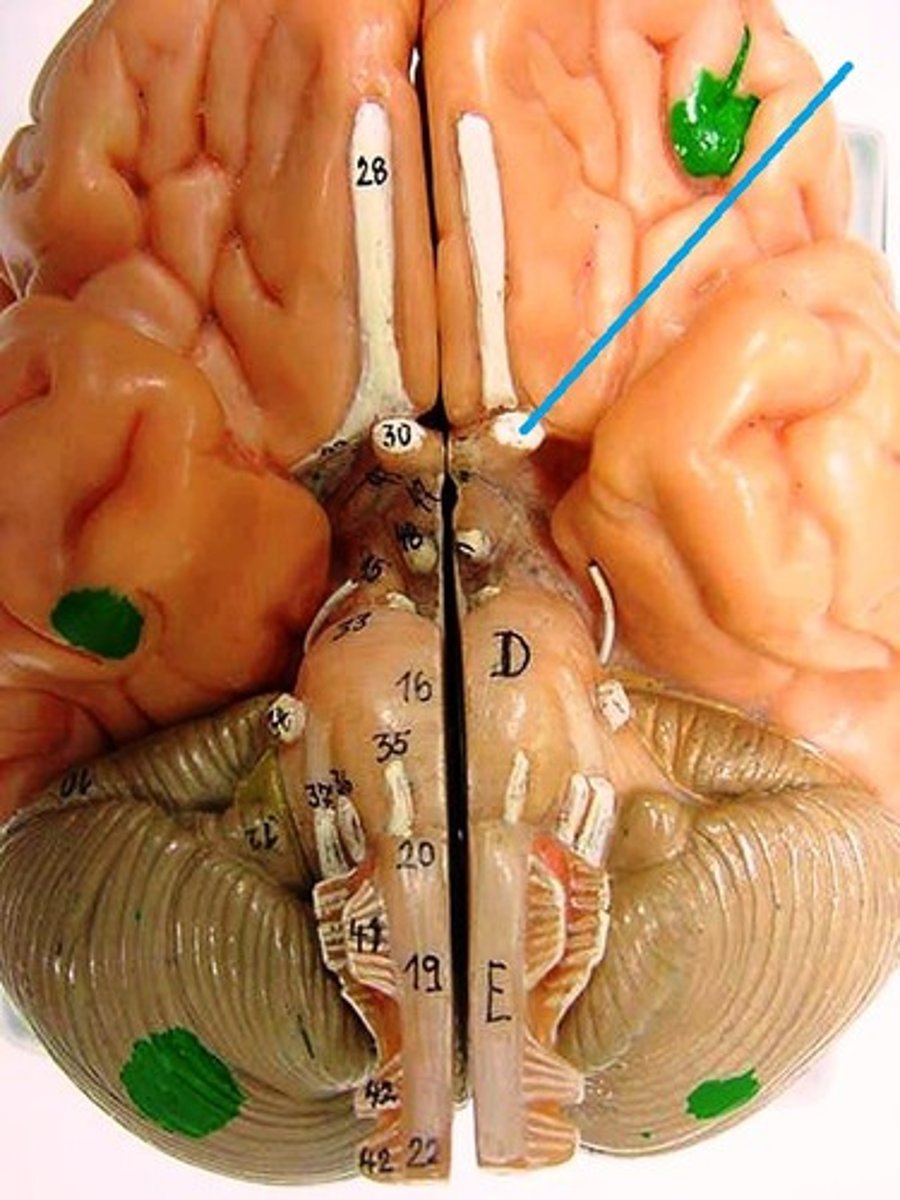
Oculomotor Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement; lid elevation, pupil contraction, lens shape
Location: Midbrain
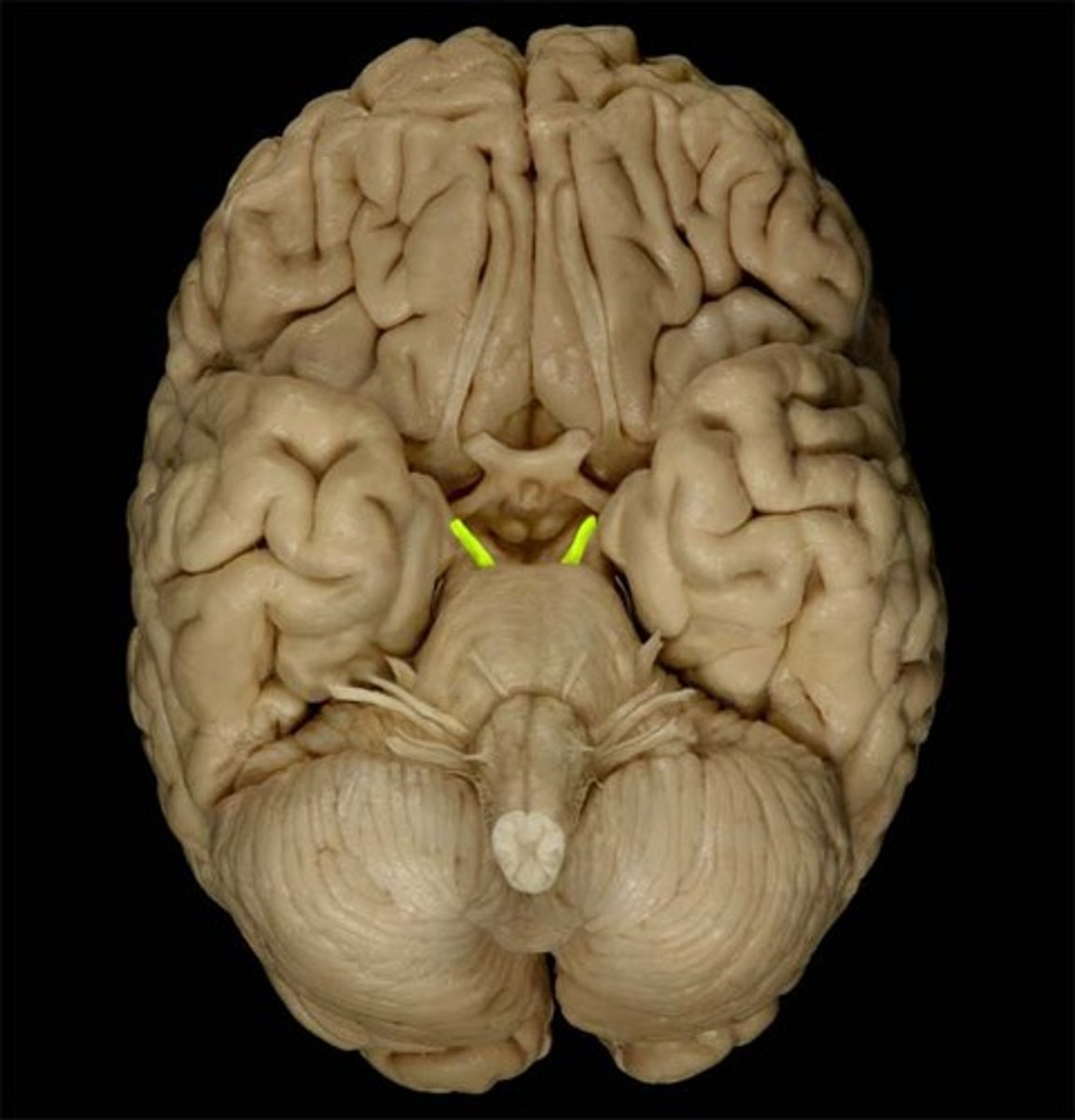
Trochlear Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement (downward and inward)
Location: Midbrain
Trigeminal Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, general sensory)- mastication, touch, pain, temperature
Location: Pons
Abducens Nerve
Function: motor- eye movement
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
Facial Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, general sensory)- facial expression, lip articulation, taste on anterior tongue, secretion of saliva and tears
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Function: special sensesory- hearing and balance
Location: Medulla-Pons junction
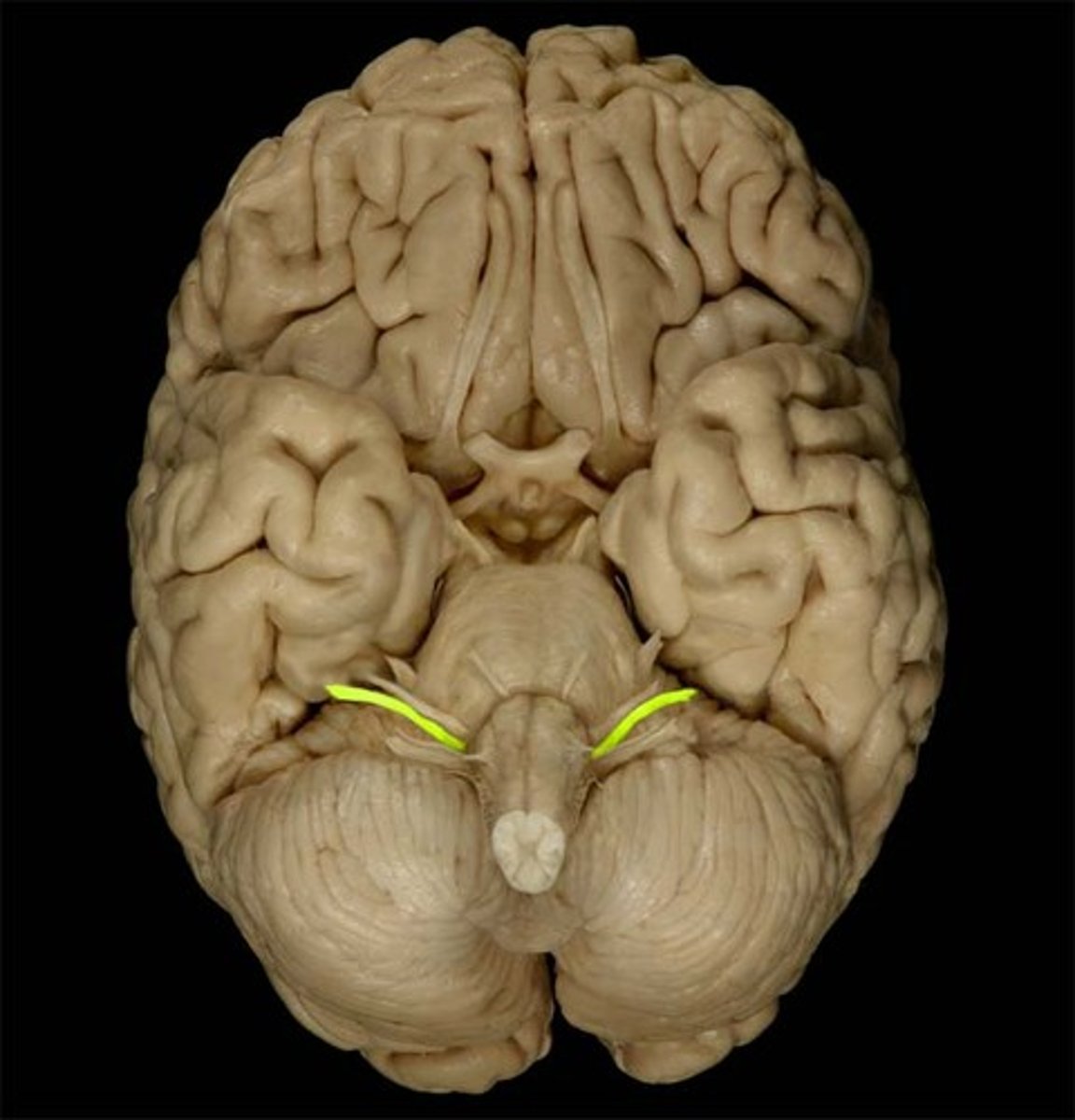
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, visceral sensory, general sensory)- taste on posterior of tongue, gag reflex, swallowing
Location: Medulla
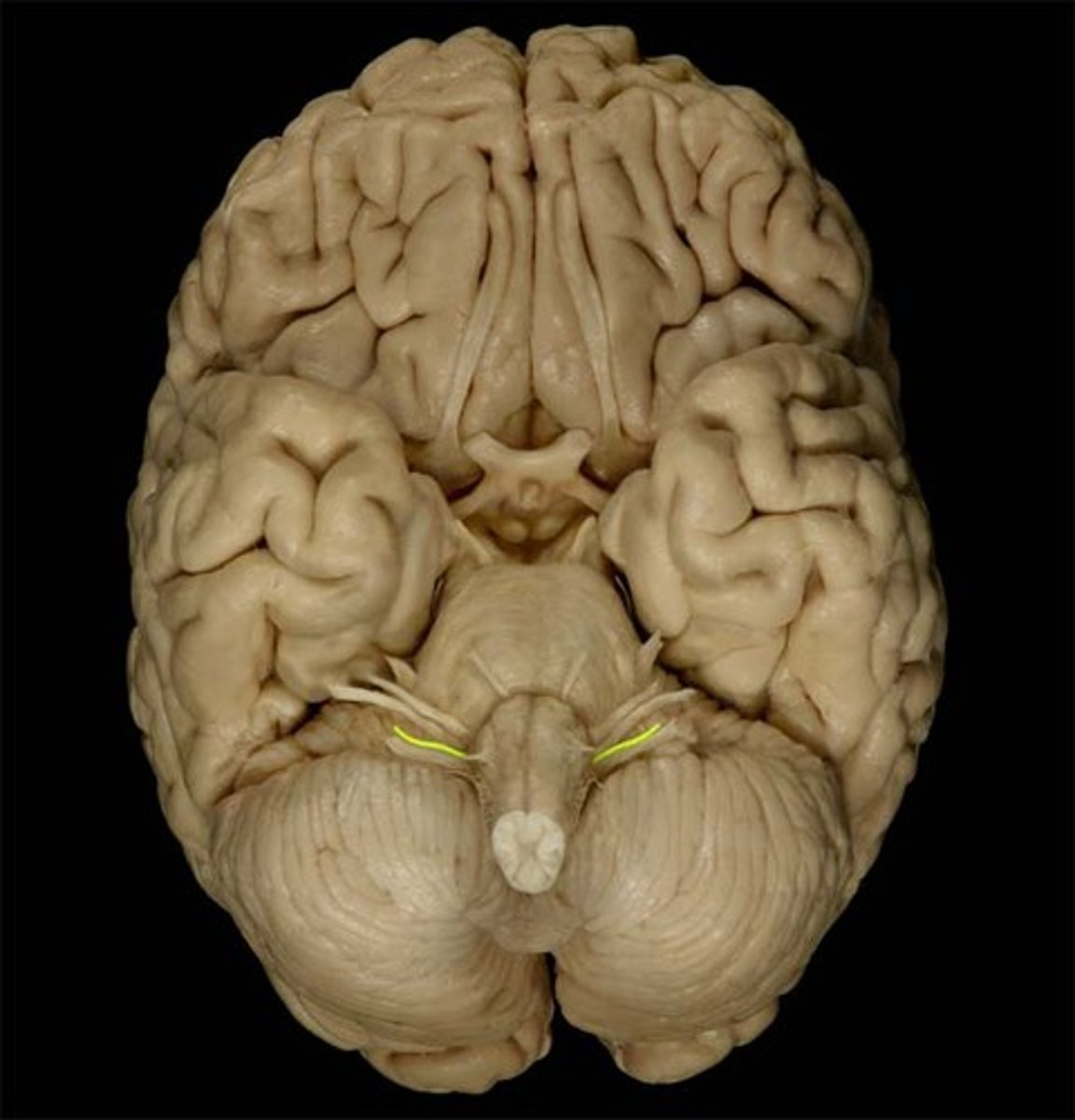
Vagus Nerve
Function: mixed (motor, parasympathetic, visceral sensory, general sensory)- visceral muscle movement (heart, lungs, intestines)
Location: Medulla
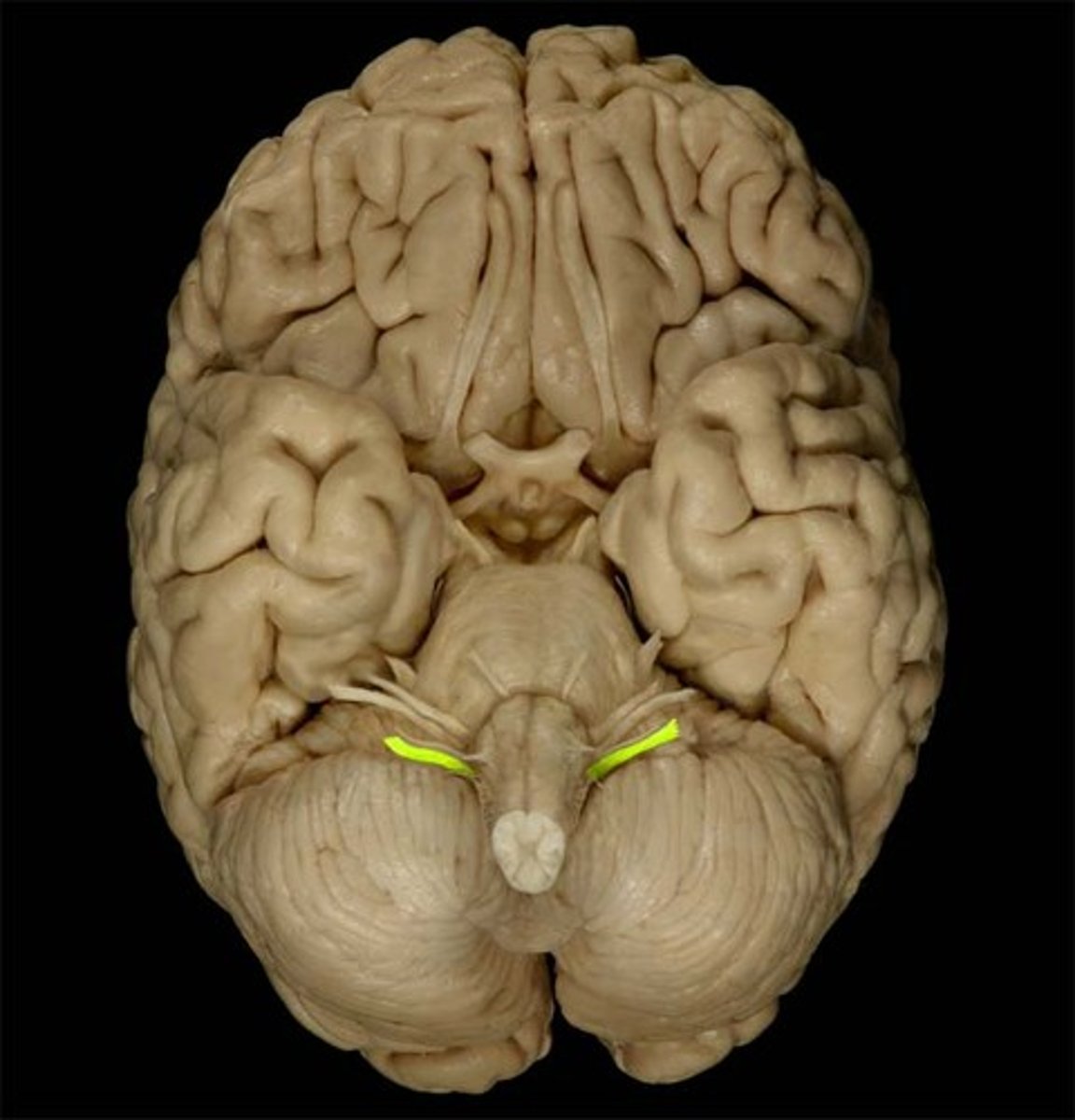
Accessory Nerve
Function: motor- movement of shoulders and neck
Location: Spinal cord
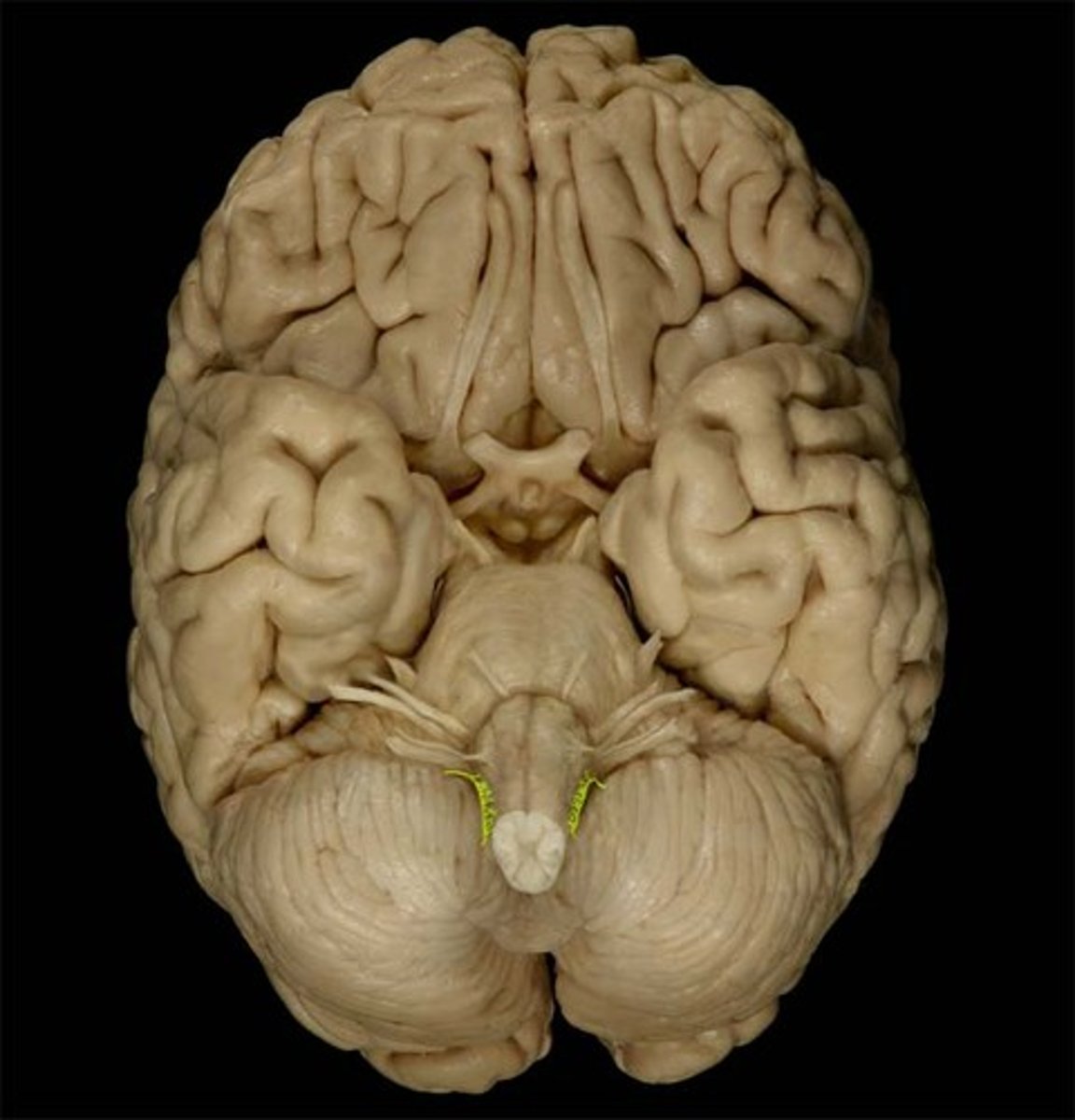
Hypoglossal Nerve
Function: motor- speech movements of the tongue, swallowing
Location: Medulla
Dorsal Root
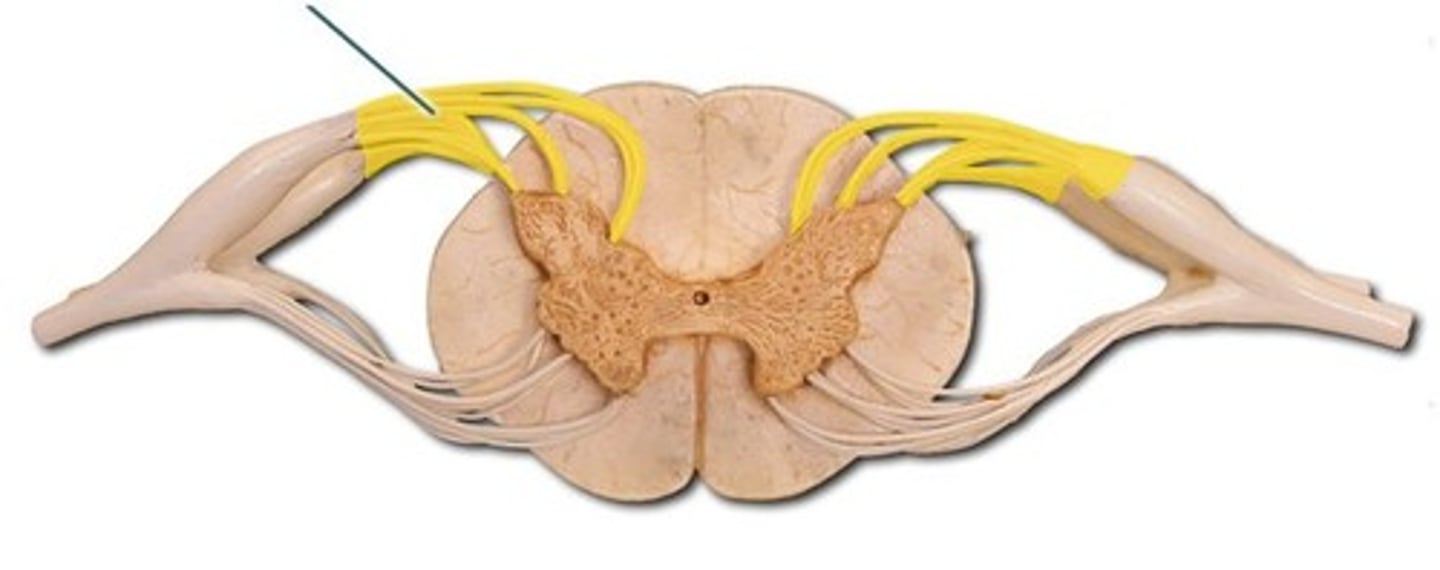
Dorsal Horn
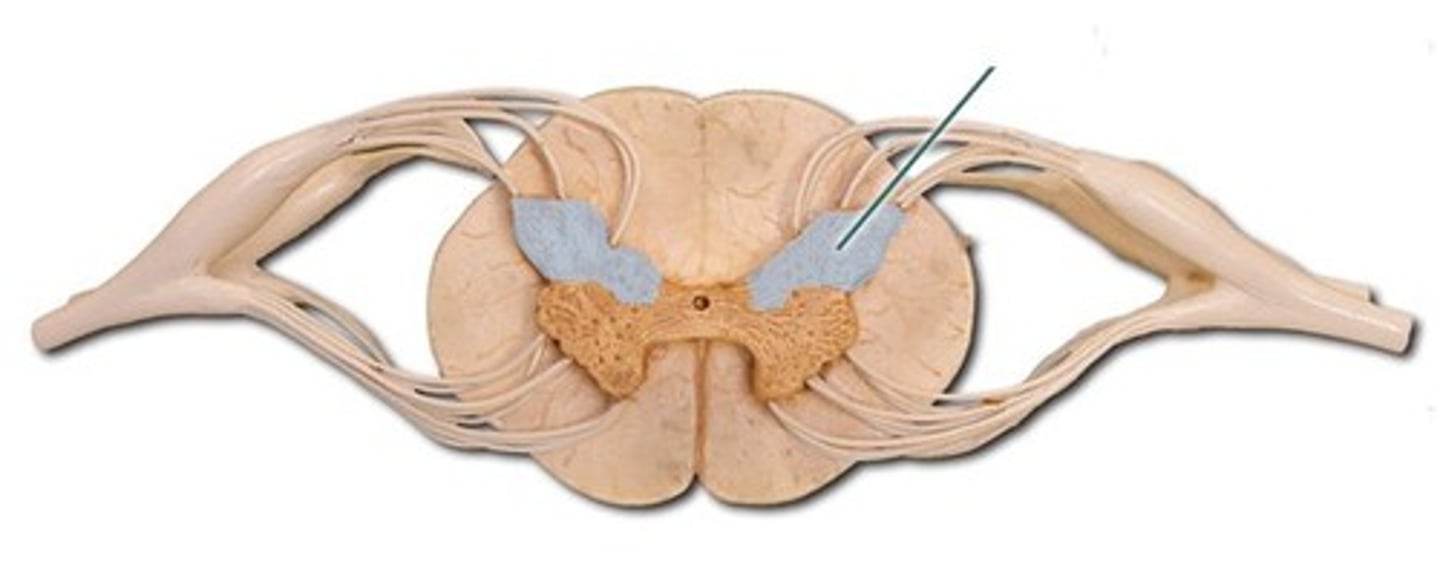
Ventral Horn
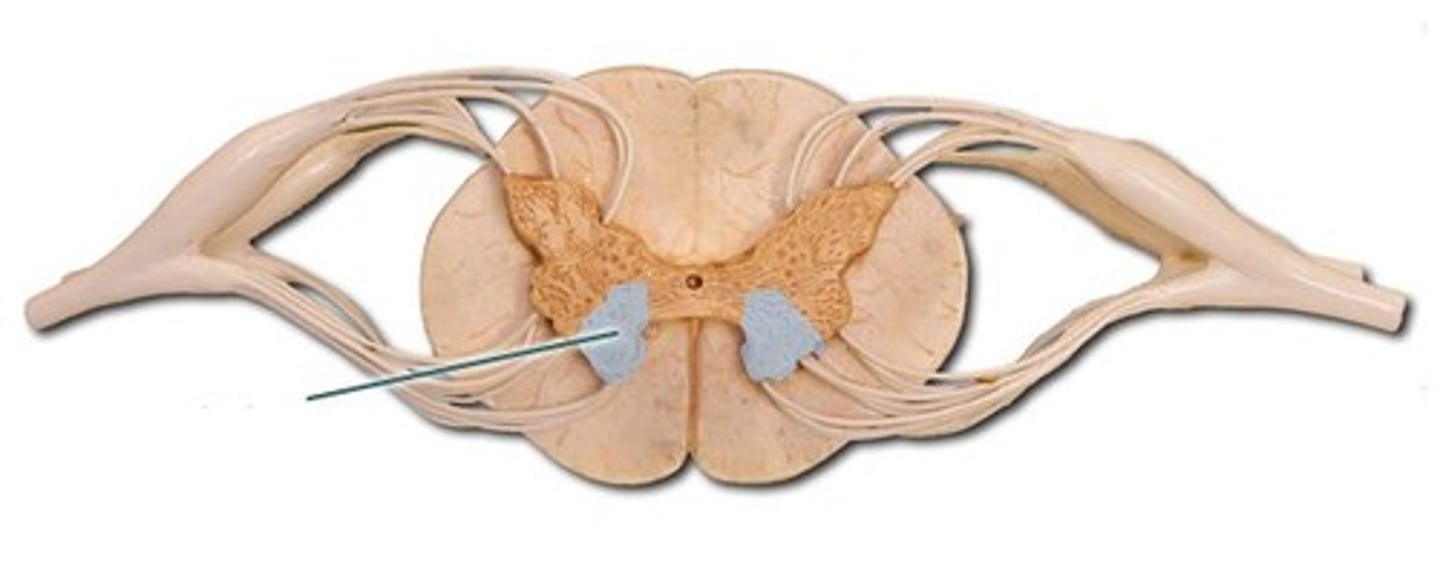
Dorsal Root Ganglion
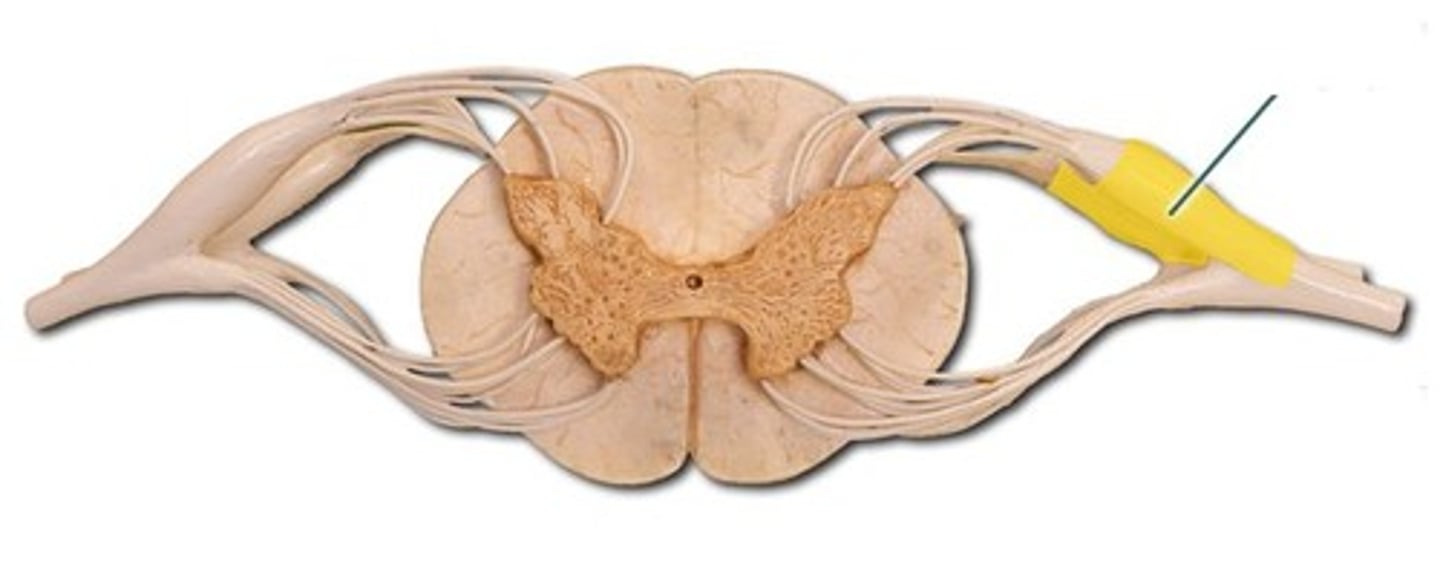
Anterior Median Fissure
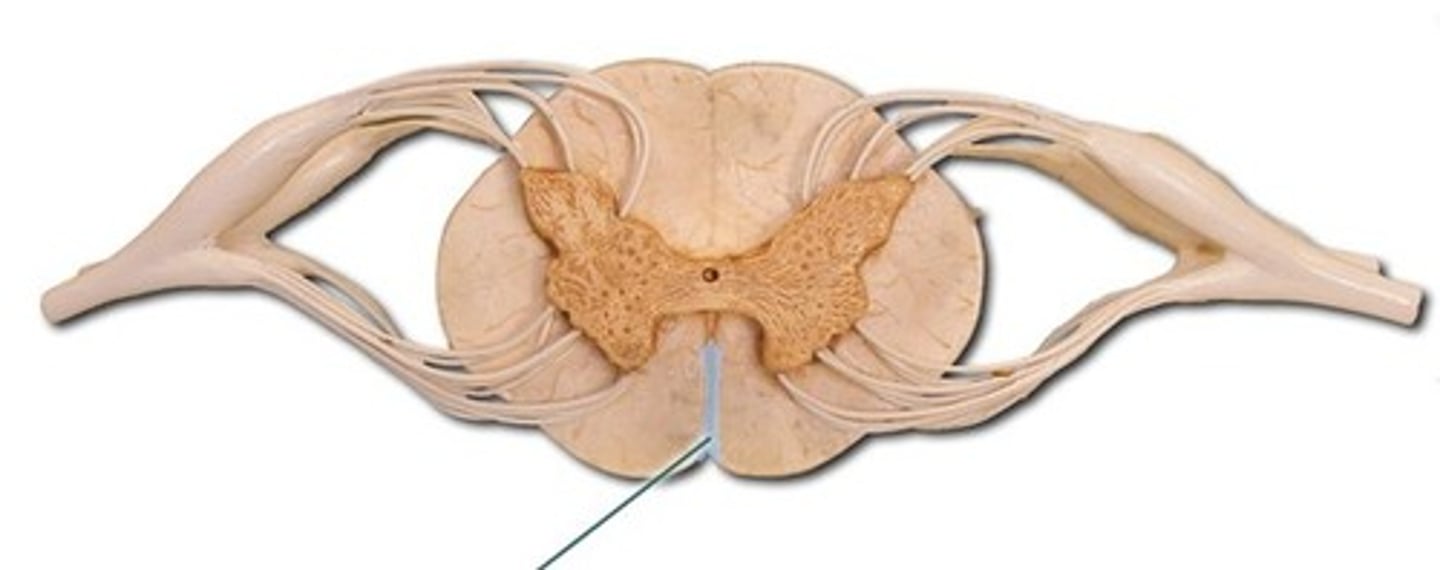
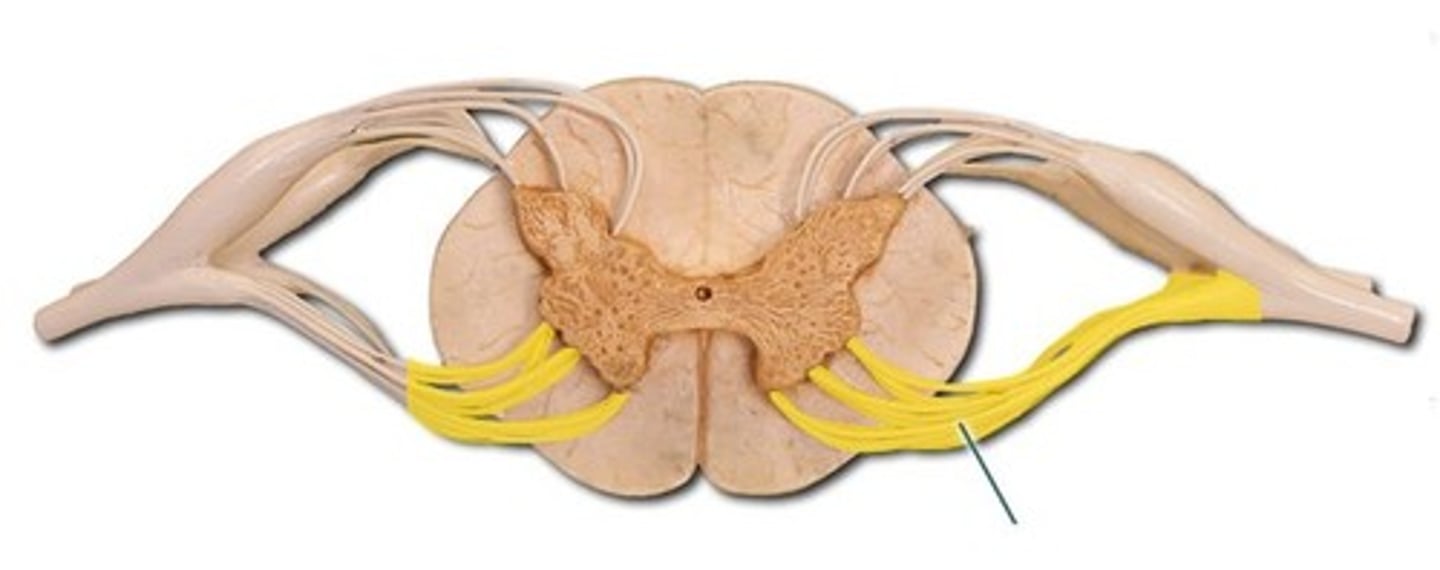
Ventral Root
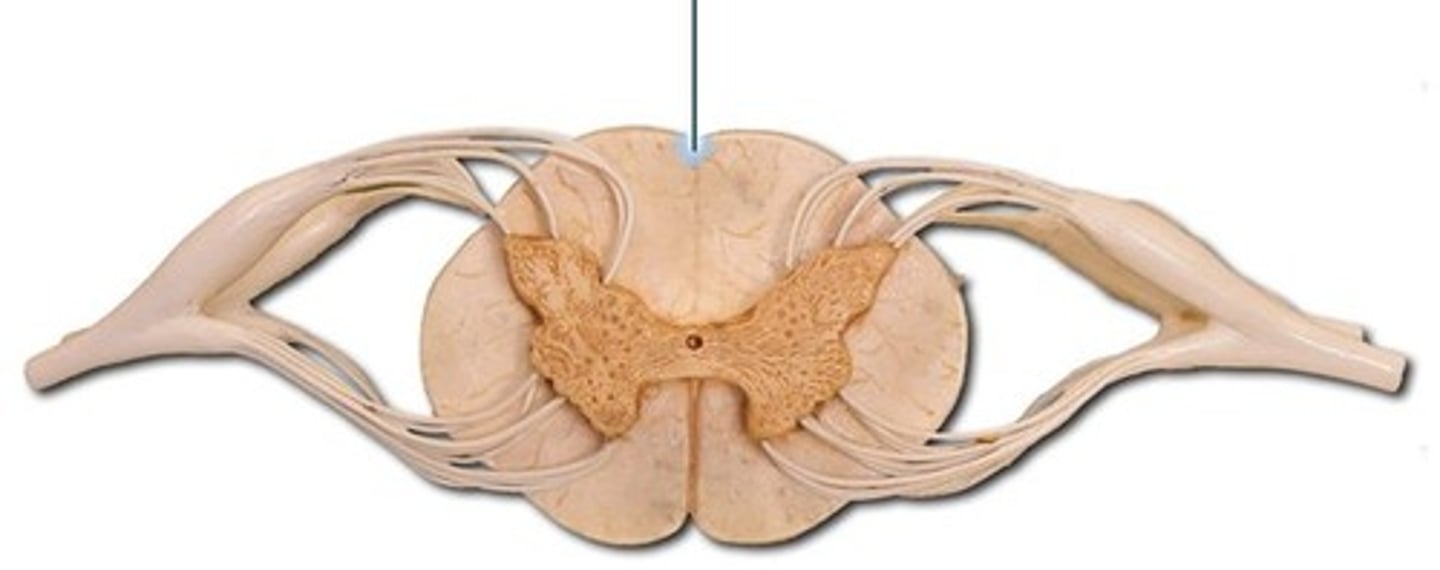
Posterior Median Sulcus
Central Canal
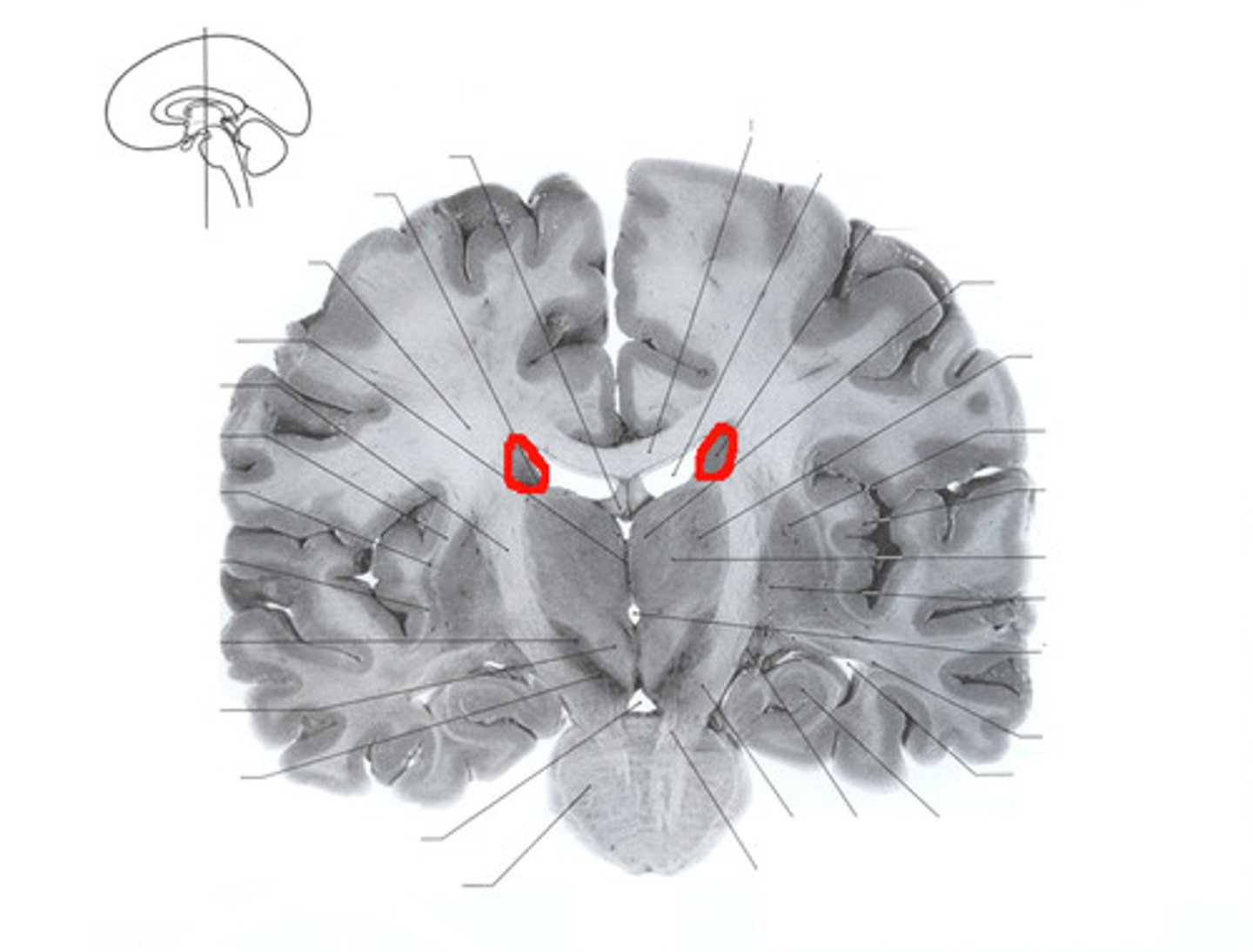
Caudate Nucleus
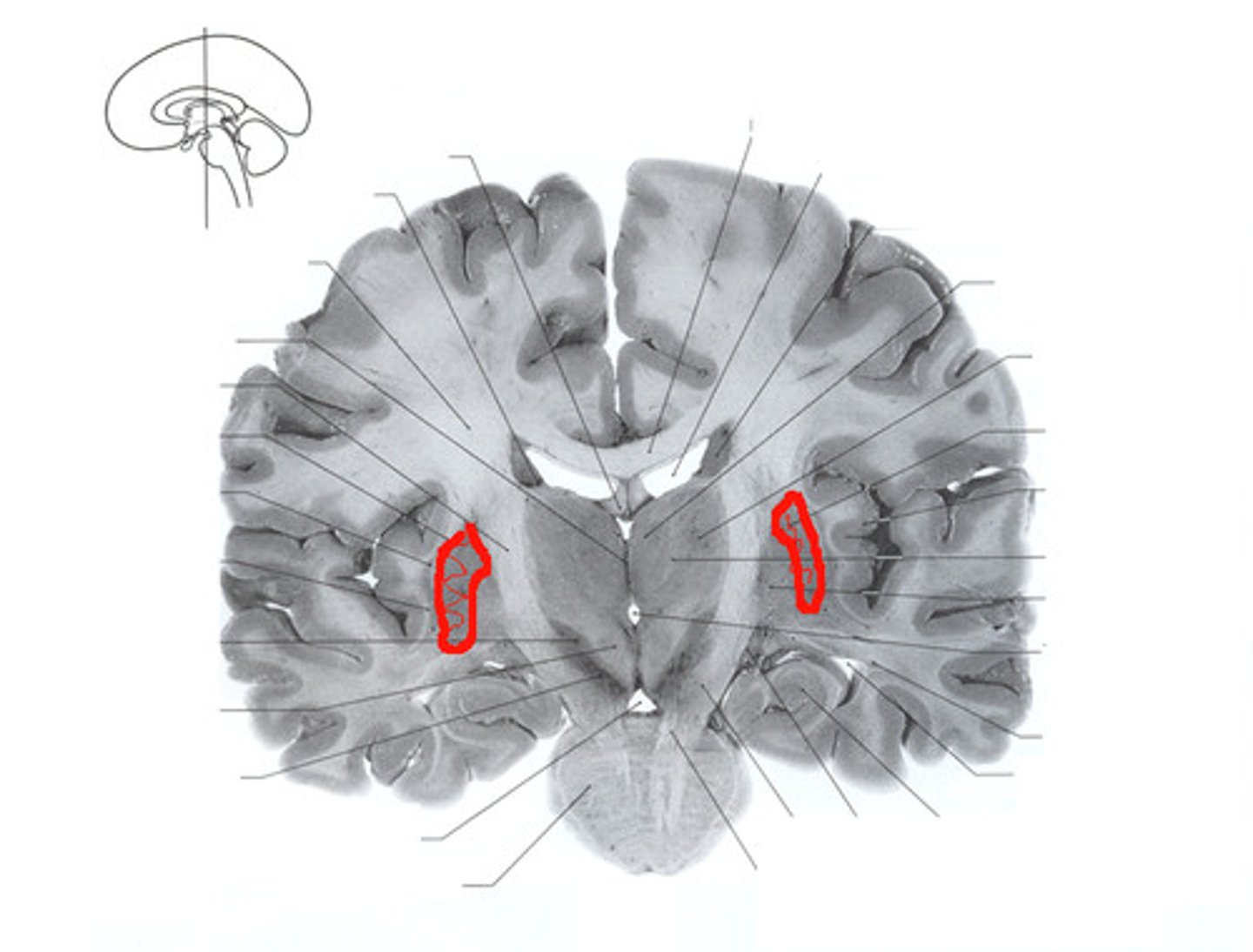
Globus Pallidus
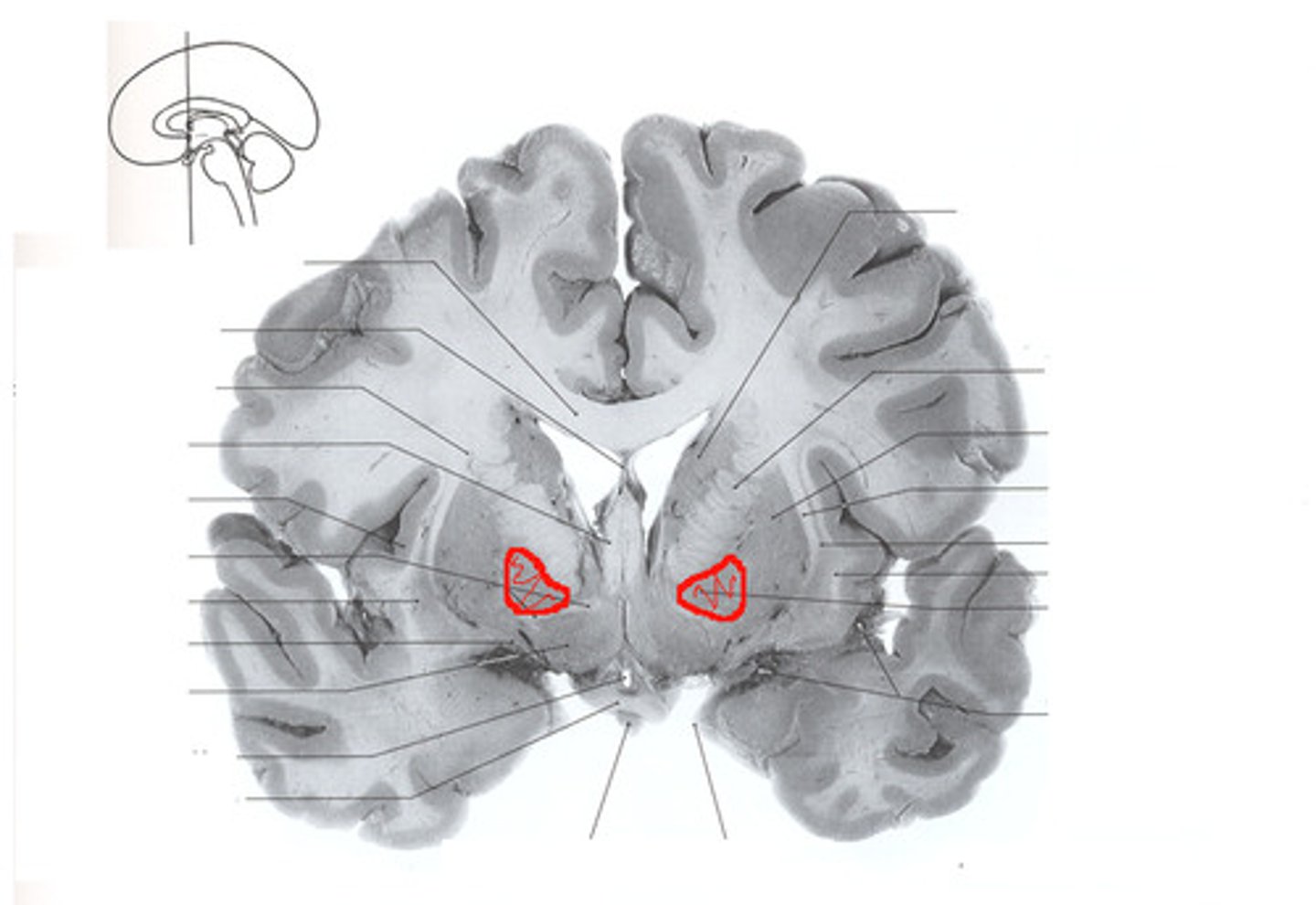
Putamen
Choroid Plexus
What are some differences between the human and sheep brain?
Human Brain:
more rounded
larger
deeper and more sulci
larger surface area
smaller olfactory bulbs
Sheep Brain:
more elongated
smaller
less sulci, more shallow
smaller surface area
larger olfactory bulbs
What is the function of mammillary bodies?
Serve as a relay center for impulses that travel through the brain. Also play an important role in recalling memories
What is the function of the fornix?
Fibers that connect the hippocampus to the hypothalamus and is associated with memory and emotions
What is the function of the pineal gland?
Responsible for reproduction and circadian rhythms (larger in sheep)
What are the different parts of the ventricular system of the brain?
Lateral ventricle, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, and fourth ventricle
Which two cranial nerves are primarily responsible for our perception of taste?
Facial nerve & glossopharyngeal nerve
When looking at cross section of the spinal cord, which region will you observe motor neurons?
Gray matter, more specifically in the ventral horn of the gray matter
In which part of the spinal cord will you have an enlarged area that reflects innervation of the lower extremities?
The lumbosacral enlargement running form L2-S3
What are the membranes of the brain?
1. Dura Matter
2. Arachnoidea
3. Pia Matter
Which artery supplies the cerebellum?
Anterior cerebral artery
Which artery supplies the occipital lobe?
Posterior cerebral artery
Which artery supplies the parietal and temporal lobes?
Middle cerebral artery
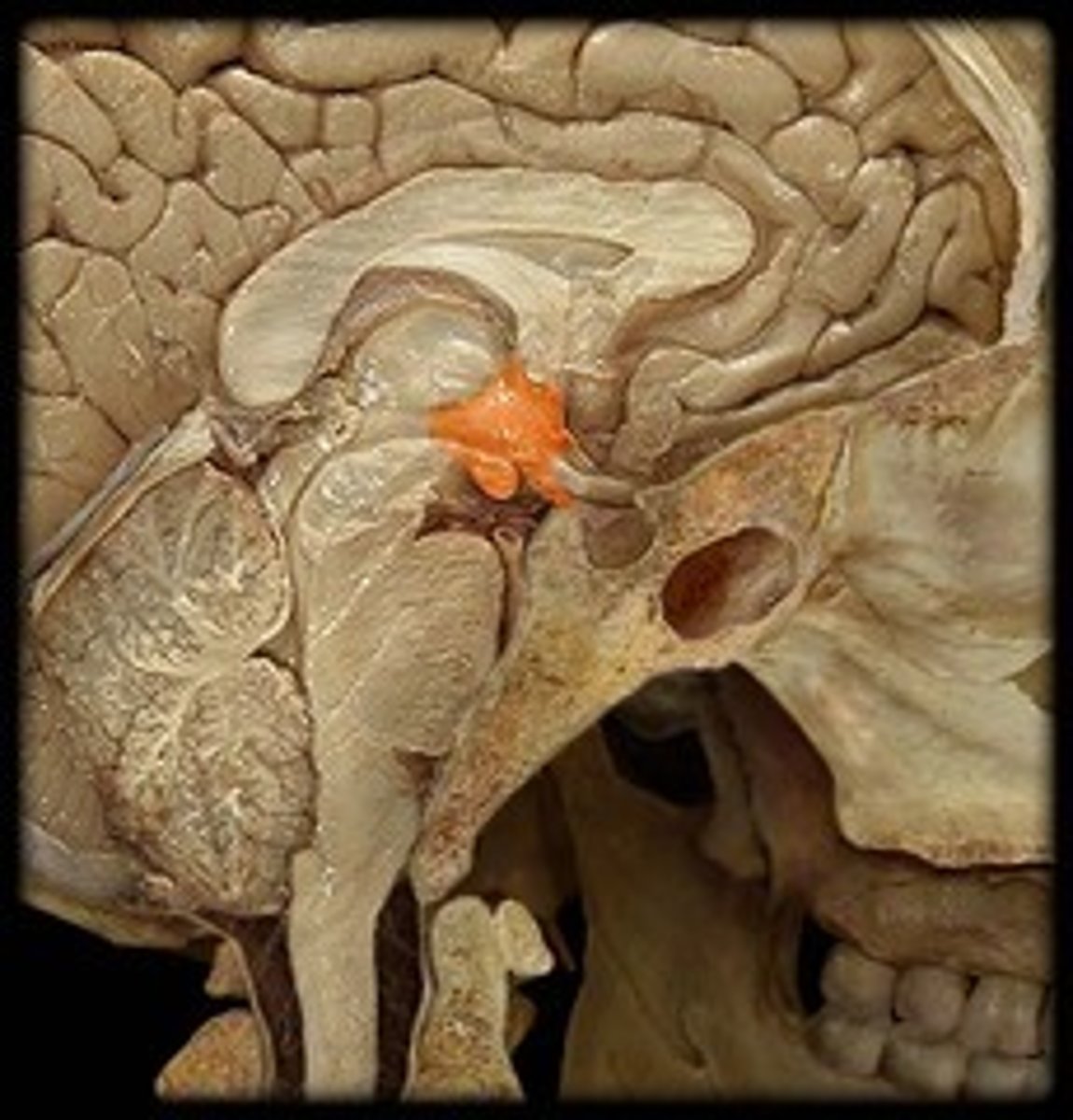
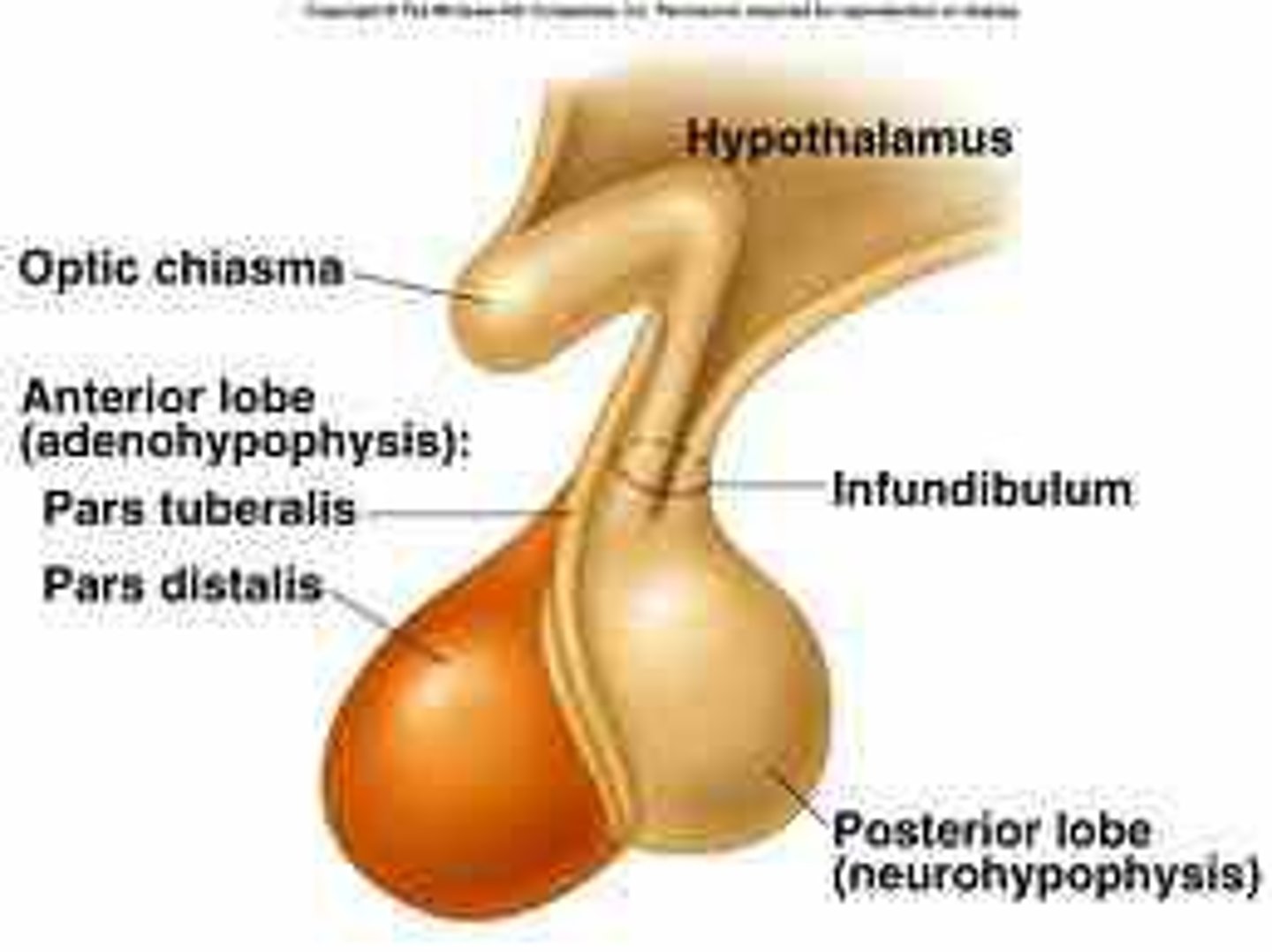
Pituitary gland
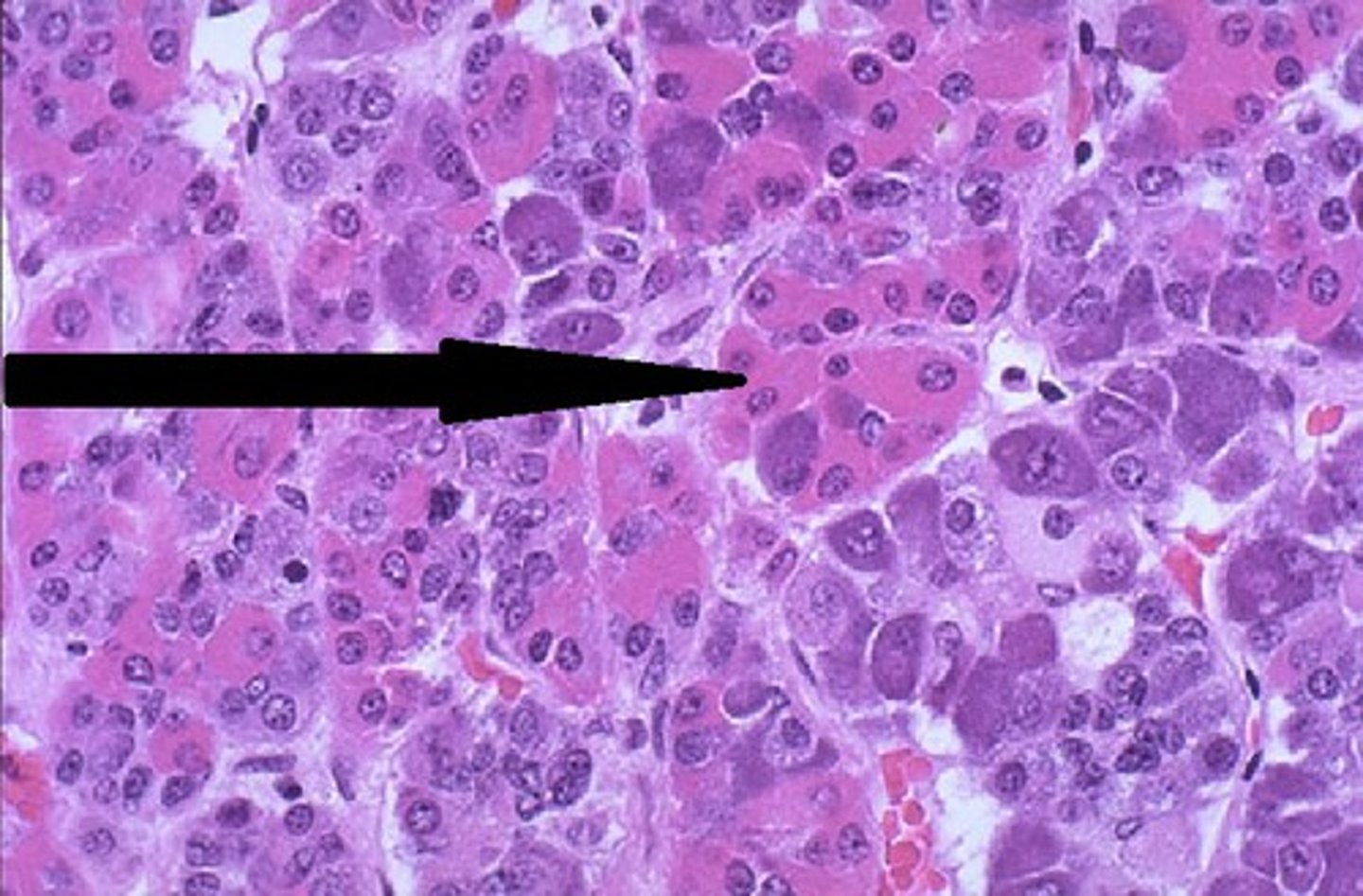
Acidophils Cells of the anterior Pituitary Gland
Secrete growth hormone, prolactin
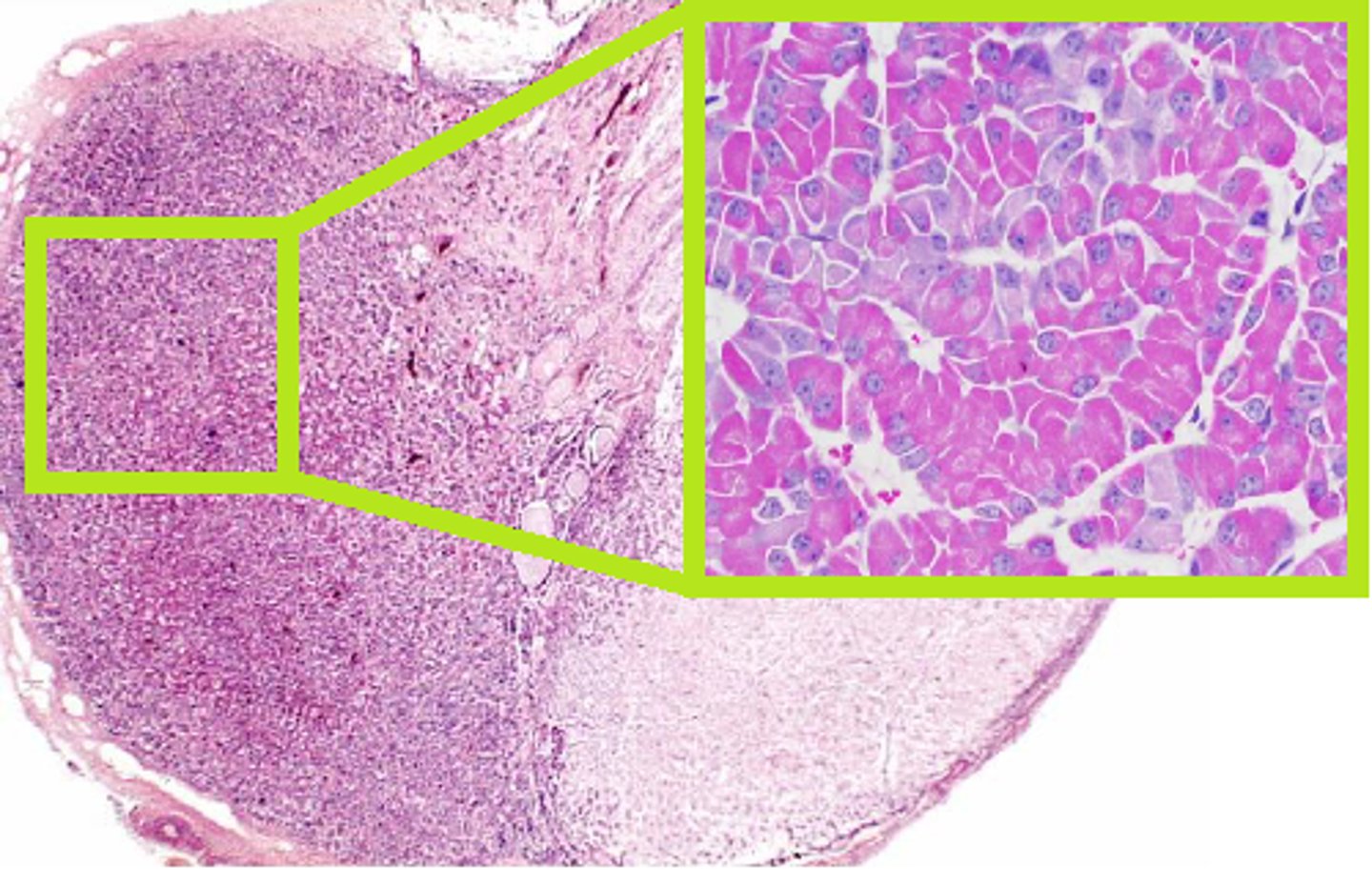
Basophils cells of the anterior pituitary gland
Secrete FSH LH and TSH
Pituicyte cells of the posterior pituitary gland
Thyroid gland cross section
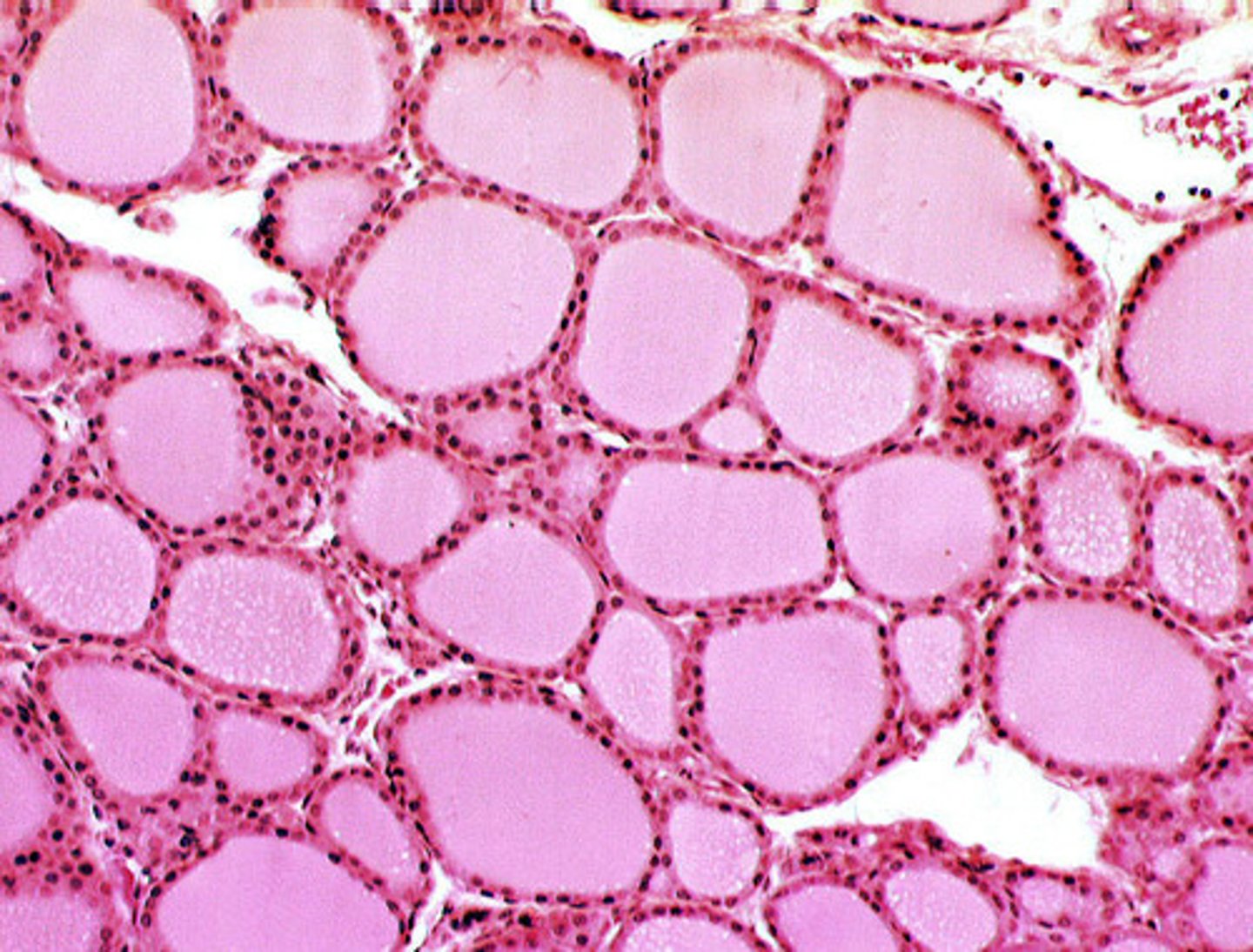
Follicles of the thyroid gland
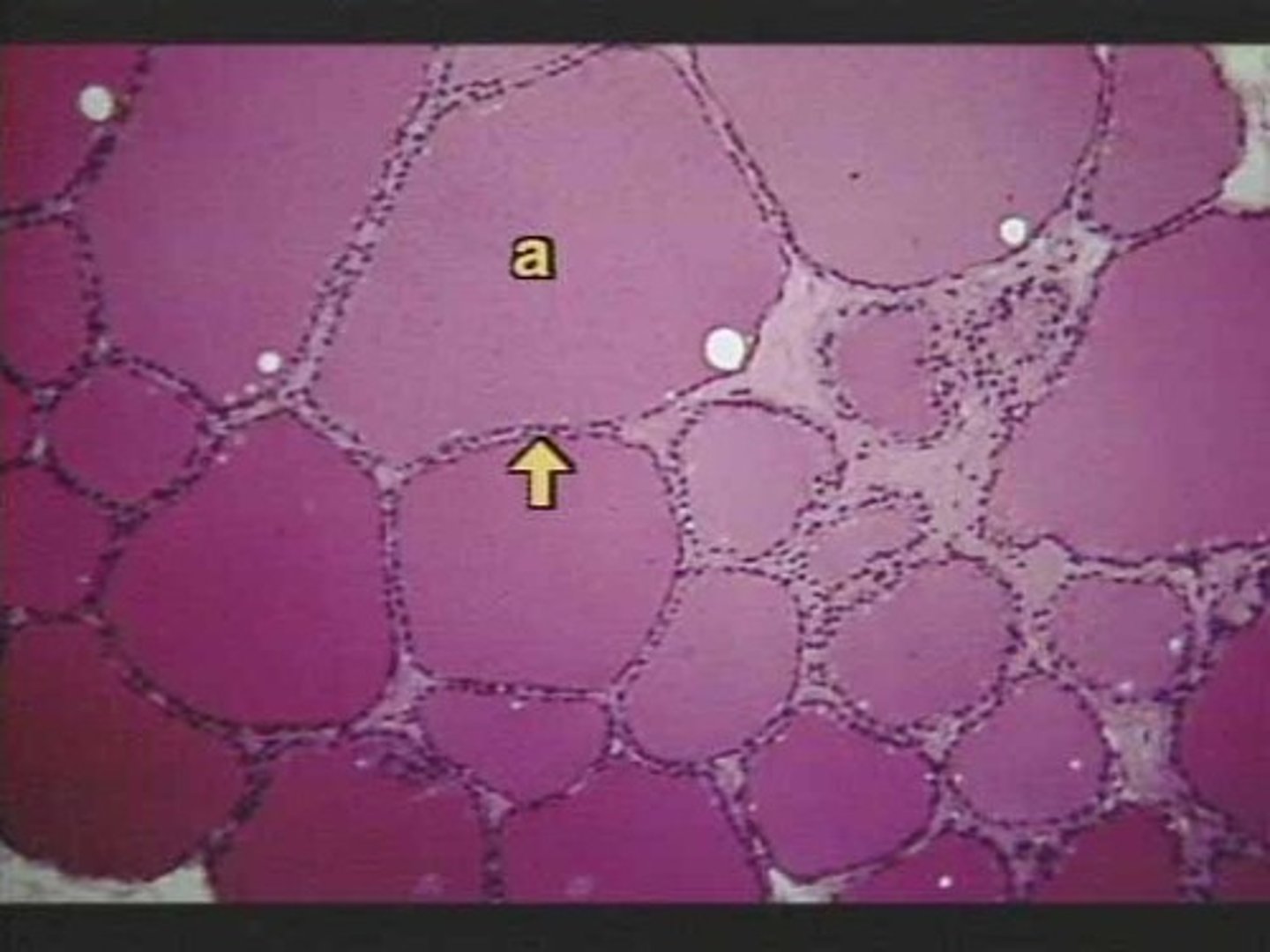
Colloid of the thyroid gland
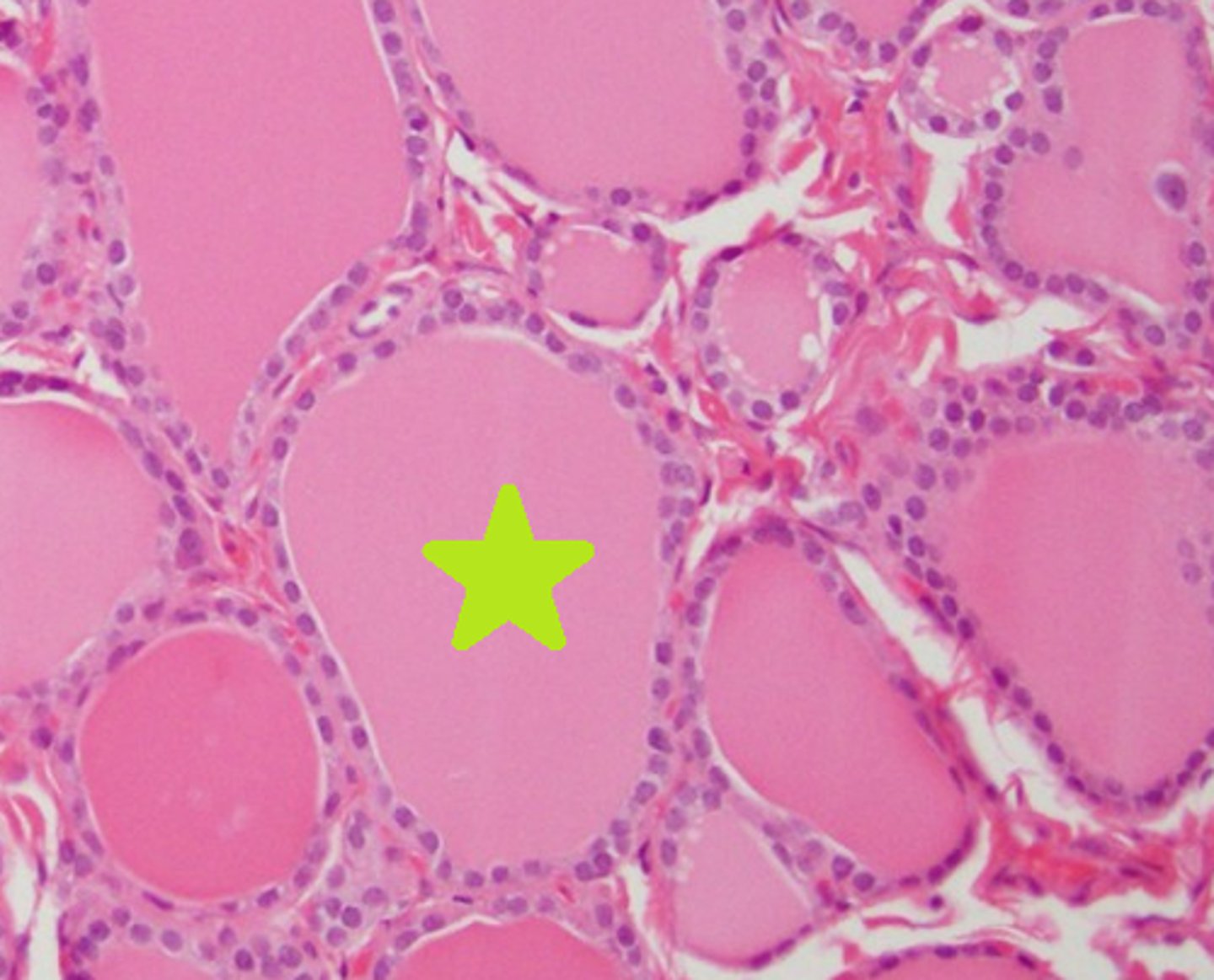
Follicular epithelial cells of the thyroid gland
1 & 3
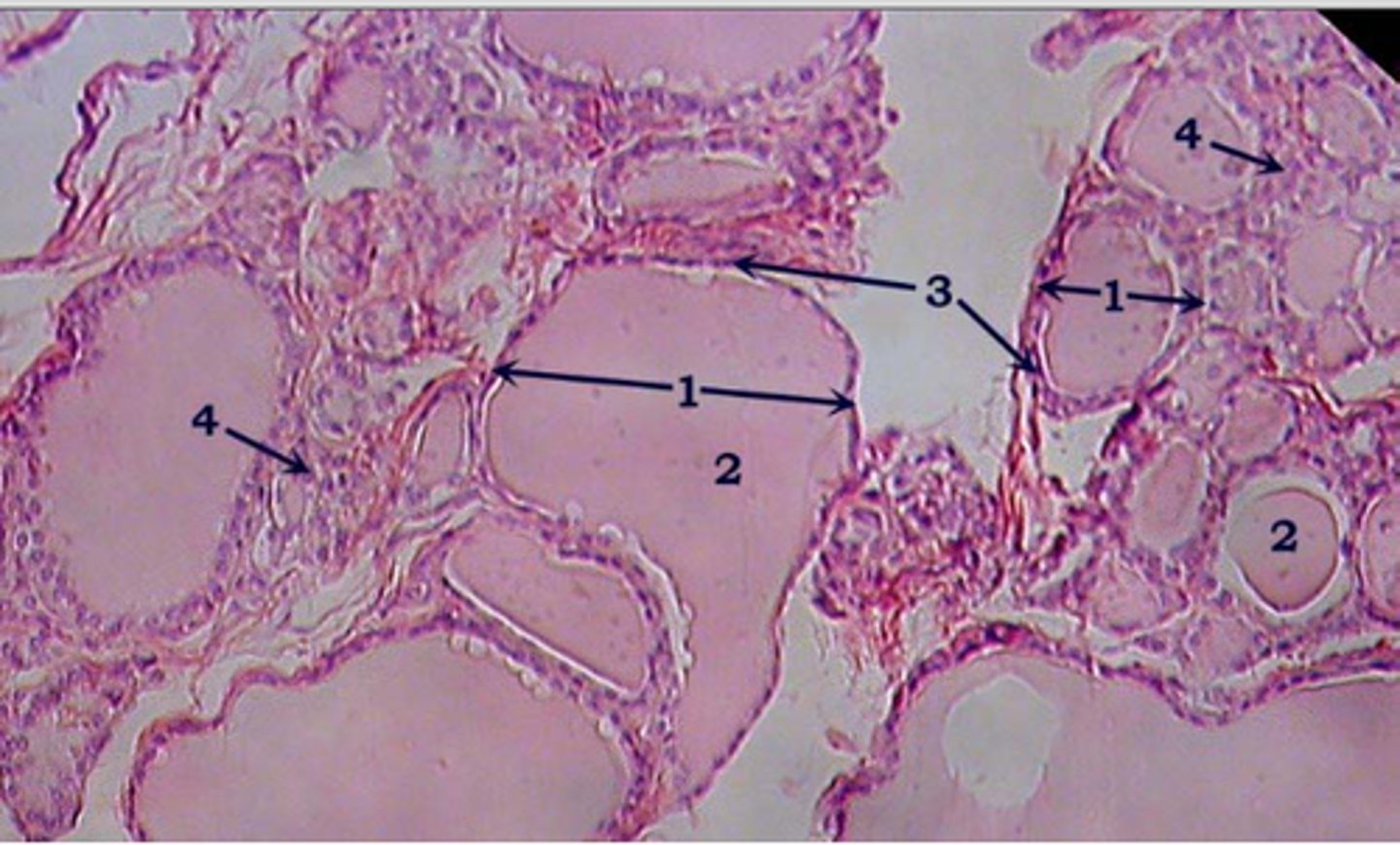
Parafollicular cells (C-cells) of the thyroid gland
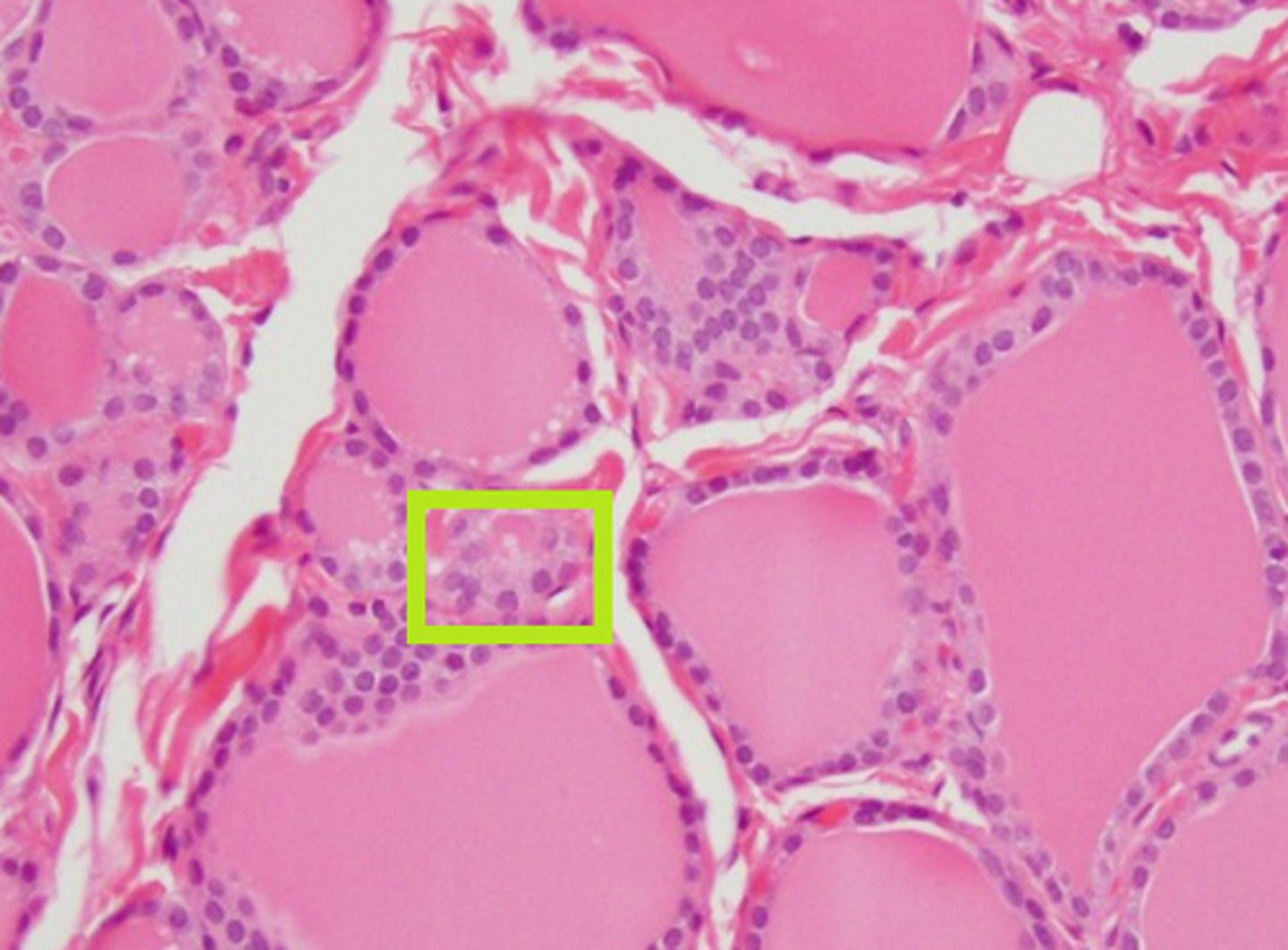
Parathyroid gland cross section
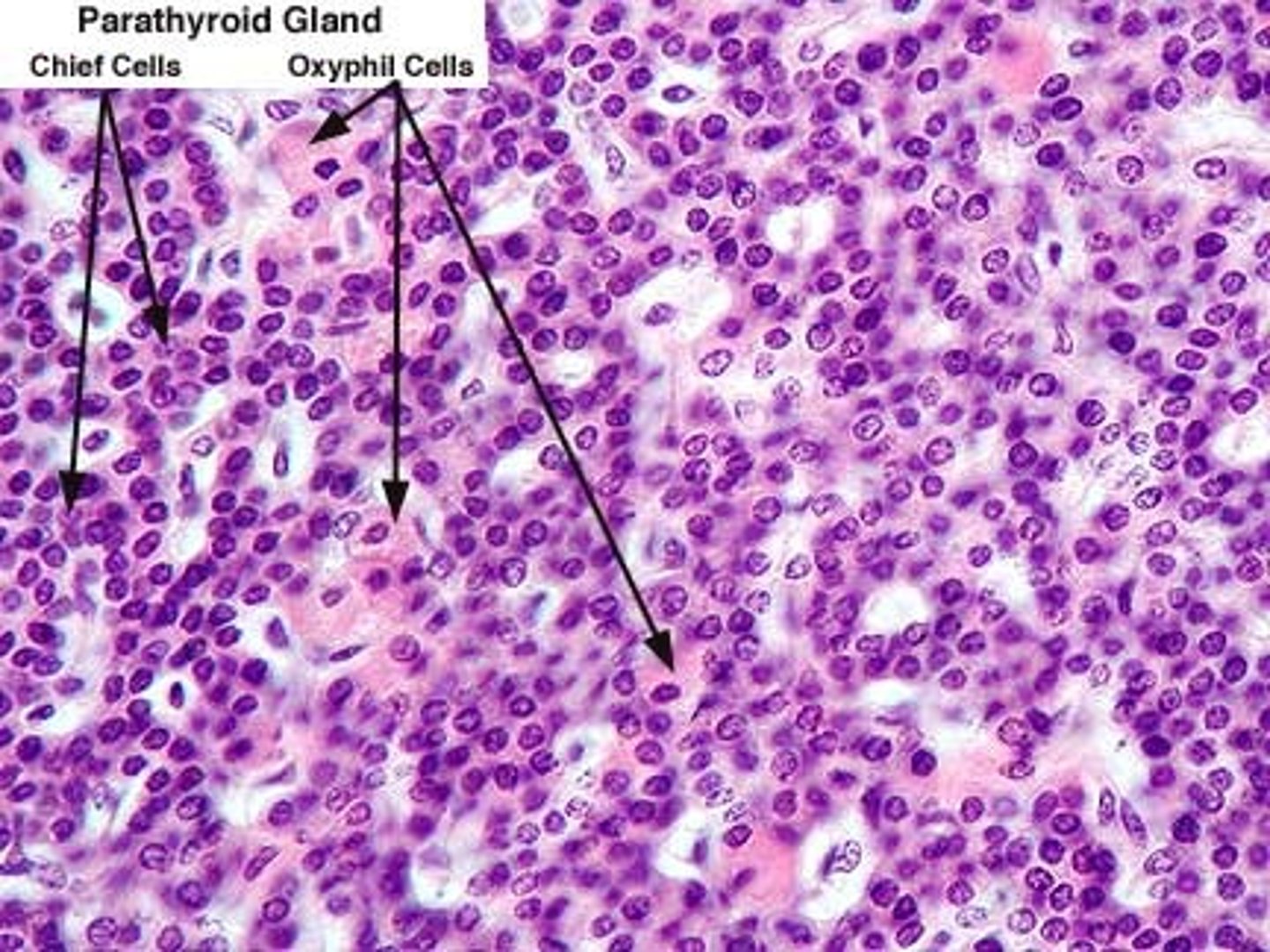
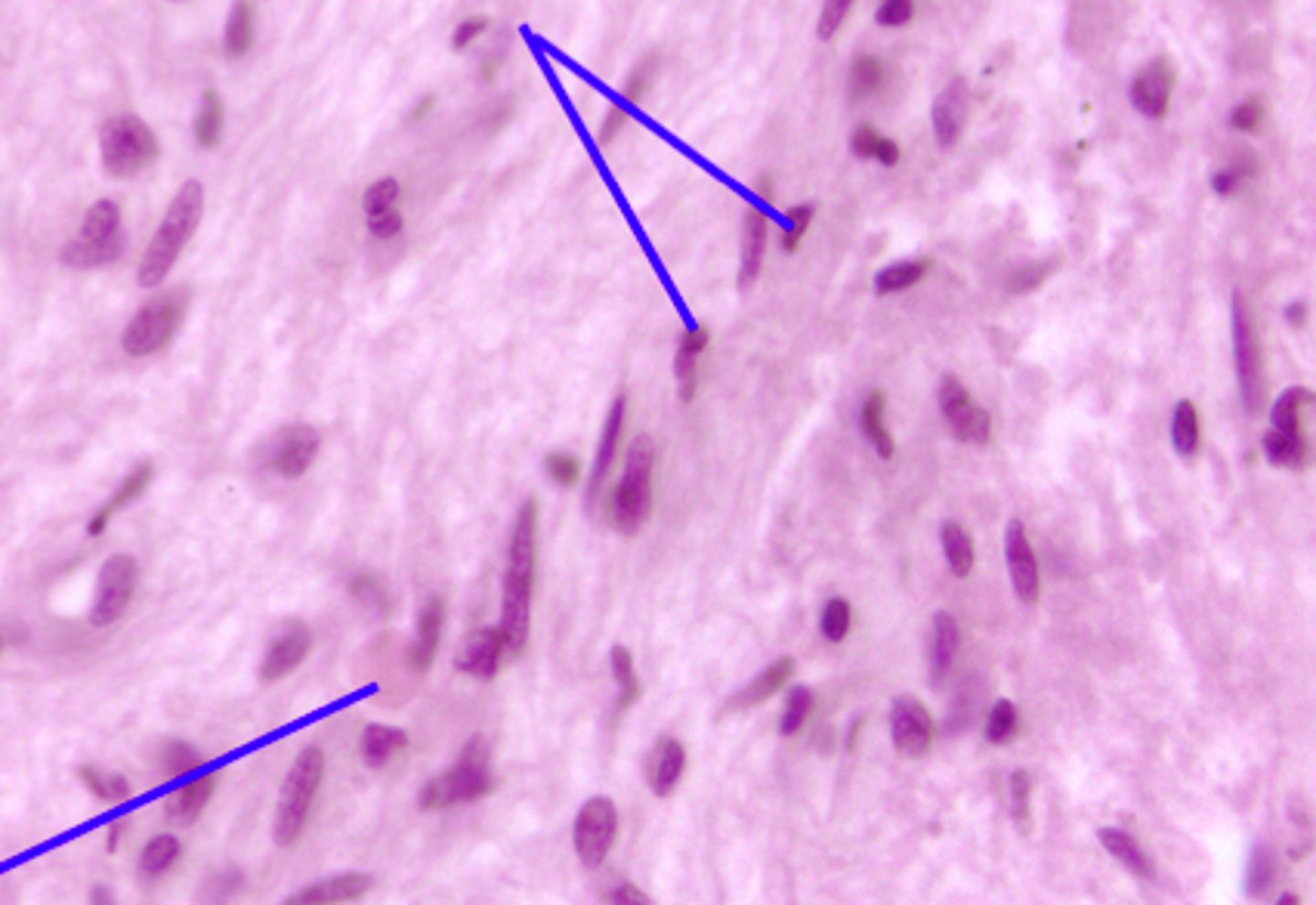
Oxyphil cells of the parathyroid gland
Second set of arrows
Larger cell type
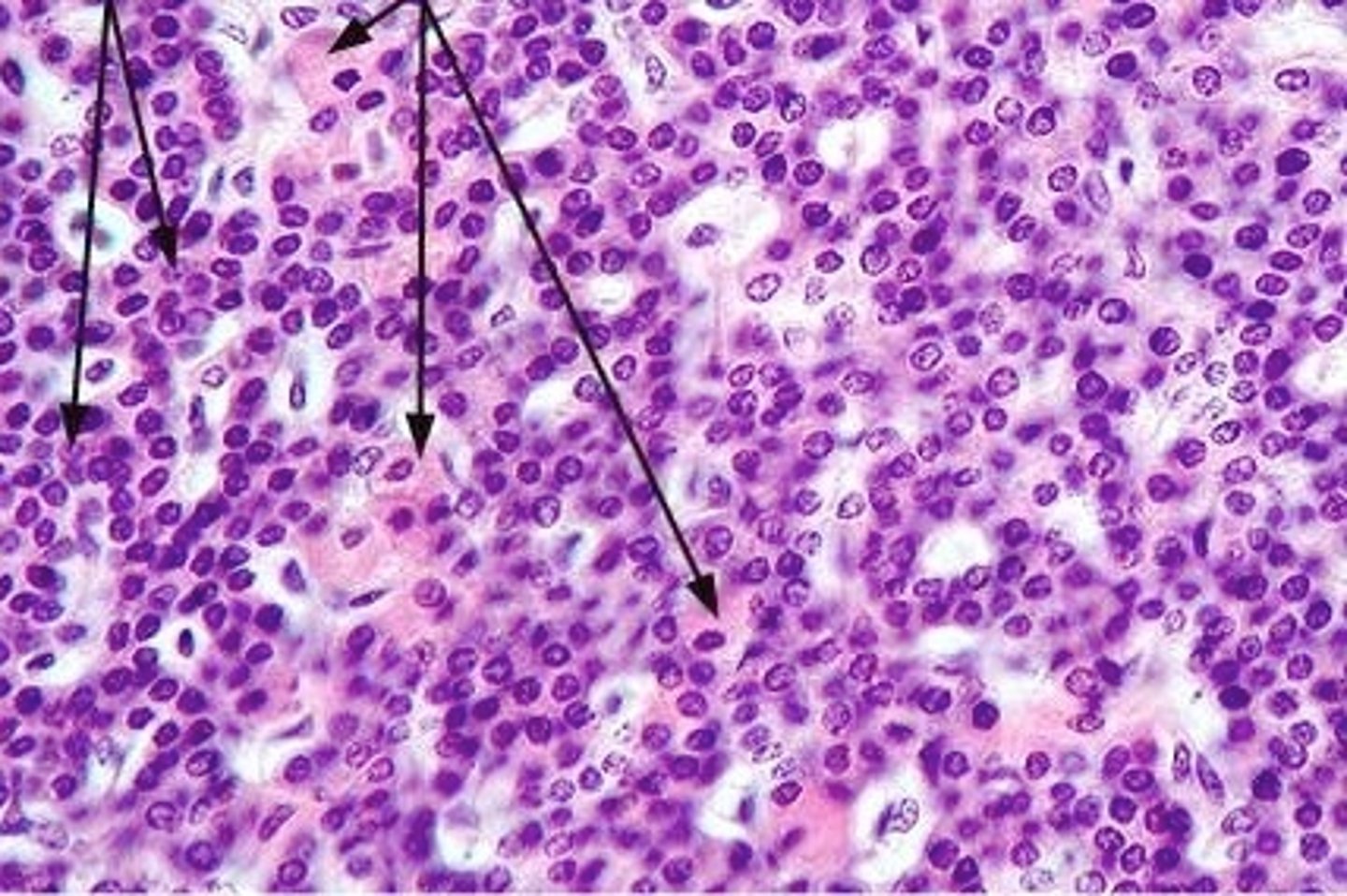
Chief cells of the parathyroid gland
First set of arrows
Most numerous cell type, smaller
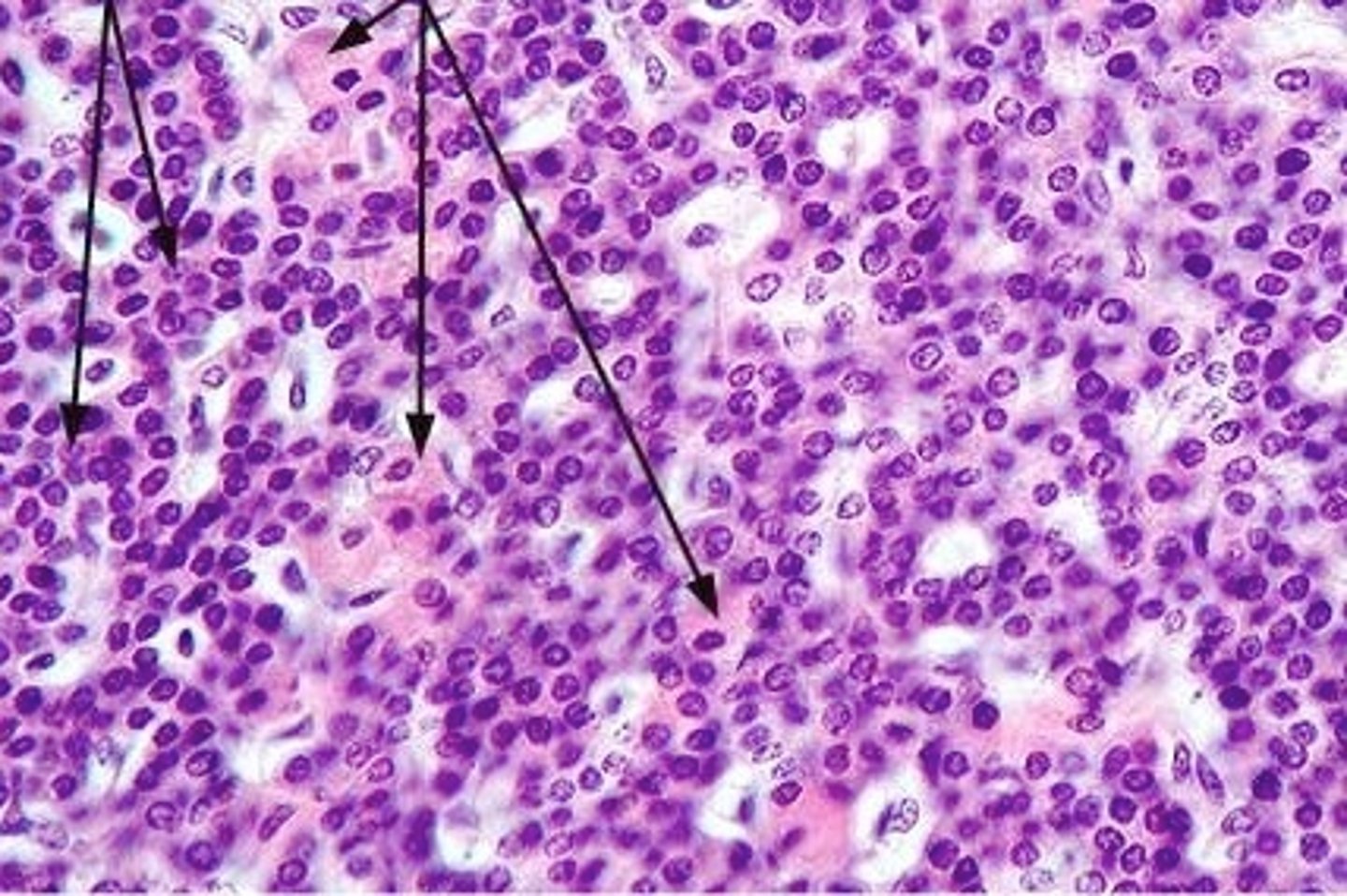
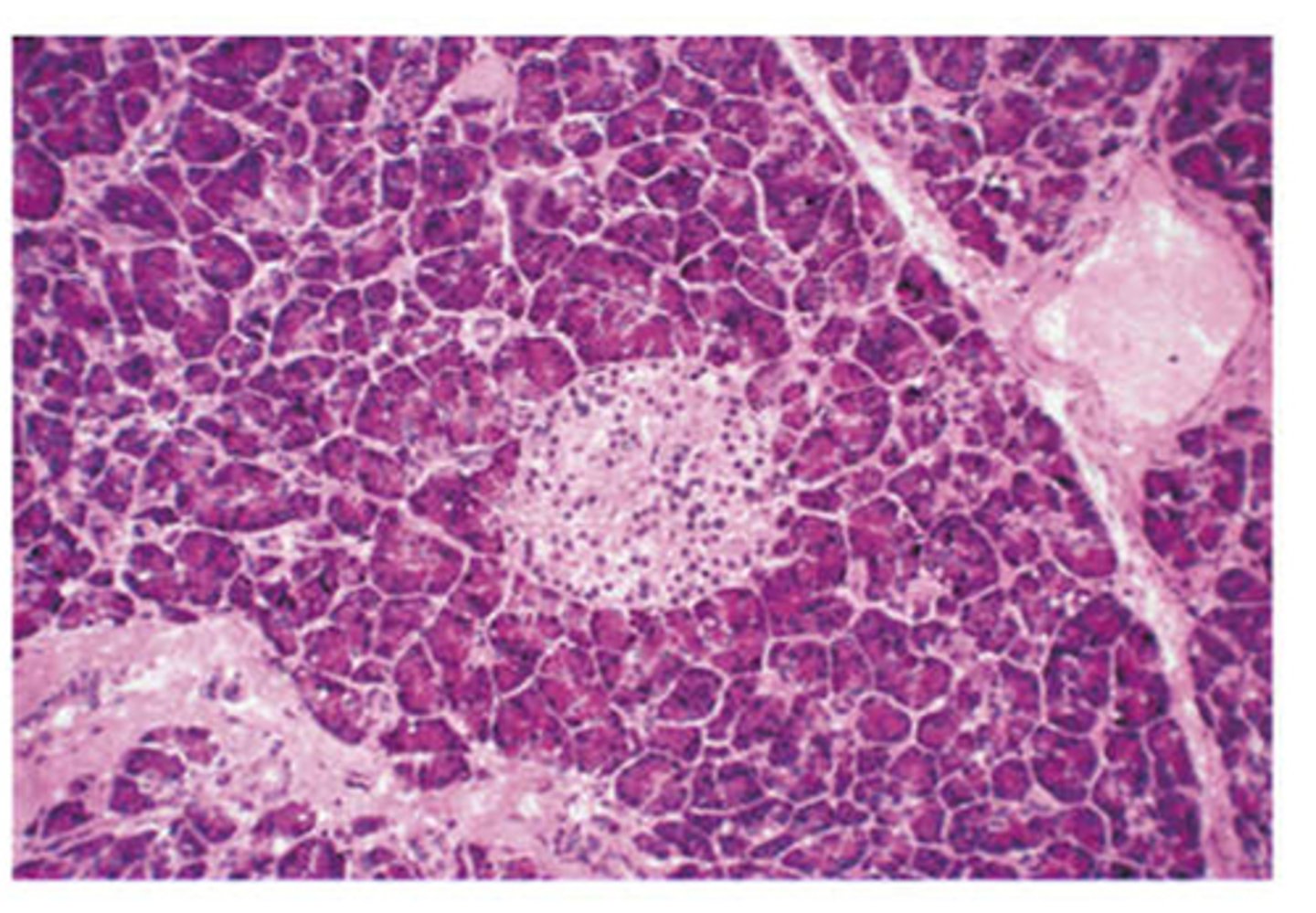
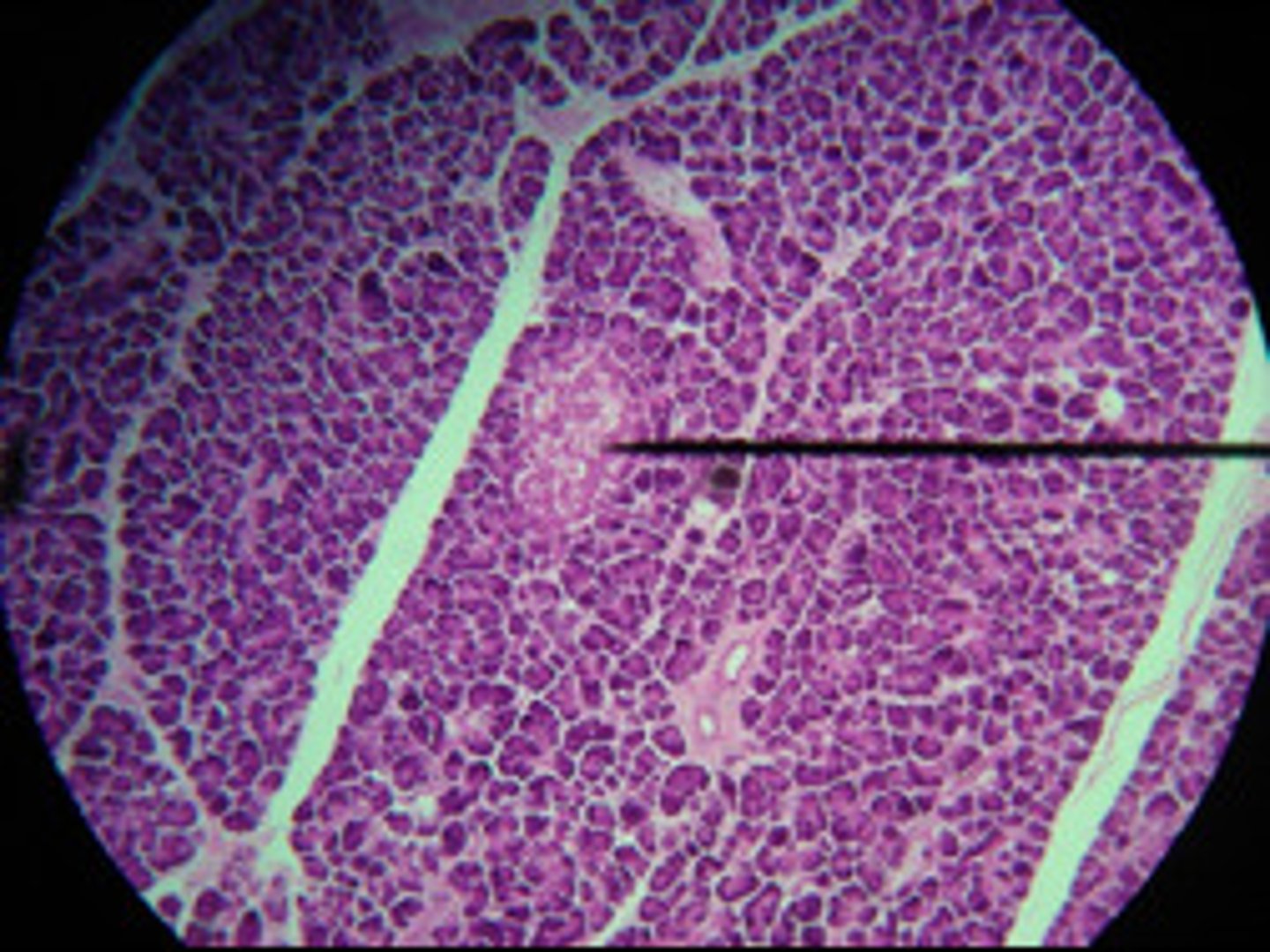
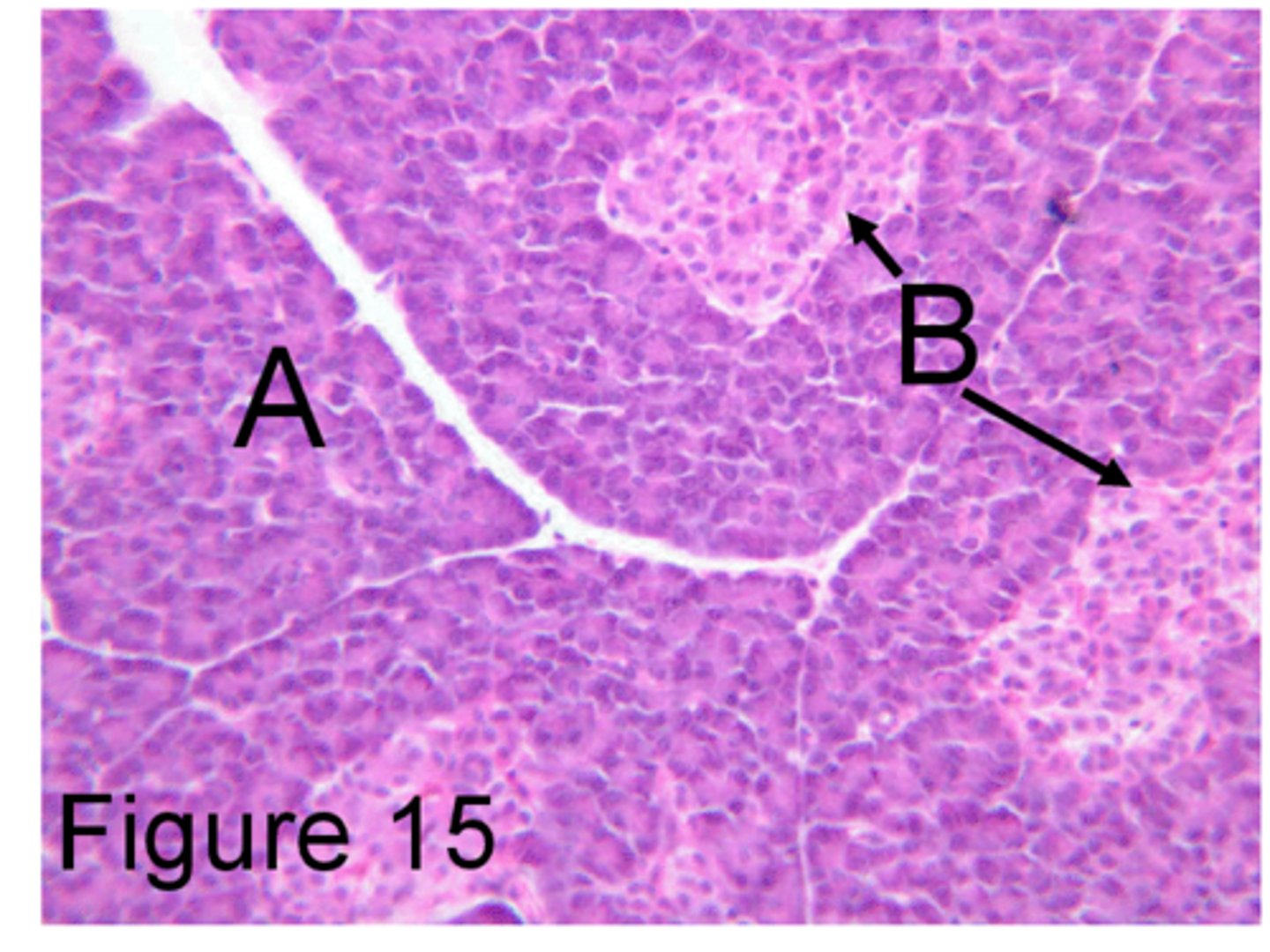
Pancreas cells cross section
Consists of exocrine cells and endocrine cells
Endocrine cells islet of langerhans of the pancreas
Secretes: insulin, glucagon, somatostatin
Exocrine Tissue of pancreas
A
Synthesizes and secretes digestive proenzymes and enzymes
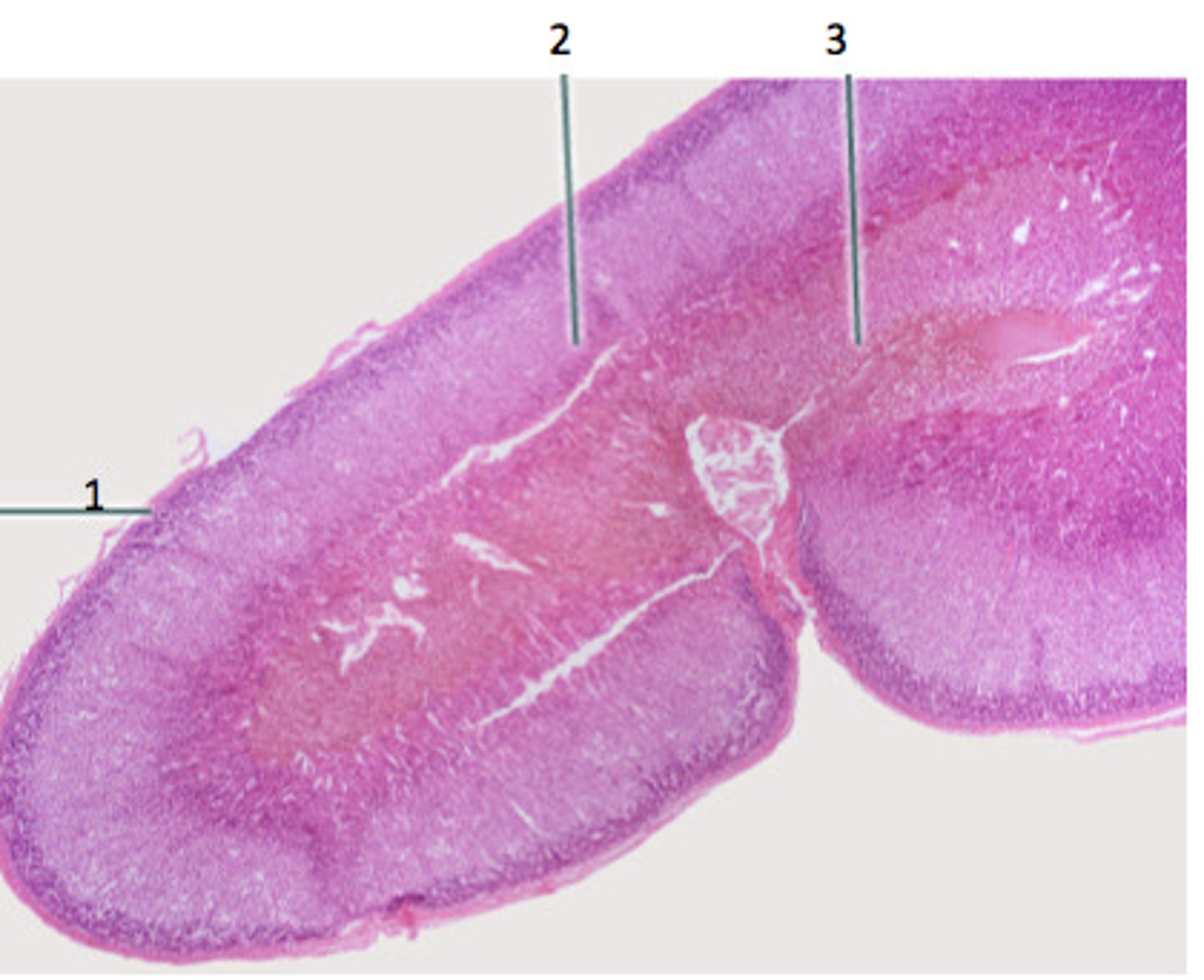
Adrenal Gland cross section
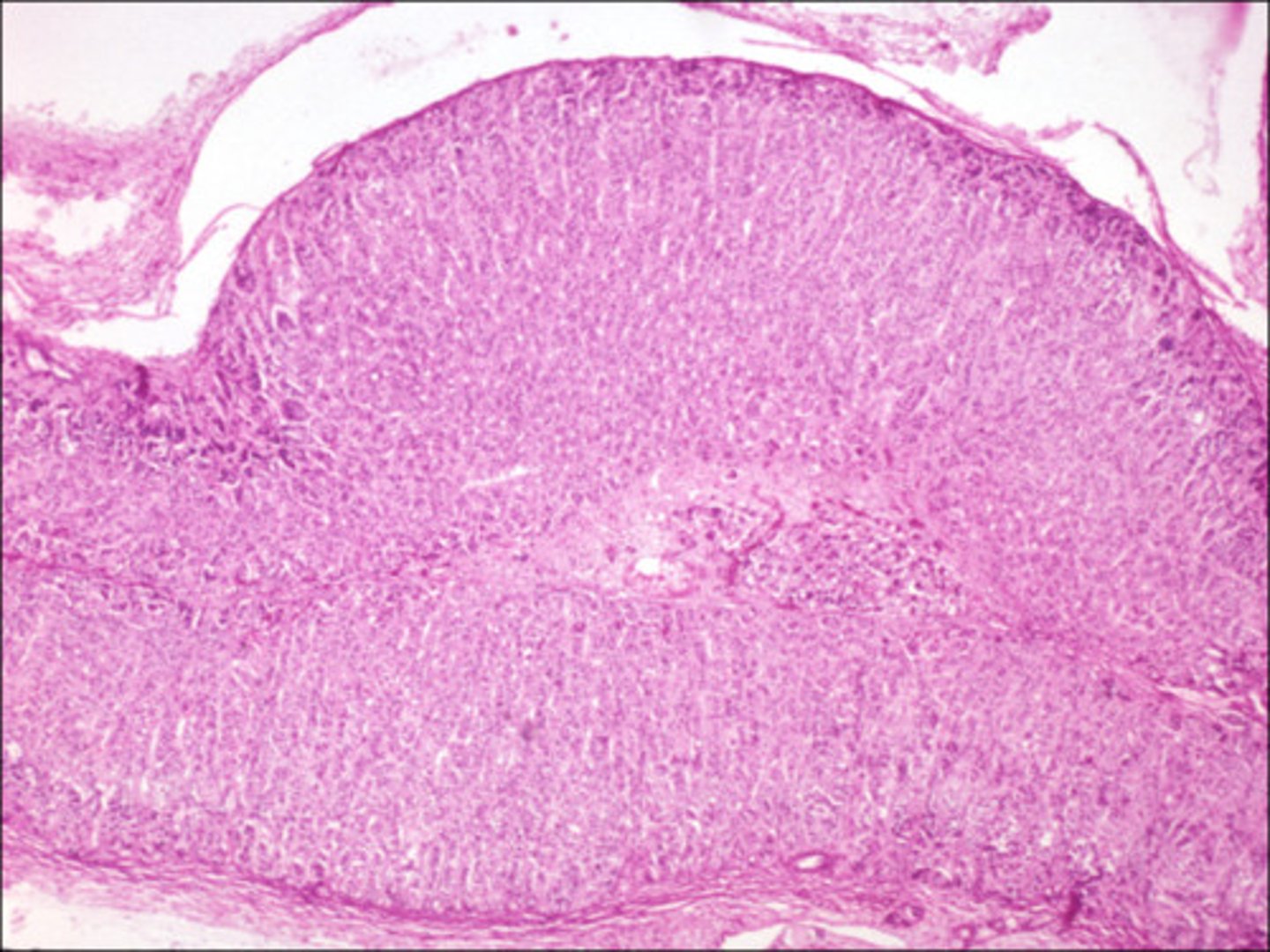
Adrenal Cortex
Thick light pink circle
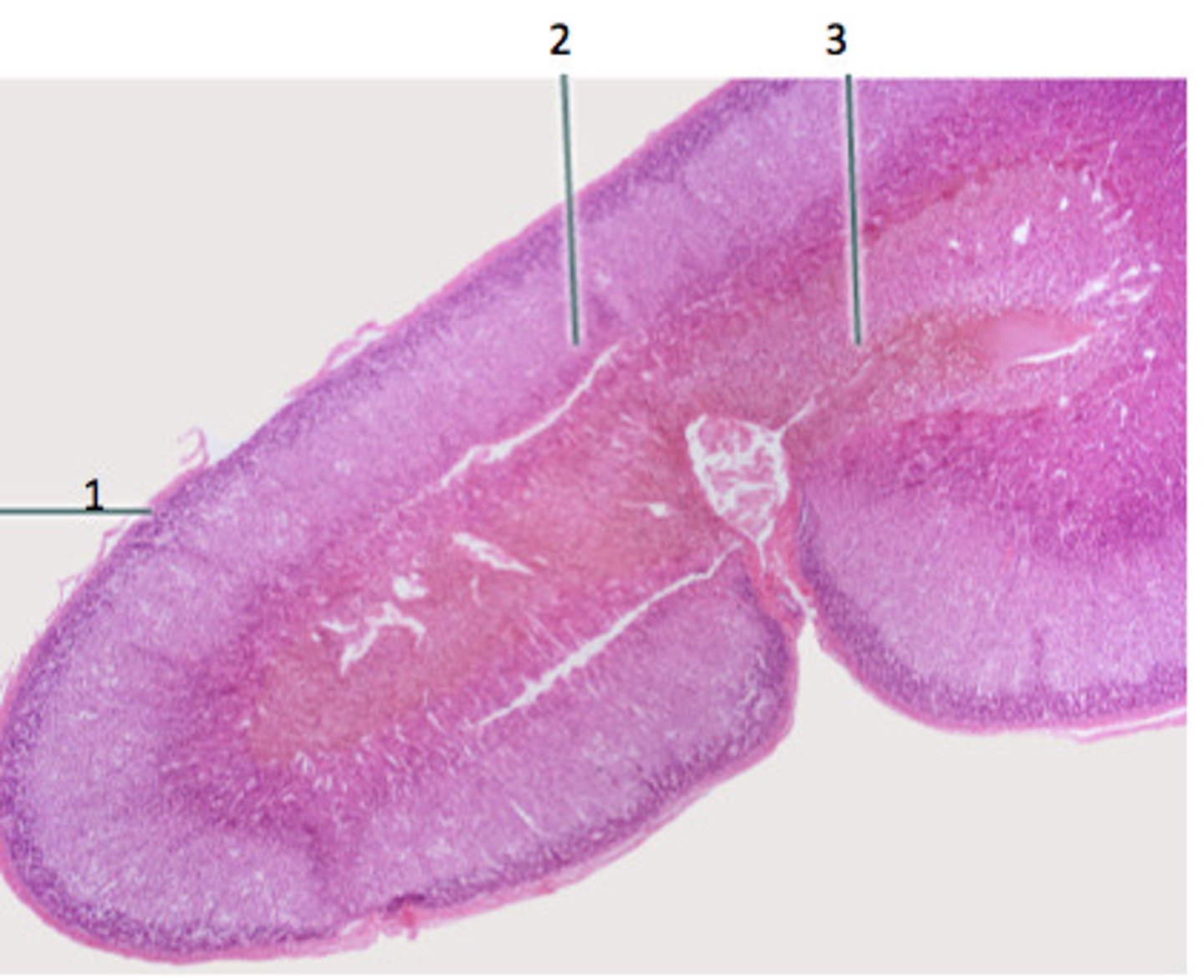
Adrenal medulla
3, inside of gland
Pupil
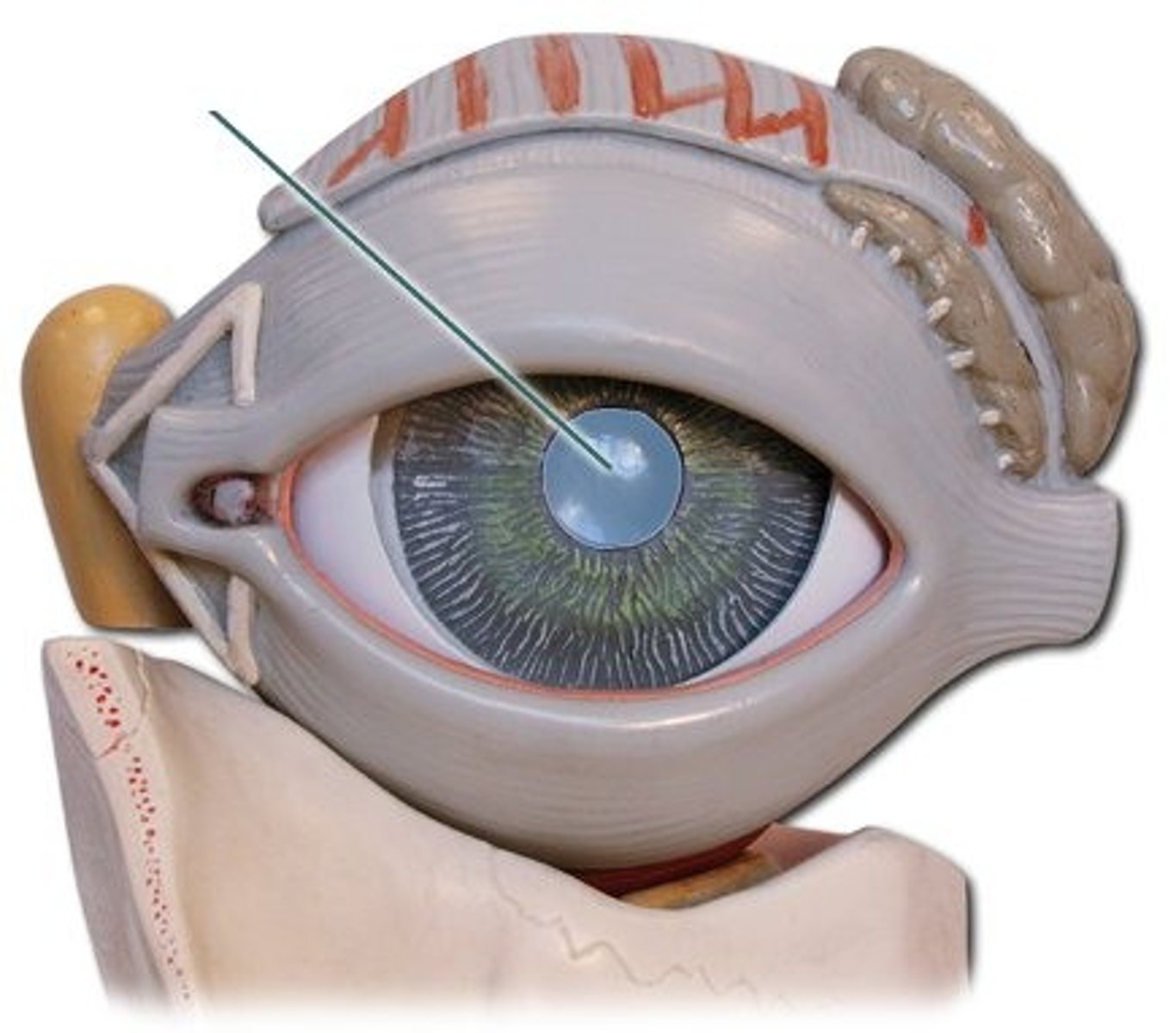
Iris
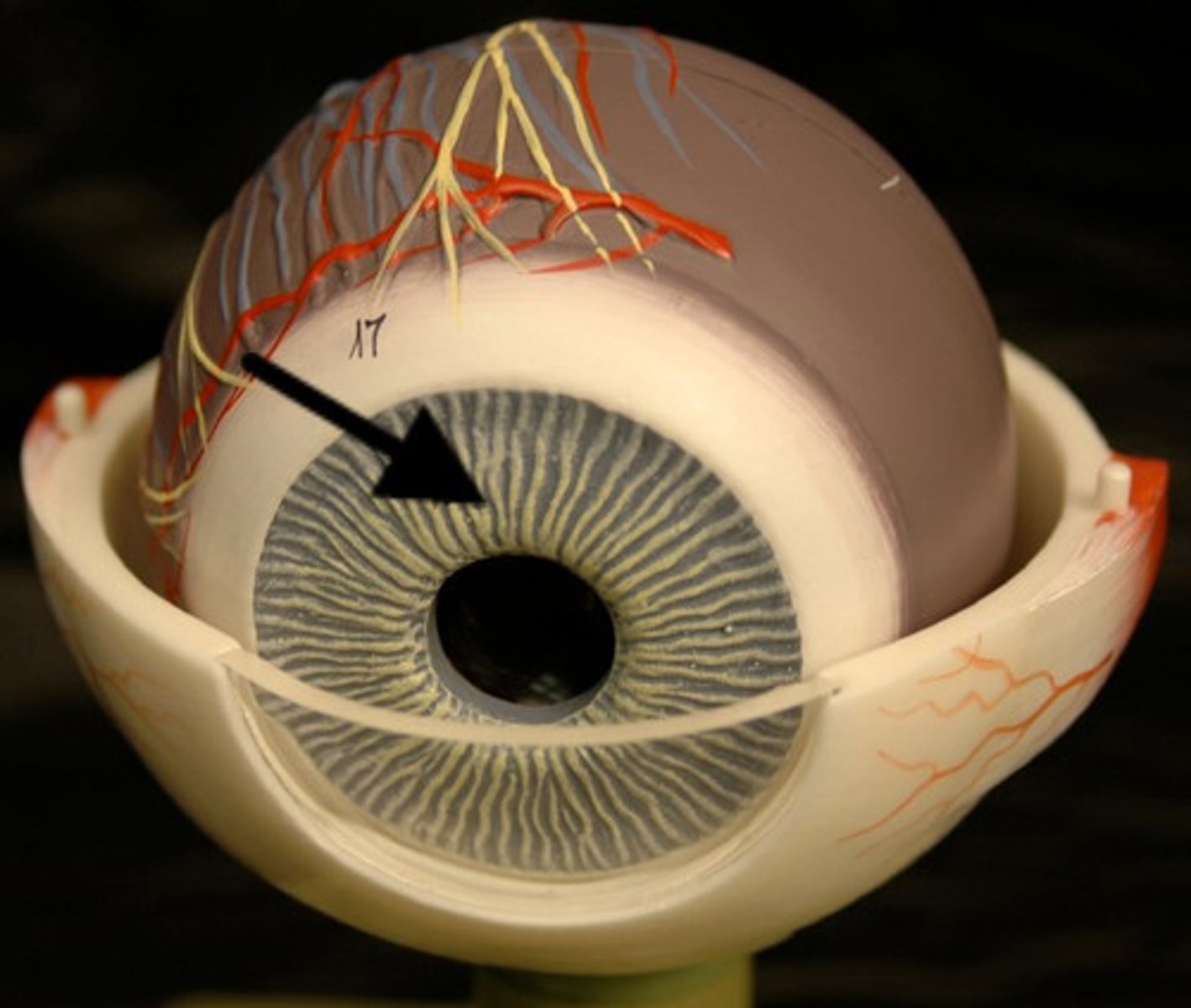
Sclera
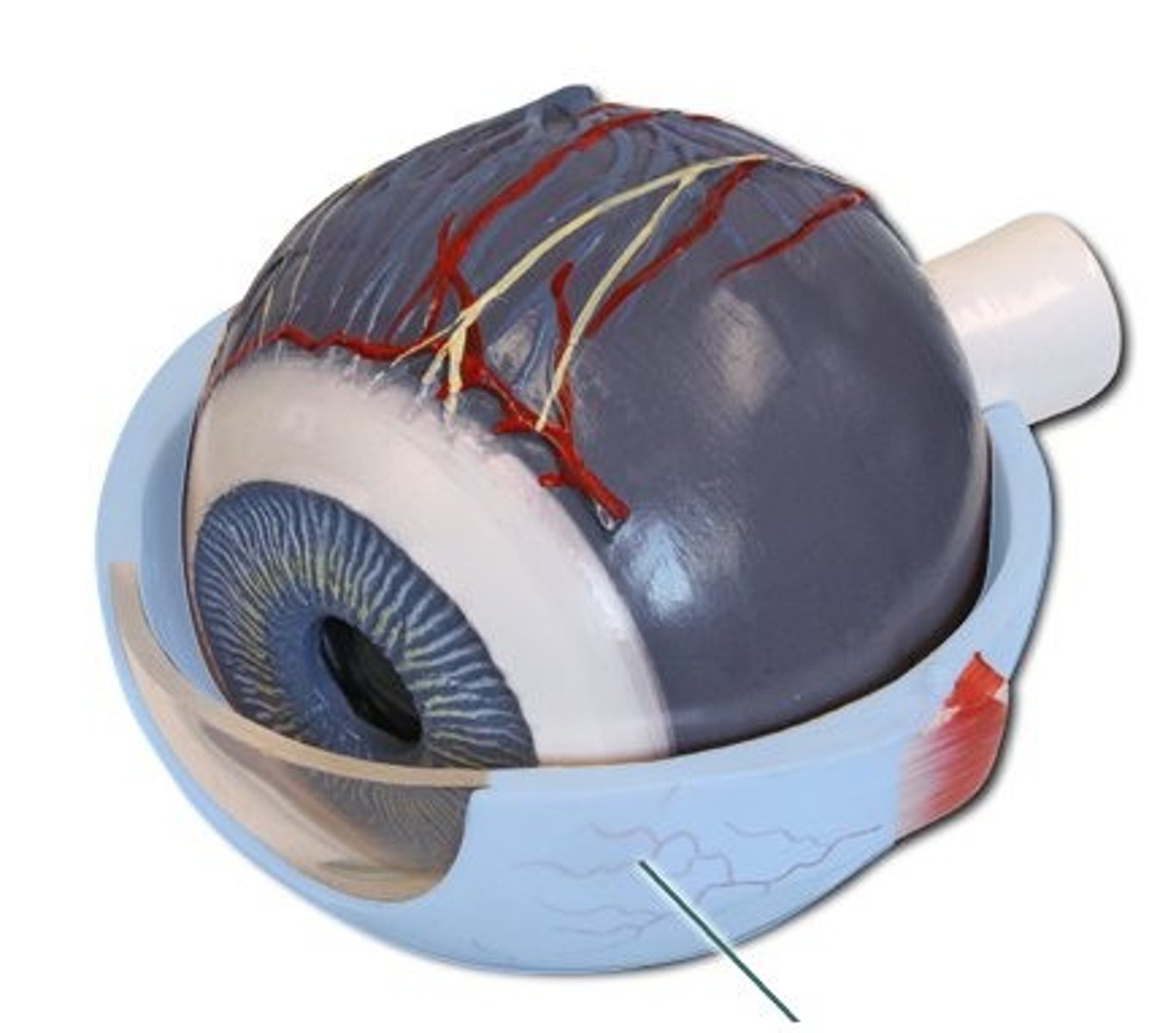
Cornea
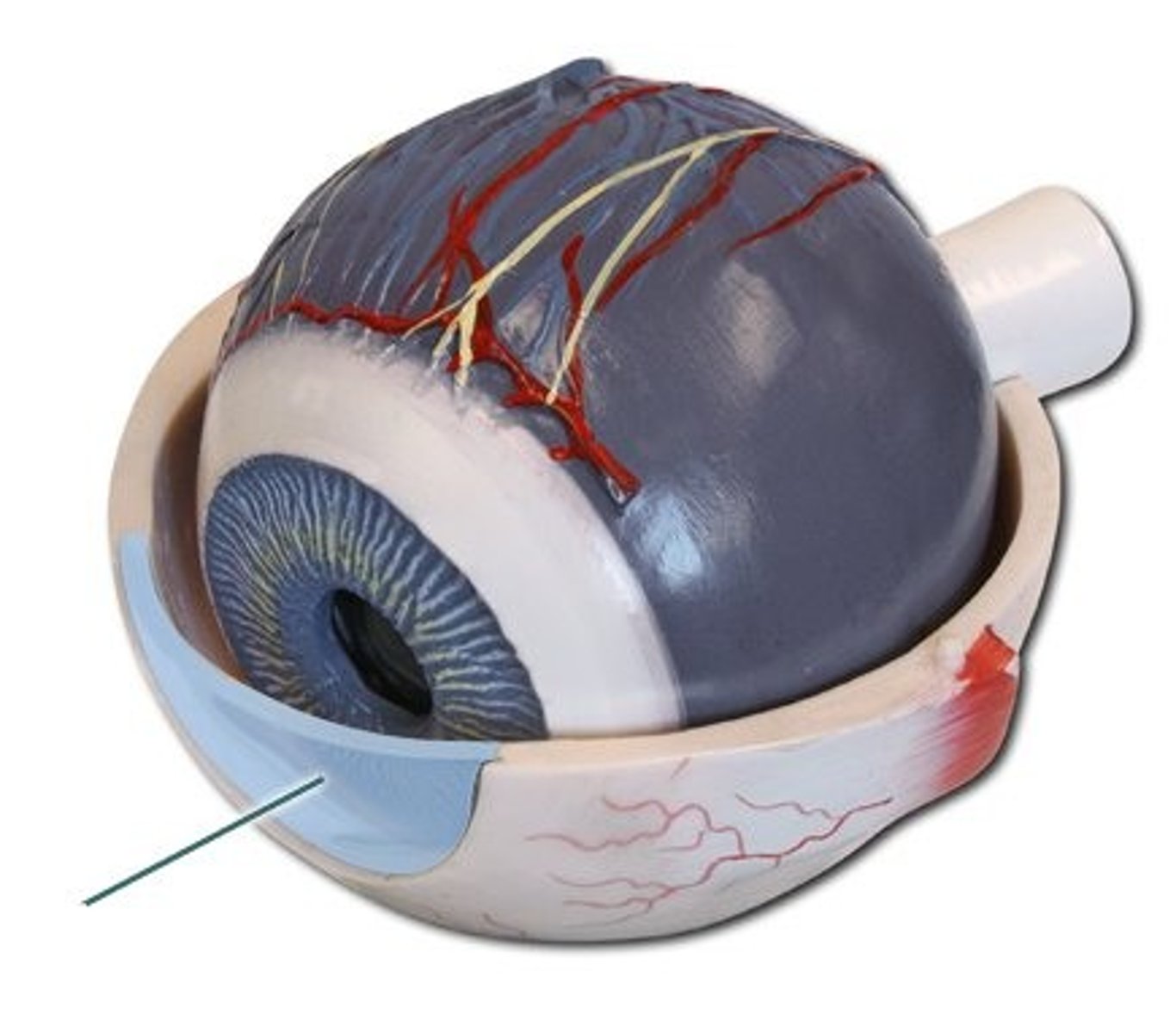
Aqueous humor
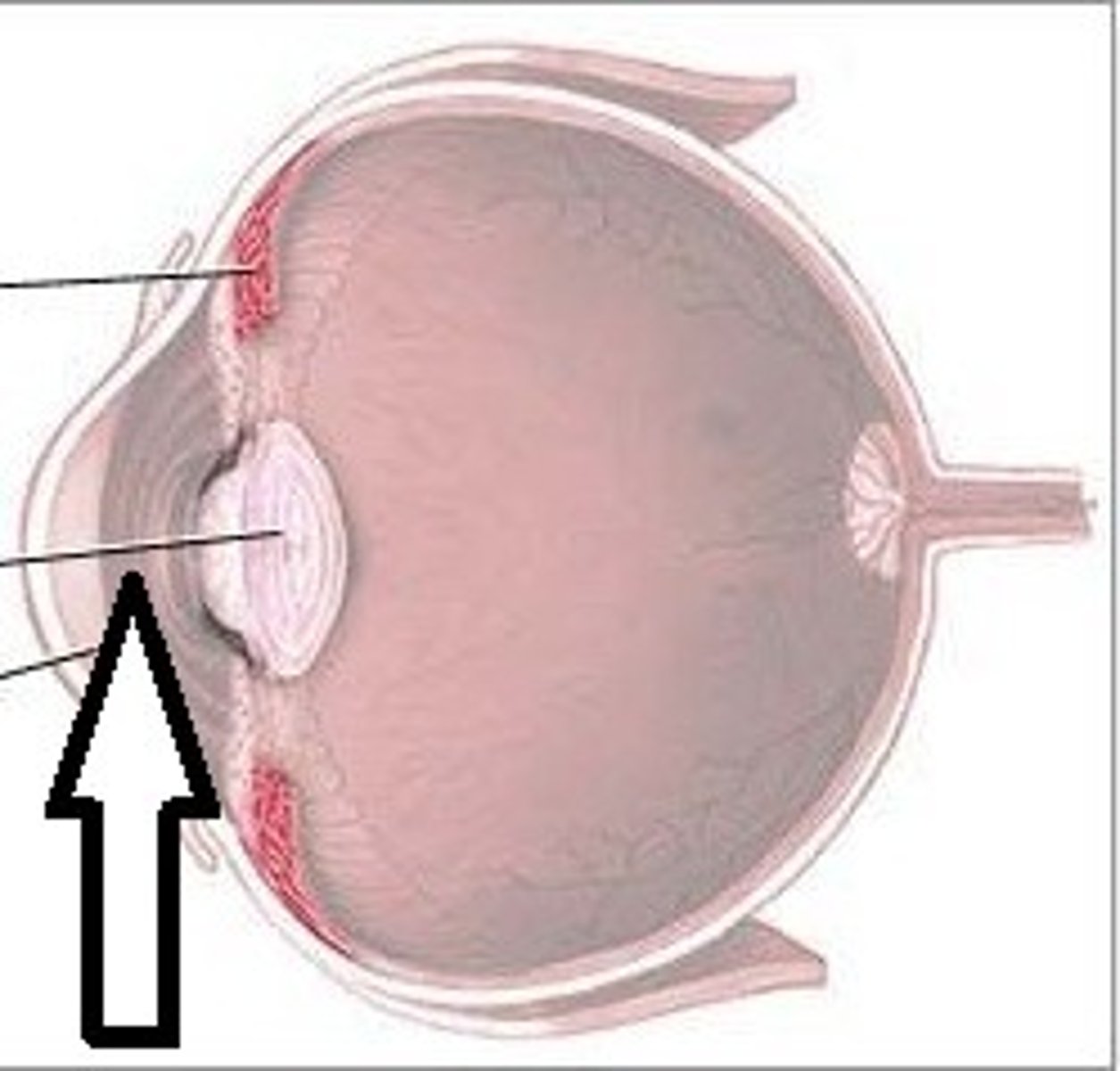
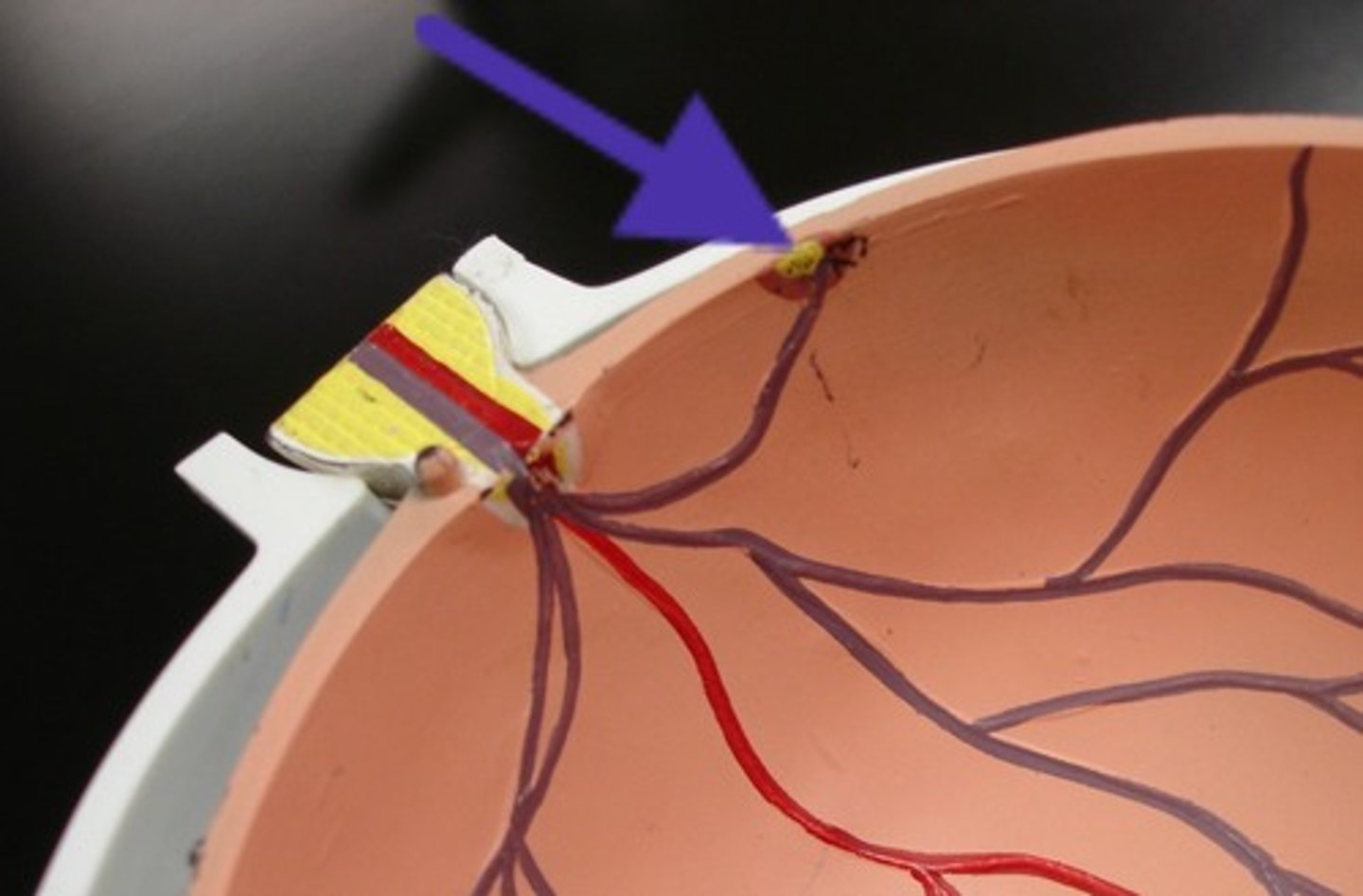
Optic disc
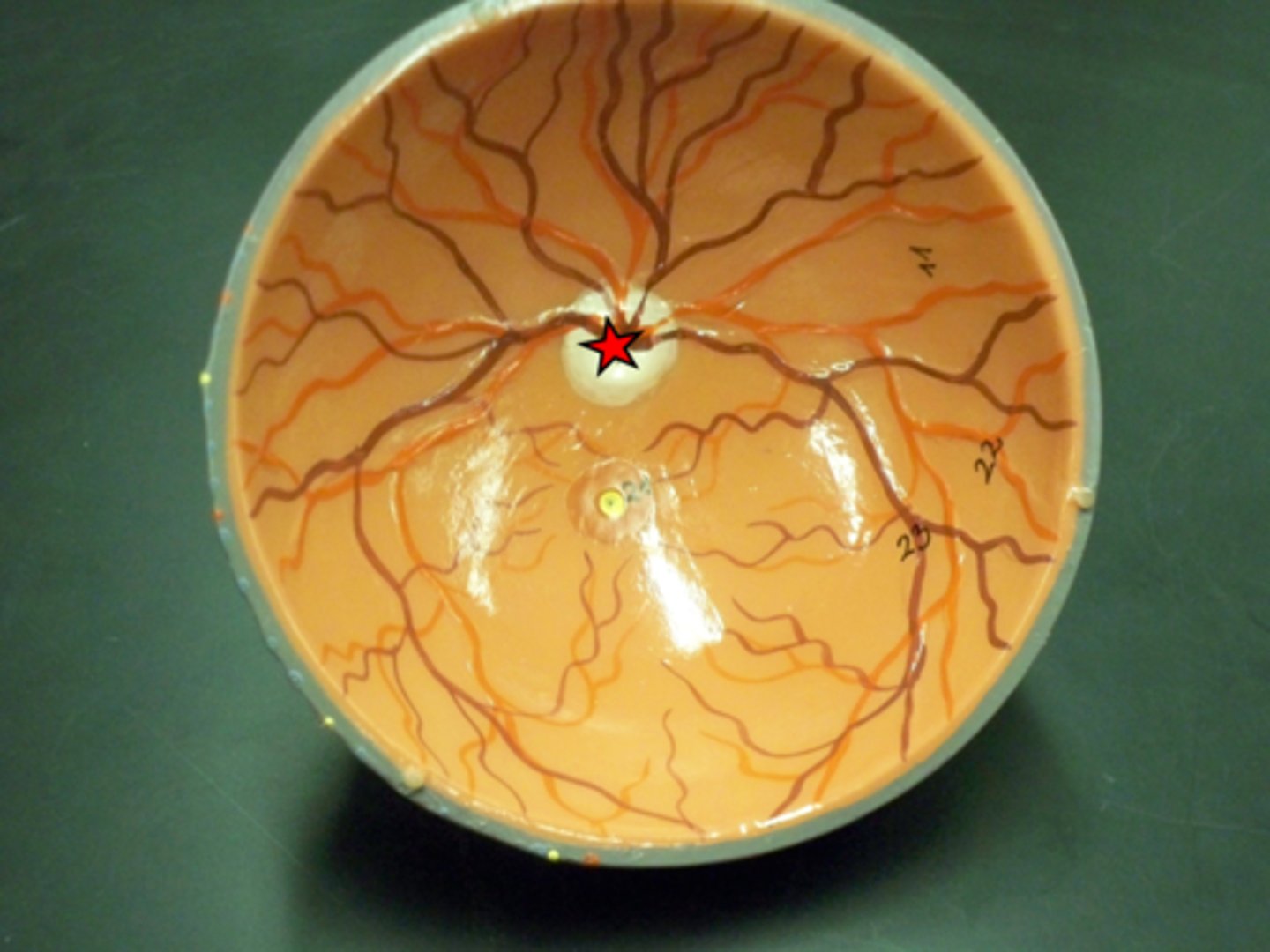
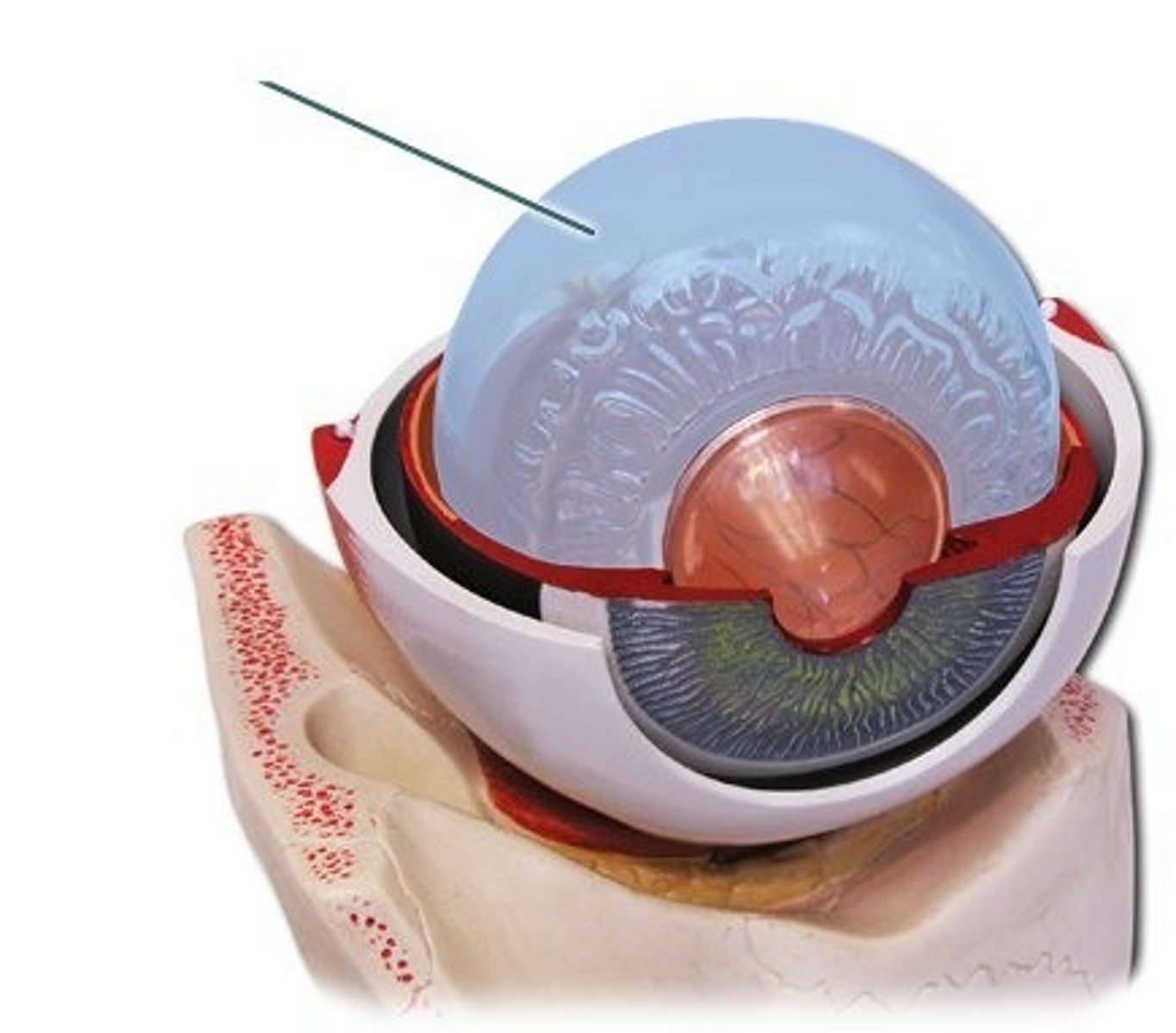
Vitreous humor
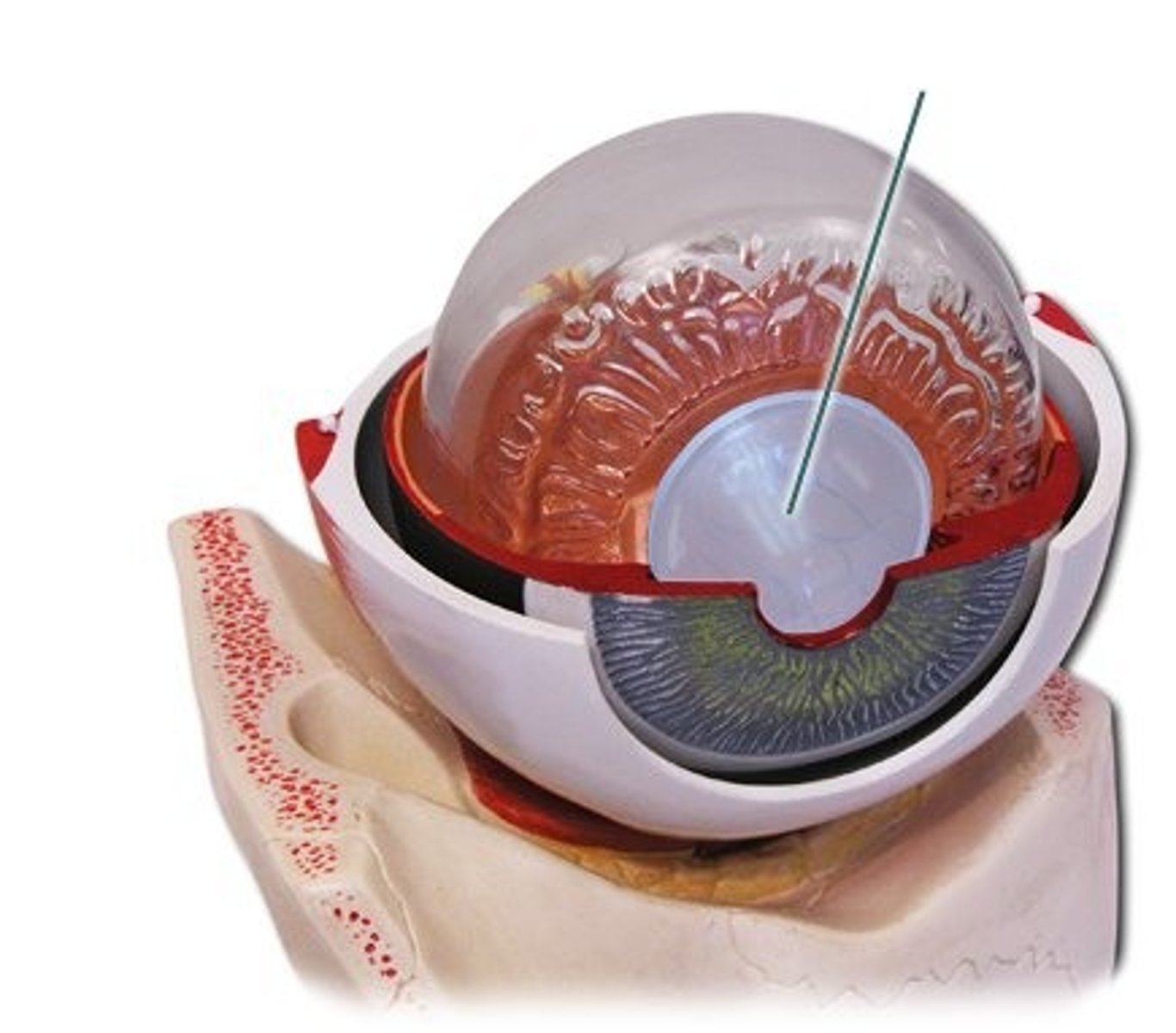
lens
ciliary body
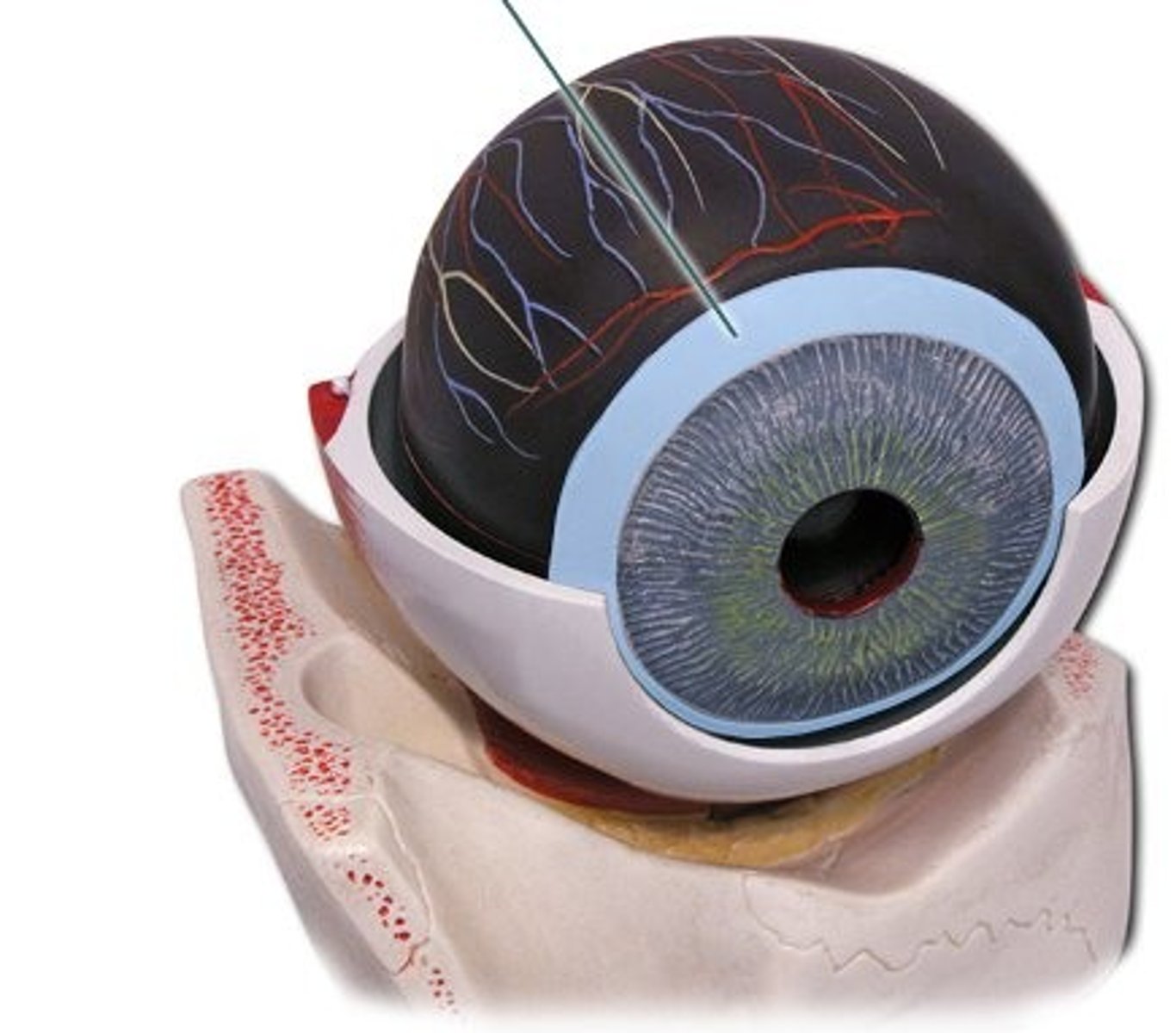
retina
layer being peeled off
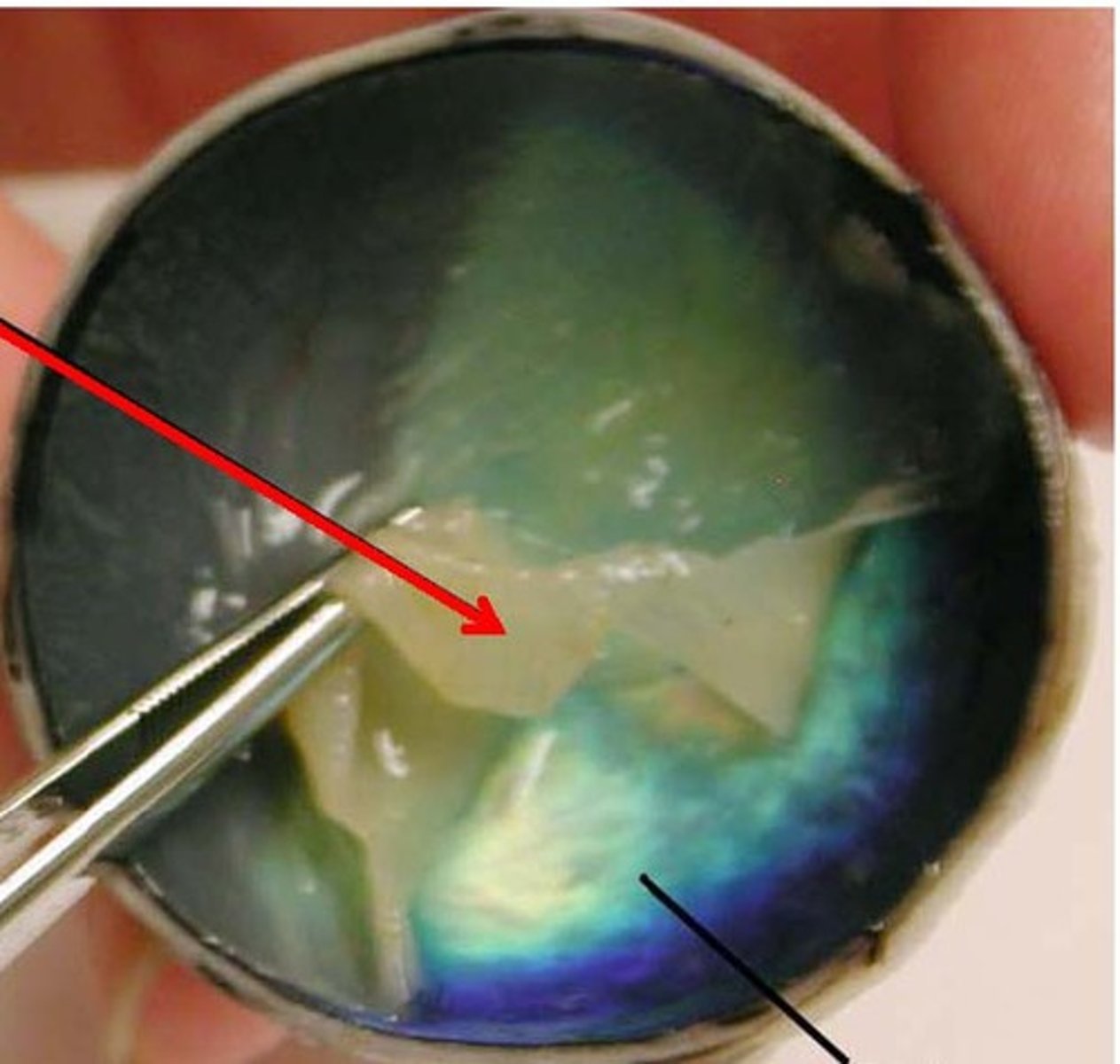
choroid
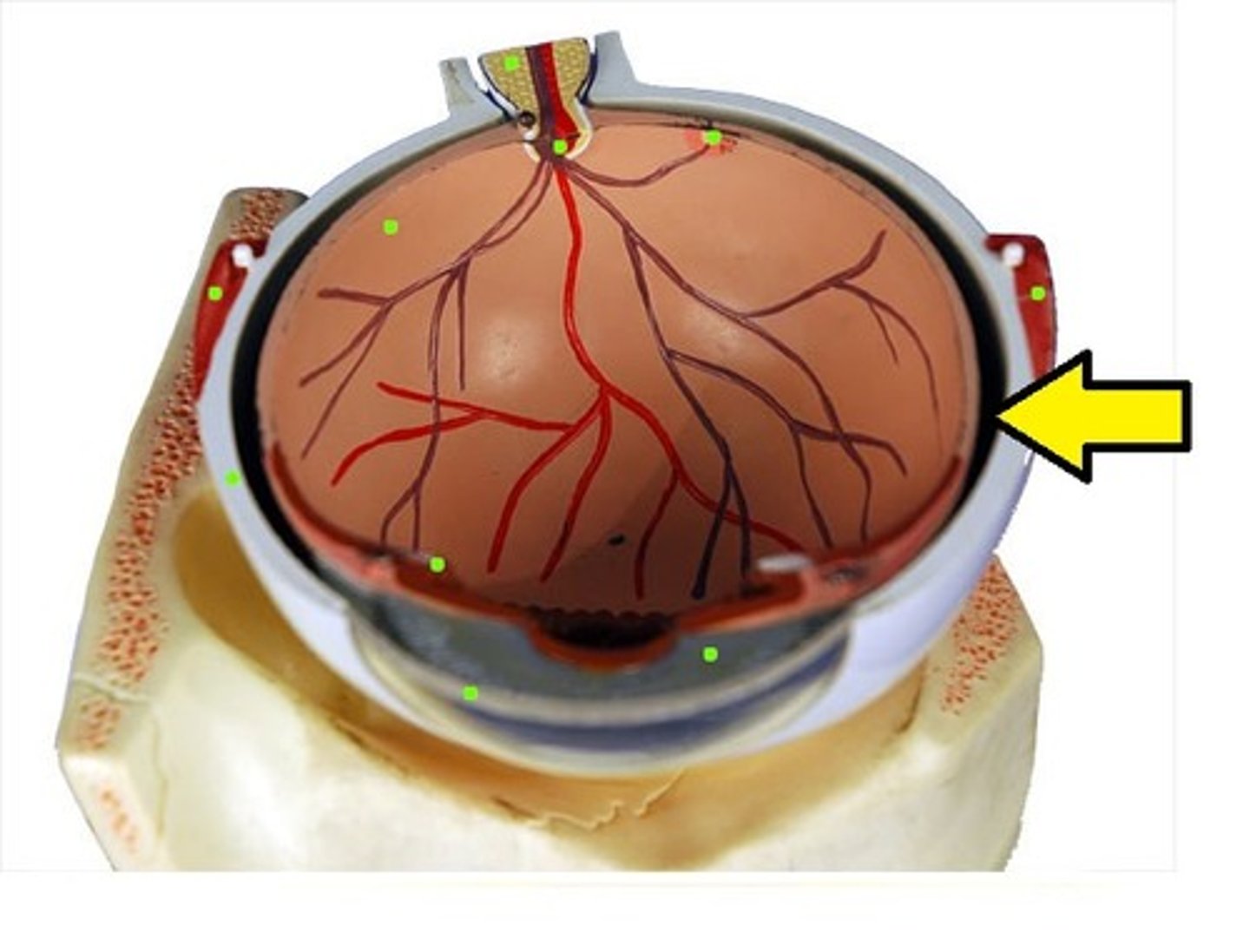
fovea centralis
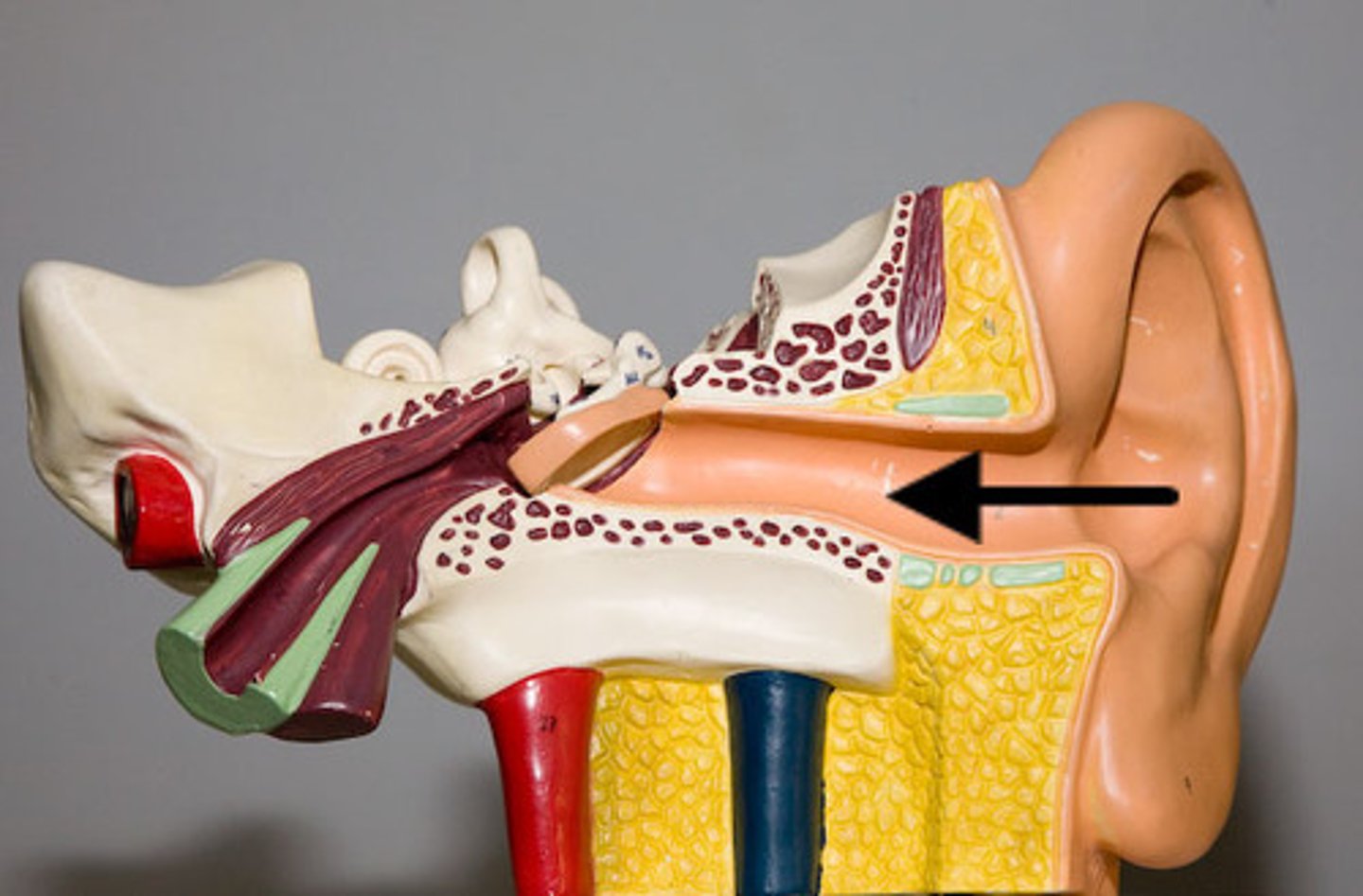
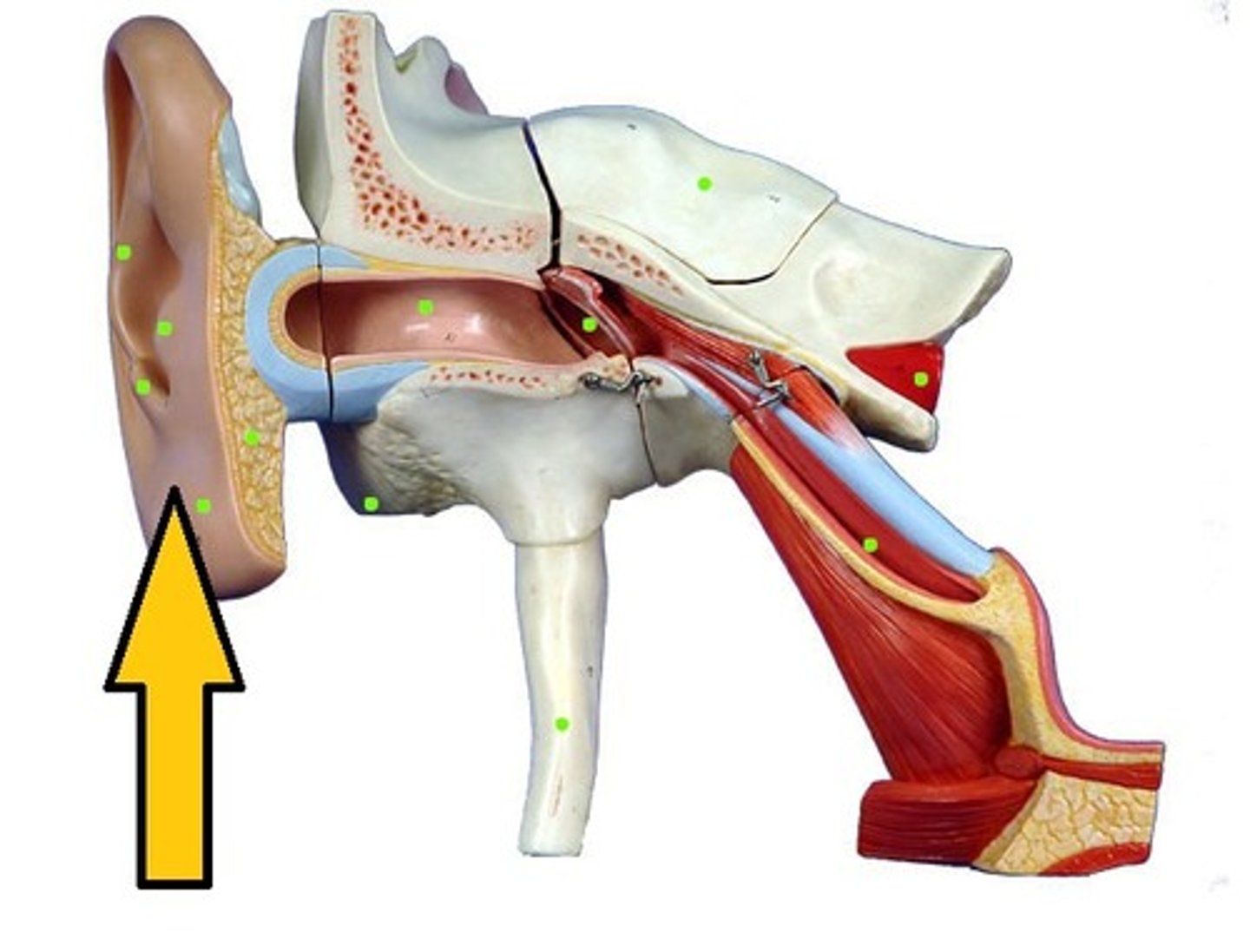
pinna (auricle)
external auditory canal