03.1B BIO Bacteria (PART B)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

35 Terms
Archaebacteria & Eubacteria
Two kingdoms that are made up solely of prokaryotes
Eubacteria
This kingdom consists of bacteria that live everywhere on Earth and have peptidoglycan in cell walls
Archaebacteria
This kingdom consists of bacteria that typically live in extreme environments, do NOT have peptidoglycan in their cell walls
Peptidoglycan
A protein carbohydrate compound found in the cell walls of eubacteria
Bacterial Cell Wall
A structure that protects and gives shape to the bacterial cell that may or may not include peptidoglycan
Bacterial Cell Membrane
A structure that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell; also contains enzymes important to cellular respiration
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance that contains DNA, ribosomes, essential compounds
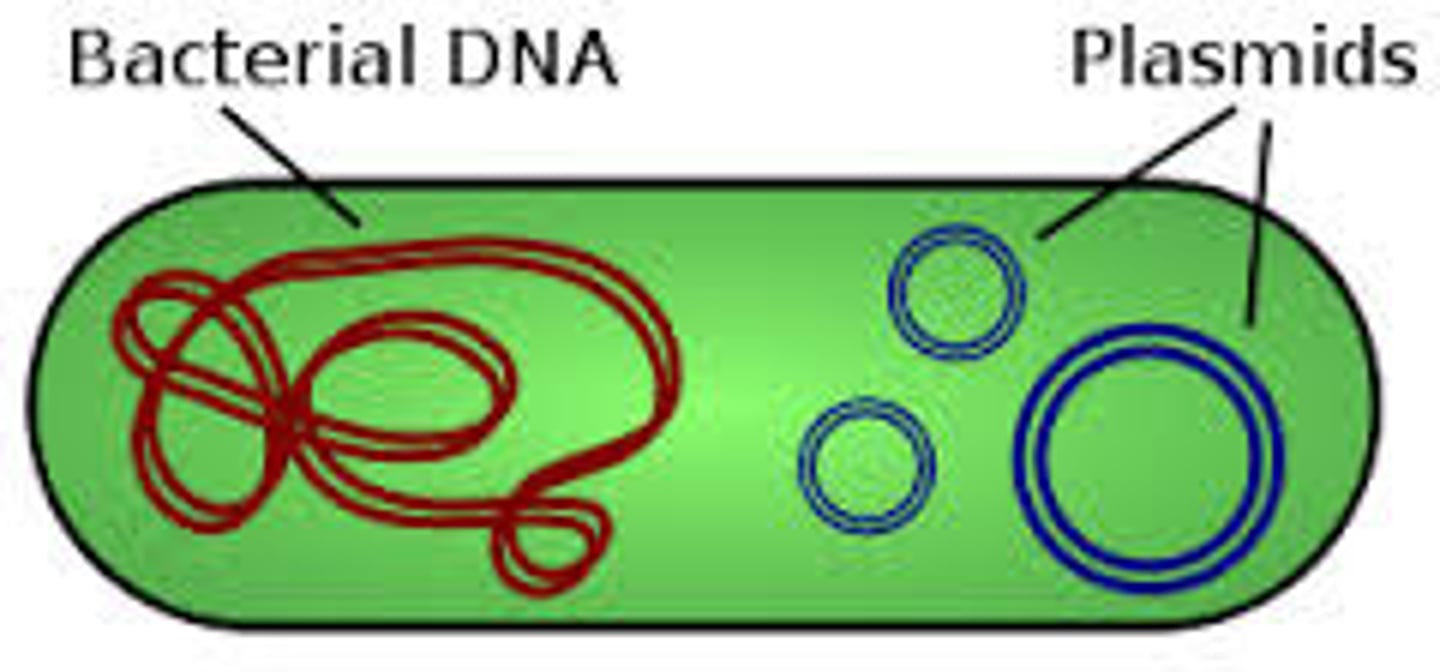
Bacterial Chromosome
circular thread of DNA that contains the cell's genetic information
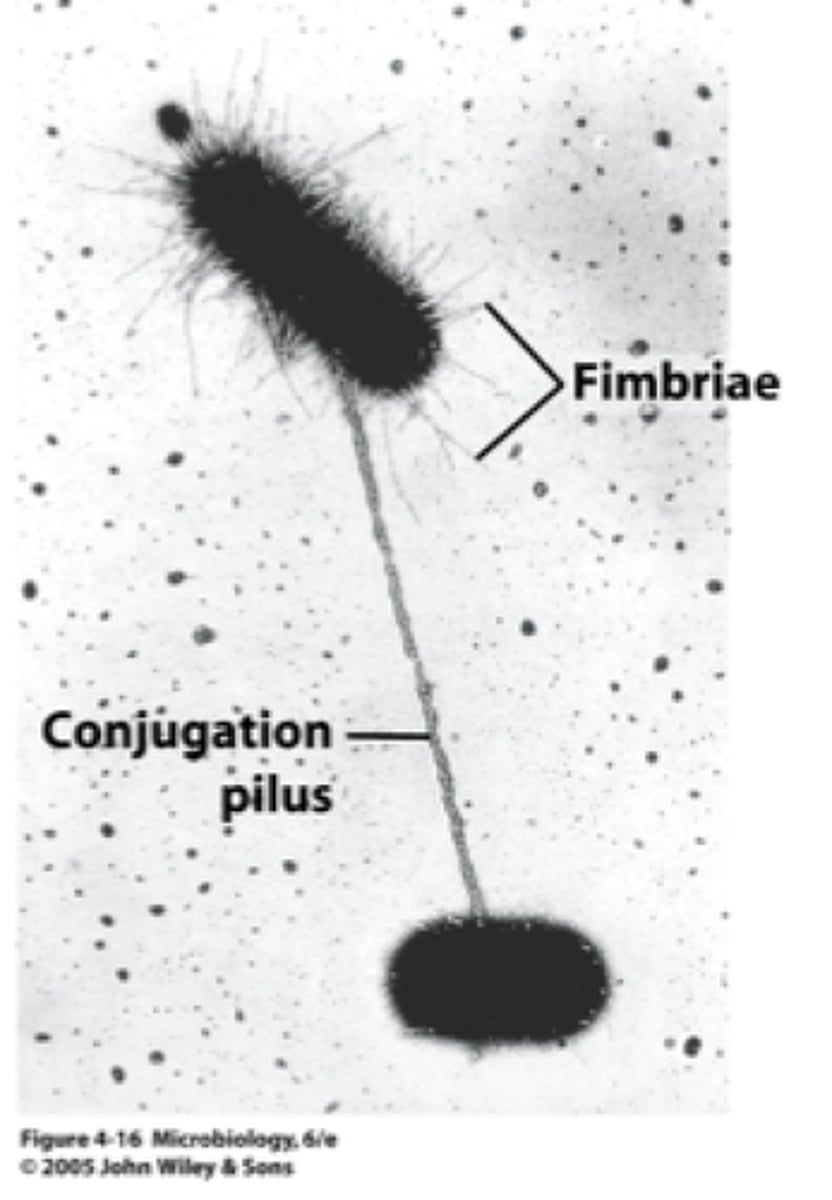
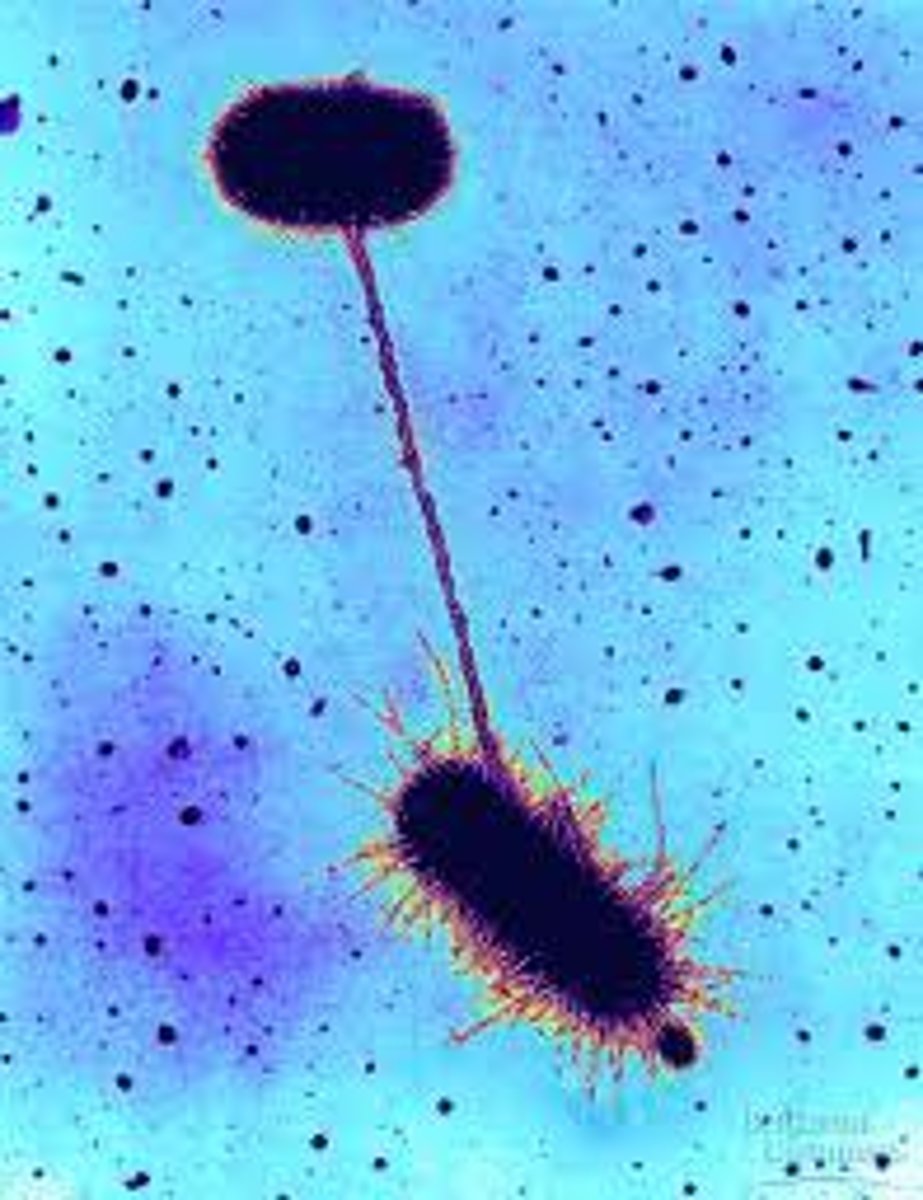
Pilus
A short. thick hair-like protein structure that allows a bacterium to attach to other bacteria and surfaces.
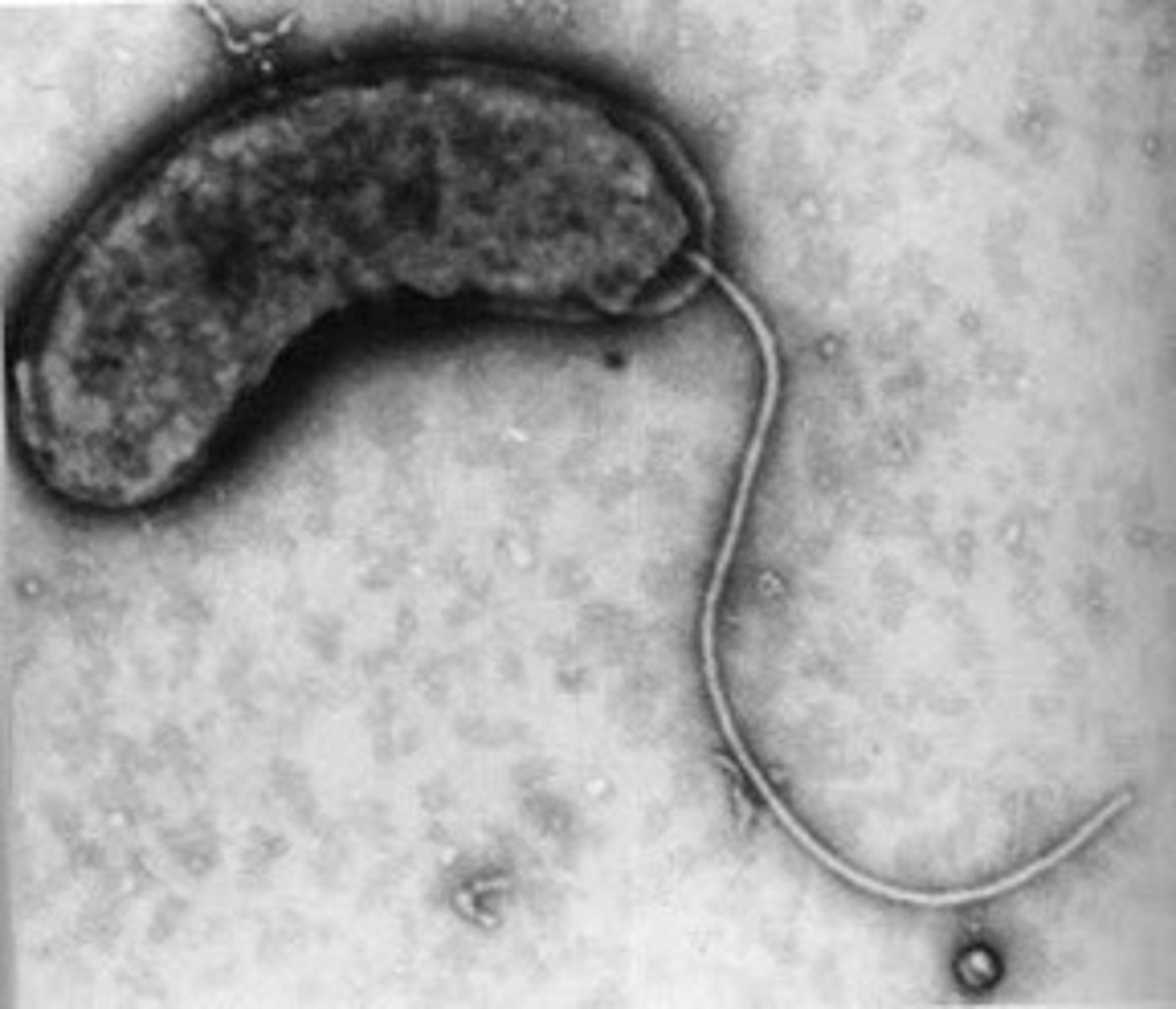
Flagellum
Long whip-like structure that allows the cell to move
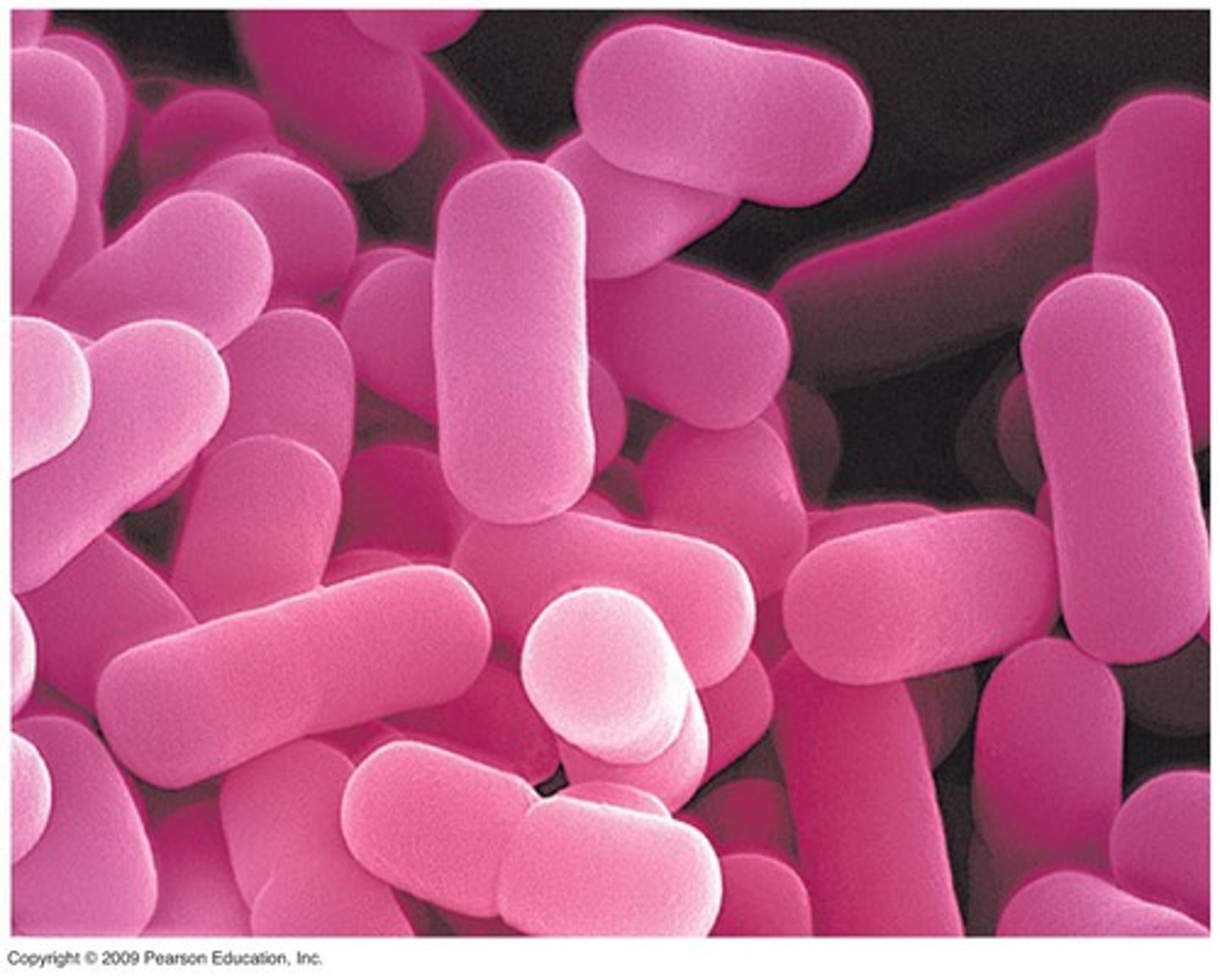
Bacilli (rod-shaped)
Bacteria that are rod-shaped; example includes Bacillus anthracis that causes anthrax
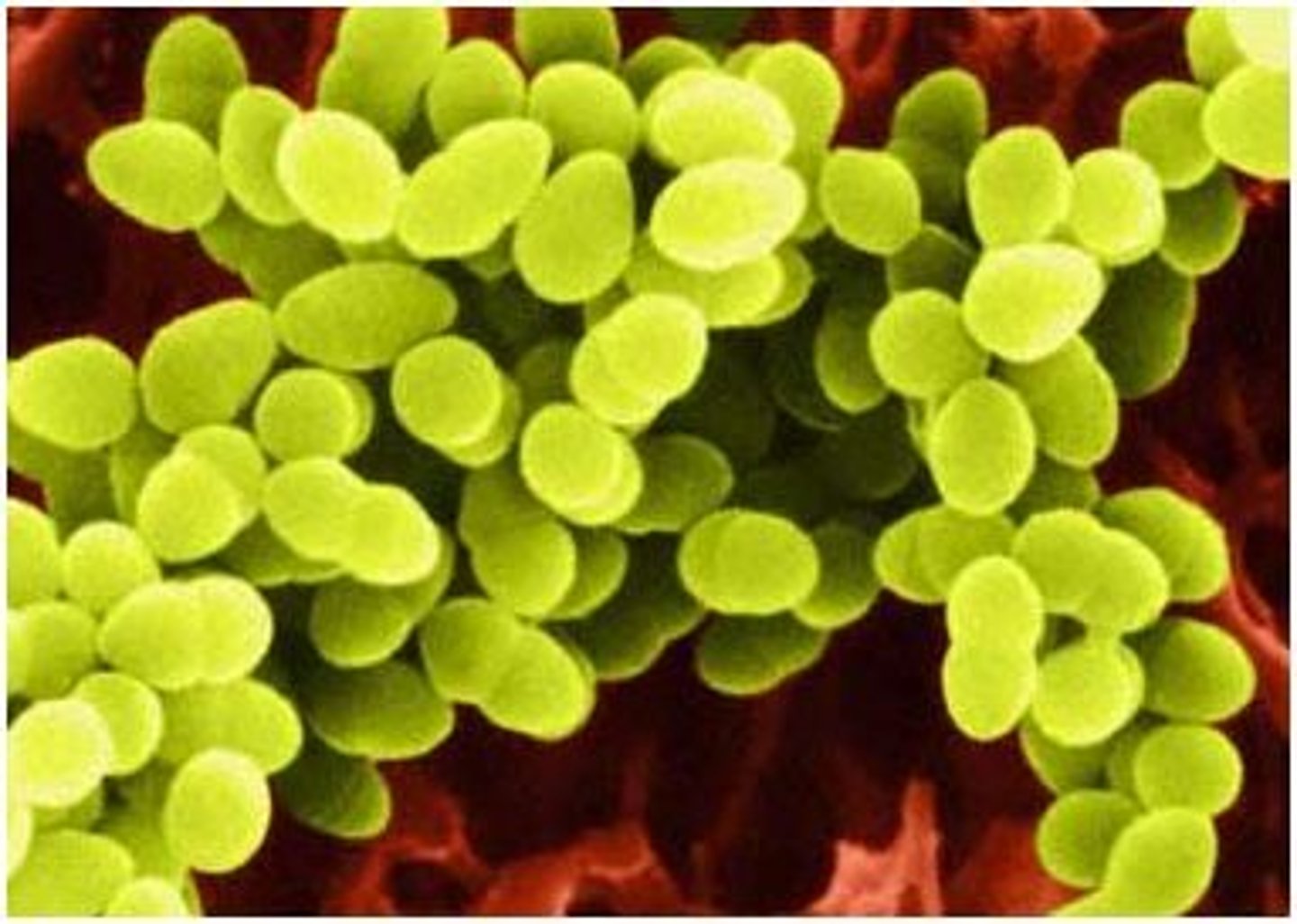
Cocci
Bacteria that are round; examples include staph infections and Gonherrea
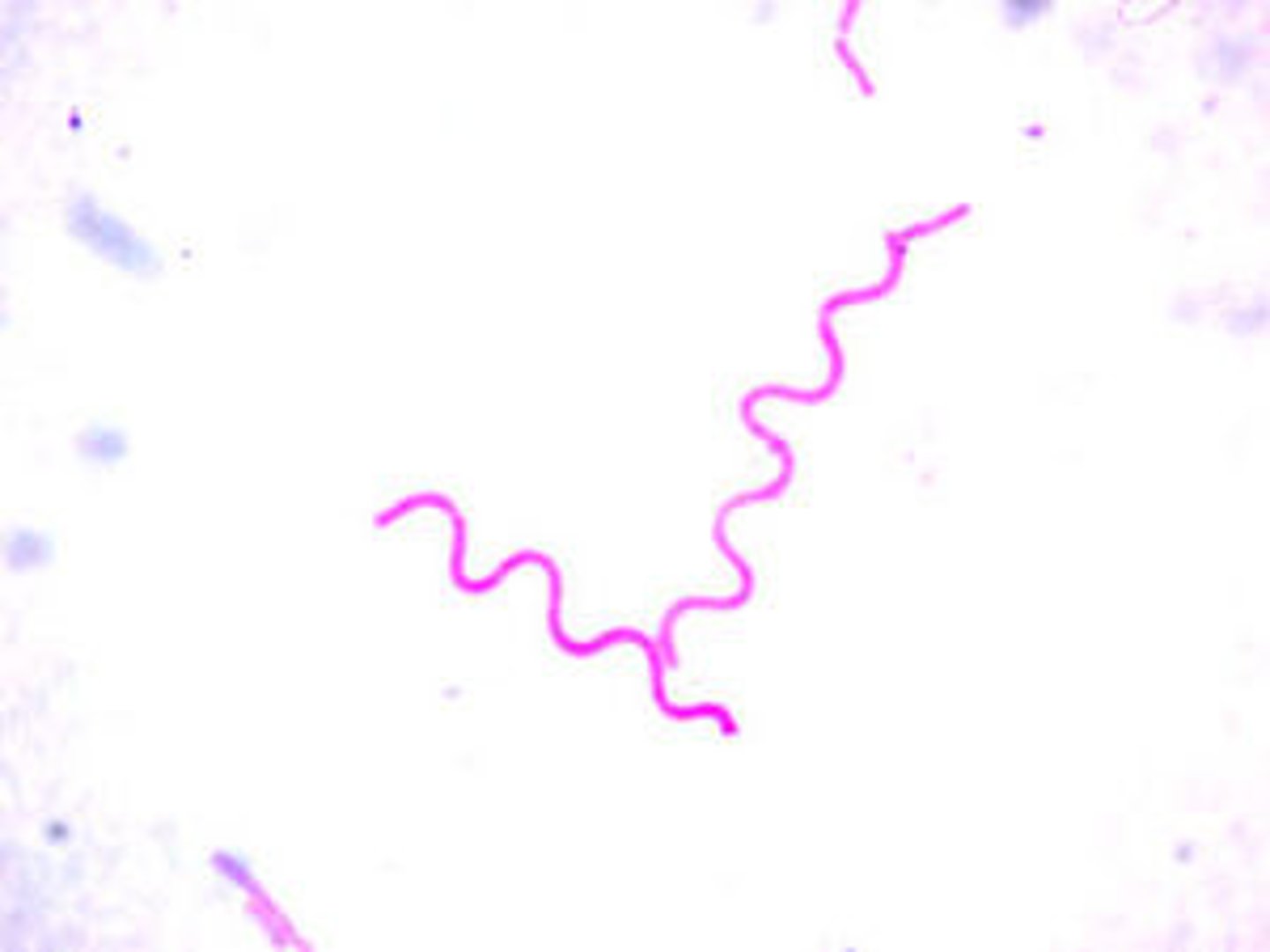
Spirillum
Bacteria that have one or more twists; examples include
Syphillis and Lyme Disease
Bacterial modes of nutrition
Phototrophs, chemotrophs and heterotrophs
Bacterial Photoautotrophs
Bacteria that use light to make their own food; example includes cyanobacteria
Bacterial Chemoautotrophs
Bacteria that use high energy molecules to make their own food; example include some archaebacteria that live in ocean vents
Bacterial Heterotrophs
Bacteria that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply; examples include decomposers
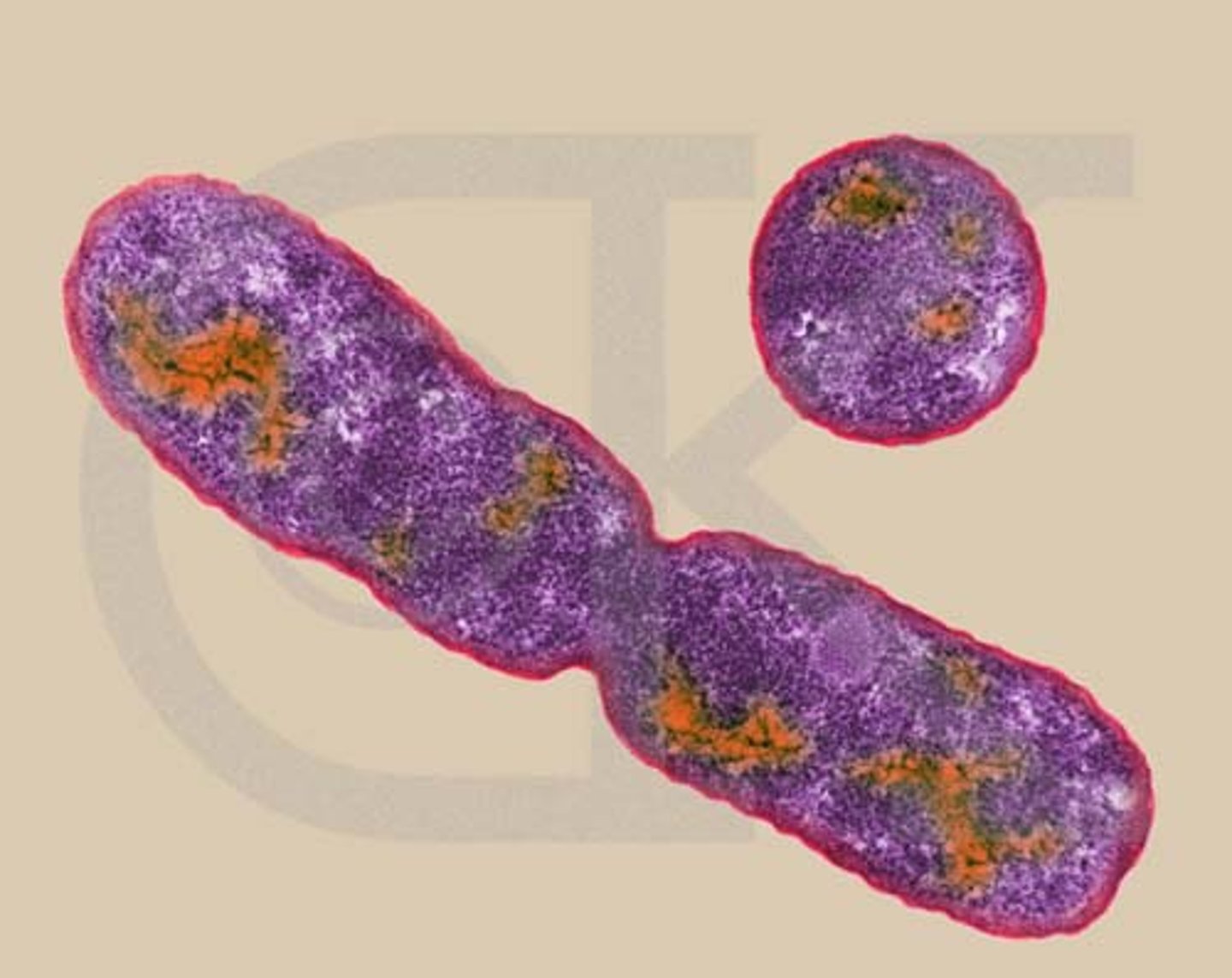
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size; most common form of reproduction
Conjugation
In bacteria, a type of sexual reproduction in which two bacteria exchange pieces of DNA through the pili.
Bacerial endopore
A structure that can be formed by many species of bacteria that allow them to survive harsh conditions
Ideal conditions for bacterial growth
Temperature between 80˚F to 100˚F
Moist
Dark
lenty of food
Role of Bacteria in the Environment
Producers in many ecosystems that capture energy by photosynthesis.
Decomposers in many ecosystems that break down the nutrients in dead matter.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria help to convert nitrogen in the atmosphere into a form that plants can use.
Bacteria as Decomposers
Bacteria help recycle nutrients and remove wastes from water
Nitrogen Fixers
Some bacteria help to convert nitrogen in the atmosphere (N2) into a form that can be used by plants
Human uses of bacteria
- Make foods and beverages such as butter, cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, and vinegar
- Tan leather, make linen, cure tobacco
- Remove wastes and poisons from water
- Mine minerals from the ground
- Synthesize drugs and chemicals via genetic engineering
- Produce vitamins in human intestines
Bacterial Infections (Examples)
Lyme Disease
Tetanus
Tuberculosis
Bacterial meningitis
Staphylococcus infection
Strep throat
Bacterial Infections (Treatment)
Antibiotics
Antibiotics
Drugs used to treat bacterial infections; examples include penicillin, ampicillin, sulfa drugs, etc.
Antibiotic resistance
Bacteria either evolve by mutation or acquire from another bacterium the ability to survive and not respond to treatment by antibiotics
Two ways bacteria cause disease
Damage the cells and tissues of the infected organism by breaking down the cells for food.
Release toxins (poisons) that travel throughout the body interfering with the normal activity of the host.
Methods used to control bacterial growth
Sterilization, disinfectants, food processing, pasteurization
Pasteurization
A process of heating food to a temperature that is high enough to kill most harmful bacteria without changing the taste of the food.
Sterilization
The process of destroying all microbes
Disinfectants
Chemical products that destroy all bacteria, fungi, and viruses (but not spores) on surfaces.
Food processing
Bacteria can cause food to spoil.
Refrigerated food stays fresh longer because the bacteria will take longer to multiply.
Boiling, frying, or steaming can sterilize certain foods.