Derivative Formulas
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Quotient rule
When to use: Use the quotient rule to find the derivative of a function that is a division of two other functions, where both the numerator and denominator are functions of the variable you are differentiating with respect to.
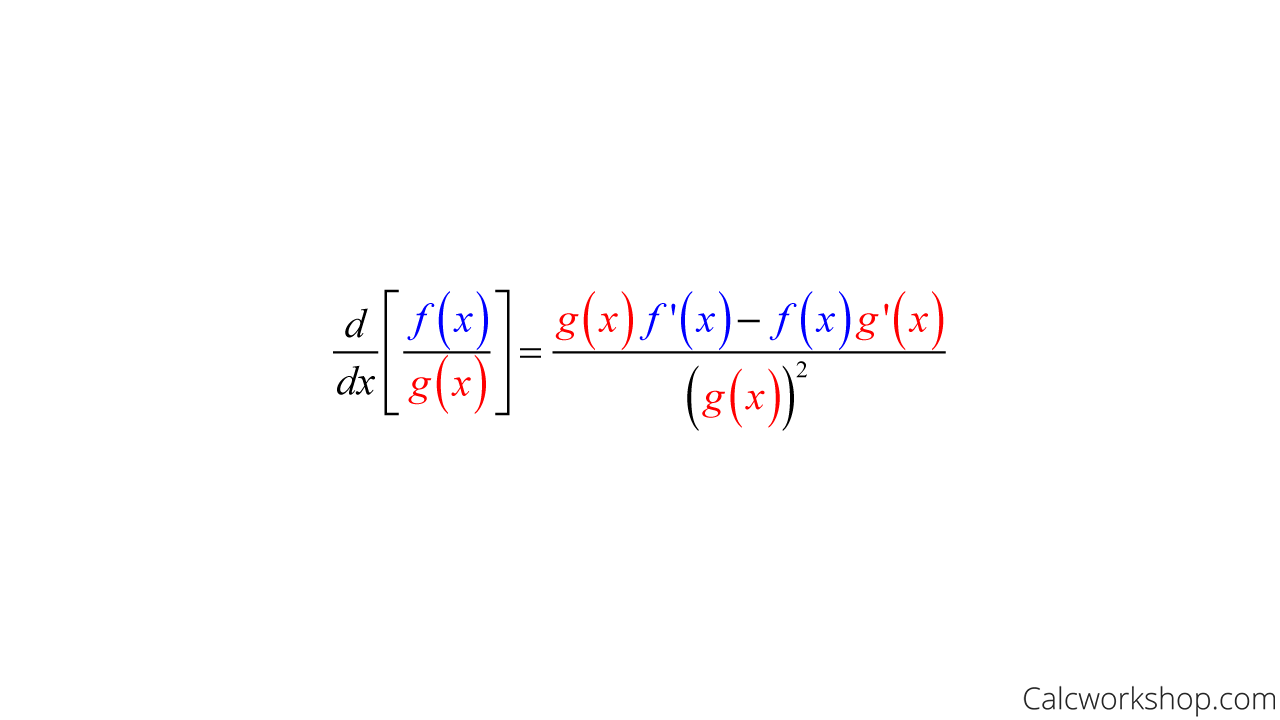
Power rule
When to use: Use the power rule to find the derivative of functions with a variable raised to a constant power (e.g., xⁿ), including polynomials, negative powers, and fractional powers. You'll use the rule when the exponent is a real number and the base is a variable, transforming the function into the format xⁿ before applying the rule to get n*x^(n-1).
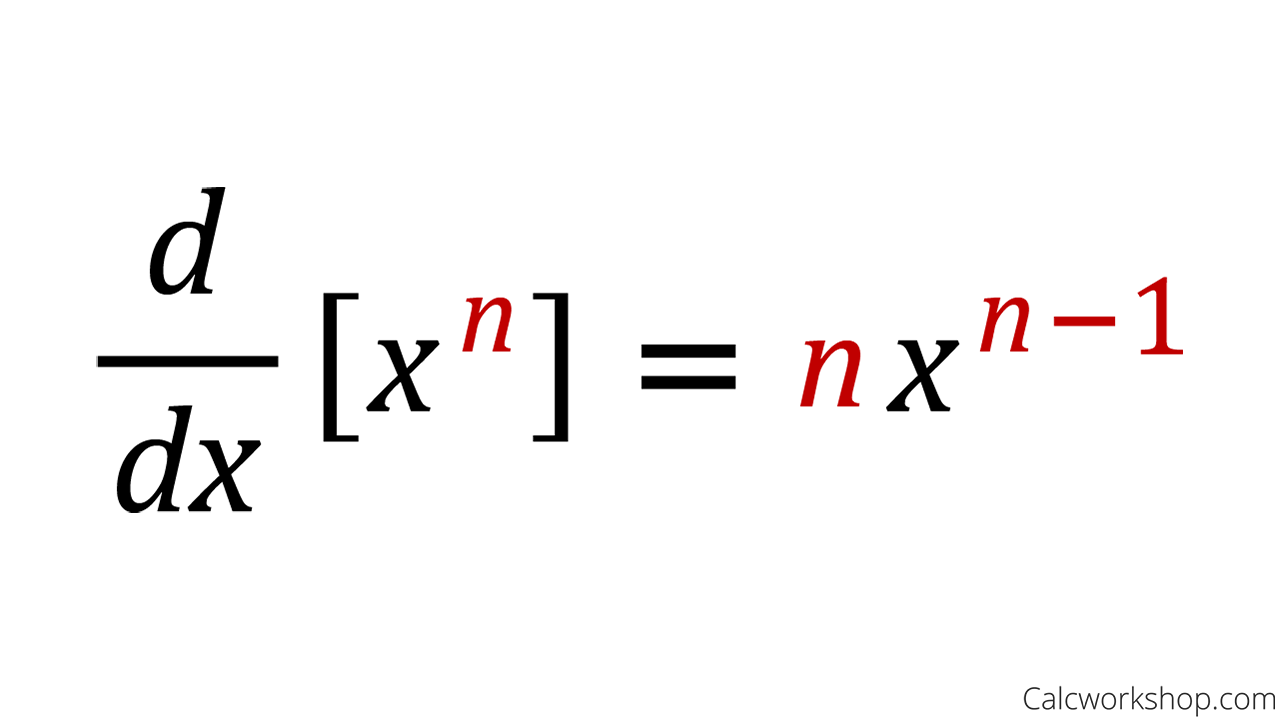
Product rule
Use the product rule to find the derivative of two functions multiplied together
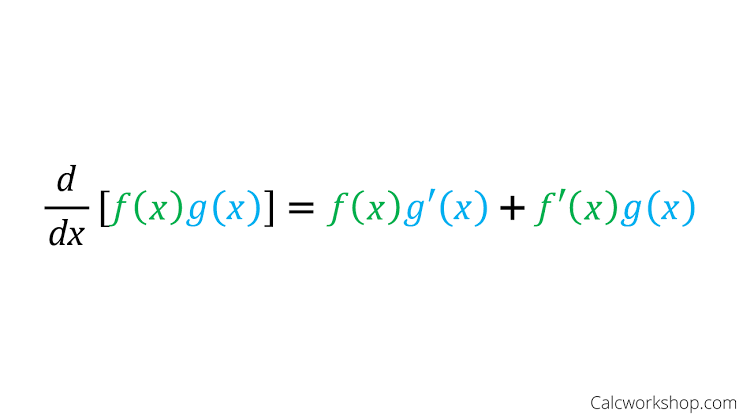
Chain rule
When to use: You should use the chain rule to differentiate composite functions, which are "functions of functions" where one function is nested inside another. You can identify when to use it by looking for expressions where a sub-expression can be substituted for a new variable, indicating a function within a function structure.
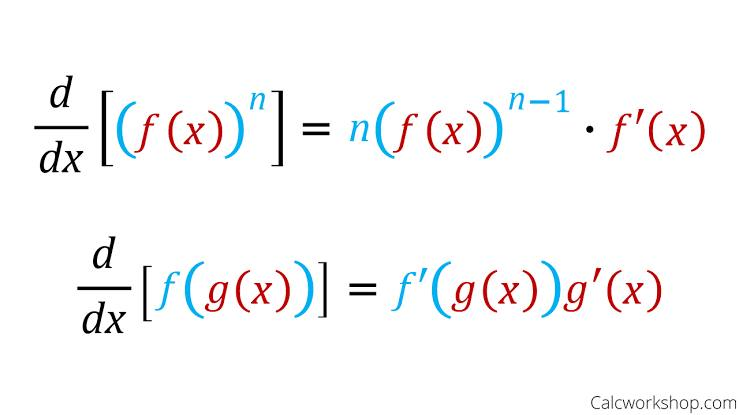
Constant rule
Derivative of a constant is always zero
Derivative of sin(x)
Cos(x)
Derivative of cos(x)
-sin(x)
Derivative of tan(x)
Sec²(x)
Derivative of cot(x)
-csc²(x)
Derivative of sec(x)
Sec(x)tan(x)
Derivative of csc(x)
-csc(x)cot(x)