Option A: Database (CS SL)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Data
Raw fact that is meaningless on it’s own / unprocessed values
Information
meaningful data that has been interpreted / added context or meaning
Information system
Collection of hardware, software and human resources that work together to transform raw data into useful information
Database
Organized of data stored electronically and is a component of the information system, it is stored in tables as records (rows, data about one particular person / company / item in a database) and fields (column, part of a record and contains a single piece of data for the subject of the record)
Created and stored by a software called DMBS (SQLite, mySQL, SQLserver)
Queries / Commands
store, retrieve, delete and edit data
Why do we use database
processing / querying data (search / sort / analyze)
generate reports
automatically support data validation / data verification when filling the database
standardized (used in multiple systems)
provides ability to sore a greater number of records compared to a spreadsheet
Data Validation
Checks that input follows rules for the type of input entered
Data Verifiction
Checks that input matches expected values in database
Entity
a real world object / person
represented by a row
referred to as a record / tuple in a database
Table
stores a set of related data called records
every record has value
records in each table share the same fields / types of data
Tuple
Collection of items that may or may not be related to one another
Collection of items that may or may not be related to one another
Primary Key
identify a given record
distinctive for each record
Foreign Key
primary key field in another table
connect record in one table to another
Data types
text, char, boolean, int, real, datetime
Secondary / Alternate Key
values that can be used as primary key (PK cannot be NULL, but SK can)
can have more than 1 SK
Candidate Key
Identify each unique record in a database
both PK and SK are candidate keys
Composite PK
when one field is not enough to uniquely identify records, but 2 fields together can work as a PK
example: name & birthday
Database Schema
defines how data is organized
overview of the database
organizational chart
Relational Database
tables are related to one another
each table has a PK
columns → attributes
rows → records, if none then tuples
Referential Integrity
row → identifier / PK
relations between table are consistent and logical
Database Management System (DBMS)
set of programs that allow to read, store, change / extract data in a database
example: SQLite, mySQL, PostgreSQL
Components of DBMS
data dictionary
data safety
query processor
storage engine
concurrency
security
Data Dictionary
file or set of files that store information about the database and the tables inside
manage metadata / metadata repository
Data Safety
backup & recovery, data integrity
Query Processor
accept queries and return appropriate output
Storage Engine
handles, create, read, update and delete operations
Concurrency
allows multiple users to access database; make sure multiple user can’t modify the same data simultaneously
example: row - locking
Security
enforce user policies, include:
access rights
audit trails: changes made to the data
data locking: lock rows that are accessed
validation: make sure new data follows rules
encryption
back ups: update copies
Database Transactions
collection of low - level tasks
set of SQL statements executed sequentially
all operations are performed and if there is an error, changes either made permanent or save changes commited if not partially or reverted or rolled back
ACID
Atomicity: all task performed or none
Consistency: all data written must be valid
Isolation: no transaction will interfere
Durability: once transaction is complete, changes are permanent even with system failure
Purpose of transaction
make sure changes don’t run into each other & is permanent
Data Integrity
data should be what the user means it to be
accuracy, completeness, validity
Data Redundancy
situation where the same piece of data is stored in 2 or more different place
pros:
faster data access
better protection
cons:
data inconsistency (updated at one place)
more storage used
Normalization
process where larger tables are divided into smaller tables while ensuring data integrity and reduce data redundancy
Why we use Normalization
reduce data redundancy (storage)
reduce table complexity (insertion, updates and deletion less error prone
make sure data is stored logically (to make querying more efficient)
The 1st Normal Form (1NF)
eliminate duplicate columns, multiple types of value
create separate tables for each group
The 2nd Normal Forms (NF)
meet requirements for 1NF
eliminate partial dependency, 2PK, columns dependent on one attribute of a composite PK
The 3rd Normal Form
meet requirements for 2NF
eliminate transitive dependency (column depending on another column)
Advantages of Normalization
less data storage required → lack of duplicates
data is more likely to be consistent
increased data security → easy to locate
operations are conducted more quickly and efficiently due to table structure
simpler queries
easier to understand as it is logically organized
Anomalies
prevented by 2NF
three types of anomaly:
insertion anomaly: or cannot be inserted due to missing data
deletion anomaly: when certain attributes are lost due to deletion of other attributes
update anomaly: data only partially updates
Database Administrator (DBA)
ensure that data is performant, secure, and recoverable by: updating database, maintaining security, managing back up procedures, and establishing recovery plan
Database Definition Language (DDL)
commands that allow us to define and modify the structure and metadata of a database
generate data dictionary
only available to DBAs
DDL commands: alter, create, drop, truncate, rename
Data Modelling
visual representation of a whole / part of an information system
helps stakeholders have a shared understanding of a system
Three types:
conceptual: rough sketch, entities
logical: 4 entities, attributes, FK
physical: data, data type, attributes, relationship
Advantages of Data Modelling
avoid issues:
redundancy
lack of integrity
lack of consistency
helps developers develop actual database
lack → deficient modelling
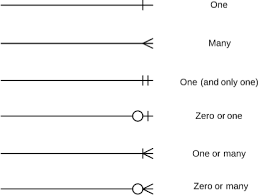
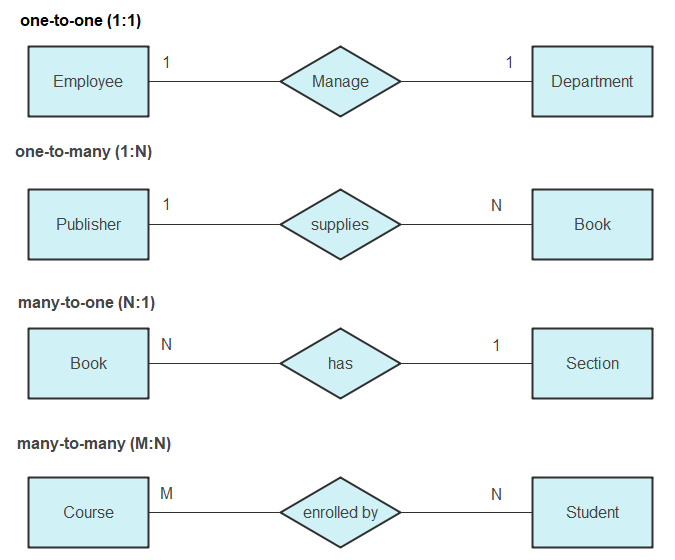
ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram)