Key Themes in AP World History Units 1-7
1/399
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
400 Terms
Confucianism
A philosophy that taught human society is hierarchical by nature, society was composed of unequal relationships. (ex: father > sons, husbands > wife's, rulers > subjects)
Filial piety
Practice of honoring one's ancestors and parents.
Neo-Confucianism
Influence of Buddhist and Daoist philosophical ideas.
Imperial bureaucracy
The Song Dynasty relied on a large bureaucracy to ensure obedience to the emperor's rule, with positions awarded based on merit through civil service exams.
Foot binding
Women had trouble walking, made foot smaller than it started (more seen in elite societies).
Tributary relationship
Korea maintained a tributary relationship with China, adopting aspects of Chinese culture, including Confucian principles and a similar civil service exam system.

Mahayana Buddhism
Buddhist teachings were available to all, emphasized compassion, made the Buddha into an object of devotion.
Theravada Buddhism
Original form, restricted to monks only for a select few.
Tibetan Buddhism
Emphasized more mystical practices (lying prostrate, elaborate imaginings of deities).
Four Noble Truths
1) life is suffering, 2) we suffer because we crave, 3) we cease suffering when we cease craving, 4) the eightfold path leads to the cessation of suffering and craving.
Eightfold path
Principles and practices that a Buddhist must follow (moral lifestyle + practice of meditation).
Song Dynasty
Both large-scale manufacturers and home-based artisans contributed to the production of iron and steel, used for warfare, trading, taxation, and agriculture.
Champa rice
A drought-resistant and high-yield crop that led to a population boom and increased agricultural output.
Song Dynasty
Expansion of the Grand Canal (travel cheaper), improvements in navigation with the magnetic compass, and advancements in shipbuilding techniques (Junk ships with rudders).
Judaism
Monotheistic religion practiced by the Jews, influenced the development of Christianity and Islam.
Christianity
Established by Jesus Christ, a Jewish Prophet; followers spread the message of salvation by grace.
Islam
Founded by the Prophet Muhammad (7th century, Arabian Peninsula); taught salvation through righteous actions (almsgiving, prayer, and fasting).
Islam
Almsgiving, prayer, and fasting.
Islam
Spread rapidly throughout the Middle East, Africa, and Europe.
Islam
Facilitated trade and led to the rise of prosperous Islamic states.
Abbasid Caliphate
8th century: ethnically Arab + in power during Golden Age of Islam.
Abbasid Caliphate
Declined → new Islamic empires rose (made up of TURKIC people).
Seljuk Empire
Central Asia, pastoral people brought in by the Abbasids as a military force to expand their empire by force.
Mamluk Sultanate
Turkic Warriors (Mamluks) seized power in Egypt under the leadership of Saladin.
Delhi Sultanate
Turkic Muslims established a state in South Asia.
Continuity in Muslim empire
1) military in charge of administration, 2) Implemented Sharia Law.
Military Expansion
Delhi Sultanate.
Merchant Activity (trade)
North Africa ruled by Muslims who stimulated trade throughout Africa.
Mali conversion to Islam
Mali converted to Islam.
Muslim Missionaries (Sufis)
Sufism - emphasized mystical experience, and was available to anyone.
Intellectual Innovations
Mathematics (Nasser): Invented Trigonometry to better understand how planets/stars move.
House of Wisdom
Established in Baghdad during the Golden Age of Islam, a library to study religion.
Preservation of Philosophy
Scholars responsible for preserving philosophy by Plato and Aristotle.
Translations to Arabic
Works would've been lost forever → translations went to Europe.
Basis for the Renaissance
Translations became the basis for the Renaissance.
Hinduism
Dominant in South Asia (India); a polytheistic belief system that involves cycling through death and rebirth (reincarnation) to achieve the ultimate goal of reuniting individual souls with the all-pervasive world soul, Brahman.
Polytheistic belief system
A belief system that worships multiple gods, setting it apart from monotheistic religions.
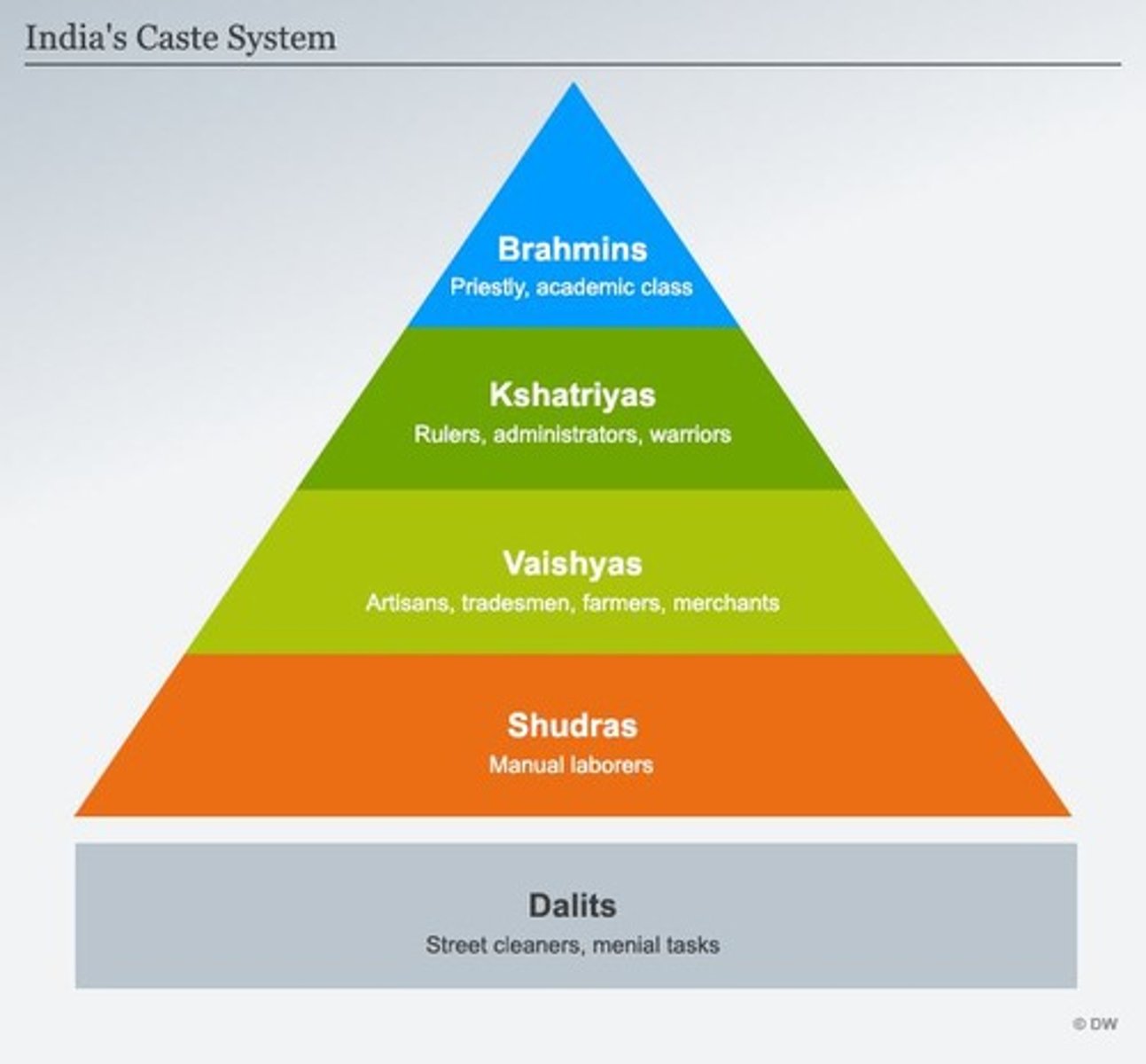
Caste system
A structured social hierarchy in India where individuals cannot move up in status.
Ethnic religion
A religion bound to a particular people in a particular place, which does not spread well.
Islam
Religion established in South Asia by Turkic Muslim invaders who set up the Delhi Sultanate, becoming the religion of the elite and spreading throughout Southeast Asia.
Buddhism
Founded in India and shared several beliefs with Hinduism; more likely to spread but its influence was declining in India by 1200.
Bhakti Movement
A movement within Hinduism that encouraged believers to worship one particular god and rejected the hierarchy of Hinduism.
Sufism
A mystical, spiritual experience-based version of Islam.
Rajput Kingdoms
Rival and warring Hindu kingdoms in India, some conquered by Muslim rulers and some remained independent.
Vijayanagara Empire
A South Indian empire whose rulers sought to extend the rule of the Delhi Sultanate to the South.
Sea-based states
States that derive their power from the sea.
Srivijaya Empire
A Buddhist empire influenced by Indian Hindu culture that controlled the Strait of Malacca and imposed taxes on passing ships.

Majapahit Kingdom
Originally a Hindu kingdom in Java that was influenced by Buddhism and maintained power through a tributary system.
Land-Based States
States that derive their power from land.
Sinhala Dynasties
A Buddhist state in Sri Lanka.
Khmer Empire
Founded as a Hindu empire, it created Angkor Wat as a representation of the entire Hindu universe and later converted to Buddhism.
Syncretism
The blending of religions.
Maya civilization
A decentralized collection of city-states that built urban centers, had a writing system, and emphasized human sacrifice.
Aztec Empire
Established by the Mexica people, who consolidated power through alliances and military prowess, claiming heritage from older Mesoamerican civilizations.
Tenochtitlan
The capital city of the Aztec Empire, known for its vast population and commercialized economy.
Inca Empire
Established around the 1400s, it borrowed from earlier civilizations and established the Mit'a System for labor on state projects.
Mit'a System
A labor system that required individuals to work for a period of time each year on state projects, such as mining or military service.
Mississippian culture
The first large-scale civilization in North America, developed around agriculture and known for extensive mound-building projects.
Cahokia
The largest urban center of the Mississippian culture.
Chaco and Mesa Verde societies
North American civilizations known for innovative water storage and building housing complexes into cliffs.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Region of Africa located south of the Sahara Desert.
Dar-al-Islam
The larger network of Islamic states and territories.
Swahili Civilization
A collection of city-states on Africa's east coast that thrived due to their access to the Indian Ocean trade.
Muslim Merchants
Traders interested in Gold, Ivory, Timber, and Enslaved people who engaged in commerce in the Swahili region.
Swahili Language
A hybrid language influenced by Arabic and Bantu languages.
Great Zimbabwe
A powerful state that controlled ports on the Indian Ocean and built the largest structure in Africa as its capital.
Hausa Kingdoms
A collection of politically independent city-states that gained power and wealth through the Trans-Saharan trade network.
Ethiopia
A Christian kingdom known for its massive stone churches and wealth from trade in the Mediterranean Sea and Indian Ocean.
Salt
The most valuable good traded by Ethiopia.
Byzantine Empire
The eastern half of the Roman Empire that preserved Christianity and influenced Europe.
Eastern Orthodox Christianity
A branch of Christianity that helped justify and consolidate power in the Byzantine Empire.
Roman Catholic Christianity
A branch of Christianity prevalent in Western Europe, characterized by a hierarchical structure.
Ottoman Empire
A Muslim power that attacked Constantinople in 1453, marking the end of the Byzantine Empire.
Kievan Rus
A state that adopted Eastern Orthodox Christianity and borrowed cultural elements from the Byzantine Empire.
Crusades
Military campaigns initiated by European Christians to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslims.
Anti-Semitism
The marginalization and persecution of Jews, often fueled by suspicion from Christians.
Political Decentralization in the West
The absence of large empires in Europe during this period.
Feudalism
a system of allegiances between powerful lords, monarchs, and knights
Manorialism
peasants (serfs) bound to land and worked in exchange for protection from the lord and his military forces
Serfs
peasants who weren't owned by the lord
Silk Roads
network of roads and trails that facilitated trade and the spread of culture and ideas (cultural diffusion) across Eurasia in and before the period 1200-1450
Chinese Silk
mainly luxury items exchanged along the Silk Roads
Paper money
merchants could deposit bills in one location and withdraw the same amount in another location
Flying Money
merchants could secure pieces of paper in one region then go to another region to exchange the paper for coins
Caravanserai
series of guest houses on routes used for rest areas + provided safety and were centers of cultural diffusion
Saddles
made riding easier + held large cargos
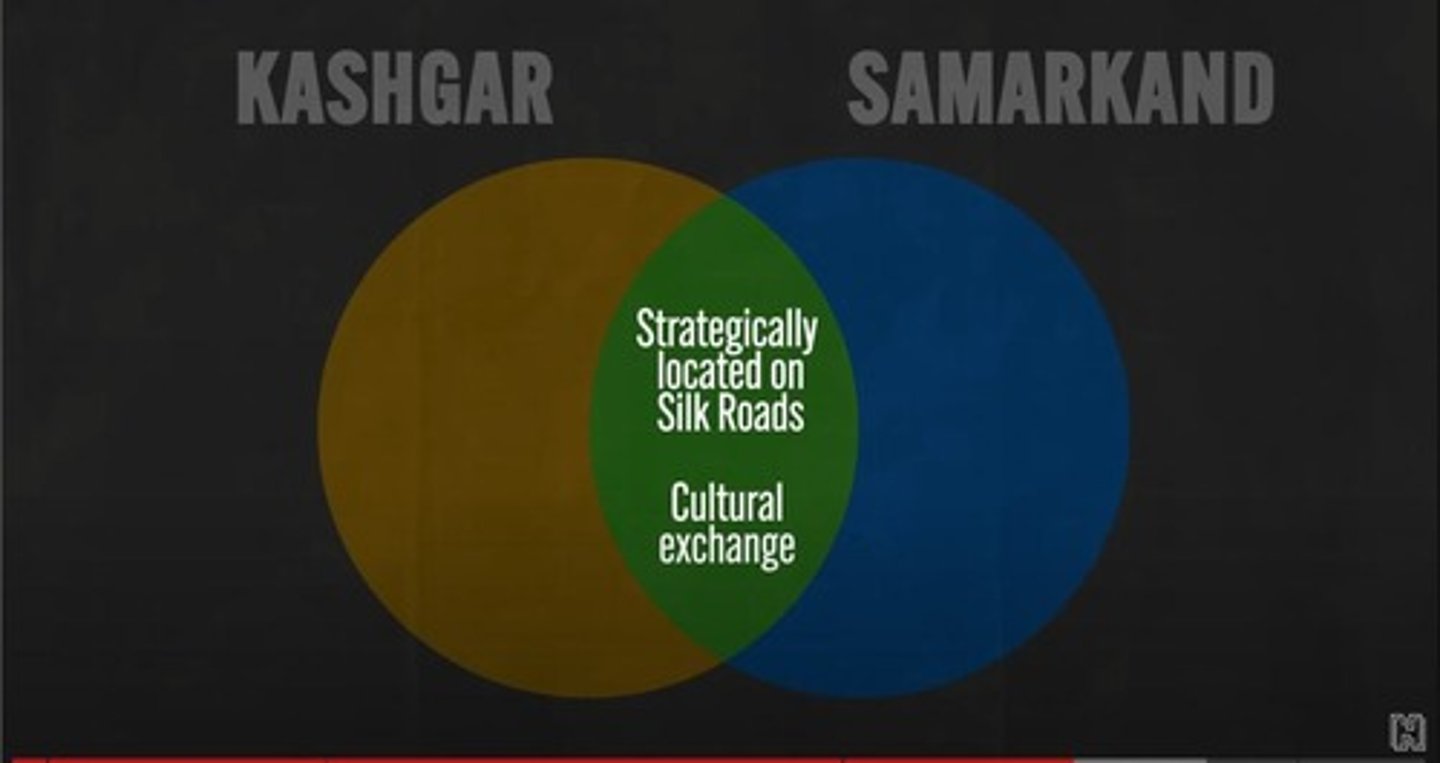
Kashgar
convergence of major routes → suitable for agriculture and had highly profitable markets
Samarkand
repeat of Kashgar
Proto-Industrialization
Process where China produced more goods than their own population could consume (extra goods sold in distant markets)
Cultural Diffusion
the spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another
Temujin
Mongol leader who united the Mongol groups and named himself Chinggis Khan (Genghis Khan)
Mongol Empire
largest continuous land-based empire
Pastoral nomads
traveling people who moved depending on the season
Chinggis Khan
the name taken by Temujin after uniting the Mongol groups
1279
the year the Mongol Empire reached its peak
Military organization
Groups of 10k, 1k, 100, and 10 + superior weaponry and skill (larger bows that shot farther + skilled horse riders)
Lucky timing
Sack of Baghdad
Reputation for brutality
Killed nearly everyone except a few so they could warn the others of them → created fear so they can surrender
Pax Mongolica
Happened after they ruled and conquered a lot
Khanates
Chinggis Khan's grandsons organized the empire into several khanates or military regions