CLPARA SLIDE REVIEW PRELIMS
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Balantidium Coli
Trophozoite
Cilia
Cytostome
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What are the structures pointed by the arrow?
(3)
Identify the structure pointed by the arrowhead
(4)
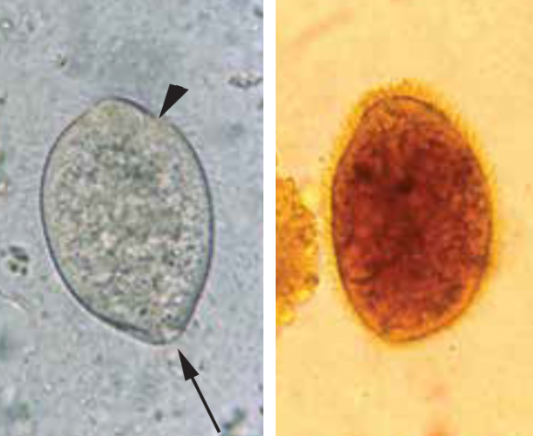
Balantidium Coli
Trophozoite
Macronucleus
Stool
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What are the structures pointed by the arrow?
(3)
What is the specimen of choice in detecting the organism?
(4)
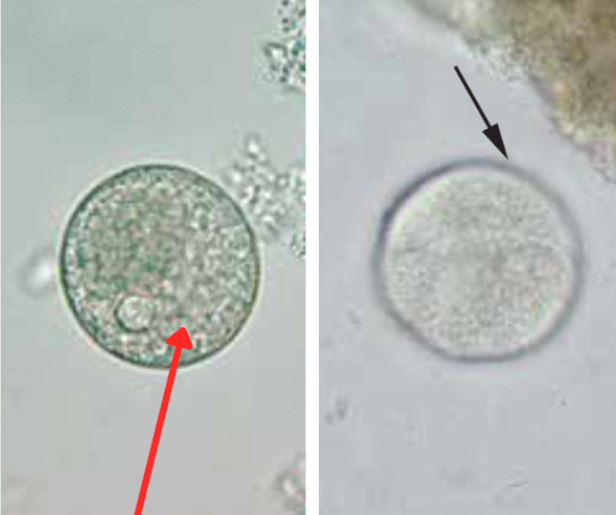
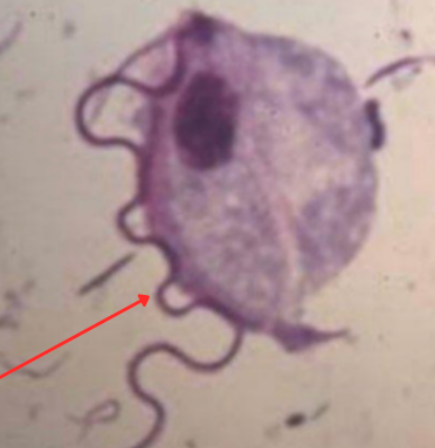
Balantidium Coli
Cyst (more round)
Cilia
Macronucleus
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What are the structures pointed by the black arrow?
(3)
What is the structure pointed by the red arrow?
(4)
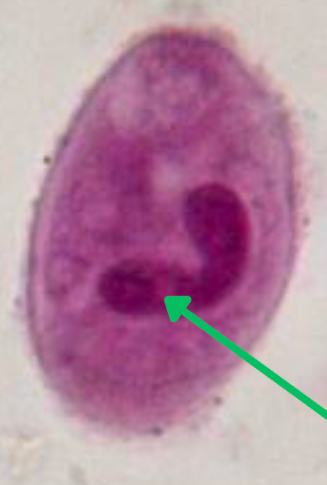
1) macronucleus
2) cilia
What is at green arrow? (1)
What is at red arrow? (2)
Giardia lamblia/Giardia intestinalis/Giardia duodenalis
Trophozoite
Falling leaf motility
Median bodies/Parabasal bodies
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What is the characteristic motility pattern?
(3)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(4)
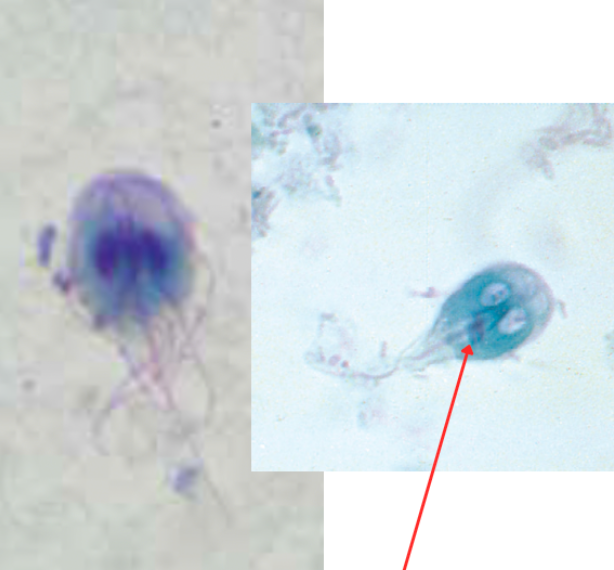
Axostyle
Sucking disc
What is at black arrow? (1)
What is at red arrow? (2)
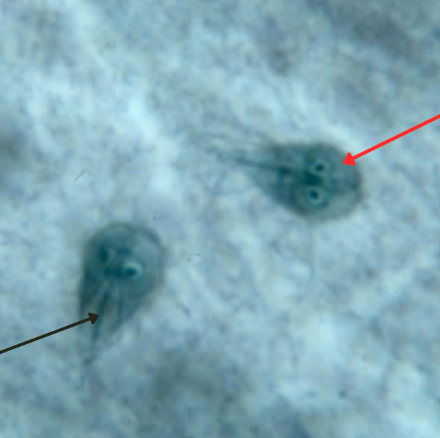
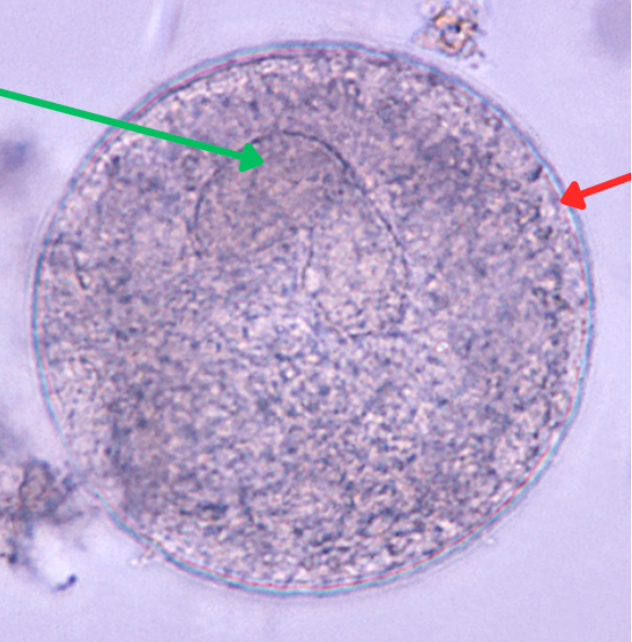
Giardia lamblia/Giardia intestinalis/Giardia duodenalis
Cyst
Axoneme
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
Clearing zone
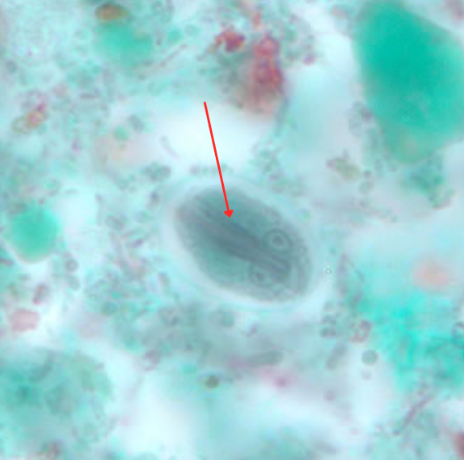
What is at red arrow?
Chilomastix mesnili
Trophozoite
Cytostome
Stiff rotary motility
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
What is the characteristic motility pattern of the organism?
(4)
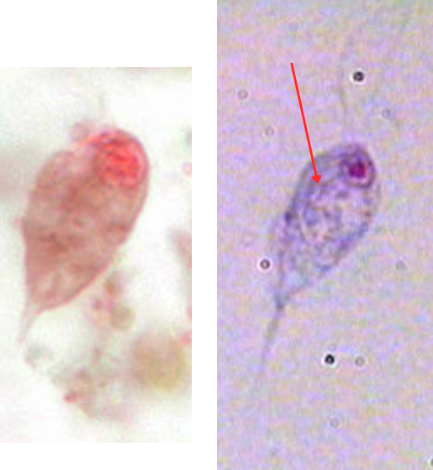
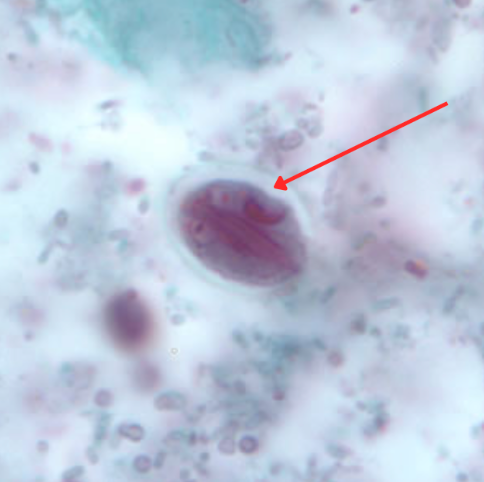
Chilomastix mesnili
Cyst
Cytostome
Clear hyaline knob
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
Identify the structure pointed by the green arrow.
(4)
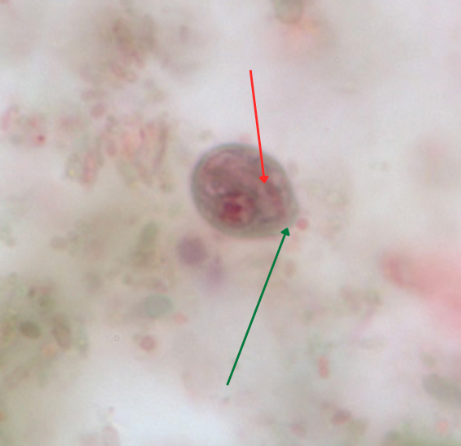
Cytosome
Nucleus
What is at green arrow? (1)
What is at red arrow? (2)
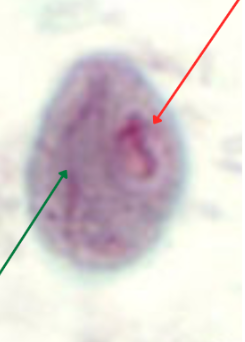
Chilomastix mesnili trophozoite
Chilomastix mesnili cyst
Identify the organism and developmental stage pointed by the red arrow.
(1)
Identify the organism and developmental stage pointed by the green arrow.
(2)
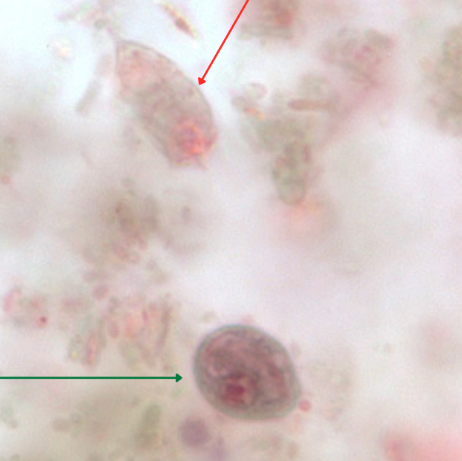
Dientamoeba fragilis
Trophozoite (no cyst stage)
Broad hyaline pseudopodia
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What feature accomplishes the organism’s progressive motility?
(3)
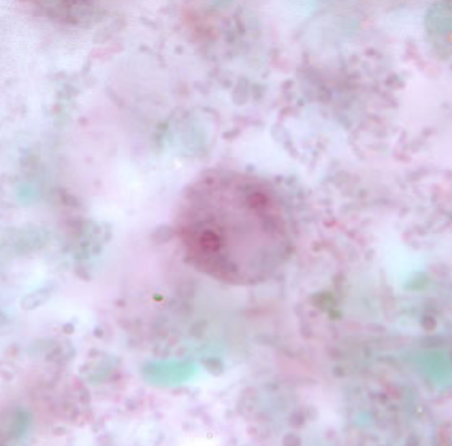
Dientamoeba fragilis
Identify the organism. Give genus and species
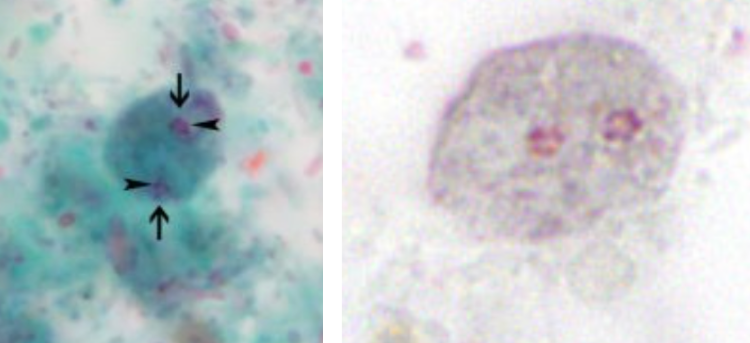
Enteromonas hominis
Trophozoite
Jerky motility
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What is the characteristic motility pattern?
(3)
Enteromonas hominis
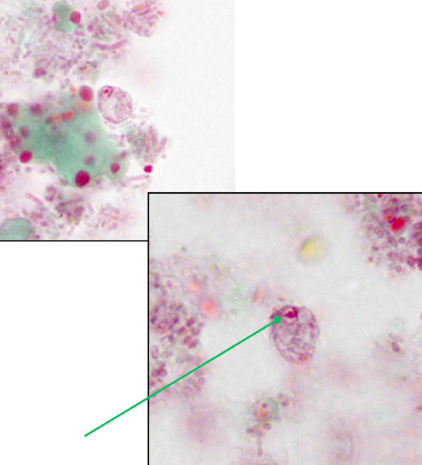
Cyst
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
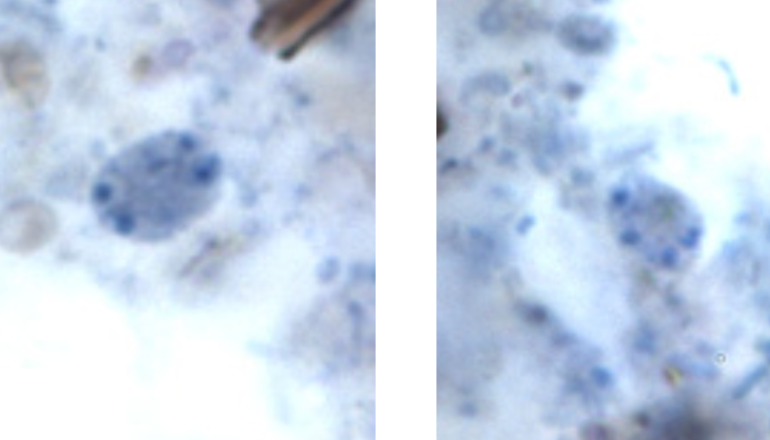
Enteromonas hominis
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
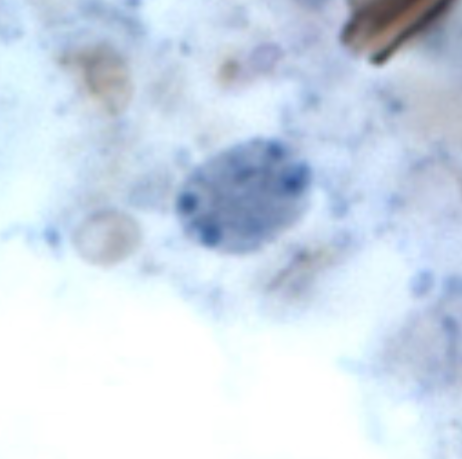
Retortamonas intestinalis
Trophozoite
Cytostome
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
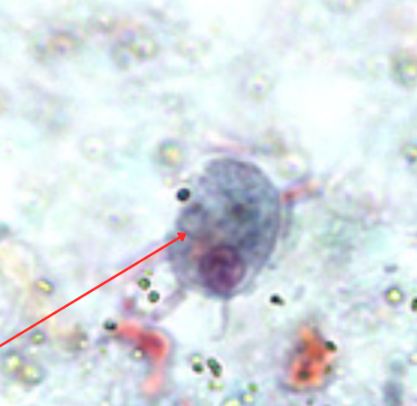
Retortamonas intestinalis
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
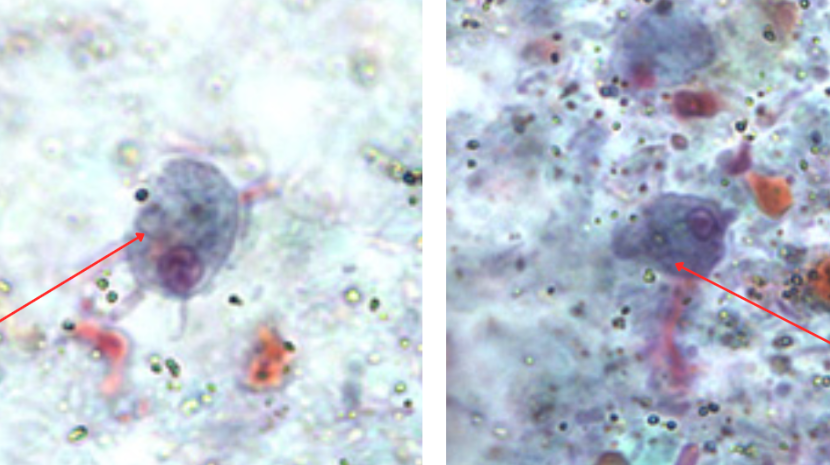
Retortamonas intestinalis
Cyst
Fused fibrils
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
Trichomonas hominis (asymptotic)/ Pentatrichomonas hominis
Trophozoite
Undulating membrane
Nervous jerky motility
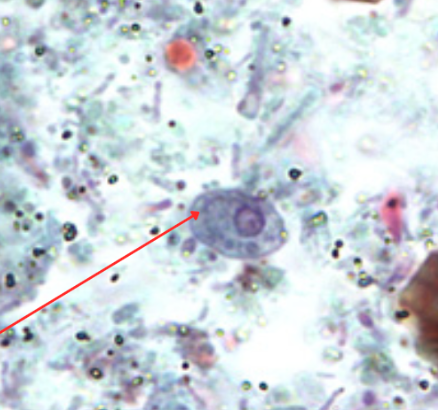
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
Identify the structure pointed by the red arrow.
(3)
What is the characteristic motility pattern?
(4)
Undulating membrane
What is at the red arrows?
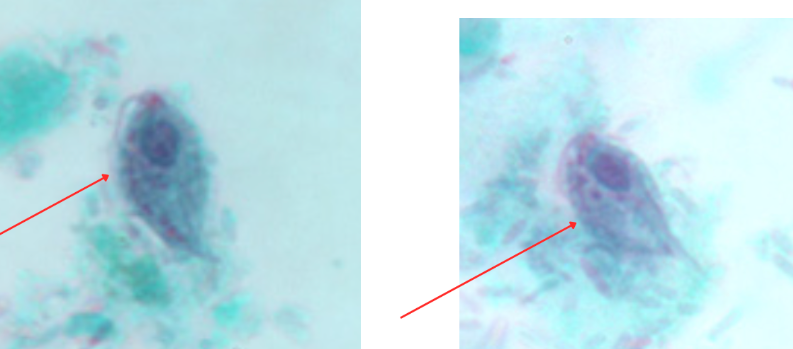
Trichomonas hominis (asymptotic)/Pentatrichomonas hominis
Identify the organism. Give genus and species
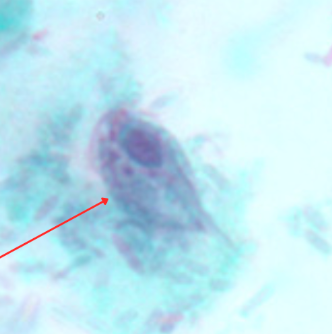
Trichomonas tenax
Trophozoite
Mouth scrapings
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What is the specimen of choice for the detection of the organism?
(3)
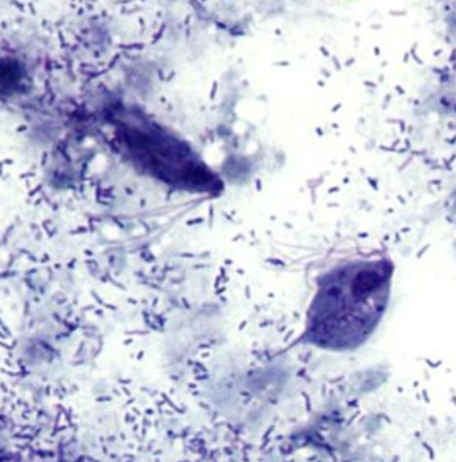
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trophozoite
Rapid jerky motility
Urine, vaginal discharge, urethral discharge, prostatic secretions
Identify the organism. Give genus and species.
(1)
What is the morphologic stage of the organism?
(2)
What is the characteristic motility pattern?
(3)
What is the specimen of choice for the detection of the organism?
(4)
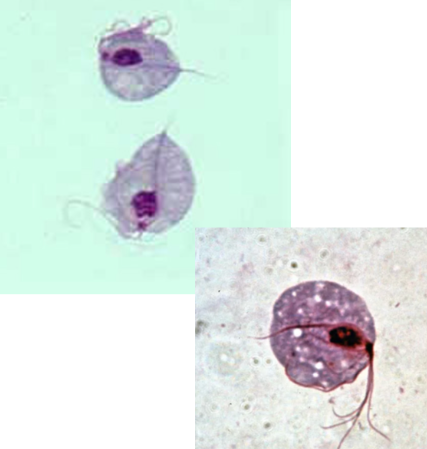
(a) T. tenax (b) T. vaginalis (c) T. or Pentatrichomonas hominis
What are these 3 trichomonads in order from left to right? Give genus and species.
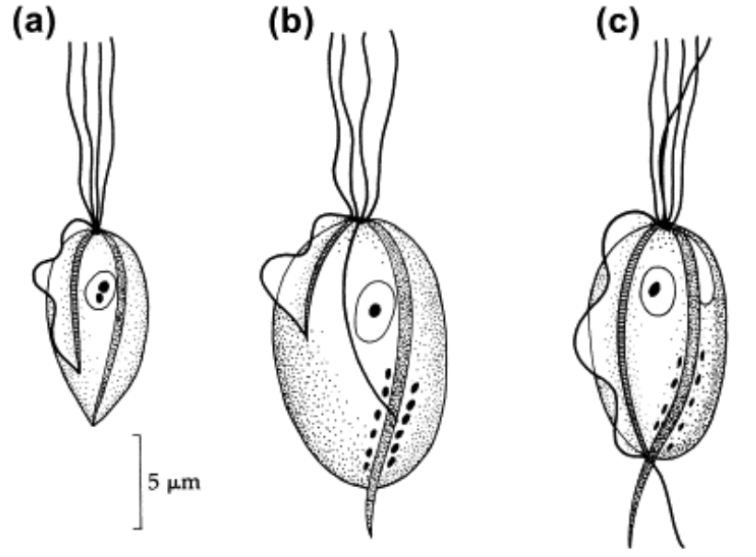
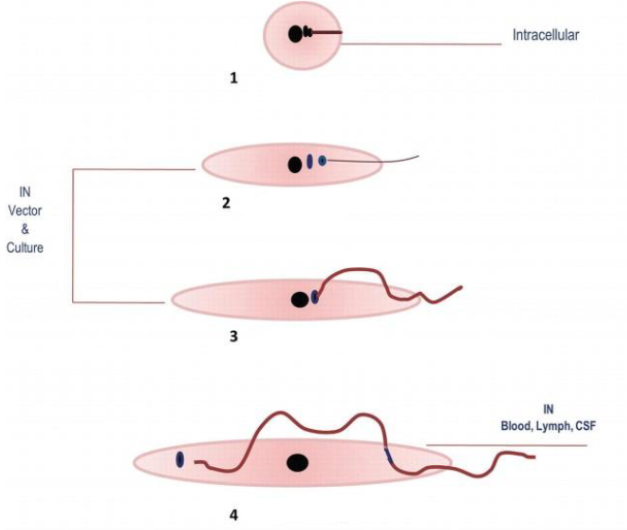
(1) Amastigote (2) Promastigote (3) Epimastigote (4) Trypomastigote
State the 4 morphologic states (stages) of tissue flagellates from top to bottom.
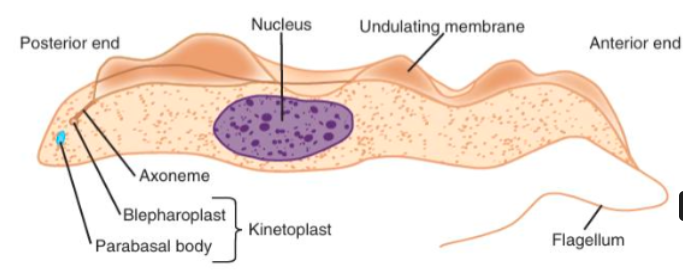
Undulating membrane
extension of cytoplasmic membrane, helps in locomotion (wavelike and reversible movements)
Axoneme
helps with springlike flexibility
Kinetoplast
crucial for replication of the parasite
contains the DNA of the parasite
Nucleus
Trypomastigote
What morphologic state is this flagellate?
(a) Epimastigote (b) Trypomastigote (c) Amastigote
State the morphologic state in order from left to right.
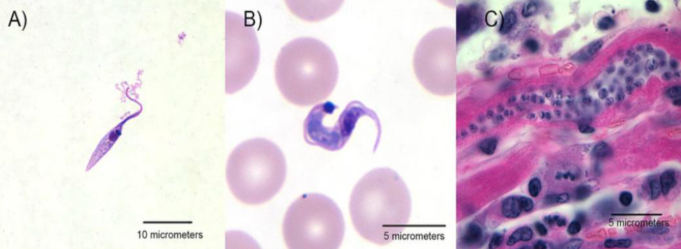
Trypanosoma cruzi
Chagas disease
What is the name of this flagellate? State the name of the disease they give to humans.
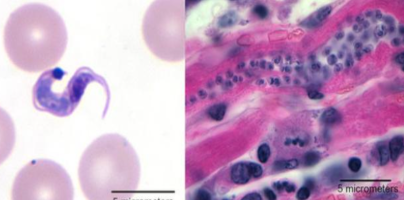
Trypanosoma brucei
What is this flagellate?
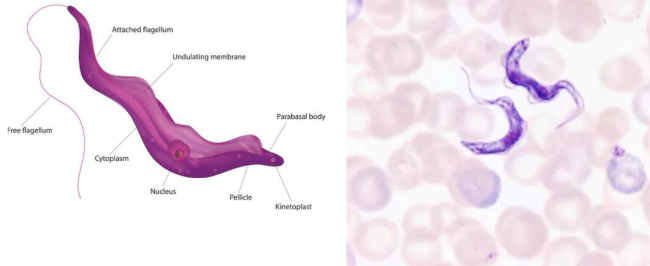
Trypanosoma brucei
What is this flagellate?
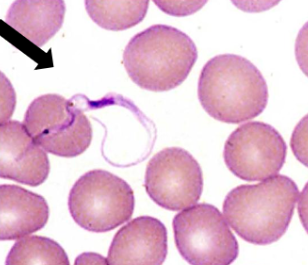
Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma cruzi
State the names of these 2 flagellates from left to right.
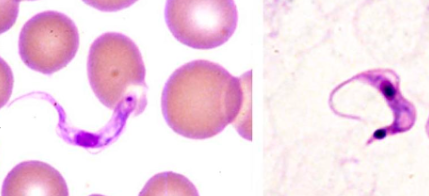
Trypanosoma cruzi
Trypanosoma cruzi or Trypanosoma brucei
Between the two, which one has a more prominent kinetoplast? (dark spot on the posterior end or opposite side of the flagella)
Leishmania
What type of flagellate is this?
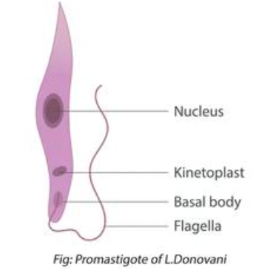
Amastigote
What morphologic state of a leishmania is this?
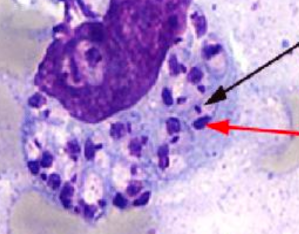
Promastigote
What morphologic state of a leishmania is this?
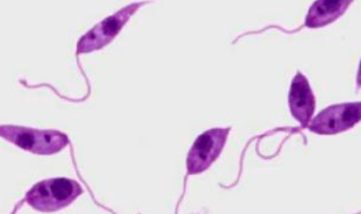
Promastigote and Amastigote
What are the two only morphologic stages of leishmania