bio 2 cell cycle and reproduction
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
cell cycle
most of the cell cycle is interphase, except for mitosis
phases of cell cycle
G1, S, G2, M, G0,
G1 phase
the cell makes mRNA and proteins to prepare for mitosis
S phrase
DNA is replicated
G2 phase
cell growth occurs
organelles are formed
overall preparation for mitosis
M phase
mitosis and cytokinesis
DNA divides into two daughter cells
organelles divide into two daughter cells
G) phase
cell cycle exit
the cell leaves the cell cycle it if doens’t need to divide
a dormant phase
growth signals (CDK and Cyclin)
CDK and cyclin bind together to create a complex
this complex phosphorylates RB and RBP
RBP changes shape and releases E2F
released E2F causes cell division to continue
No CDk-cyclin complex
Blocks phosphorylation
E2F remains attached
No positive growth signal halting the cell cycle.
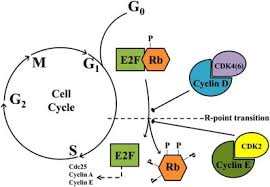
visual representation
if CDK and cyclin form a complex, RB is phosphorylated, E2F is released and the cell cycle progresses, If not, E2F remains bound leading to cycle arrest.
sex chromosomes
xx females
xy males
total chromosomes
23 pairs (36 total chromosomes)
one chromosome from each parent per pair
23 from mom, 23 from dad
x-linked disorders
males express them because they only have one X chromosome.
females can be carriers because they have two x chromosomes
if one X has the disorbers, the other might be normal, preventing expression
y chromosome
little genetic information
few genes resulting in a phenotype
mitosis
pMAT: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
ploidy is 2n throughout
prophase
DNA condenses
centrioles migrate to opposite poles
microtubules from (centrioles form microtubules, two centrioles from a centrosome).
Nuclear envelope disappears, exposing DNA
DNA is in condensed form called chromatin
metaphase
chromosomes line up in the middle
anaphase
chromosomes are pulled apart
each chromosomes is pulled in half
telophase
chromosomes decondense
nuclear membranes reform
cytokinesis occurs finalizing daughter cell formation
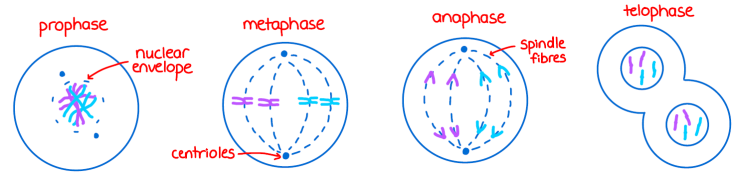
spindle fiber
centrosomes, sister chromatids bound together
interphase: normal cell state
prophase: chromosomes condense and duplicate, attaching at the center point, spindle fibers form
metaphase: chromosomes align in the middle. nuclear envelope disappears
anaphase: sister chromatids are pulled apart
telophase: nuclear envelope reforms. cytokinesis occurs forming two daughter cells
ploidy in mitosis: 2n throughout. chromosome number remains constant even when DNA count doubles (sister chromatids attached)
meiosis
similar to mitosis but with key difference
prophase I
chromosomes condense
homologous chromosomes pair up (from from mom, one from dad)
metaphase 1
homologous chromosomes line up in the middle
crossing over occurs exchanging genetic material.
what is the purpose of metaphase I
to split apart homologous chromosomes, not sister chromatids
anaphase i
homologous chromosomes are split apart
telophase I
chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms (sometimes)
cells divide resulting in two haploid daughter cells of unequal size
prophase II
haploid cells prepare for division
metaphase ii
chromosomes align in the middle
anaphase ii
sister chromatids are split apart
telophase ii
chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms
cell divide, resulting in four haploid daughter cells
overall of meiosis vs mitosis
mitosis: parent cell (diploid)→ daughter cells (diploid)
meiosis: parent cell (diploid) → daughter cells (haploid)
nondisjunction
occurs during anaphase
chromosomes don’t split properly resulting in daughter cells with extra or missing chromosomes
can lead to conditions like down syndrome (trisomy 21)
aneuploidy: abnormal chromosome count
loss of segregation: normal segregation or disjunction
what is p53
important for cell cycle checkpoint control