(Diagnostics) Malley - Chapter 4 - Blood Gas Electrodes (COPIED) STUDY THIS
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
One must be especially cautious in interpreting ________ in a patient with leukemia.
PaO2
The effects of excessive liquid sodium heparin on a blood gas sample are:
1. related to the partial pressures of the gases in the liquid.
2. related to the pH of the liquid heparin.
3. related to the buffer systems in the heparin.
1. related to the partial pressures of the gases in the liquid.
2. related to the pH of the liquid heparin.
Which of the following suggest a blood gas sample may be venous?
1. Observation of a flash of blood as the syringe begins filling
2. Bluish coloration of the blood sample
3. Failure of syringe to auto-fill
4. Brownish coloration of blood
2. Bluish coloration of the blood sample
3. Failure of syringe to auto-fill
Temperature correction of blood gases:
1. clearly provides the optimal way to guide clinical decision-making.
2. is only indicated when patient temperature exceeds 40° C.
3. is easily accomplished with most blood gas machines.
3. is easily accomplished with most blood gas machines.
Placing a blood sample in an ice-water solution will interfere with analysis of blood:
Electrolytes
An instrument that measures an unknown voltage by comparing it with a known reference voltage is?
Potentiometer
Dr Bescey and his ARNP M. Armstrong are arguing over what electrode the "SANZ" is. They ask you and you confidently tell them...
pH
A substance through which electrons can flow is called?
Conductor
Of the 3 Electrodes, which is the least accurate?
Clark
The Half-Cell where the actual electrochemical change takes place is called the
Working Half-cell
(T/F) Janine has just moved to the Tampa area and has been an RT for 30 years. She is not ready to retire yet but also does not want to be on her feet for 12 hours a day. She finds and is offered a job in Tampa General's blood gas lab. She started to re-educate herself on Blood Gas Errors and she thinks she remembers someone telling her the following "A blood gas lab has to determine the mean and standard deviation for each of its instruments"?
True
The Lab has to perform Linearity and Correlation studies on a_____
6 month basis
(T/F) Co-oximitry is less accurate the pulse oximitry
False
In reference to Cooximetry, Up to how many wave lengths are used to determine the fractional components ofhemoglobin?
23
What amino acid breakdown produces NO (Nitric Oxide).
L-Arginine
Which of the following is NOT a NO Synthase (NOS) enzyme?
Glycine
What year was NO (Nitric Oxide) first detected in exhaled breath
1991
(T/F) iNOS are thought to be the main contributor to elevated exhaled NO in asthmatics?
True
(T/F) An adult with a eNO level of 76 ppb would be considered in a normal range and has no inflammation process happening.
False
Asbestosis
Shipyard worker
Beryllium Disease
Aerospace worker
Silicosis
Sand blasters
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
mushroom farmer
Fred is a cabinet and countertop fabricator, and has been for 20 years. He is at a higher risk of contracting this disease.
Silicosis
From the list of gases, which one is colorless and used during WWI as a chemical weapon
Phosgene
Brendon worked for NASA until 2001 in the shuttle fleet prep assembly building. Soon after retiring Brendon started having breathing issues, after extensive testing he was diagnosed with this disease ___________________________, which was a direct result of being exposed at his workplace.
Beryllium Disease
(T/F) The safety committee at Hawks Hospital is comprised of Sarah, Kyle, Diane and Jeff After much research and debate the decide that limiting exposure and Ventilation systems are both examples of prevention goals concerning occupational exposures.
True
If you take inspiratory Capacity and subtract Tidal volume you get this
IRV
Subtract ERV from FRC and you are left with this?
Residual Volume RV
Subtract IRV and ERV from VC and you are left with?
Tidal Volume
What volume can not be measured with spirometers
Residual Volume RV
ERV in obstructive diseases will be?
Decreased or Normal
Adding ERV and RV will give you this?
FRC
If you take TLC and you subtract RV you are left with?
VC
This capacity usually makes up 60% to 70% of the Vital Capacity (VC)
Inspiratory Capacity IC
What makes up TLC
All 4 volumes (IRV, ERV, RV and Tidal Volume)
With a restrictive disease your FVC and FEV1 will be?
Reduced
Normal FEV1/FVC ratio
70% or greater
What are the two primary measurements that are measured in a body box?
FRC and Raw
This type of expiratory maneuver is used when measuring a FVC?
Forced Exhalation
Measuring a patients maximal inspiration produces this capacity?
Inspiratory Capacity IC
The amount of air exhaled forcefully in one second is known as this?
FEV1
What is the name of the Scale used in the 6 minute walk test?
Borg
Bronchoprovocators like histamine and methacholine are used in this test?
Bronchial challenge
This test ends when N2 < 1% for 3 breaths
Nitrogen Washout
This test has the patient breathe as fast and deep as possible for 12-15 seconds?
Maximum Voluntary Ventilation MVV
Decreased DLCO (< 80% of predicted) would indicate which of the following diseases?
COPD
FVC 81%, FEV1 76%, FEV1/FVC 79%
Is this Normal, Obstructive, Restrictive or Mixed?
Normal
FVC 50%, FEV1 44%, FEV1/FVC 75%
Is this Normal, Obstructive, Restrictive or Mixed?
Restrictive
What is the minimum percent increase in forced spirometric volumes after a bronchodilator is given that would indicate reversible airway obstruction?
Greater then 10-12%
FVC 80%, FEV1 50%, FEV1/FVC 50%
Is this Normal, Obstructive, Restrictive or Mixed?
Obstructive
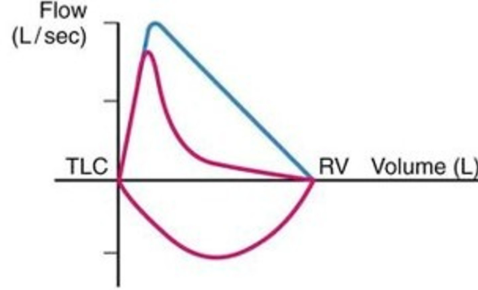
Which of the following flow-volume graphs shows emphysema?
Normal for MVV?
170 L/min
Volume inspired with normal breath?
Tidal Volume
Bronchial challenge testing typically used to determine this disease?
Asthma
Body Plethysmograph (BODY BOX)
is based on what law?
Boyle's Law
Substance used in bronchial provocation test?
methacholine (sometimes histamines)
A person who is born and lives at sea level will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high altitude. Why? What causes this?
Because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude which, as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream
"Control moving in one direction– heading toward an “out of control” value" is a definition of what?
Trend
what is the statistical measure of the amount of which a set of values differ from the arithmetic mean:
Standard Deviation
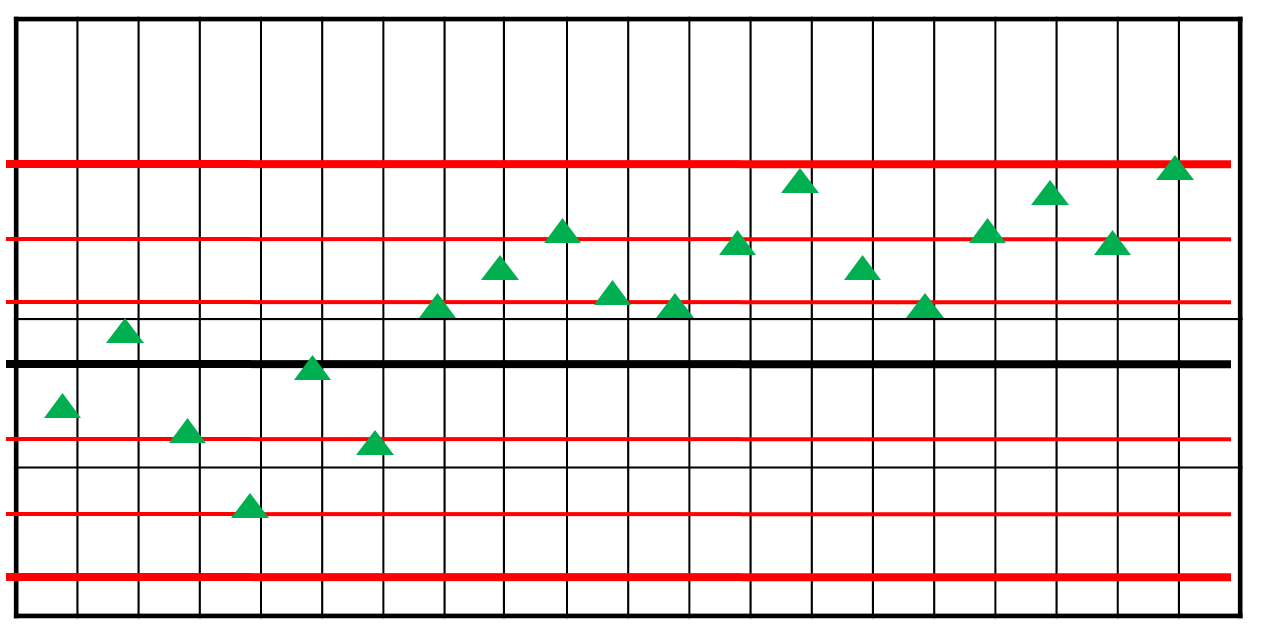
What is shown here?
Shift
The three regulation agencies for blood gas labs are ACHA, PAC, JCAHO
False
Electricity is defined as what?
§ Type of energy resulting from flow of electrons through a substance
Conductor is defined as what?
Substance the electrons flow through
Energy source is defined as what?
Battery or generator that provides power, 2 connections from electrons to flow
Cathode is defined as what?
Negative pole on energy source of excess of stored electrons
Anode is defined as what?
Positive pole on energy source, lack of electrons
What is work?
Electrons move away from the cathode through the conductor moving through to the anode.
What direction does electricity flow?
Negative to positive
What is volts?
Voltage refers to electromotive potential
What is current?
The flow of electrons through the conductor
What is Ampere? or AMP
The unit of measure of the current
What is resistance?
The materials tendency to resist the flow of a charge
What is Omh?
Measurement unit of the resistance of a material.
Formula for Ohms law?
Volt = Current x resistance
What is watts?
Consumption of electric power
Watts formula?
Volts x AMP
What electrode is the Clark electrode?
Po2
What electrode is the SANZ electrode?
pH
What electrode is the Severinghaus one?
Pco2
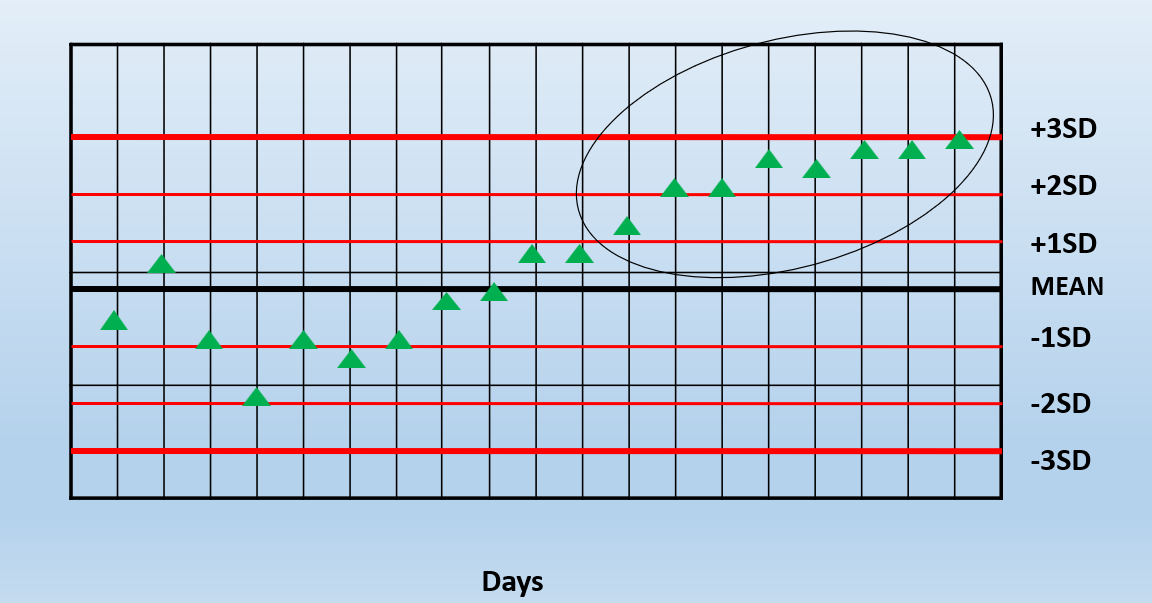
What is going on in the image?
Trend