Bipolar
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
List the acute goals of therapy for the acute treatment of bipolar disorder
Immediate treatment in response to current mania or depressive episodes
Mania
abnormally elevated or irritable mood and energy, symptoms last at least 1 week (if hospitalized duration doesn't matter)
→ Inflated self-esteem
→ Decreased need for sleep
→ More talkative
→ Distracted
→ Racing thoughts
→ increase in goal-directed activity
→ Excessive involvement in activities that have a high potential for painful consequences
Hypomania
4 consecutive days
→ Inflated self esteem
→ Decreased need for sleep
→ More talkative
→ Distracted
→ Racing thoughts
→ increase in goal-directed activity
→ Excessive involvement in activities that have a high potential for painful consequences
*Not severe enough to cause impairment in social functioning or necessitate hospitalziation
Mixed states
symptoms of mania and depression at the same time or in rapid sequence
Bipolar 1
At least one lifetime manic episode.
Bipolar 2
Hypomanic episode and major depressive episode
List the maintenance goals of therapy for the treatment of bipolar disorder
prevention after stabilization of acute mania or depressive episodes
Medication algorithm for acute mania
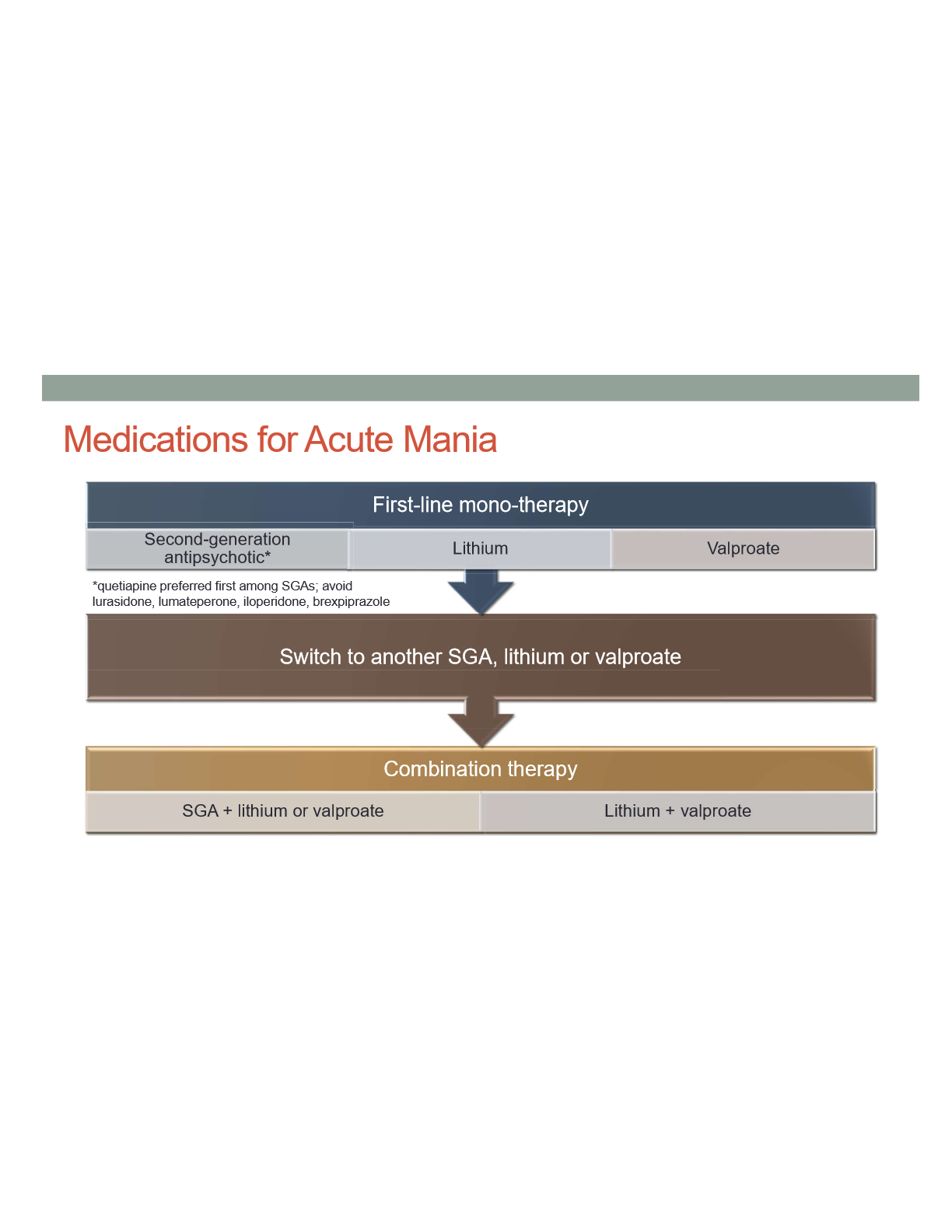
Which SGAs should you avoid for acute mania
Lurasidone, Lumateperone, iloperidone, brexipiprazole
Which SGAs is preffered for acute mania
Quetiapine
Medication algorithm for acute bipolar depression
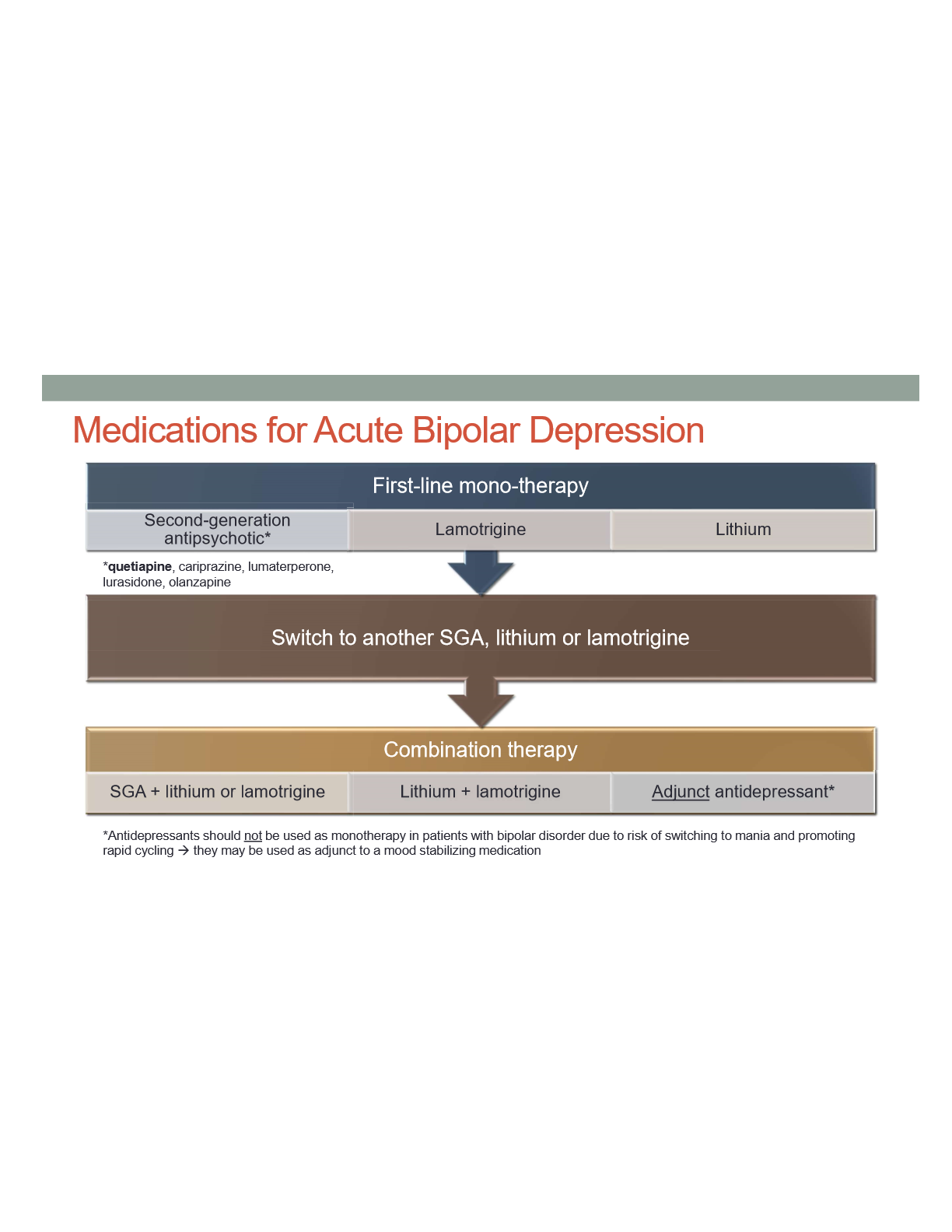
Which SGAs are preffered for acute bipolar depression
Quetipaine, cariprazine, lumaterperone, lurasidone, olanzapine
Can lamotrigine be used for mania?
No
Can antidepressants be be used as monotherapty for bipolar?
No becuase it risks switching to mania
What are mixed episodes?
Aspects of both mania and depression present
What meds are preffered for mixed episodes
Second gen antipsychotics
What medications should you consider for bipolar with rapid cycling?
Antipsychotic , VPA
What medications should you avoid for bipolar with rapid cycling?
Antidepressants, lithium
What medications should you consider for bipolar with high suicide risk?
Lithium, ECT (electro convulsive therapy )
What medications should you consider for bipolar with psychosis?
Antipsychotic, ECT
What medications should you consider for bipolar with anxiety ?
Antipsychotic, VPA
Describe the purpose of maintenance treatment for bipolar disorder, and how medications are selected or used for this purpose
• Goal: prevent relapse
→ meds used for acute symptoms should be continued as maintenance
→ combo therapy is better than mono therpay
Transient side effects of lithium
N/V, GI upset
Diarrhea
Fine hand tremor
Somnolence
Ataxia
Cognitive impairment
Long term side effects of Lithium
Weight gain
Tremor
Polyuria and polydipsia
Increased WBC
Hypothyroidism
Hypercalcemia & hyperparathyroidism
Renal failure (rare)
Cardiac abnormalities
Provide recommendations for managing or minimizing lithium ADEs.
Slow titration, Lower Dose, ER formulation, Split daily dosing
Describe when lithium levels should be checked following initiation of lithium or dosage change to ensure steady state trough levels are obtained.
•Draw levels 12 hours post dose (trough levels)
•First level should be drawn within 5-7 day (steady state)
Mild/Early Lithium toxicity symptoms
Develops gradually over several days
drowsiness
confusion
course hand tremor
ataxia
dysarthria / slurred speech
reappearance or worsening of GI symptoms
How to manage Mild/Early Lithium toxicity
Hold dose, check blood level, monitor vitals/symptoms
Determine cause of elevated level and educate patient
Adjust lithium dose if interacting medication cannot be stopped
Moderate-Severe lithium toxicity symptoms
Gradual or sudden onset
Muscle tremor
Hyperreflexia
Seizures
Cardiovascular collapse
Coma
Death
How to manage moderate/ Severe lithium toxicity
Hold doses
Li Level
Hydration
Gastric Lavage
Supportive Therapy
ECG
Labs
Hemodialysis
Identify common drug interactions that occur with lithium, and the impact of these interactions on lithium levels (i.e. elevated or reduced).
•Diurectics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs increase lithium concentrations
dehydration can also increase lithium levels
Recommend baseline and follow-up laboratory values to evaluate the safety and efficacy of lithium in the management of bipolar disorder.
SCr / BUN / eGFR
Thyroid function
CBC
Electrolytes
Pregnancy test
Weight or BMI
ECG if CVD or risk factors
List important education points for a patient newly starting on lithium therapy for bipolar disorder
Do not alter dose or stop lithium without contacting HCP—inconsistent medication taking, or rapid discontinuation increase risk for relapse
Birth control recommended while taking lithium—contact HCP if pregnant or considering
Maintain adequate fluid intake to avoid dehydration, contact HCP if diarrhea or vomiting or acutely ill
Avoid OTC NSAIDS—acetaminophen is an OTC pain/fever med that won’t interact with lithium
Importance of consistent f/u with prescriber and lab monitoring
Lithium Half life
24 hours
steady state after 3-5 half lives
How to titrate lithium for acute mania
every 5-7 days based on levels and symptoms
Estimate time to benefit on manic symptoms following initiation of a medication to treat bipolar disorder
Initial response: 1-2 weeks
Max beenfit: 3-4 weeks
Estimate time to benefit on depressive symptoms following initiation of a medication to treat bipolar disorder
Initial response: 2 weeks
Mac beenfit: 6-8 weeks
Describe how medications should be discontinued in a manner that reduces risk for relapse and withdrawal in a patient receiving treatment for bipolar disorder
•Engage in discussion of risks
•Taper slowly, 4 week or longer
•educate patient on monitoring for relapse & importance of re starting meds