UF CHM 2045L Final Exam
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
Measurement
_________: the act or process of measuring. This can be simple (reading a thermometer) or complex (all operations required for analysis).
Precision
_______: reproducibility. A precise measurement is close to other values obtained in the same way.
Accuracy
_________: correctness. An accurate measurement is close to the true value or the accepted value if the true value is unknown.
Error
_______: anything causing a measurement to differ from the true value. The amount by which the measured value differs from the true value is also called the error.
Range
_____ = maximum value - minimum value
Standard Deviation
__________ measures how closely the individual values are clustered around the mean. If the measurements follow a normal distribution curve, 68% of all values will fall within the interval (xbar) +/- s. A small standard deviation indicates greater precision or a more closely clustered data set.
Error
______ = measured value - true value
% Error
_______ = |experimental - theoretical|/theoretical x 100%
Density
________ is an intensive property of matter; it is characteristic at a given temperature and pressure. The density of a liquid can be easily determined through measurements of mass and corresponding volume. We commonly use g/mL as units of density.

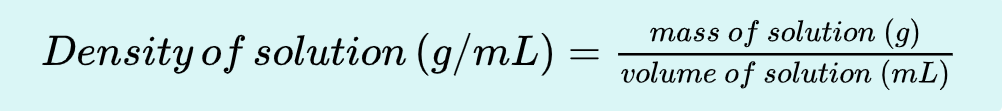
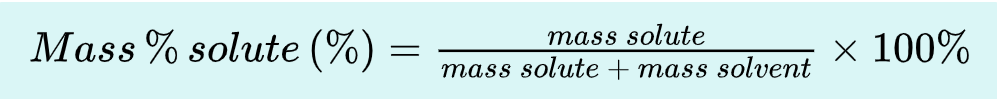
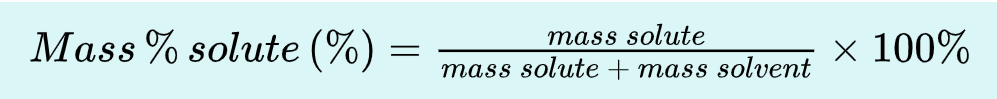
X-Axis
Independent Variable is plotted on the ____
Y-Axis
Dependent Variable is plotted on the ______
Scientific Method
a systematic and logical approach used by scientists to investigate natural phenomena, acquire new knowledge, or refine existing knowledge.
Hypothesis
a testable statement or educated guess that predicts the outcome of an experiment or the relationship between variables.
Variable
any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types and can be measured or observed in an experiment.
Independent Variable
the variable that is intentionally manipulated by the researcher in an experiment to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
the variable that is observed and measured in response to the changes in the independent variable; it represents the outcome of the experiment.
Control Group
a group in an experiment that is not subjected to the experimental treatment and is used as a baseline for comparison with the experimental group.
Experimental Group
the group in an experiment that is exposed to the treatment or variable being tested to observe the effect.
Null Hypothesis
a hypothesis stating that there is no significant difference or effect; it is often used for statistical testing.
Alternative Hypothesis
a hypothesis that contradicts the null hypothesis, suggesting that there is a significant difference or effect.
Controlled Experiment
an experiment in which all variables are kept constant except for the independent variable being tested.
Replication
the process of repeating an experiment to verify the results and ensure the reliability of the findings.
Observation
the act of gathering information through the use of the senses or instruments; it is often the starting point of the scientific method.
Data
facts, figures, and other evidence gathered through observations and experiments that can be used to support a hypothesis or draw conclusions.
Conclusion
a summary of the results of an experiment, including a discussion of whether the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
Peer Review
the evaluation of scientific work by other experts in the field before it is published, ensuring the quality and validity of the research.
Theory
a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on empirical evidence and has stood up to repeated testing and scrutiny.
Bias
systematic error introduced into sampling, testing, or reporting, leading to a distortion of results.
Ethics in Research
the principles and standards that guide researchers to conduct their work responsibly, ensuring the well-being of subjects and the integrity of the scientific process.
Scientific Law
a statement that describes a consistent and universal relationship observed in nature. Unlike a theory, which explains why or how something happens, a scientific law simply describes what happens. Scientific laws are well-established and have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experimentation.
Hydrate
a crystalline compound in which one or more water molecules are combined with each formula unit of the salt. The water molecule(s) is termed the water of hydration.
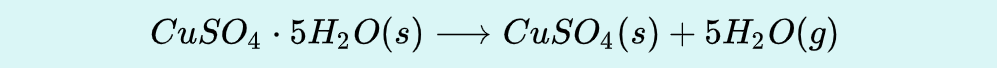
Efflorescene
Some anhydrous compounds spontaneously absorb water from the air to form hydrates; these are termed hygroscopic or deliquescent compounds. Compounds can lose waters of hydration spontaneously, in a process called__________
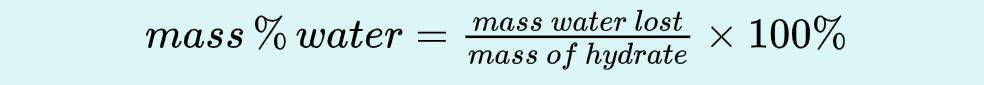
Use wet hydrate
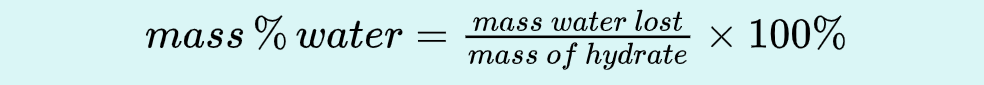
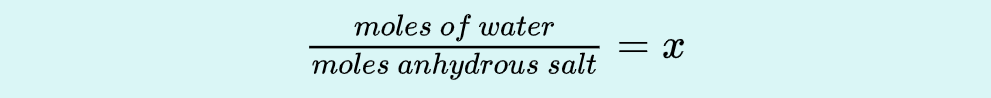
Use dry hydrate
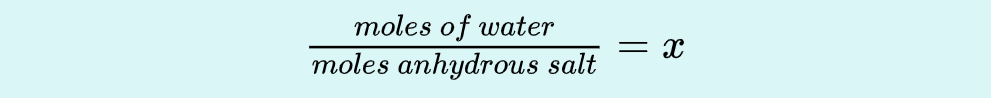
Tutration
a technique used to determine the concentration of a substance (analyte) in a solution by reacting it with a known volume and concentration of another substance (titrant).
Analyte
the substance in a solution whose concentration is being determined through titration.
Titrant
the solution of known concentration that is added to the analyte during titration.
Endpoint
the point in a titration where the reaction between the analyte and titrant is complete, often indicated by a visible change in the indicator.
Equivalence Point
the point in a titration where the stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of the analyte and titrant have reacted.
Molarity (M)
a measure of concentration expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution.
Redox Titration
a titration based on redox reactions, where the transfer of electrons determines the endpoint.
Quantitative Analysis
the determination of the amount or concentration of a substance in a sample.
Excess Reactant
reactant present in an amount greater than required by the reaction stoichiometry.
Oxidation
the process in which an element’s oxidation number is increased by loss of electrons.
Oxidation Number (also, oxidation state)
the charge each atom of an element would have in a compound if the compound were ionic.
Oxidizing Agent
a substance that brings about the oxidation of another substance and, in the process, becomes reduced.
Reducing Agent
a substance that brings about the reduction of another substance and, in the process, becomes oxidized.
Reduction
the process in which an element’s oxidation number is decreased by a gain of electrons.
Stoichiometry
the relationships between the amounts of reactants and products of a chemical reaction.
Titration Analysis
a quantitative chemical analysis method that involves measuring the volume of a reactant solution required to completely react with the analyte in a sample.
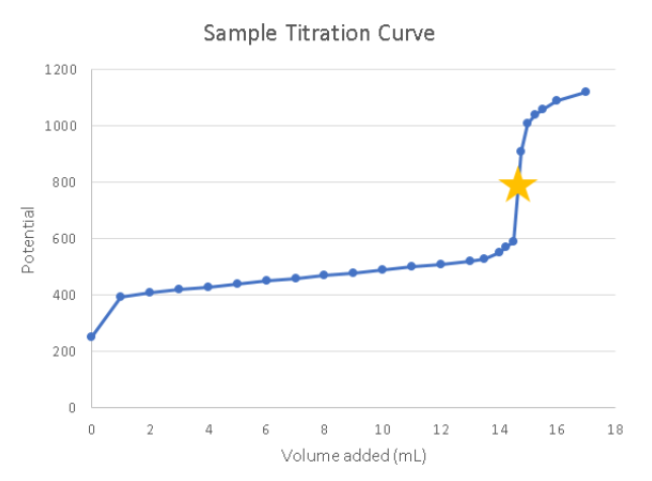
The star is the ___________, or the point at which the oxidation/reduction reaction is complete. This point in the curve has the greatest potential change per volume added (the steepest part of the curve)
Point Slope
y2 - y1 = m(x2-x1)
Titrant
The _________is what you are adding to the solution of unknown concentration with DI water.
Analyte
The _______ is the substance whose concentration is unknown in the titration.

Health Hazard
Carcinogen
Mutagenicity
Reproductive Toxicity
Respiratory Sensitizer
Target Organ Toxicity
Aspiration Toxicity

Flame
Flammables
Pyrophorics
Self-Heating
Emits Flammable Gas
Self-Reactives
Organic Peroxides

Exclamation Mark
Irritant (skin and eye)
Skin Sensitizer
Acute Toxicity (harmful)
Narcotic Effects
Respiratory Tact
Irritant
Hazardous to Ozone Layer (Non-Mandatory)

Gas Cylinder
Gases Under Pressure

Corrosion
Skin Corrosion/Burns
Eye Damage
Corrosive to Metals

Exploding Bomb
Explosives
Self-Reactives
Organic Peroxides

Flame Over Circle
Oxidizers

Enviornment (Non-Mandatory)
Aquatic Toxicity

Acute Toxicity (fatal or toxic)
Absolute Zero
the temperature at which the volume of a gas would be zero according to Charles’s law.
Atmosphere (atm)
the unit of pressure; 1 atm = 101,325 Pa.
Avogadro’s Law
the volume of a gas at constant temperature and pressure is proportional to the number of gas molecules.
Barometer
a device used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressuress
the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases equals the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases.
Ideal Gas
a hypothetical gas whose physical properties are perfectly described by the gas laws.
Ideal Gas Constant (R)
a constant derived from the ideal gas equation R = 0.08206 L atm mol-1 K-1 or 8.314 L kPa mol-1 K-1.
Ideal Gas Law
the relation between the pressure, volume, amount, and temperature of a gas under conditions derived by the combination of the simple gas laws.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
the theory based on simple principles and assumptions that effectively explain ideal gas behavior.
Manometer
a device used to measure the pressure of a gas trapped in a container.
Partial Pressure
the pressure exerted by an individual gas in a mixture.
Pressure
the force exerted per unit area.
Standard Conditions of Temperature and Pressure (STP)
273.15 K (0 °C) and 1 atm (101.325 kPa)
Standard Molar Volume
the volume of 1 mole of gas at STP, 22.4 L for gases behaving ideally.
Vapor Pressure of Water
the pressure exerted by water vapor in equilibrium with liquid water in a closed container at a specific temperature.
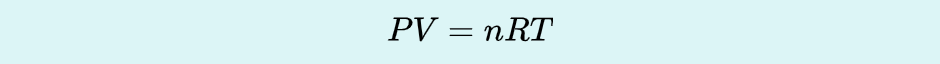
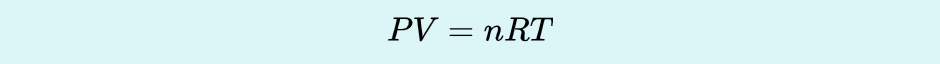
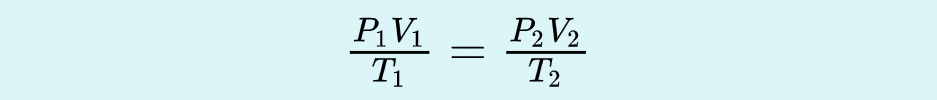
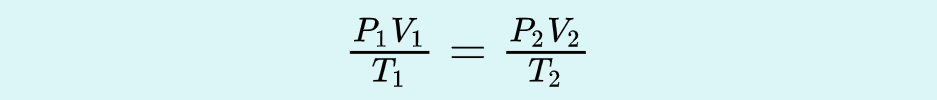
Molar Volume
_______ = volume of gas/ moles of gas (L/mol)
Thermochemistry
the area of science concerned with the amount of heat absorbed or released during chemical and physical changes.
Energy
the capacity to supply heat or do work.
Potential Energy
the energy of an object due to its relative position, composition, or condition.
Kinetic Energy
the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
Thermal Energy
kinetic energy associated with random motion of atoms and molecules.
Temperature
a quantitative measure of "hot" or "cold."
Work
a force acting on something, causing it to move, is an example of work.
Heat
the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies at different temperatures.
Exothermic Process
a chemical reaction or physical change that releases heat.
Endothermic Process
a chemical reaction or physical change that absorbs heat.
Units of Heat
calories (cal) or joules (J).
Specific Heat Capacity
the quantity of heat (q) an object absorbs or releases when it experiences a temperature change (ΔT) of 1°C.
Calorimetry
the process of measuring heat involved in a chemical reaction or physical change.
System
the substance or substances undergoing the chemical or physical change.
Surroundings
all other matter not in the system.
Hazard
The three most common categories of _____ in research are agent, condition, and activity