urinary system
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
micturition / urination
process of releasing urine from urinary bladder through urethra
what makes urine yellow in colour ?
urochrome/urobilin from haemoglobin breakdown
micturition can be accelerated using ?
diuretics
where are the kidneys located ?
retroperitoneal space
what structures make up the lobes of the kidney ?
renal pyramids
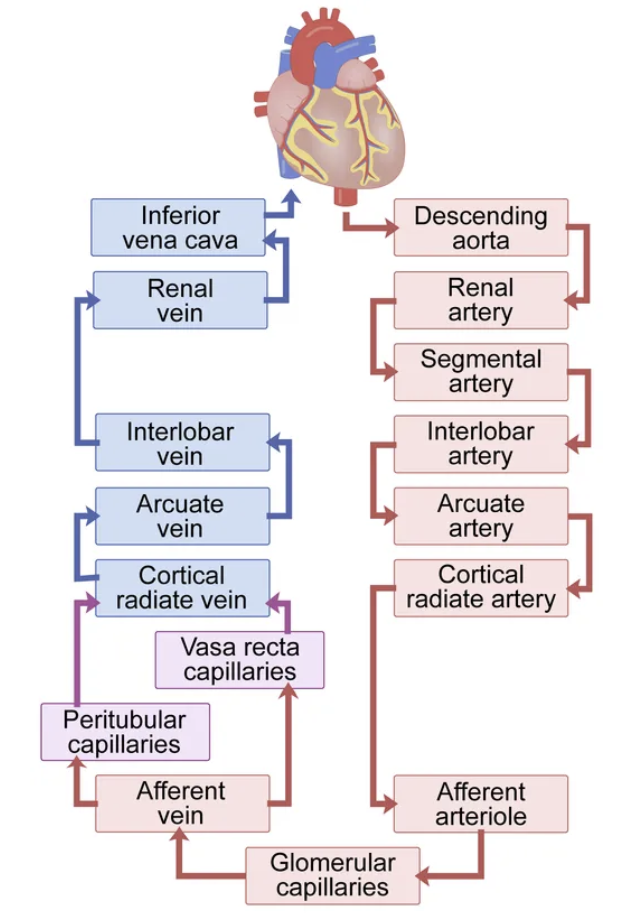
the kidneys are supplied by what artery ?
renal
blood supply to and from kidneys
arcuate, cortical radiate
3 major functions of kidneys
regulate blood volume
remove urea
regulate acid-base balance
what hormones do the kidneys produce ?
erythropoietin and renin
what is the glomerulus ?
tuft of capillaries adapted for filtration
the Bowman’s capsule is connect to the PCT by
the urinary pole
how much plasma is filtered per minute by the kidneys (avg. GFR rate) ?
120-140ml
what is filtrate ?
plasma without proteins or cells
how much plasma is reabsorbed after filtration ?
119 - 124ml
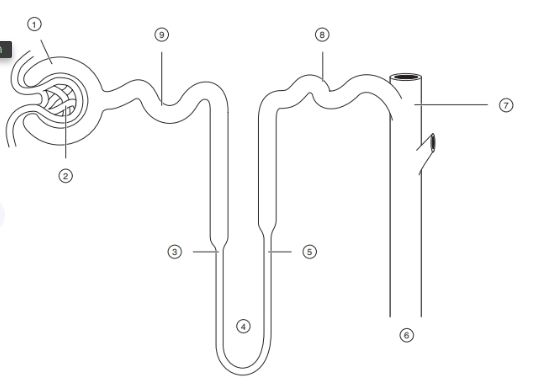
label the nephron structures
1 - bowmans capsule
2 - glomerulus
3, 4, 5 - loop of henle
6, 7 - collecting duct
8 - distal CT
9 - proximal CT
the loop of Henle lies in what section of the kidney ?
medulla
what are the functional units of the kidney ?
nephrons
3 stages of nephron function
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption
tubular secretion
what regulates GFR ?
arteriole vasoconstriction
mesangial cell contraction
podocyte permeability
what is reabsorbed in the PCT ?
K+ Na+ amino acids glucose water
what is reabsorbed in the loop of Henle
Na+
what is reabsorbed in the collecting duct
water
how much urine is produced per minute on average ?
1ml / min
how long are the ureters and where are they located ?
20cm either side of vertebral column
what prevents urine back flow from the bladder to kidneys ?
ureterovesical valves
what are the three layers of the ureter wall ?
inner mucosa
muscularis
outer adventitia
how much urine can the bladder hold ?
500ml (max 1000)
what are the 3 layers of the bladder ?
mucosa - transitional epithelium
muscular layer - longitudinal and circular muscles
fibrous adventitia
the internal / bladder neck urethral sphincter is composed of what muscle type ?
smooth muscle - involuntary
what muscle controls voluntary urination ?
external urethral sphincter - skeletal muscle
urine passes from where to the ureter ?
renal pelvis
how do the male and female urethra differ ?
length - male urethra longer
nervous control of micturation
sympathetic - senses stretch relaxes bladder and internal sphincter
parasympathtic - external sphincter, automatically contracts bladder
blood in the urine indicates
infection
what is diuresis ?
increased production of urine
what’s the difference between water diuresis and osmotic diuresis ?
water - more water ingested than body requires
osmotic - more solute excreted than normal
how do diuretics work ?
increase water and NaCl excretion via kidneys
indirect vs direct diuretics
indirect - modify composition of filtered fluid
direct - act directly on cells of nephrons
role of kidneys in homeostasis
remove urea
control water/ion balance
regulate BP
maintain pH
what organ carries out the urea cycle ?
liver
where do the first 2 steps of the urea cycle occur ?
mitochondrial matrix
in the urea cycle ammonia is converted to
urea and excreted in urine
what is the waste product of protein metabolism ?
nitrogen - accumulates as ammonia
osmolarity
total number of dissolved particles in solution
what is the standard body fluid osmolarity ?
295mOsml/L
what is the juxtaglomerular complex ?
structure that regulates each nephron's function
next to glomerulus
isoosmotic solutions have
equal osmolarity
hypoosmotic
one solution has lower osmolarity
hyperosmotic
one solution has higher osmolarity than the other
what cells detect NaCl in the distal tubule ?
macula densa cells
in 1L of water what has higher osmolarity 1mmol of CaCl2 or NaCL ?
CaCl2 - dissociates into 3 molecules of Ca2+ and 2x Cl-
NaCl only dissociates into 2 - Na+ and Cl-
name 3 ways GFR is regulated
myogenic mechanism
tubuloglomerular feedback
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
what triggers renin release ?
low BP, low NaCl or SNS activation
how does ADH increase BP ?
increases water
urea and sodium reabsorption
vasoconstriction
where are macula densa cells located ?
end of ascending loop of Henle, distal CT
role of macula densa cells
chemo/osmoreceptors
respond to changes in solute conc. of filtrate
how does the myogenic mechanism regulate GFR ?
dilates and constricts afferent arteriole to maintain GFR despite fluctuations in BP - protects glomerulus from damage
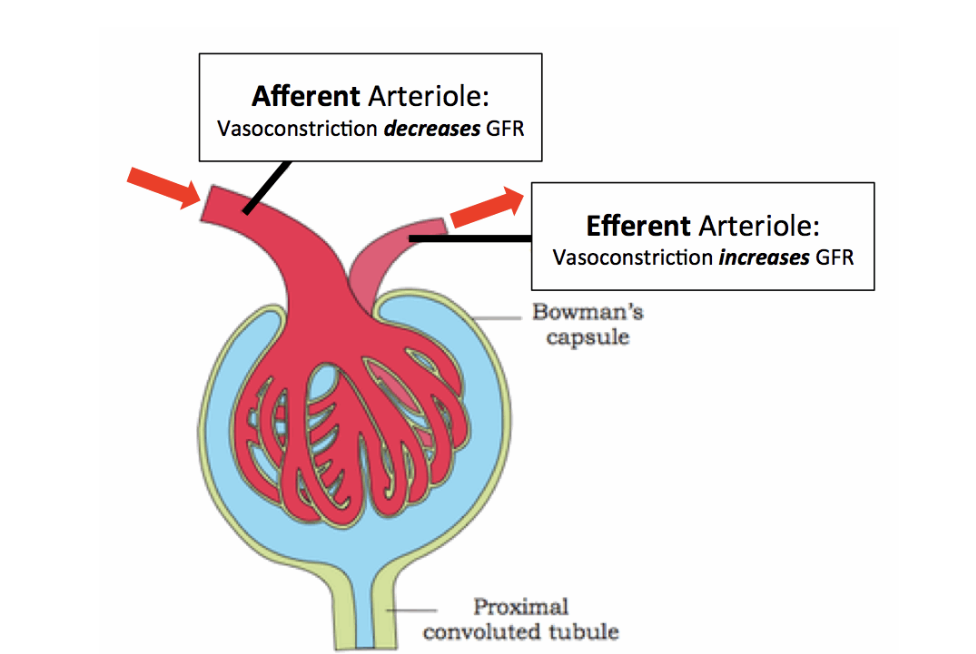
how does tubuloglomerular feedback regulate GFR ?
senses changes in tubular fluid composition, particularly NaCL at macula densa and alters filtrate flow accordingly
decreases / increases reabsorption time by constricting / dilating afferent arteriole
what does high NaCl conc. in renal filtrate suggest ?
GFR too high
the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is the main mechanism for…
increasing BP
what are the 3 triggers for renin release ?
direct simulation by SNS
low NaCl - detected by macula densa cells
reduced stretch of granular cells (low BP)
renin is released by what cells ?
granular / juxtaglomerular
what enzyme circulates in pulmonary blood ?
angiotensin converting enzyme
where is ADH produced and released ?
hypothalamus - released by posterior pituitary
ADH is also referred to as…
vasopressin
how does aldosterone increase BP ?
increases sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in kidneys
leads to water retention and thus increase in BP
what stimulates ADH release ?
hyperosmolarity - high solute conc. in blood
angiotensin II
what inhibits ADH release ?
high blood pressure
how does ADH increase BP ?
increases water, Na+ and urea reabsorption
vasoconstriction