Physio 12: Daltons Law & Gas Transport (Resp 2)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Capillary gas exchange
exchange of O2 to RBC (found in capillary) for CO2 at the alveolar space

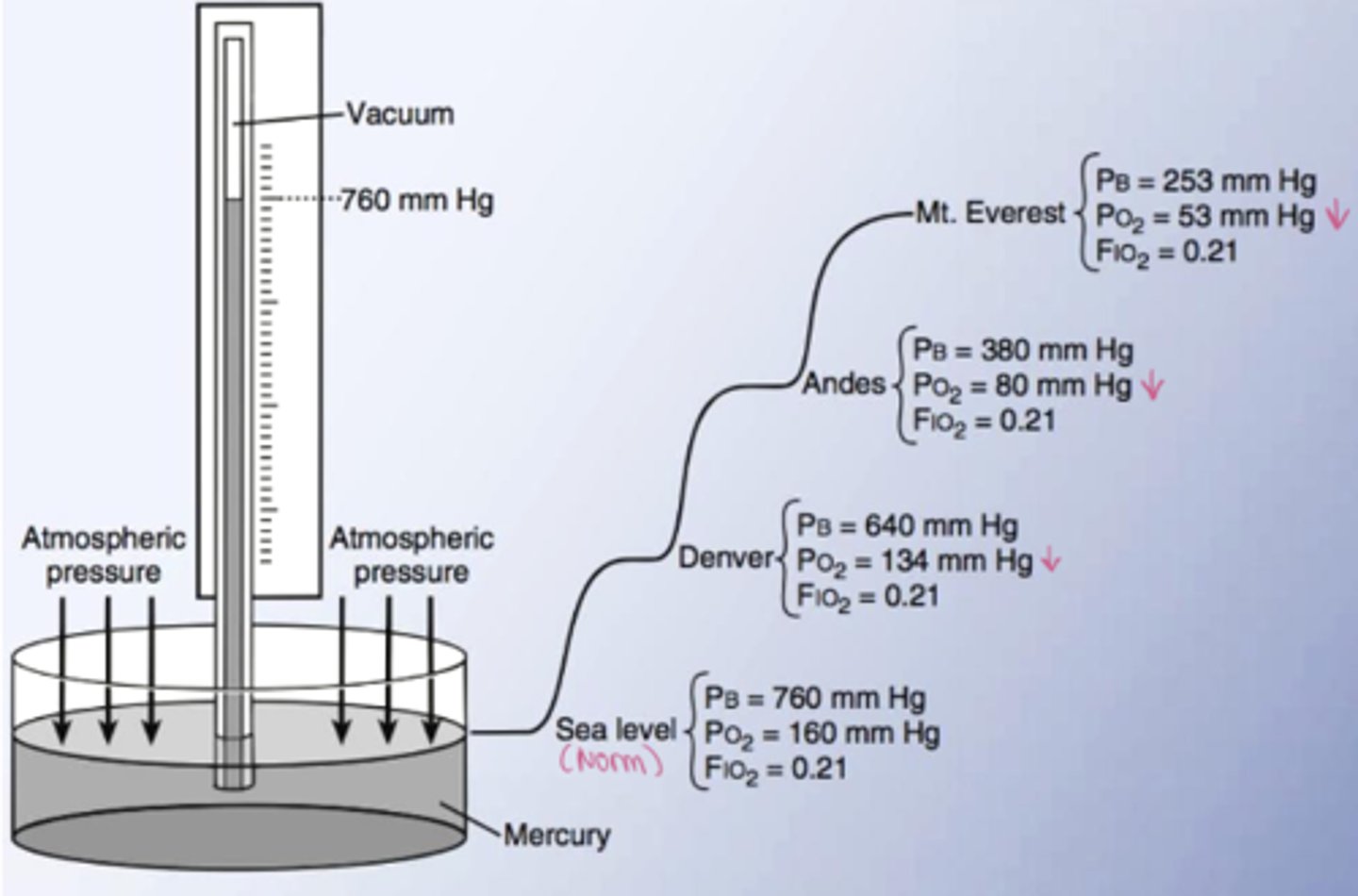
Know the different partial pressures at different altitudes
Dalton's Law
Total pressure equals sum of all partial pressures.
Pb = PN2 + PO2 + PCO2
Air is predominantly composed of
Nitrogen (78%) and Oxygen (21%) and CO2 (0.04%)
Sea level pressure
760 mmHg
Solve for partial pressure of Nitrogen
PN2 = 0.79 x (760 - 47) = 563 mmHg
Why subtract 47 when solving for partial pressure according to daltons law?
subtract the water vapor which is 47
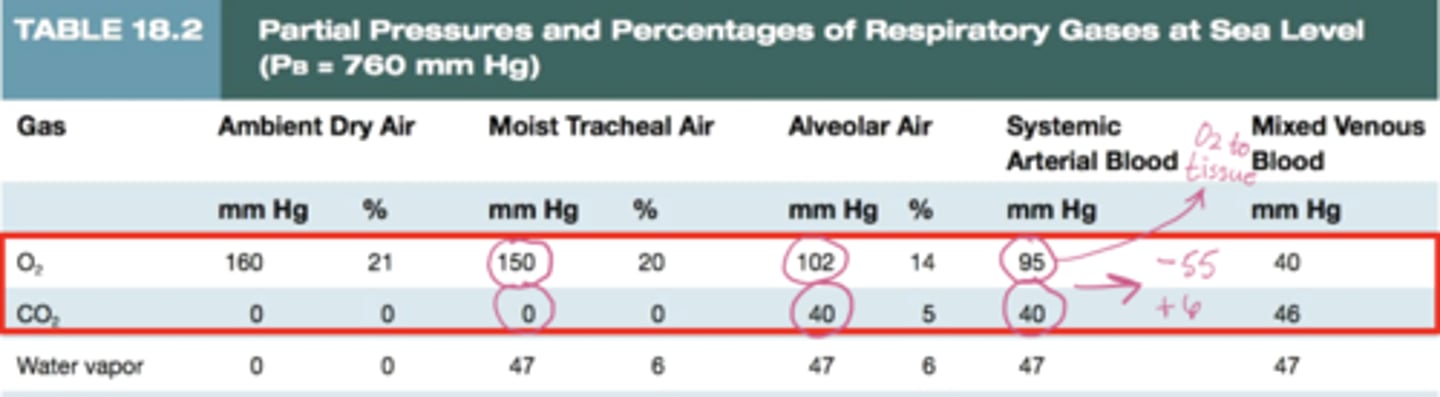
Partial pressure values to know
What does the concentration of O2 in the alveoli depend on?
1) rate at which we get O2 from ventilation
2) rate at which it is removed from blood
The more rapidly O2 is absorbed, what happens to concentration?
the lower its concentration in the alveoli
Diffusion of gaseous molecules depends on
- Volume of gas diffusing per min
- Surface area
- Diffusion coeficient
- Change in partial pressure
- Membrane thickness
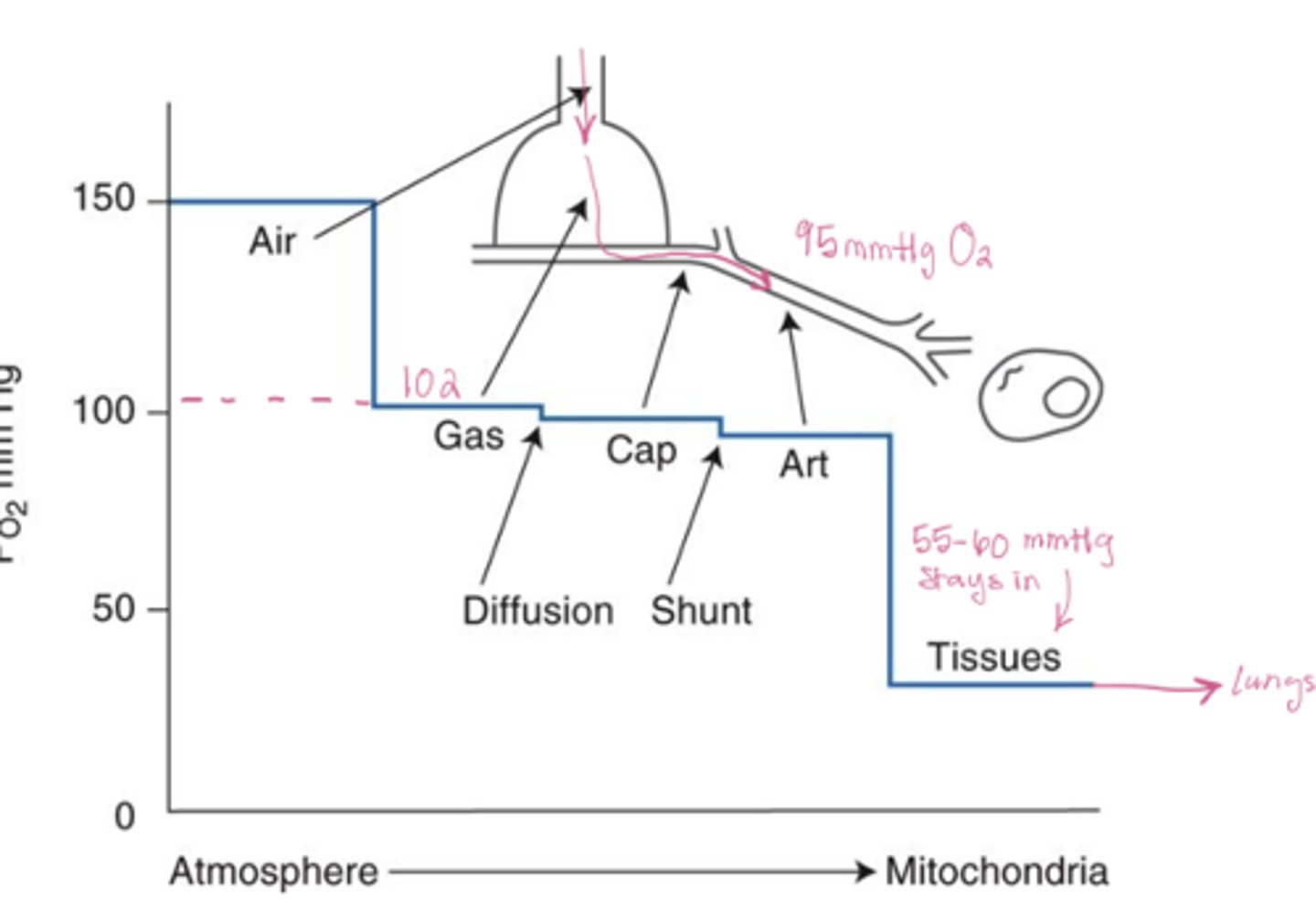
Oxygen partial pressure changes from air to tissue
Air (150) --> alveoli (102) --> arteries (95)--> tissue (40)
What is the A-a gradient
difference between alveolar O2 (PaO2=102) and arterial O2 (PAO2= 95) which equals ~ 7 mmHg
What is the A-a gradient caused by
pulmonary shunt (some venous blood mixes wit oxygenated blood) causes a minor V/Q mismatch in lungs
At steady rate, how much O2 is being transferred to pulmonary circulation and how much CO2 is being removed
250mL , 200mL
What is the respiratory exchange ratio
200/250 = 0.8
What is the biggest determinant of gas exchange (ventilation)
amount of surface area
What is the ΔPO2 and ΔPCO2 across the alveolar-capillary membrane
ΔPO2 ≈ 62 mmHg and ΔPCO2 ≈ 6 mmHg
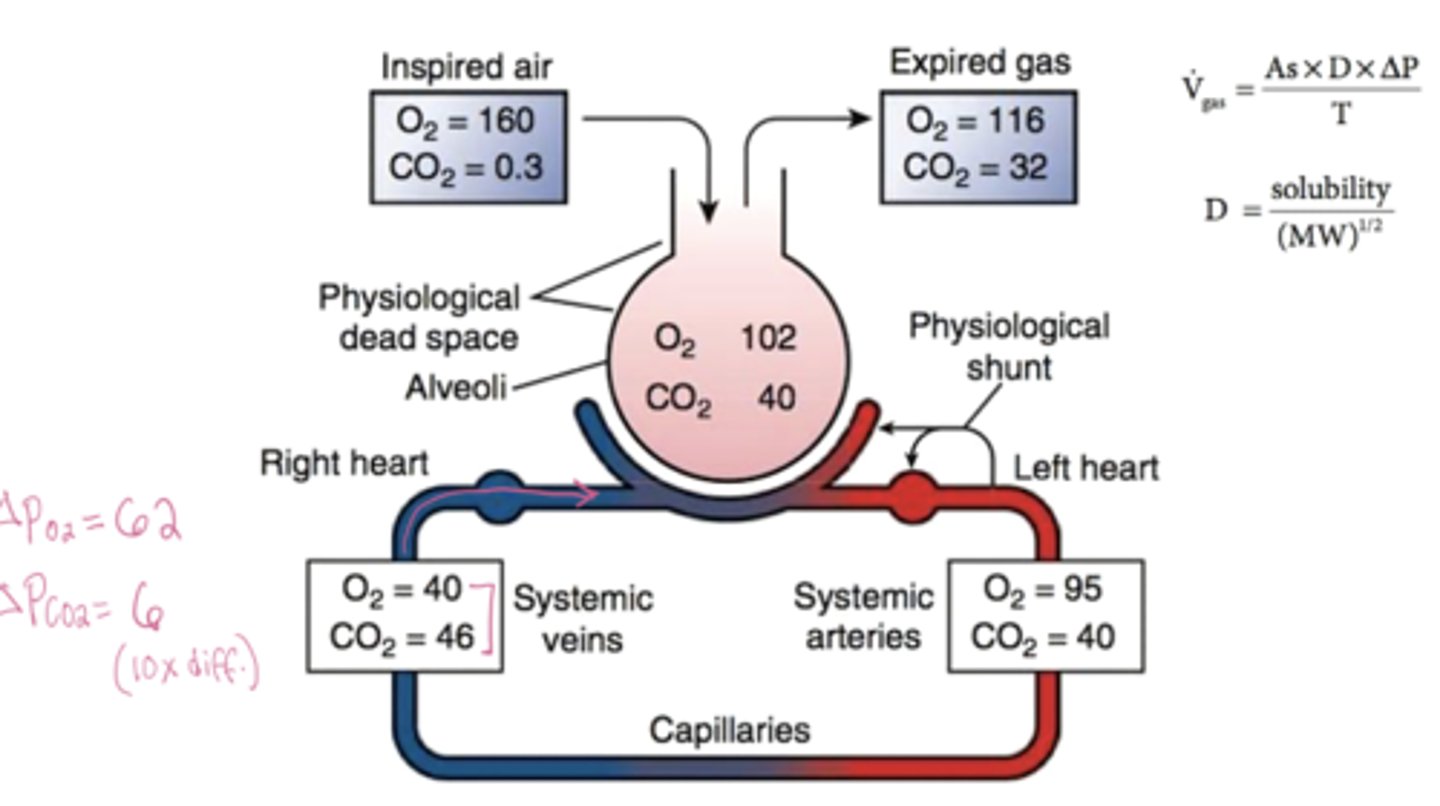
Which gas has the higher diffusion coefficient? Why does this gas diffuse easily despite its small gradient?
CO2 is 20x more soluble (higher diffusion coefficient) than O2, so even though its pressure gradient is 10x smaller, both gases diffuse across the membrane at nearly the same rate
WHich gas has the higher pressure gradient?
O2 partial pressure is 10x greater than CO2
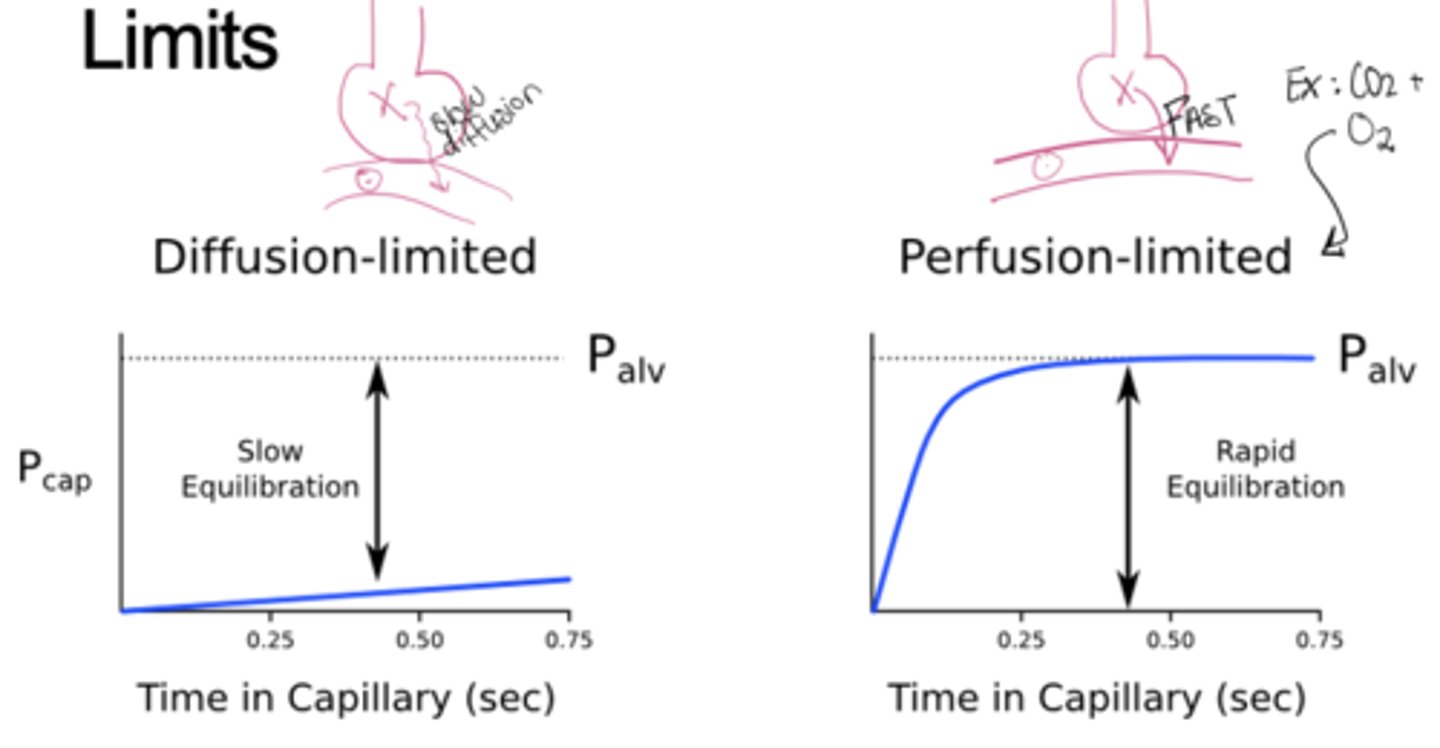
Under normal conditions, is gas exchange diffusion-limited or perfusion-limited?
Perfusion-limited, exchange depends on blood flow, not diffusion rate both gases equilibrate fully
How is O2 carried to the tissue (include percentages)
98% of O2 is in RBCs which are bound to hemoglobin and 2% is dissolved in the blood
What is oxyhemoglobin (HbO2)?
hemoglobin bound to oxygen (98%)
What is deoxyhemoglobin (HHb)?
hemoglobin with no O2 (2%)
What are the loading, unloading, and plateau phases of the oxyhemoglobin equilibrium curve
The loading phase occurs in the lungs where PO2 is high; hemoglobin binds O2 rapidly until it’s nearly saturated. The plateau region shows that even if alveolar PO2 drops slightly, O2 saturation stays high, this protects against hypoxia. The unloading phase happens in tissues where PO2 is low; hemoglobin releases O2 easily to supply cells for metabolism
Understand the oxyhemoglobin-equilibrium curve
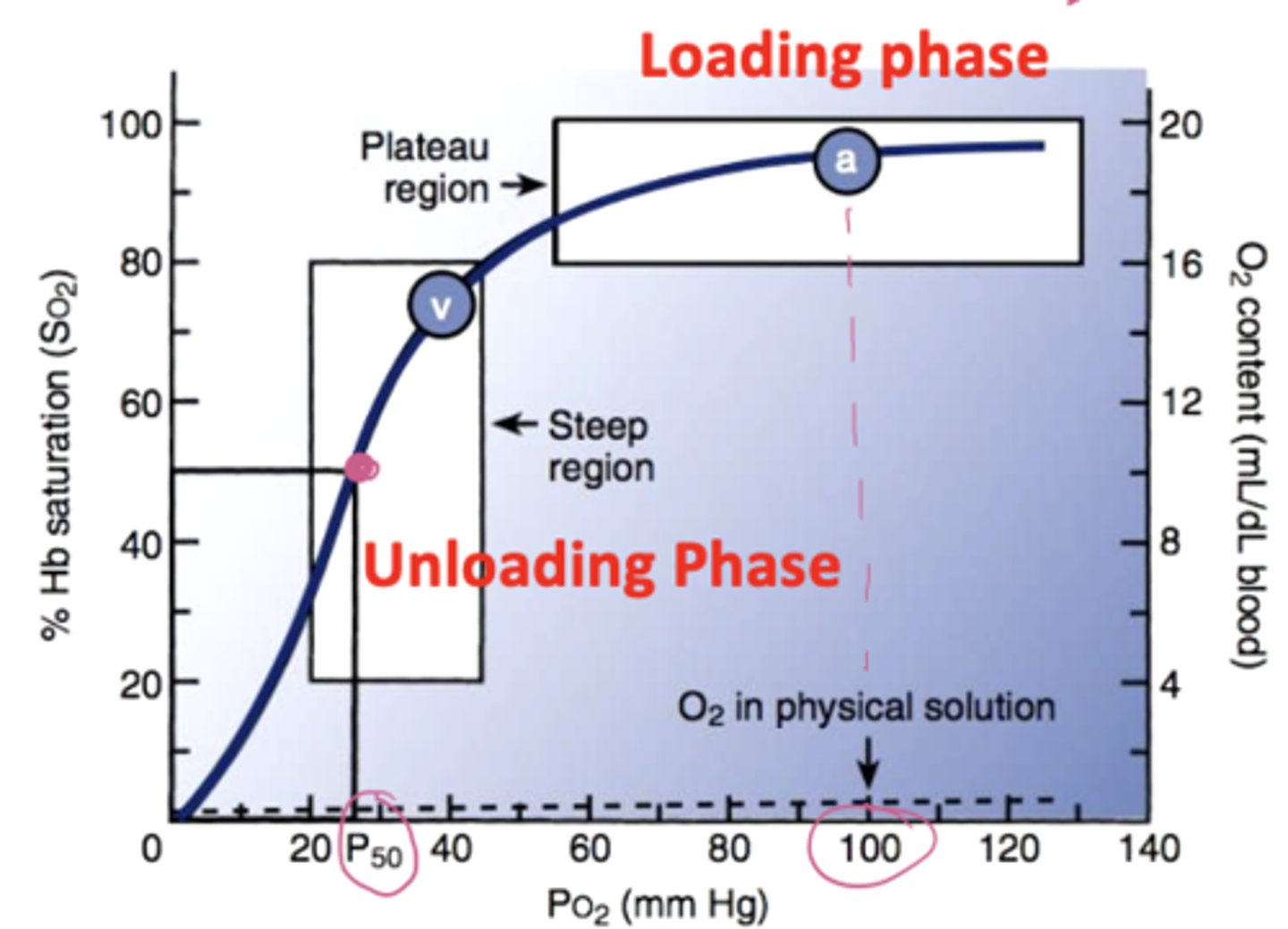
What does a right shift in P50 mean on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
high P50 means hemoglobin’s affinity for O2 decreases, O2 unloads more easily to tissues. This occurs with high CO2, high temperature, high DPG, and low pH (Bohr effect)
What does a left shift in P50 on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve mean?
low P50 means hemoglobin’s affinity for O2 increases O2 binds tightly and is less released to tissues. This occurs with low CO2, low temperature, low DPG, and high pH
Brain's respiratory centers table
What is the P50 value?
The amount of oxygen needed to saturate 50% of hemoglobin
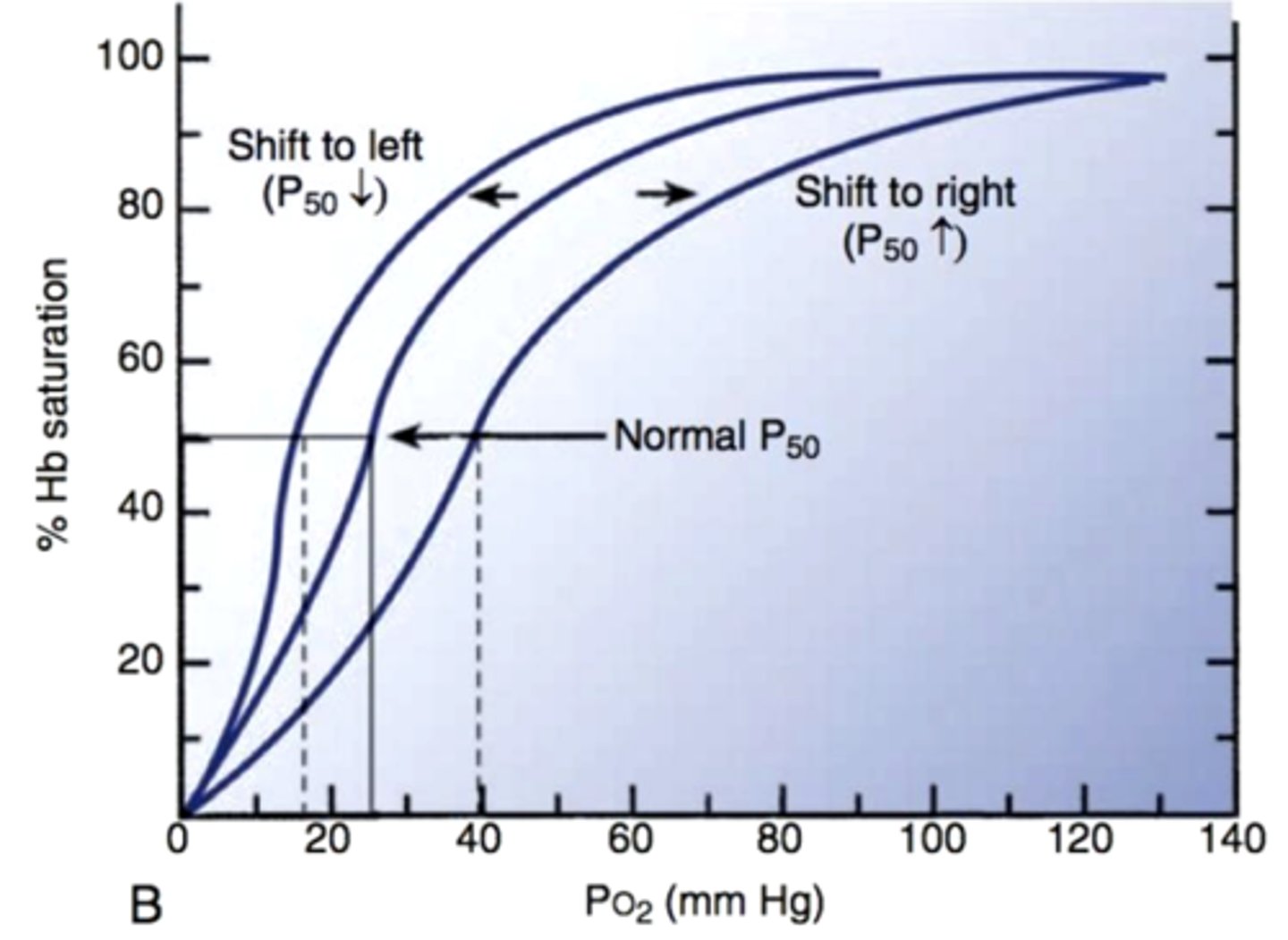
What does a lower pH do to O2 and Hb?
Caused Hb to release more oxygen (think exercising muscle)
What does a higher pH do to O2 and Hb?
Hb releases less oxygen
In what form is most CO2 transported? (percentages)
10% dissolved in plasma, 60% as bicarb, and 30% as carbamino protein
What does carbonic anhydrase do
Converts CO2 and H2O into H2CO3 (carbonic acid), which is eventually broken down bicarbonate and hydrogen ions (inside RBCs)
What is the chloride shift
Bicarb leaves the RBC and Cl enters to maintain electrical neutrality
What is carbaminohemoglobin
CO2 bound directly to deoxygenated hemoglobin
What is the exchanger bicarb/chloride exchanger known as
AE1
What is the main determinant of respiratory rate?
CO2
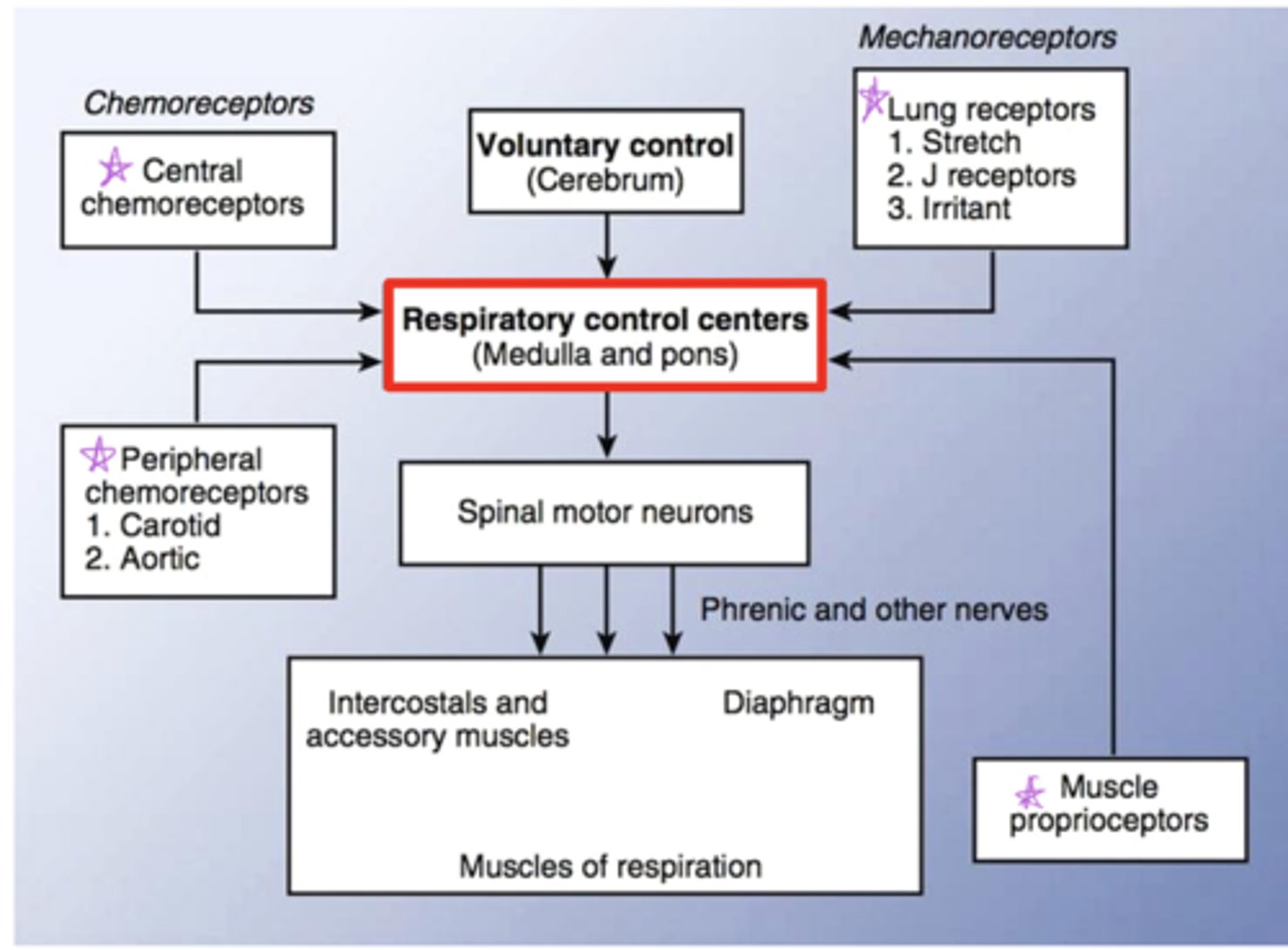
Diagram of control of respiration flowchart
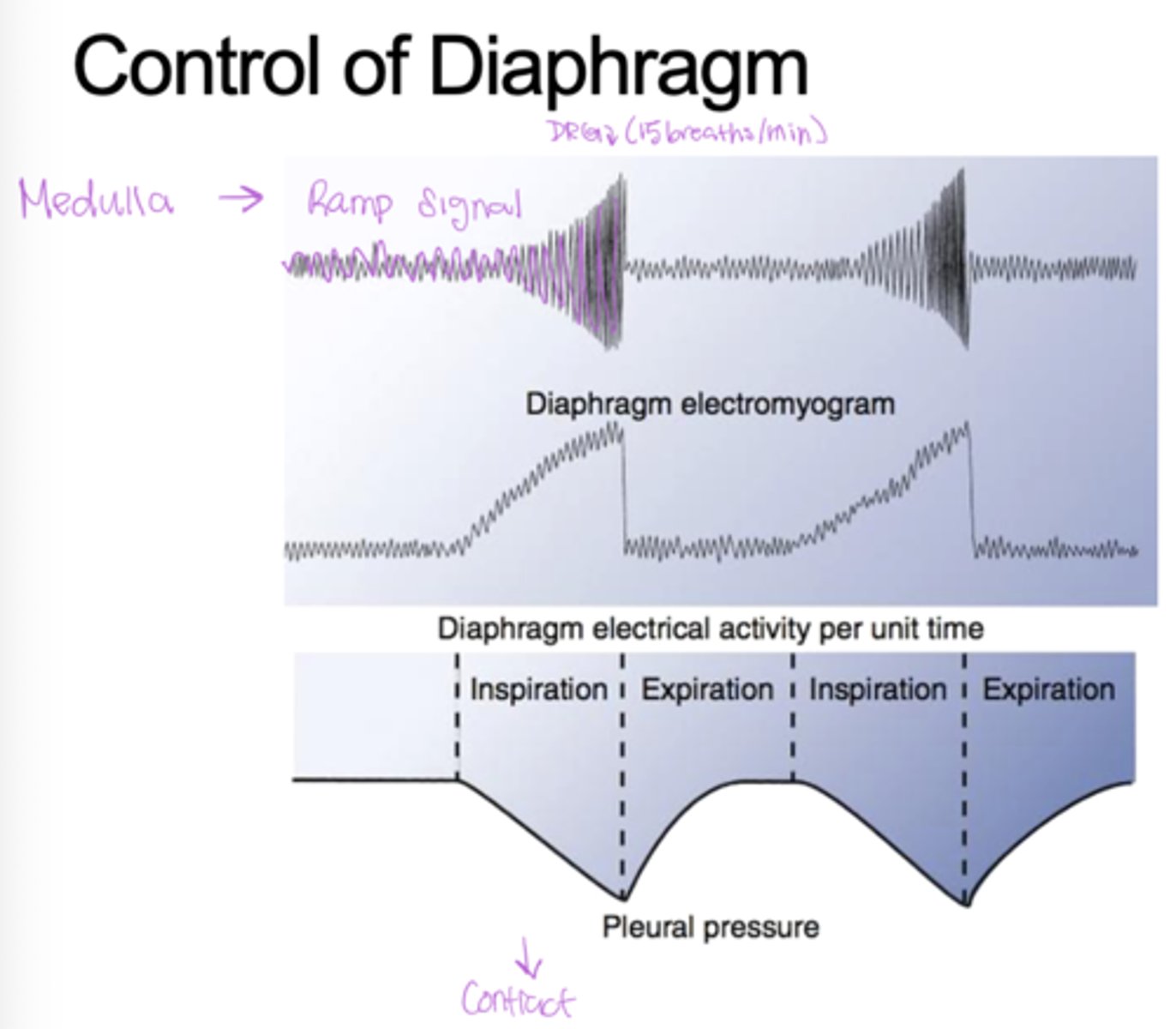
Know the control of diaphragm diagram
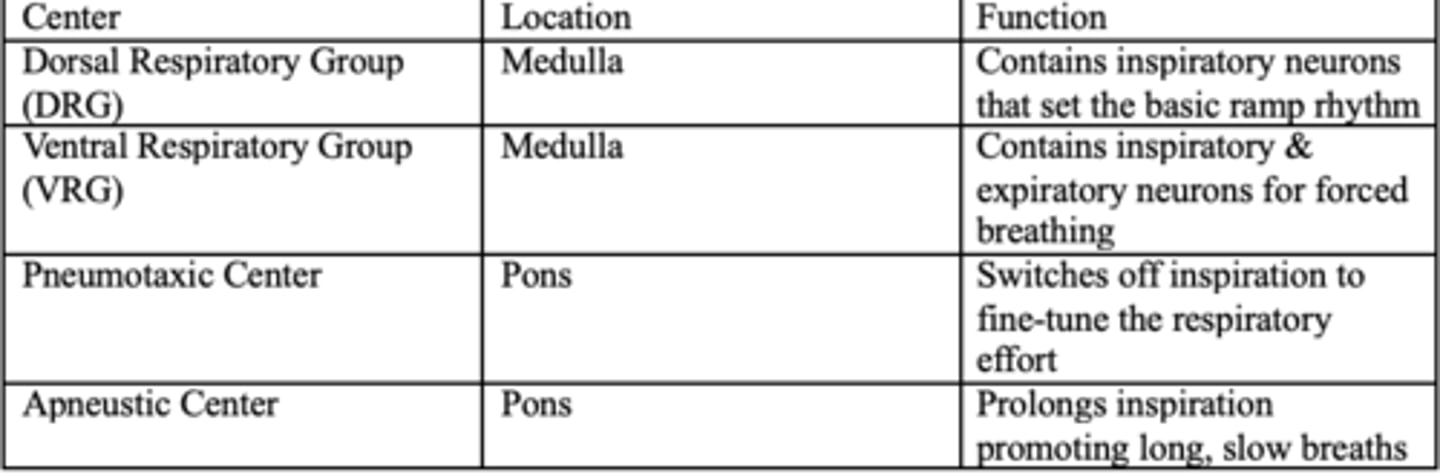
What are the two respiratory control centers in the medulla?
DRG and VRG
What is the function of the DRG
Controls inspiration. Controls diaphragm and external intercostals. Integrates input from the stretch receptors and the chemoreceptors in the periphery (responsible for Ramp signal, drives regular, quiet breathing)
What is the function of the VRG
Active during forced breathing (exercise, stress) recruits and activates accessory inspiratory + expiratory muscles (think VRG very strong breaths)
What makes up the pontine respiratory groups (PRG)?
Pneumotaxic and apeustic center
What is the function of the pneumotaxic center?
Prevents overinflation of the lungs (can inhibit DRG and inspiration)
What is the function of the apeustic center?
Causes short gasps, interrupted by expiration, responsible for prolonging the inspiratory ramp signal that maintains force in the diaphragm
What is the function of the medullary respiratory center?
Sets the basic rhythm of breathing
What is the function of the hypothalamus
monitors emotional state and body temp
What is the function of proprioceptors?
monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
What are the two phases of expiration?
Phase I - brief, active braking by inspiratory muscles to slow airflow.
Phase II - passive recoil of lungs pushes air out; no muscle activity.
Chart the flow chart associated with inspiration?
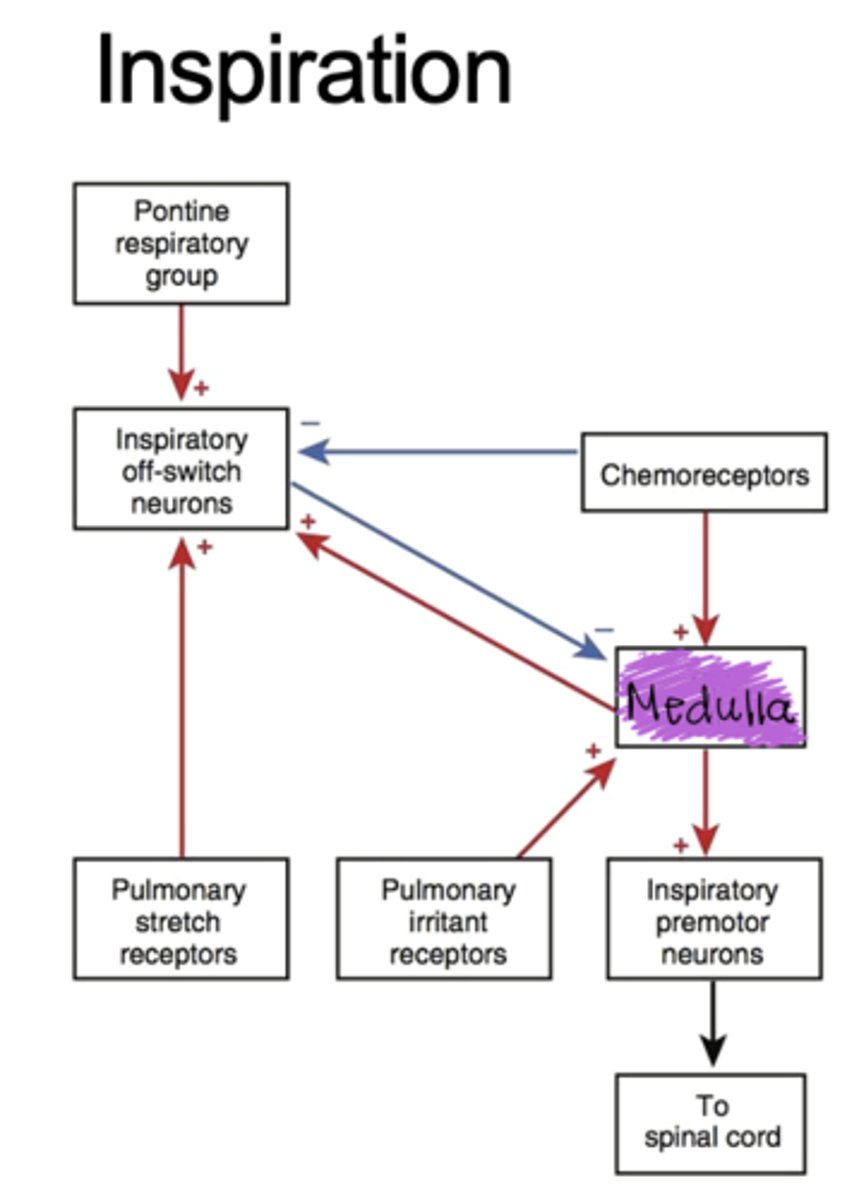
what are the pulmonary stretch receptors?
slowly adapting stretch receptors in the sensory terminals of myelinated afferent fibers within the smooth muscle layers of the airway. Firing leads to the excitation of the inspiration blocking switch
Where are irritants receptors found, what is their function and physiological response?
found on sensory terminals of myelinated afferent fibers in large conducting airways. Respond to dust, smoke -- COUGH!
What is the function of J receptors? what are they stimulated by?
Result in rapid shallow breathing, bronchoconstriction, and cardiovascular depression. Stimulated by lung injury, large inflation, or acute pulmonary congestion.
Where are the juxtapulomonary capillary receptors found?
C-fiber ending situated near the alveoli and bronchial circulation
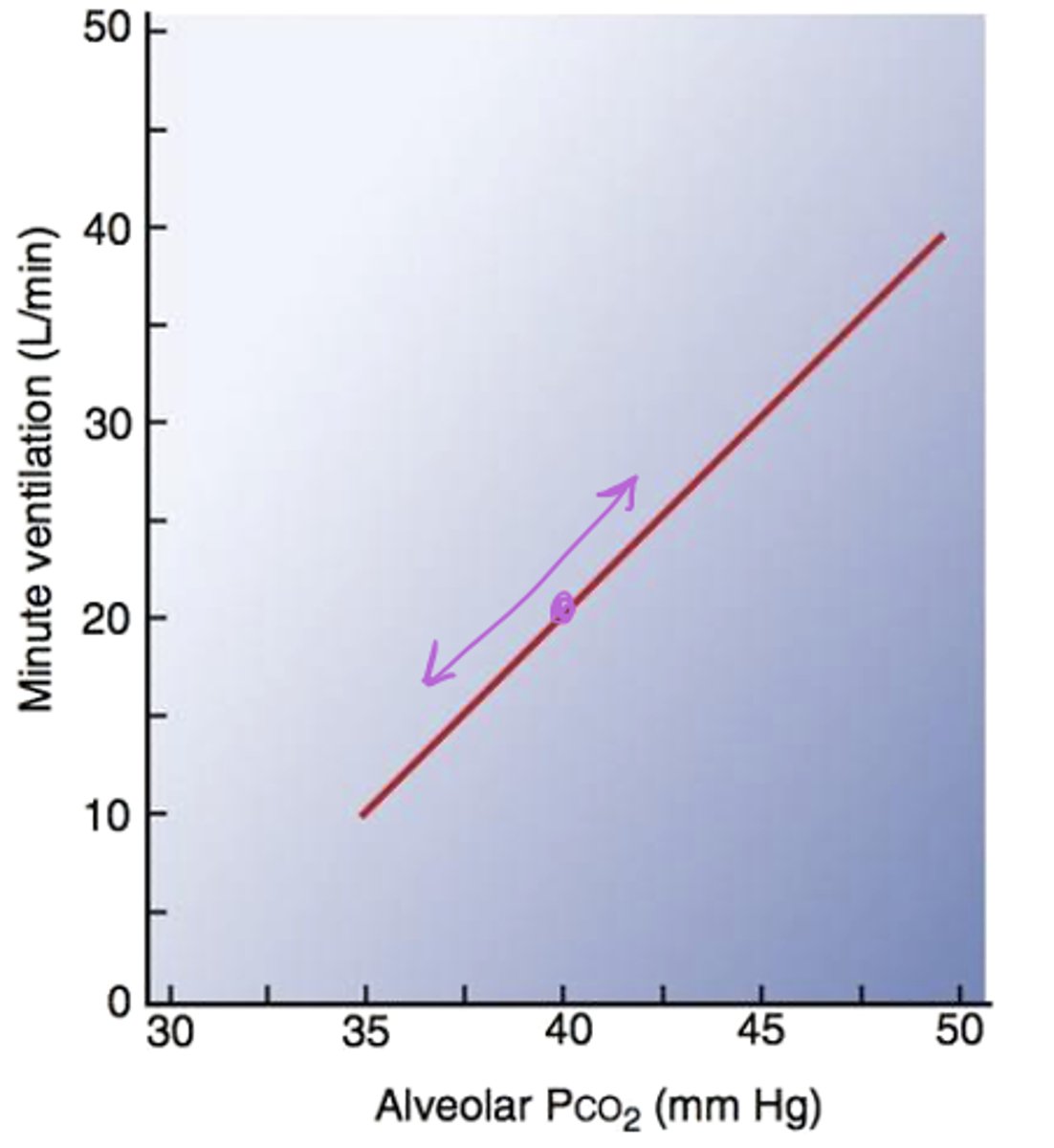
What type of relationship is found between alveolar PCO2 and minute ventilation?
Linear! Because CO2 is a byproduct of metabolism and a volatile acid that we want to get rid of
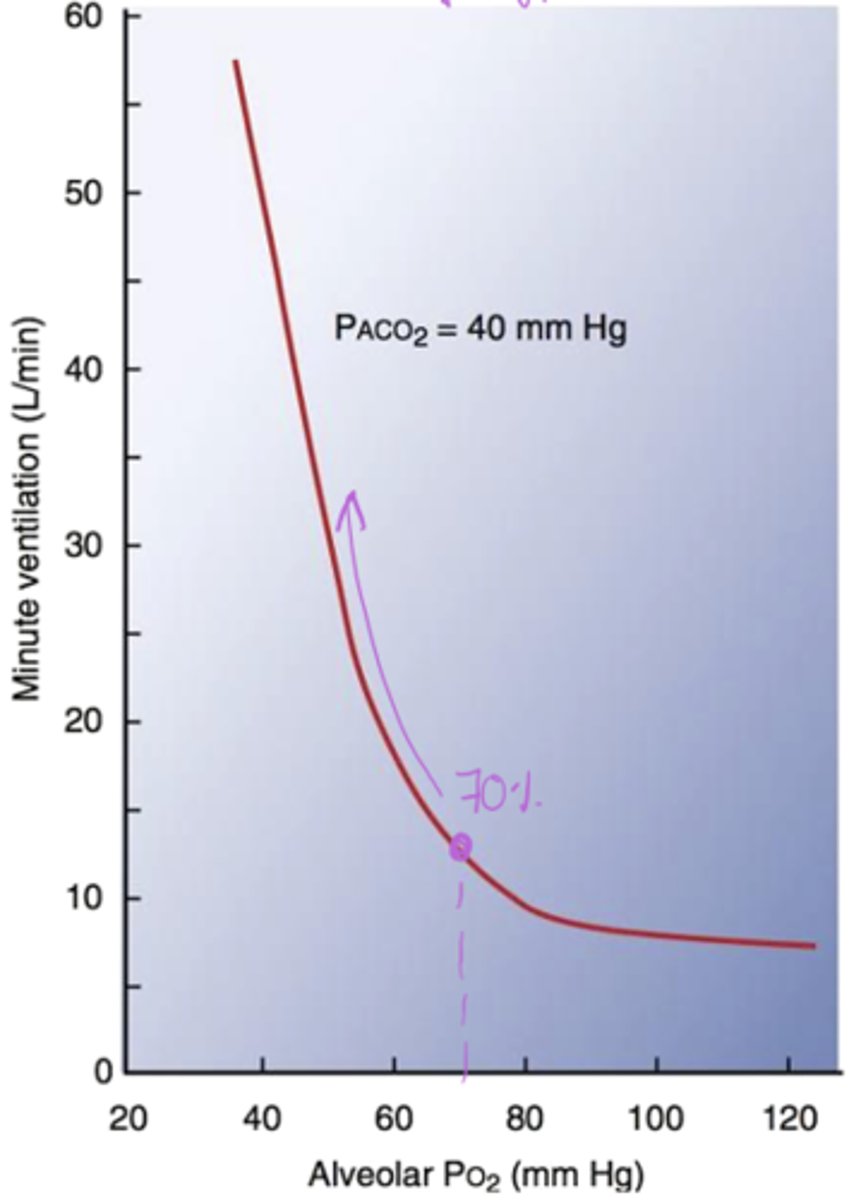
What is the relationship between Alveolar PO2 and minute ventilation?
Not linear! - As O2 increases, ventilation decreases, but it's not linear
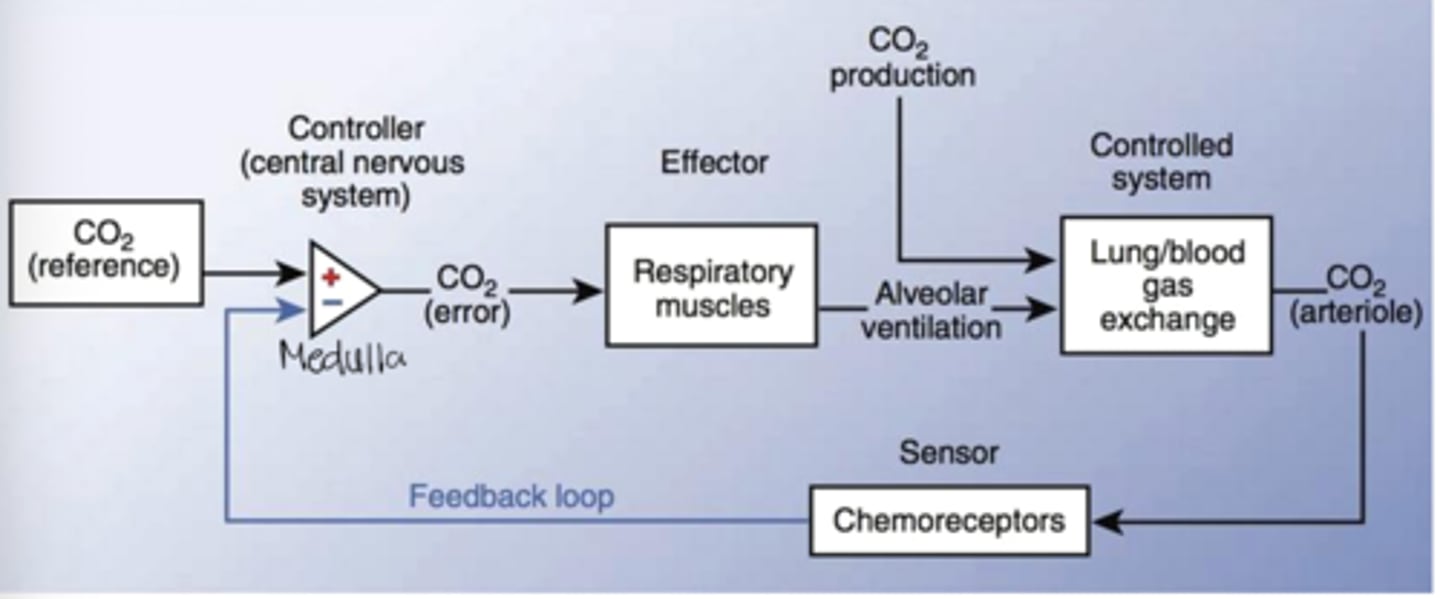
Draw the CO2 feedback control mechanism monitoring CO2 levels
Respiratory and ventilation rates are largely driven by what kind of receptor activation
chemoreceptor activation
What is the primary driver of respiration?
Mainly CO2 drives respiration but H+ also modestly changes total pH
What causes the creation of the H+ near the chemoreceptors
CO2 causes the creation of H+ wil leads to the activation of these receptors
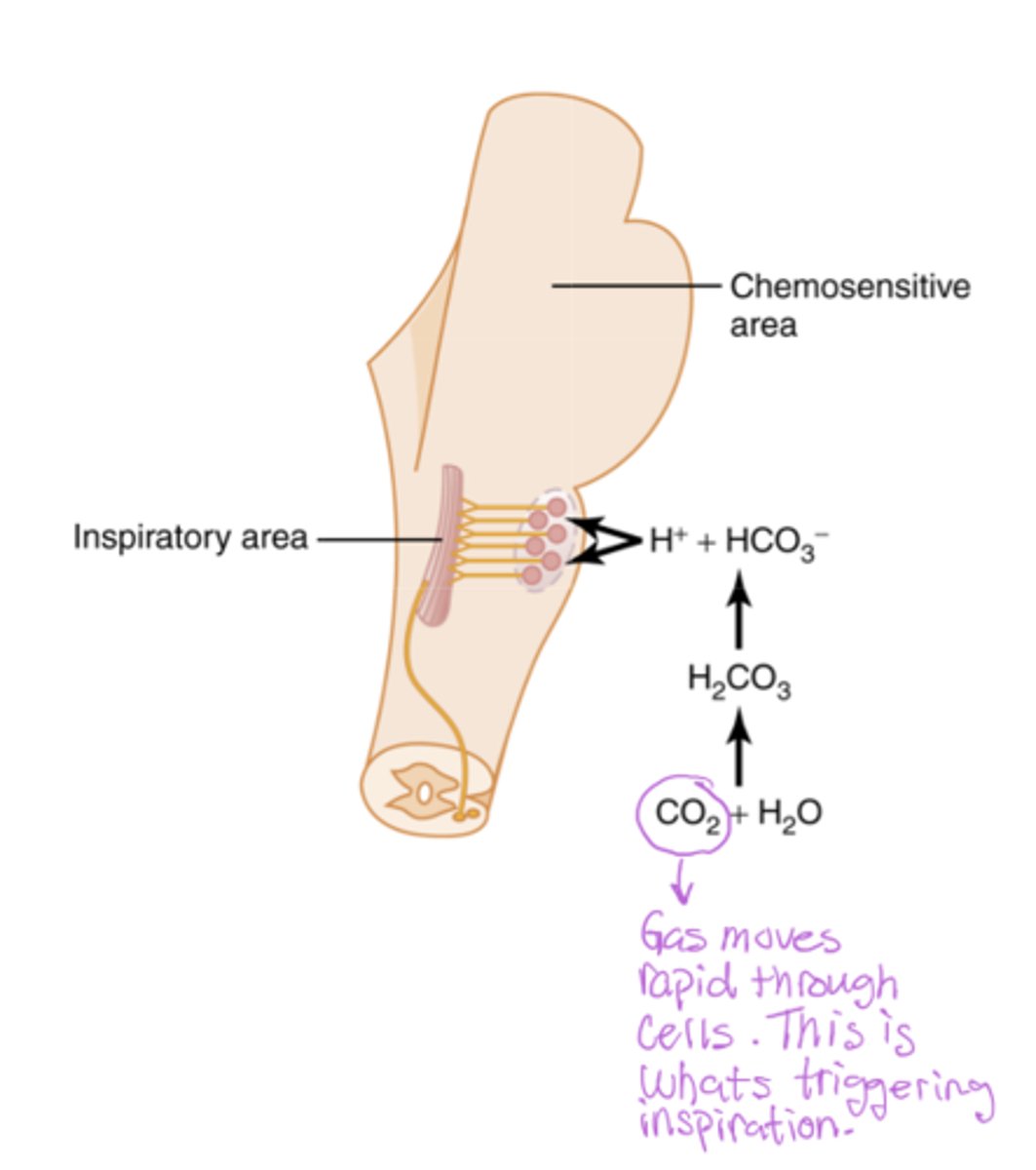
Draw the central chemoreception
CO2 (gas) can diffuse across the blood brain barrier and trigger chemoreceptors of the brain (which only respond to CO2 changes)
H+ can't go in

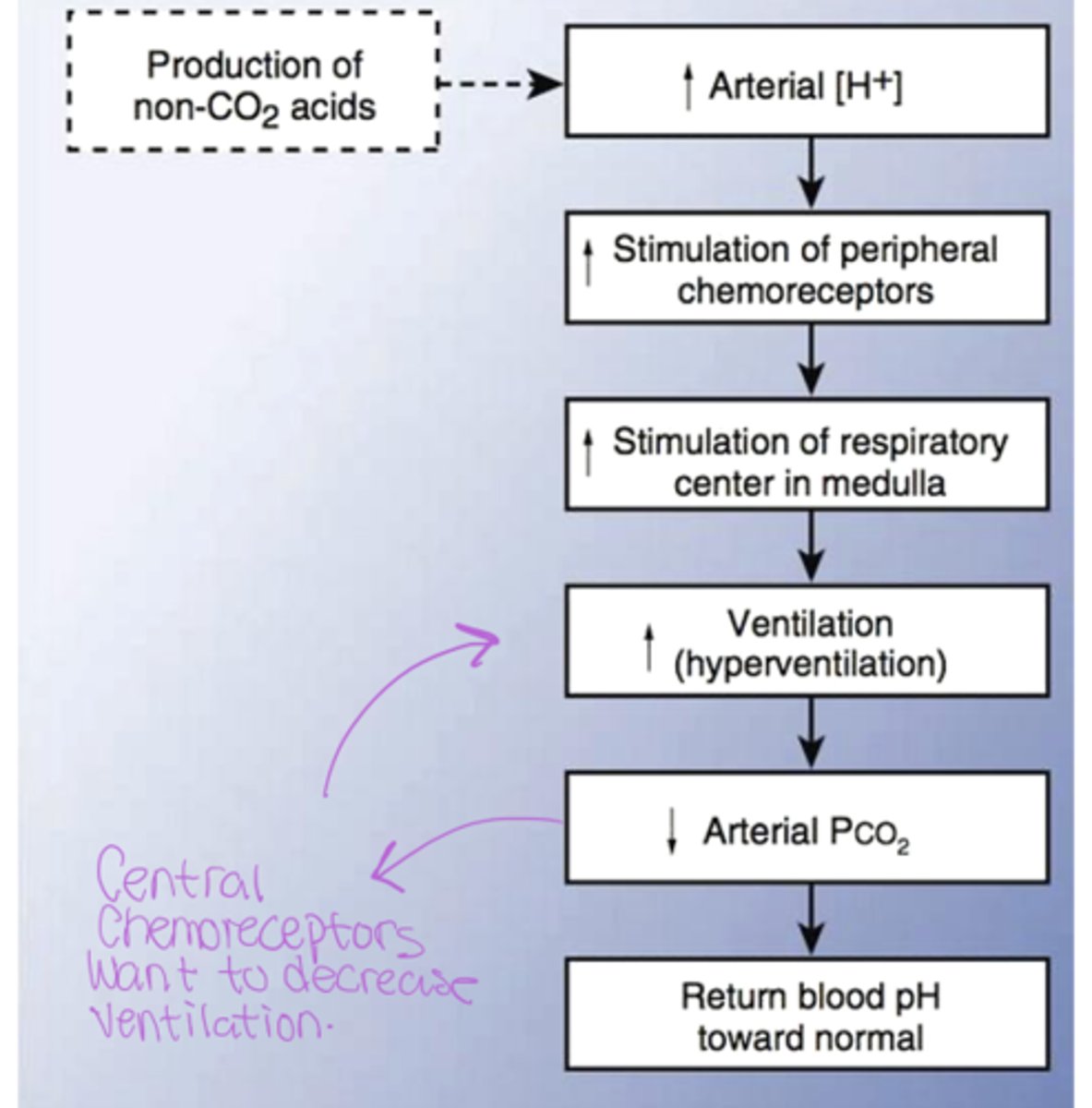
Metabolic acidosis flowchart
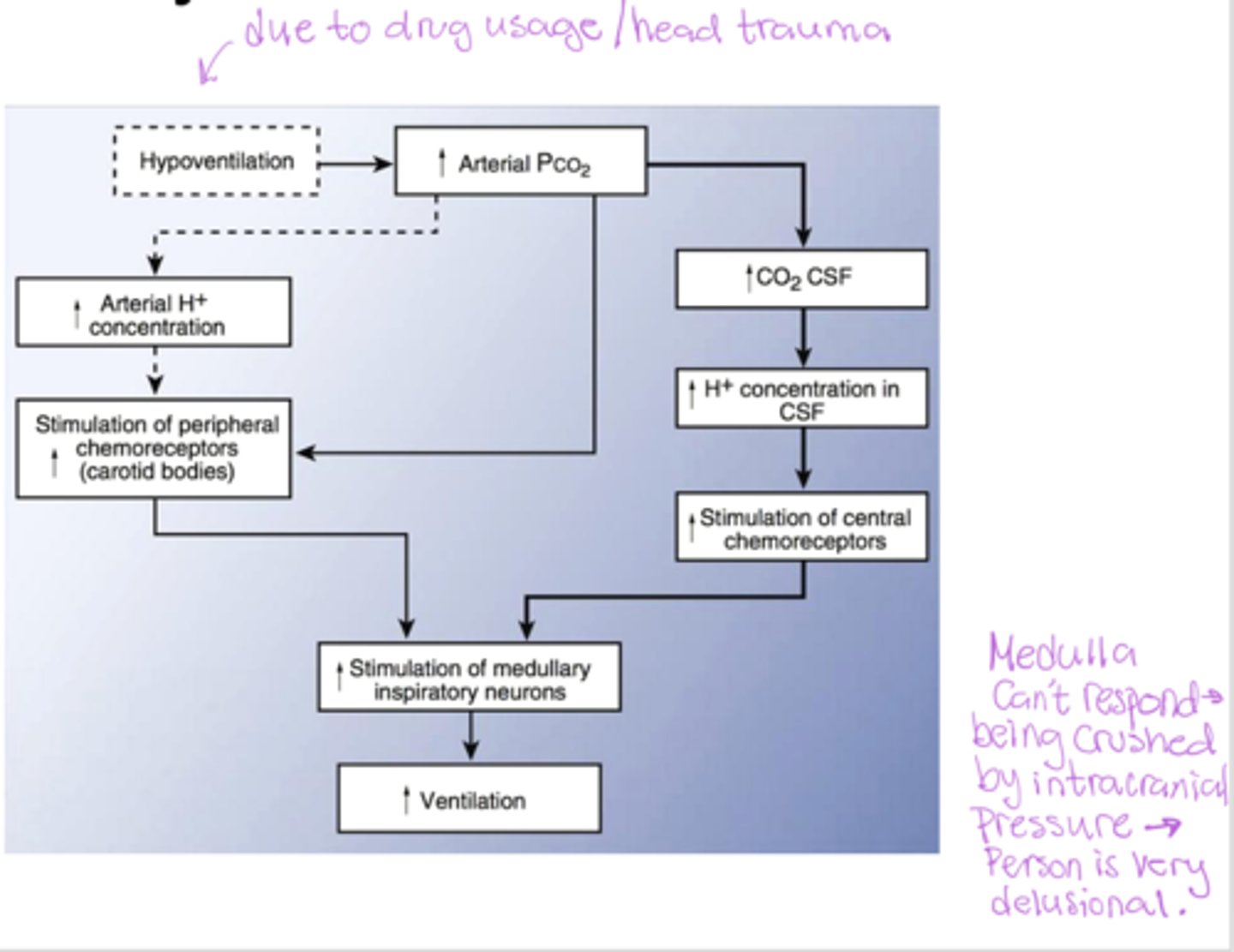
Respiratory acidosis flowchart
Explain metabolic acidosis and how the body will try to regulate it?
If your blood becomes acidic, the H⁺ in the blood stimulates the peripheral chemoreceptors in your carotid and aortic arteries. These receptors then signal the brain to increase ventilation to blow off more CO2, helping to correct the blood pH
Role of central chemoreceptors vs peripheral chemoreceptors in metabolic acidosis?
Peripheral chemoreceptors sense the high H+ and stimulate ventilation to lower CO2, as CO2 levels fall, the central chemoreceptors detect the low CO2 levels and reduce ventilation
Why isn't O2 the main driver instead of CO2?
Hemoglobin is incredibly effective at carrying and delivering oxygen. It acts as a buffer, ensuring tissues get a steady supply. Because of this efficiency, your body doesn't need to adjust its breathing in response to small changes in O2.
What causes respiratory acidosis and how does the body respond?
Caused by hypoventilation --> increase CO2 and H+, decrease pH causes the peripheral and central chemoreceptors to stimulate the medulla to increase ventilation but if the medulla is depressed (drugs/trauma) then compensation fails --> severe respiratory acidosis because CO2 keep rising.
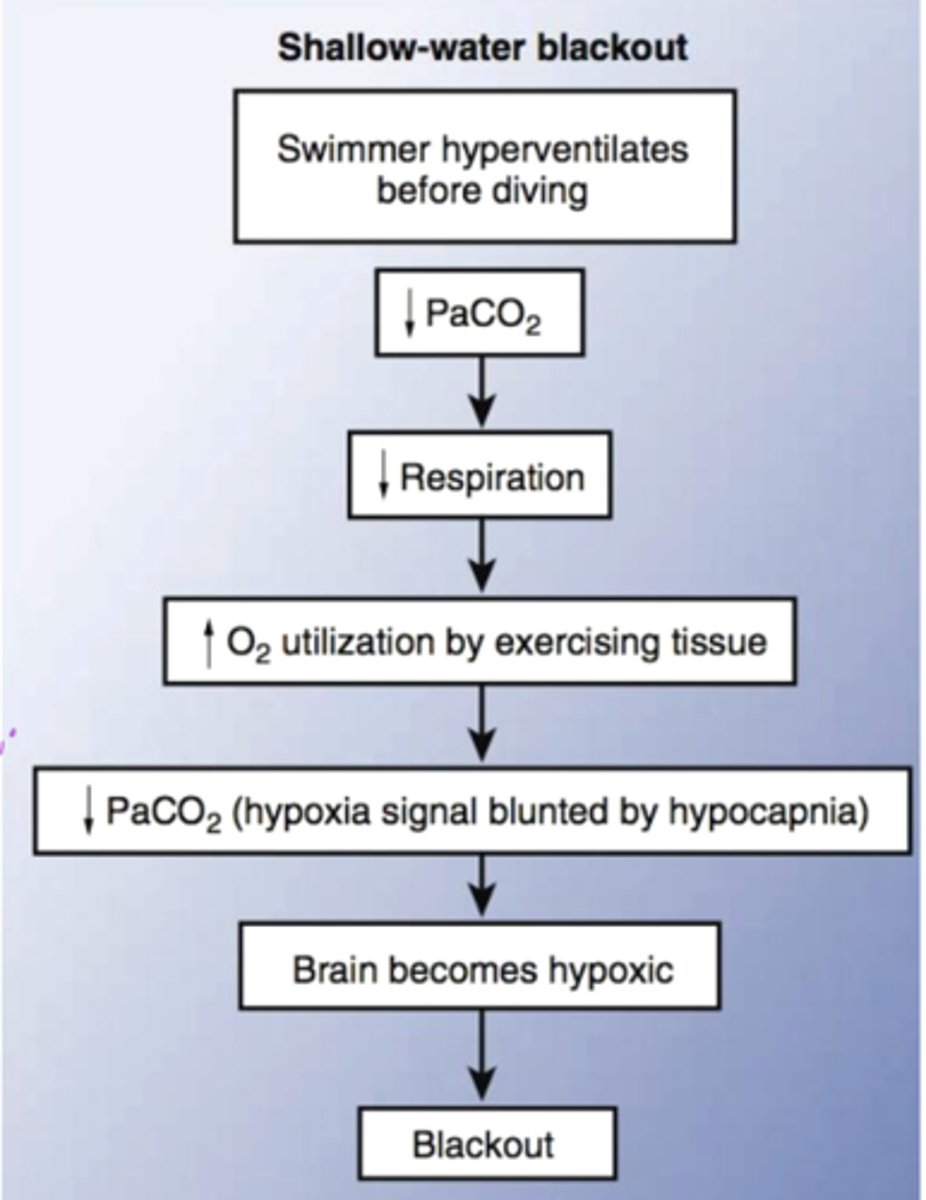
Explain shallow water blackout phenomenon and how it occurs
when a swimmer intentionally hyperventilates before going underwater. Hyperventilating lowers CO2 --> causes a delayed urge to breathe --> O2 runs out --> faint underwater.
Shallow water blackout flowchart