Syntax Lecture Notes
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Syntax Lecture Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Syntax
The arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language.
Phrase
A group of words that functions as a single unit in the syntax of a sentence.
Valency/transitivity
ability of verbs to open up slots around themselves, which must be filled.
Subject
Direct object
Indirect object
Complements
Intransitive Verb
A verb that requires a subject.
jump, sleep, walk (causatives)
Transitive Verb
A verb that requires a subject and a direct object.
See, eat, sell, discuss
Ditransitive Verb
A verb that requires a subject, a direct object, and an indirect object.
Give, place, donate,
Structural constituents
The building blocks of a sentence.
(e.g. NP, VP, PP)
Functional constituents
Constituents that relate to particular grammatical roles.
(e.g. subject, predicate, object)
simple sentences
sentences which consist of only one clause
Source
The semantic role that refers to the origin of the action.
Direct object
Who or what is affected by the action denoted by the verb
Semantic role = “the patient”
Alex saw Peter.
Paul likes cats.
Indirect object
To whom or for whom is/was something done?
The goal of the action or the element which profits from it
Semantic role= “the recipient” or “the benefactive”
Peter gave Mandya cat.
Experiencer
Semantic role that receives the effect of an action.
Two meaning of complement
General: complement vs. modifier
Narrow: indirect vs. subject complement vs. object complement
complement (Genreral meaning of complement )
obligatory sentence constituent (required for grammaticality)
Modifier (Genreral meaning of complement )
non-obligatory sentence constituent (can be left out)
Complement (Narrow meaning of Complement)
a sub-type of obligatory element required by certain verbs
e.g.call+ direct object+ object complement (She called her a genius.)
Subject complement (Narrow meaning of Complement)
Not new entities but refer back to the subject and describe it in further detail
underlined NPs are not objects but subject complements
Paul seems a complete idiot.
Nancy is a shop assistant.
Bodie has become a ghost town.
Object complement(Narrow meaning of Complement)
Not new entities but describe the direct object in further detail
underlined NPs are not objects but object complements
Mary called John a blessing.
Sue considered it a real chance.
We named her Kayla
Modifiers
Any units that are not required
Mary told me to be home by noon.
→ complement (to tell sb. to do sth.) →object adverbial
Mary left early to be home by noon.
→ modifier (to leave) →can be left out grammatically
7 Most Common Sentence Types
Intransitive (no objects, e.g. sleep)
Monotransitive (verb takes a direct object, e.g. massage):
Ditransitive (verb takes an indirect and a direct object, e.g. give)
Copular (e.g. seem):
Complex transitive (e.g. elect, name)
Intransitive
(no objects, e.g. sleep)
SV He was working
Monotransitive
(verb takes a direct object, e.g. massage)
SVO I read a book
Ditransitive
(verb takes an indirect and a direct object, e.g. give):
SVOO We sent him a parcel
Copular
(e.g. seem):
SVC He became President
SVA We live in London
Complex transitive
(e.g. elect, name):
VOC I find cats fascinating
SVOA I put the book on the shelf
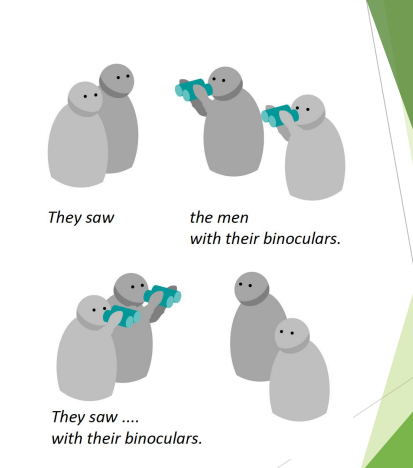
Structural Ambiguity
Sentence meaning and syntax Syntactic structure of a sentence is relevant to its meaning The cat killed the mouse. The mouse killed the cat. Structural ambiguity Sometimes identical word strings can have several possible meanings They saw the men with their binoculars
Semantic Role = Thematic Role 8
Agent
Patient
Theme
Source
Experiencer
Benefactive
Goal
Locative
Agent (Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
the doer of an action
The boy ran down the street.
He was chased by the dog.
Patient(Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
person or thing affected by the action caused by agent. Involves verbs such as eat, kill, smash, hit, bite, kick, etc.
The cat ate the mouse. The cake was eaten by Mary.
Theme(Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
one person or thing that is moved by the action denoted by the verb, or the topic of discussion
The book is red. I’m sending this letter to Paris.
Source(Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
the origin or starting point of the action or state identified by the verb.
She flew from Berlin to Vienna. This rumor caused a murder
Experiencer (Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
receives the effect of an action which is usually related to physical senses, feelings,emotional experience
He was scared. Lucy loves the new car. She felt the pain.
Benefactive (Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
entity which benefits from the action or event denoted by the predicate
She opened the door for Tom. I bought you this cake.
Goal (Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
the place to which something moves, or thing toward which an action is directed.
John swam to the raft. London was his destination.
Locative (Semantic Role = Thematic Role)
locationor spatial orientation of a state or an action
It rains in Spain. The paper is in the folder.
Subject changes, agent doesn‘t
The cat ate the rat. The rat was eaten by the cat.