Computer Science: Data Types and Number Systems
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Integer
Whole numbers, 1 12 37 (Int)
Floats
Numbers with decimal, 16.05 36.92 (Float)
String
"I like music" (Str)
Array
List of vales ['Dog, 'cat 'mouse']
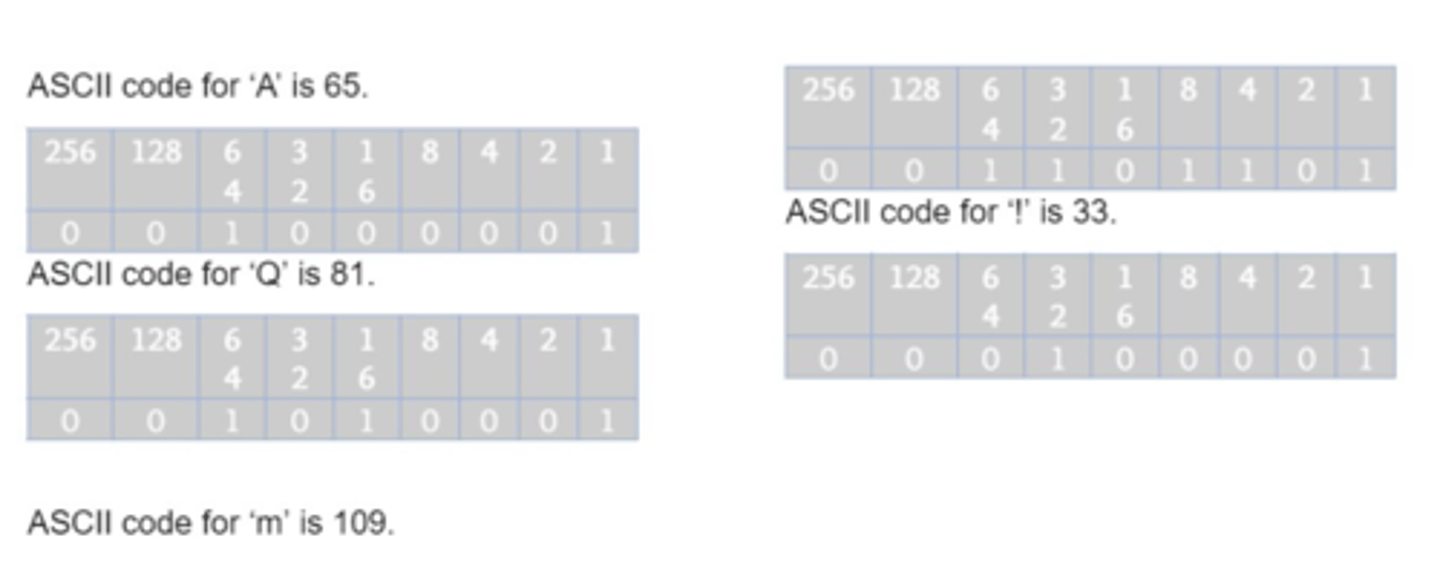
ASCII
( American Standard Code for Information Interchange ) is a character encoding standard for electronic communication.
How is Ascii Encoded
Unicode
is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems.
How is Unicode Encoded

Unicode vs ASCII
-Both are important as they allow data to be encoded in a standard way. They allow for worldwide communication in electronic form
-As ASCII is encoded in 7-bit or 8-bit ( New ASCII) it is only capable of storing 128 characters
-ASCII was invented in the 1960s and emoiis were not invented at the time
-Unicode is encoded in 32-bit meaning it can store up to 4 billion characters including English letters, Chinese symbols and emoiis.
UTF-8
-an encoding standard used by Unicode.
-It consists of up to four bytes of 8-bits each
-Each bit represents either a number (1-9 ) or a letter ( A-F )
Converting Binary to Decimal
-first step is to always label the digits of the binary number with the corresponding 8-bit number
-Then you simply add up all the numbers above a 1
Converting Decimal to Binary
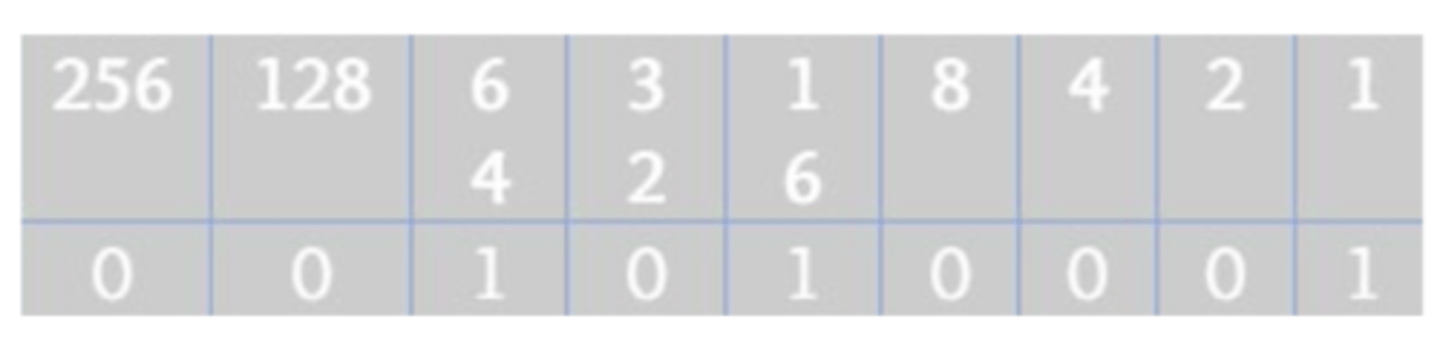
-If you are given a decimal number ( we'll use 81 ) and asked to convert it to binary | first you write out the 8-bit numbers (256 128... 2, 1).
-Then you take each number and see if it divides into the decimal number
-Does 256 divide into 81? No so we write 0. 128 doesn't either, so another 0. 64 does divide into 81. In this case we write 1 and take the remainder 17.
-This is our new decimal number. 32 doesn't divide into 17 but 16 does. So 0. we write 1. and take the remainder which is 1.
-8, 4 or 2 doesn't divide into 1 but 1 does. So | we write 1 and now we have no remainder. so the process is complete
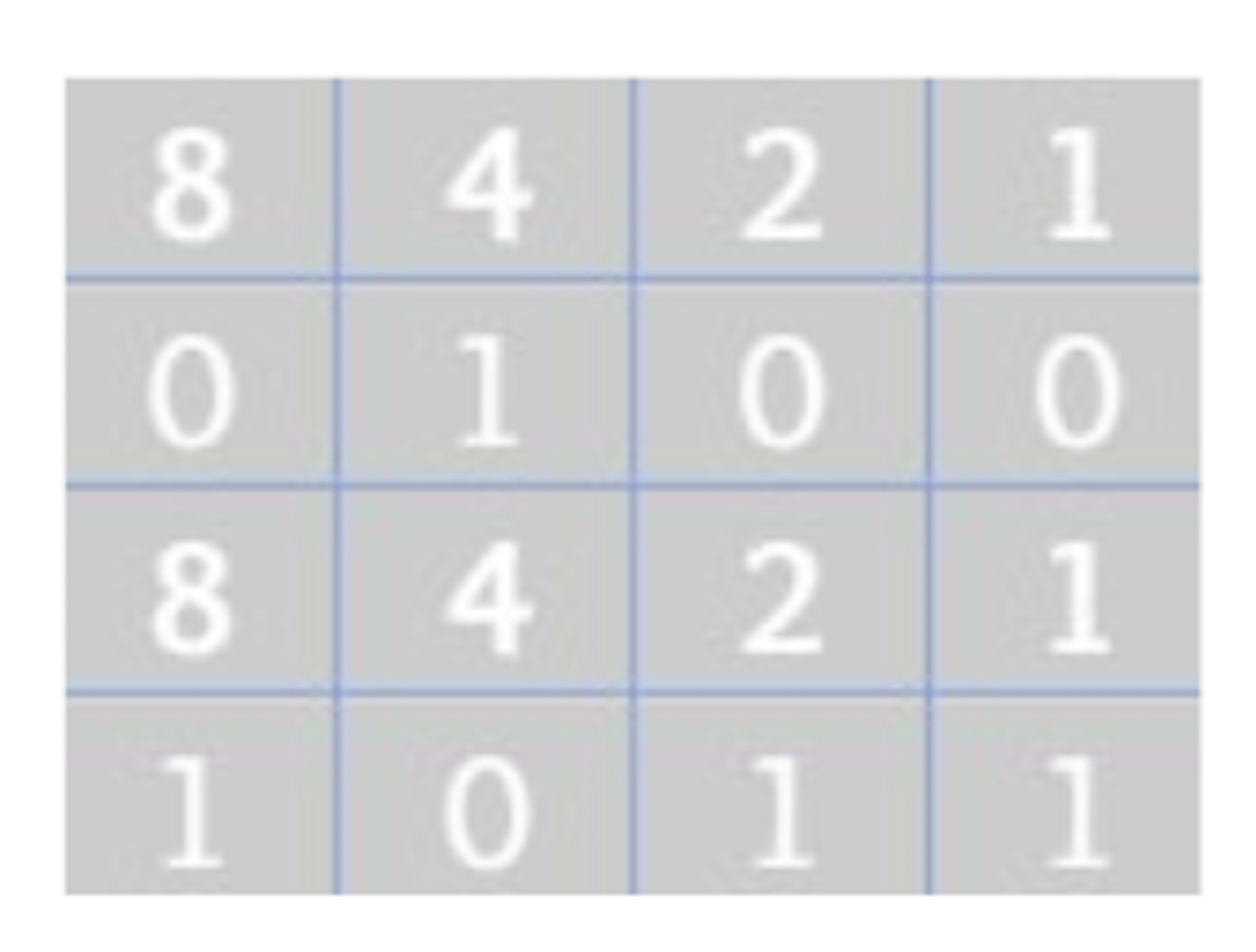
Converting Binary to Hexadecimal
-the first step is to split the binary into groups of 4 going from left to right. Then label them with 4-bit numbers
-Then we add up the numbers 0100 comes out to 4 and 1011 comes out to 11 but remember that in Hexadecimal 11 represents B so 01001011 is 4B in Hexadecimal
Converting Hexadecimal to Binary
-The first step of this conversion using 1F44D as an example
is to take each character individually and convert them to Hexadecimal.
-1 and 4 stay as 1 and 4 but F changes to 15 and D changes to 13
-Now this is the very same as converting decimal to binary, label each number with the 4-bit numbers and carry out the repeated division.
-Try this for yourself and you should come out with 0001 1111 0100 0100 1101.
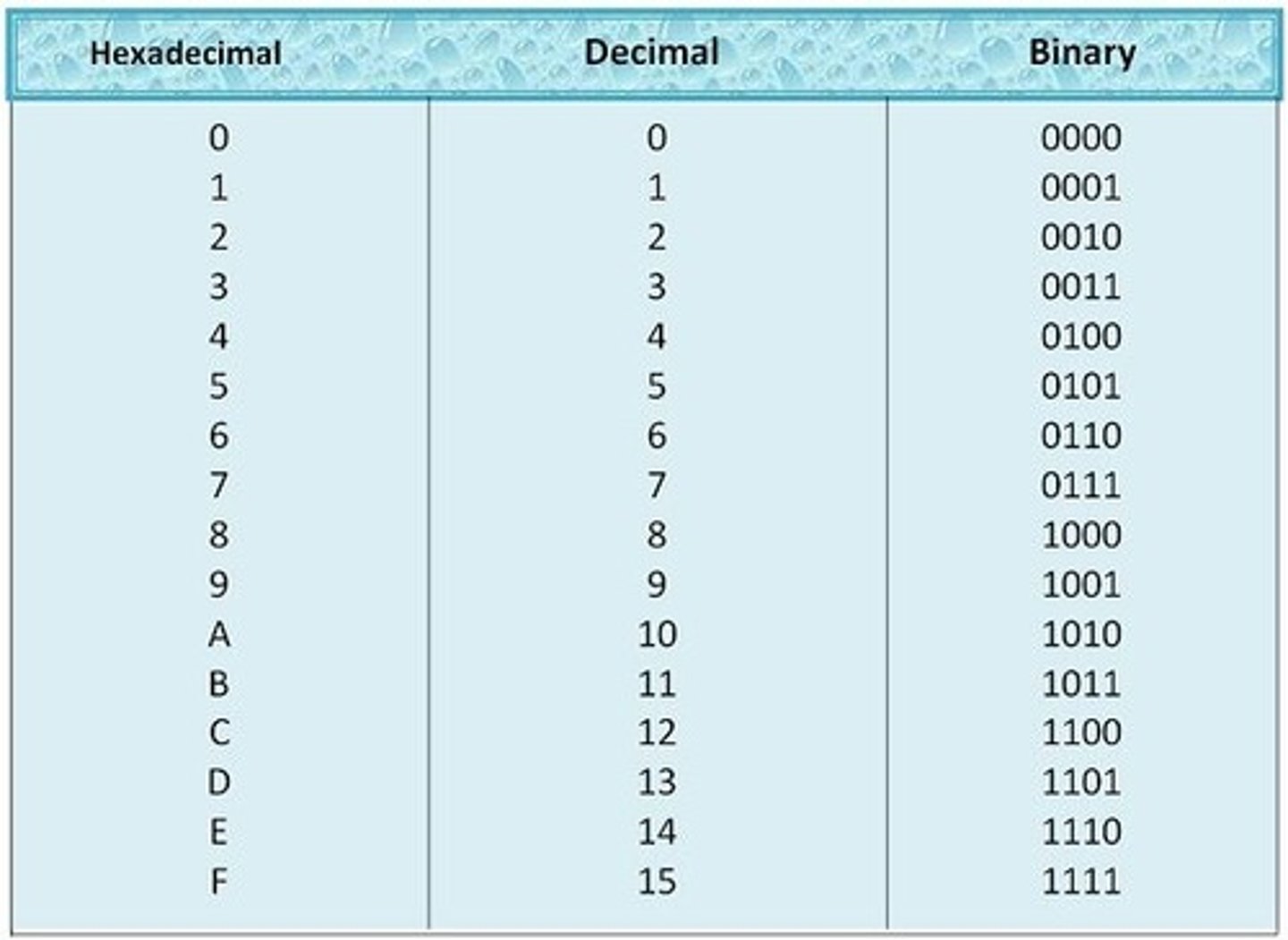
Converting Decimal to Hexadecimal
hen converting decimal to hexadecimal I we divide by 16 as hexadecimal is a base 16 system The most important thing about this conversion is that we are only concerned about the remainder. If we take 45 as an example I 45 : 16 = 2 with a remainder of 13. Then 2 : 16 = 0 with a remainder of 2. Now we take the remainders in reverse order. giving us 2. 13. But 13 is D in hexadecimal | so we get 2D
Adding Binary Numbers
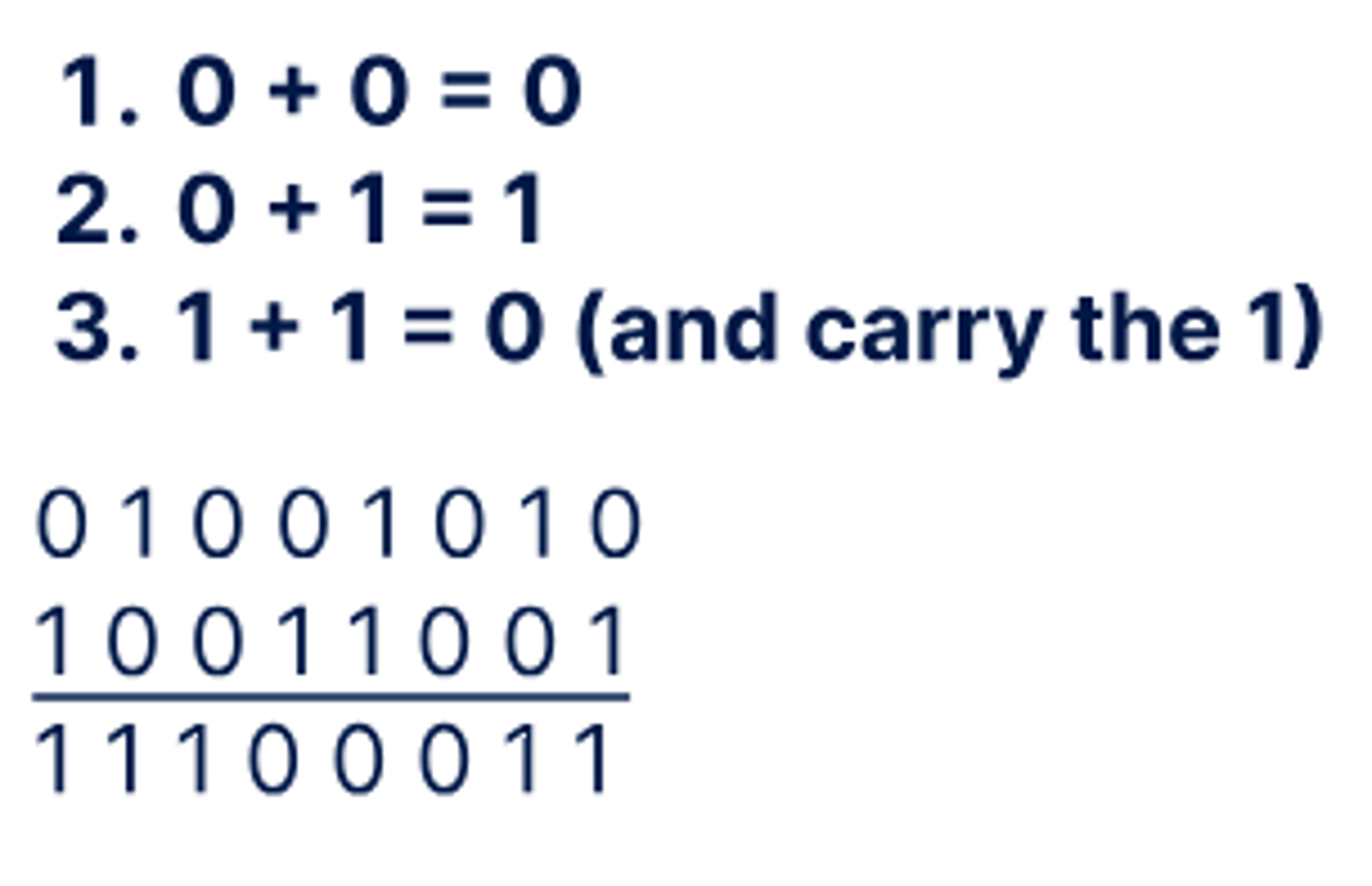
Binary Numbers
-base 2 numerical system; a system of numbers using only 0s and 1s
-each digit is called a bit
Benefits of Using Binary Numbers
Simplicity>only use 2 digits>simpler to understand and manipulate in digital systems
Compatibility with Digital Electronics>directly correspond to the on-off states of electronic switches in digital circuits>simplifies design and implementation
Efficiency in Data Storage and Transmission>require less space compared to other number systems
Ease of Binary Operations: straightforward and easily implemented in digital circuits