functional groups
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Alkanes
simple C and H compounds with only sigma (single) bonds
Generally CnH2n+2
Cycloalkanes have CnHn
n = subscript number
in order from 1-10 carbons:
methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, heptane, octane, nonane, decane
Alkenes
contain C-C double bonds attached to an alkyl, aryl, or H
Alkynes
contain C-C triple bond attached to alkyl, aryl, or H
Alcohol
contain an -OH group attached to an alkyl (a C)
|
—C—OH
|
Alkyl Halide
contains a halogen bonded to an alkyl
|
—C—X
|
where X is a halogen
Amine
contains an N attached to an alkyl or aryl group
|
—C—N
|
Amide
Contains O,C,N → double bond b/w O—C and Single bond between C—NR2
Attached to an alkyl, aryl, or H
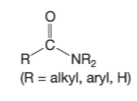
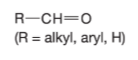
Aldehyde
O—C Double bond and C—H single bonded attached to an alkyl, aryl, or H
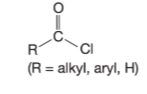
Acid: carboxylic and chloride
Carboxylic acid: COOH attached to alkyl or aryl group → looks like acid chloride but replace Cl with -OH
Acid Chloride: COCL attached to alkyl/aryl/H
alkyl groups
substituents derived from alkanes
aryl groups
substituents derived from benzene