Atoms and Elements
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the formula for relative atomic mass (RAM)?
isotope abundance * isotope mass number / 100
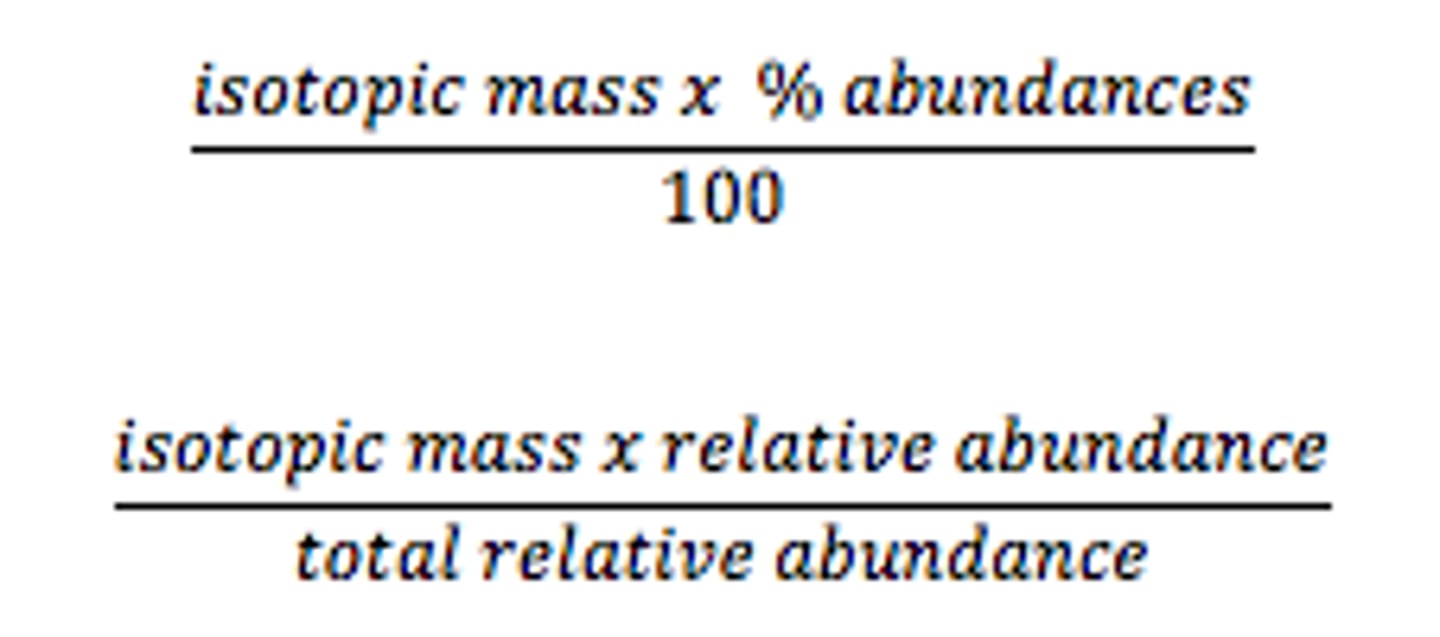
What is a mixture?
Two or more substances that are not chemically bonded
How to do paper chromatography? (practical)
1) draw a line in PENCIL near the bottom of a filter paper
2) add a spot of ink to the line and place the paper in a beaker of solvent (e.g. water)
3) make sure the ink isn't touching the solvent
4) place a lid on top to stop the solvent evaporating
5) the solvent will seep up the paper, carrying the ink with it
6) each dye with move up at the different rate - so they separate
= each dye will spot in a different place
7) when the solvent has nearly reached the top - take the paper out the beaker to dry
What are two ways to separate soluble solids from solutions?
Evaporation and Crystallisation
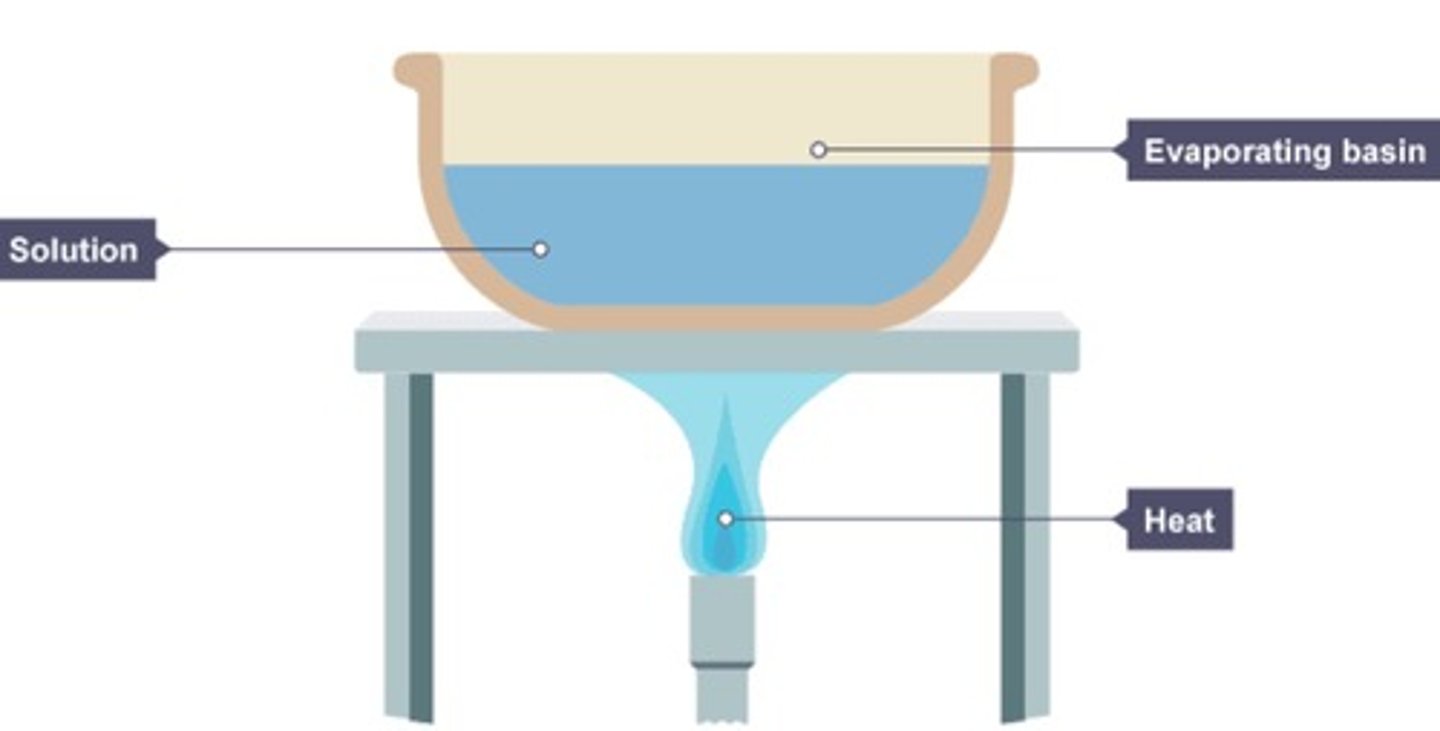
How would you separate soluble solids from a solution using evaporation?
1) Pour the solution into an evaporation dish
2) Slowly heat the solution which will cause the solvent to evaporate and the solution to get more concentrated. Eventually crystals will form
3) Keep heating the evaporating dish until all you have left are dry crystals
How would you separate soluble solids from a solution using crystallisation?
1) Pour the solution in an evaporating dish and gently heat the solution. Some of the solvent will evaporate and the solution will get more concentrated
2) Once some of the solvent has evaporated, or when you see crystals start to form remove the dish from heat and leave it to cool
3) The salt should start to form crystals as it becomes insoluble in the cold, highly concentrated solution
4) Filter the crystals out of the solution, and leave them in a warm place to dry.
What is simple distillation?
Separating out a liquid from a solution
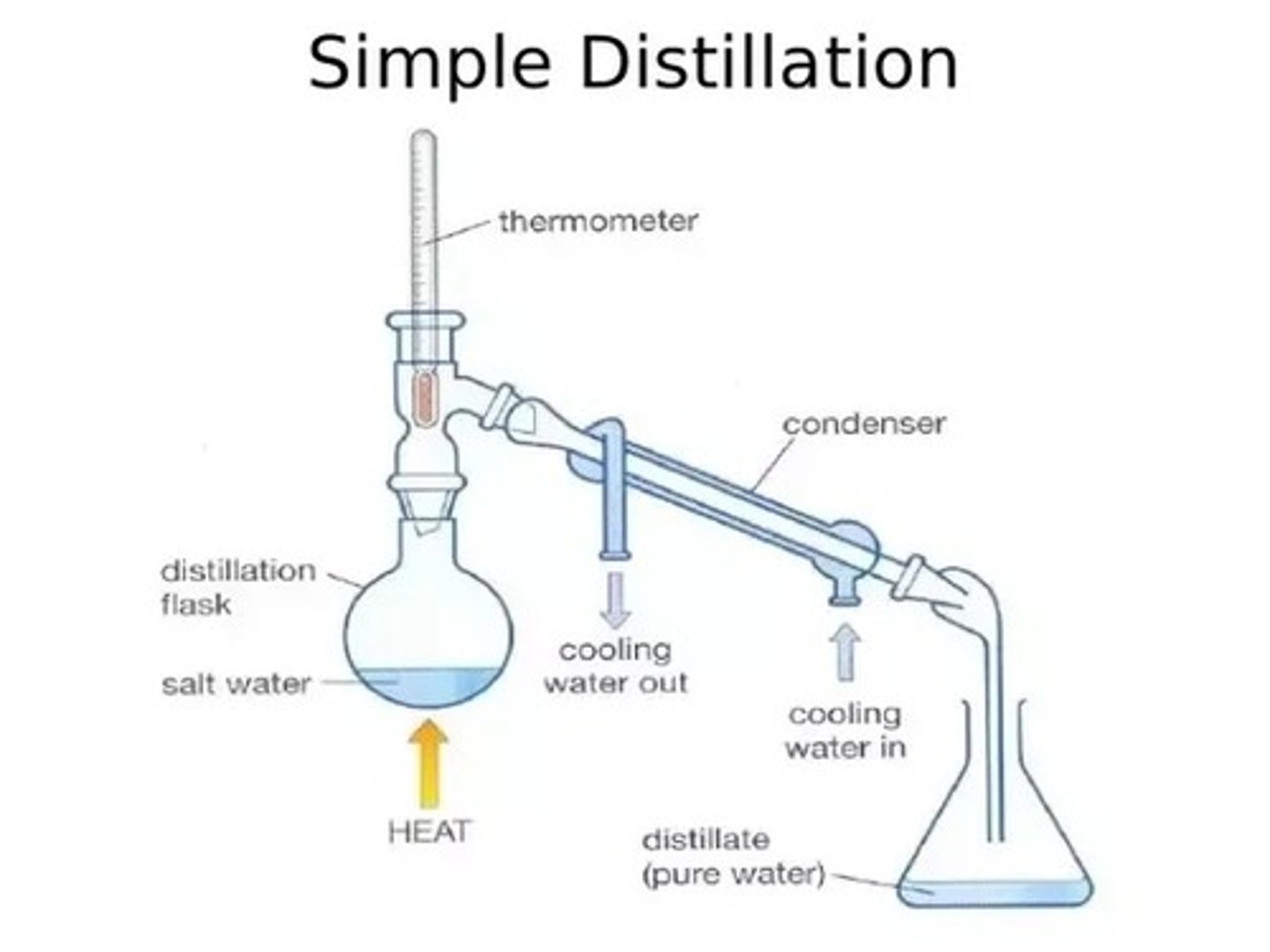
How is simple distillation used to separate out solutions?
1)The solution is heated and the part of the solution that has the lowest boiling point evaporates first
2)The vapour is then cooled, condenes (turns back into a liquid) and is collected
3)The rest of the solution is left behind in the flask
What is the problem with simple distillation?
You can only use it to separate things with very different boiling points
(need fractional distillation to separate a mixture of liquids with similar boiling points)
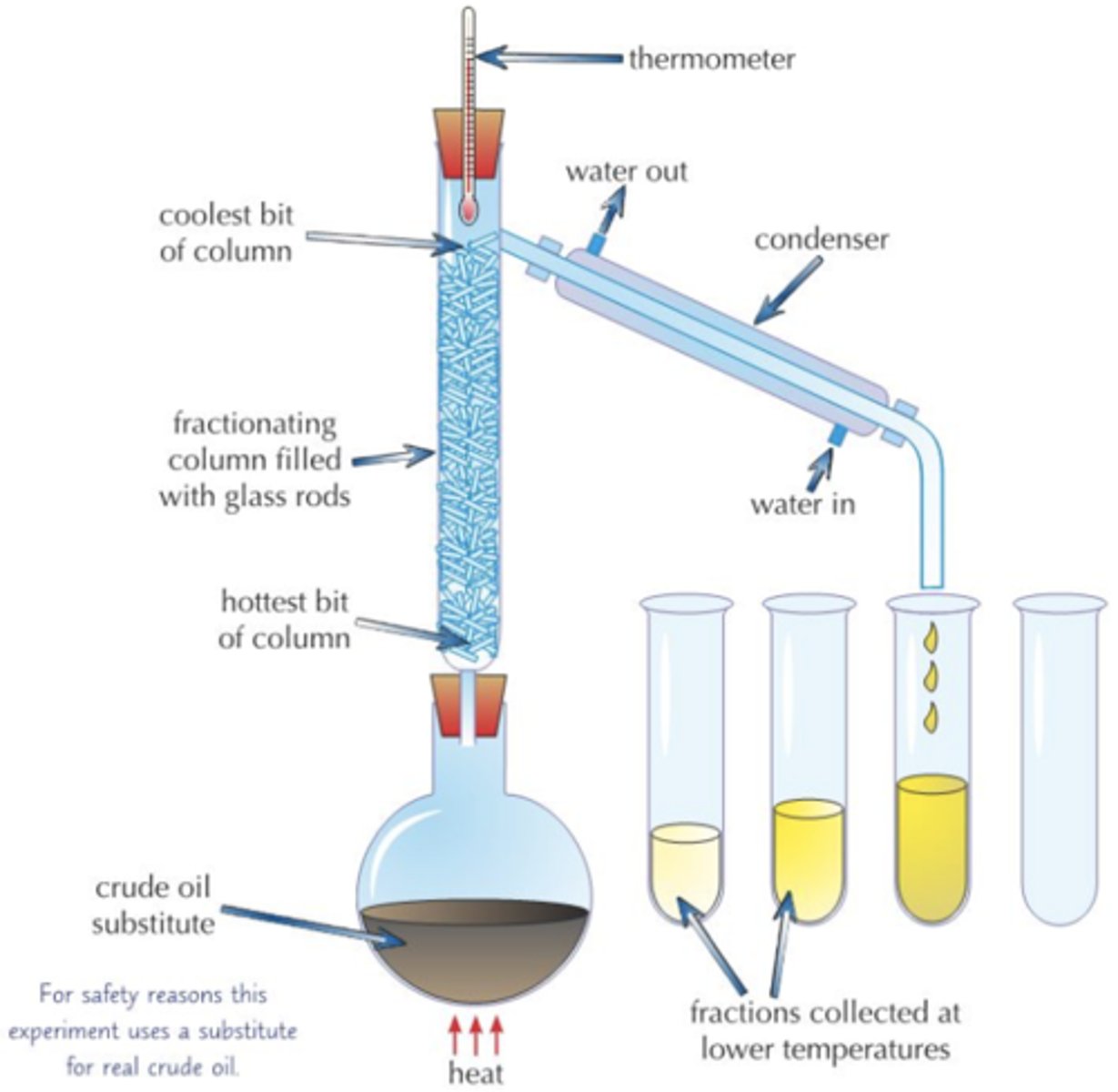
How would you use fractional distillation to separate a mixture of liquids?
1) Put your mixture in a flask and stick a fractionating column on top, then you heat it
2) The different liquids will all have different boiling points - so they will evaporate at different temperatures
3) The liquid with the lowest boiling point evaporates first. When the temperature on the thermometer matches the boiling point of this liquid, it will reach the top of the column
4)
What did john Dalton describe atoms as?
Solid spheres
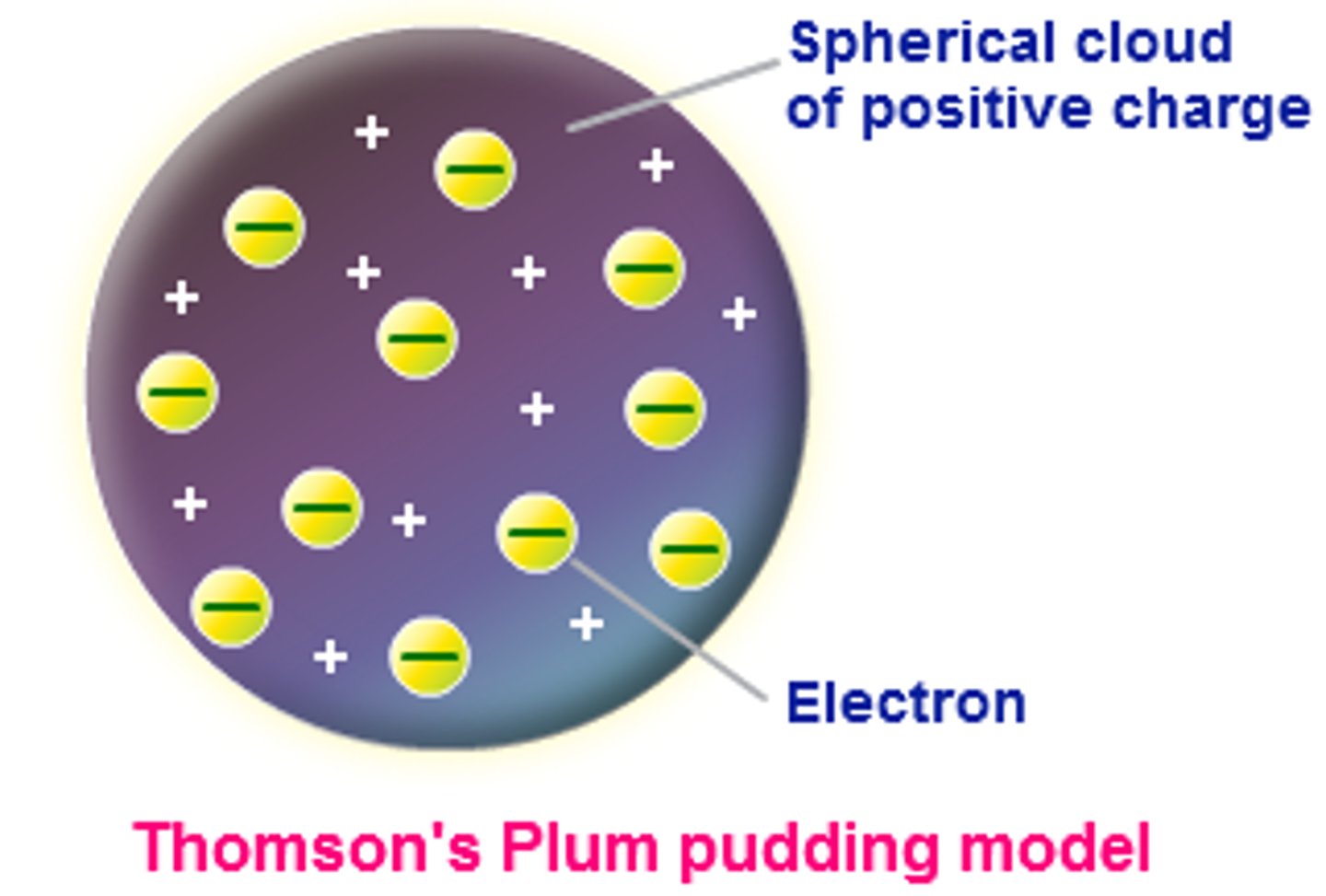
What was the name of JJ Thomson's atomic model?
Plum pudding model
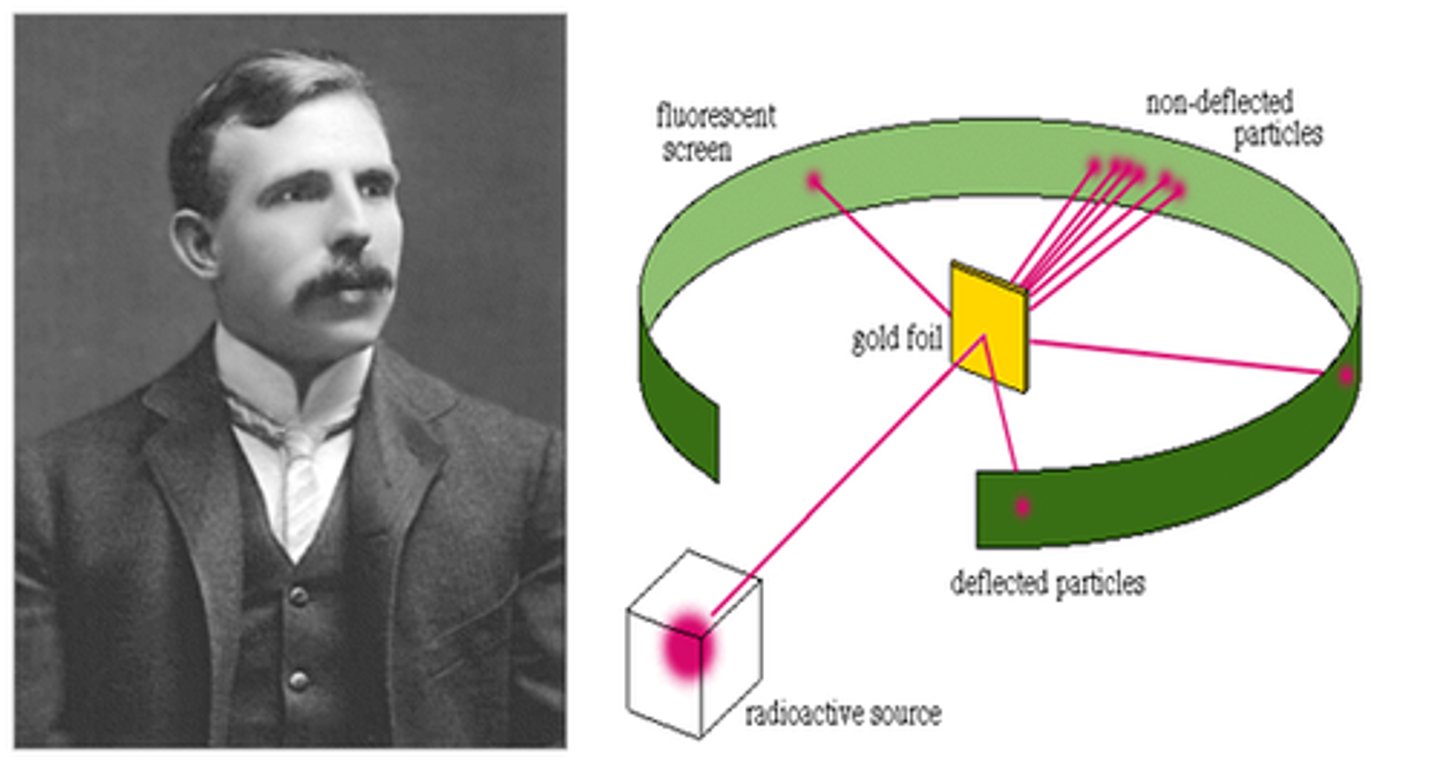
How did Rutherford discover the nucleus?
-in his gold foil experiment he sent alpha particles to fly through a sheet of gold foil
-some would be deflected back because they were approached the nucleus
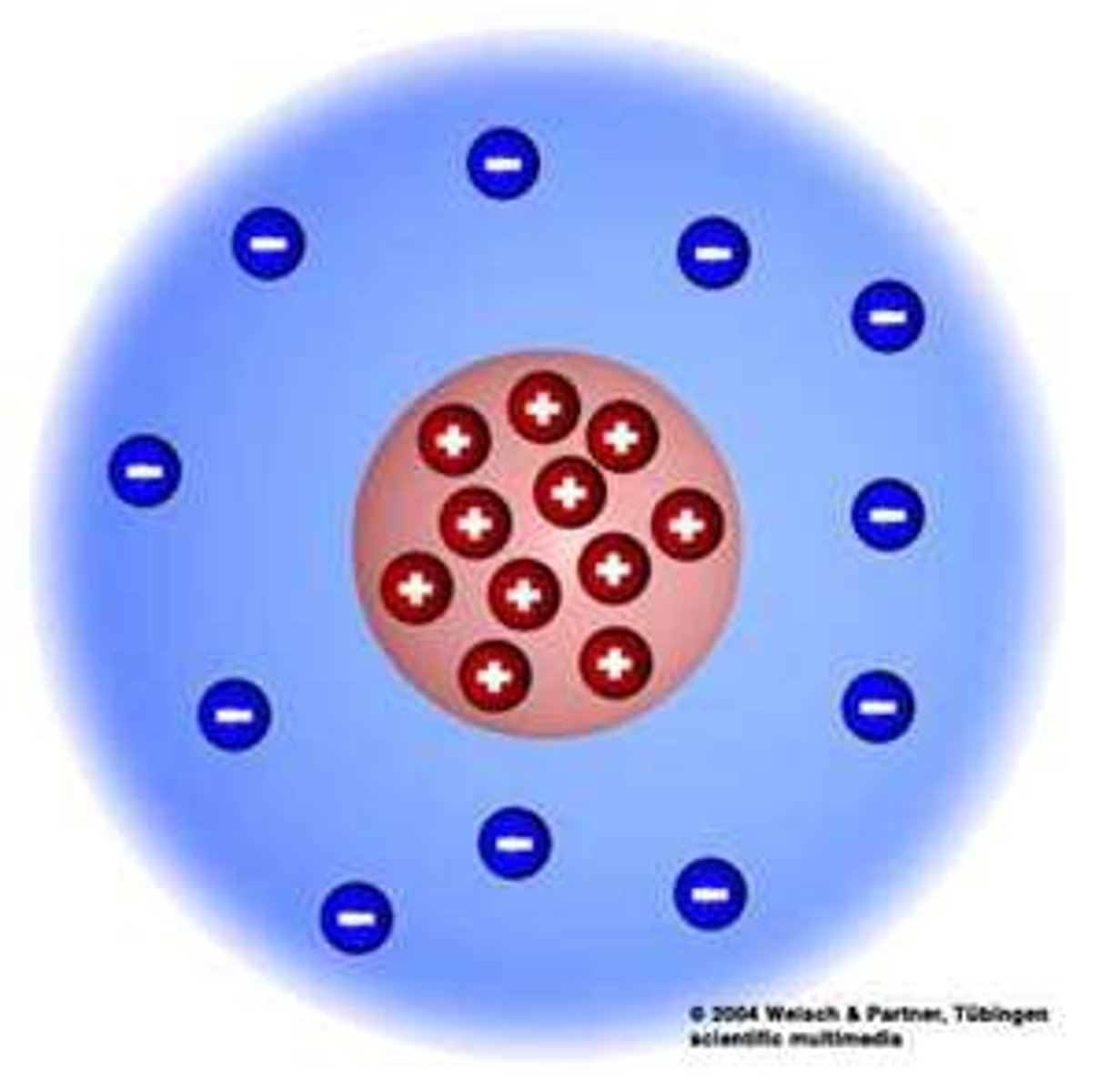
How did Rutherford show that the Plum Pudding Model was wrong?
- From the plum pudding model, they were expecting the particles to pass straight through and some to be slightly deflected, but more were deflected than usual
- Meaning the atom isn't a positive ball of charge and the positive charge is at the centre of the atom (the nucleus)
What did Bohr suggest about the planetary model? (Rutherford's model)
1) Electrons in a cloud around the nucleus of an atom will cause the atom to collaspe
2) Bohr proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells
What subatomic particles did J.J Thomson, Rutherford and James Chadwick discover?
1) J.J Thomson = electron
2) Rutherford = proton
3) Chadwick = neutron
In the early 1800's, how were elements arranged?
1) Physical and chemical properties
2) Atomic weight
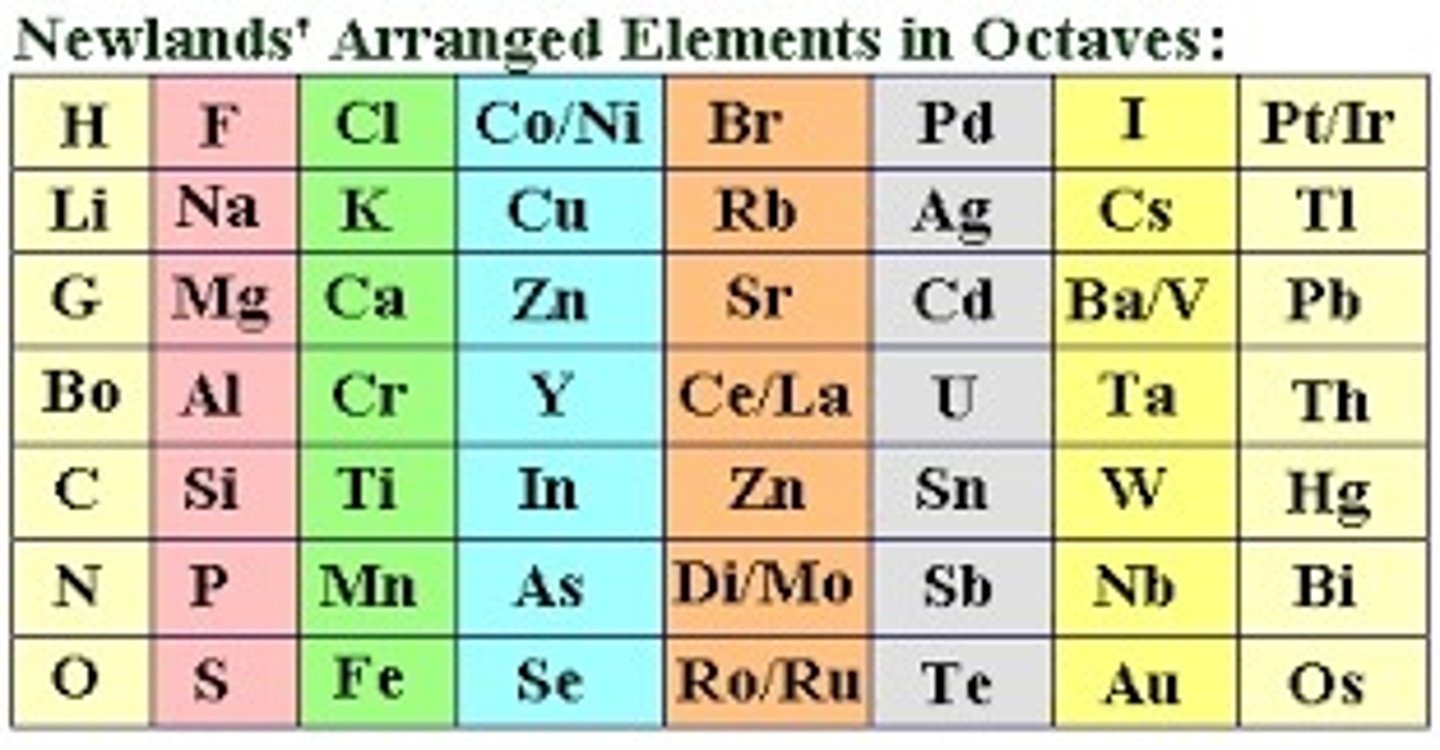
How did Mendeleev organize his periodic table?
1) Put elements in order of atomic mass and similar properties
2) Left gaps in his table indicating the undiscovery of new elements
What are the physical properties of metals?
1) Strong and malleable
2) Good at conducting heat/ electricity
3) High boiling/melting point
What are physical properties of non mentals?
1) Dull
2) Brittle
3) Bad at conducting heat/electricity
What are the special properties of transition metals?
1) Can have more than one positive ion
2) Transition metal ions are coloured
3) They make good catalysts
What are the trends of Group 1 elements as you go down the group?
1) Increased reactivity ( the outer electron is more easily lost)
2) Lower melting and boiling points
3) Higher relative atomic mass
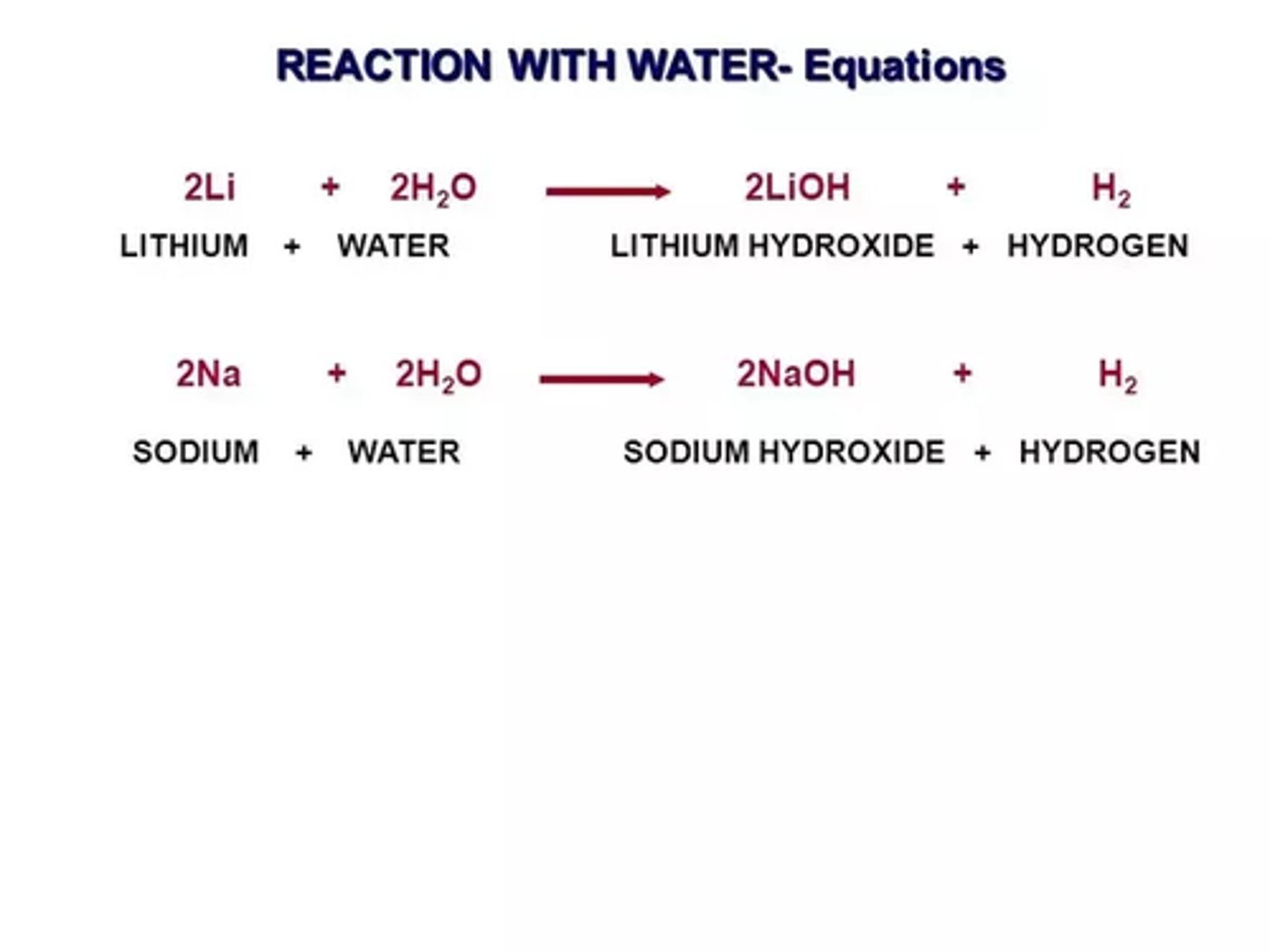
What does alkali metals and water produce?
Metal hydroxides and hydrogen gas
What happens when alkali metals react with chlorine gas?
The group 1 metals react vigorously to form white metal chloride salts.
What does alkali metals and oxygen produce?
Metal oxide
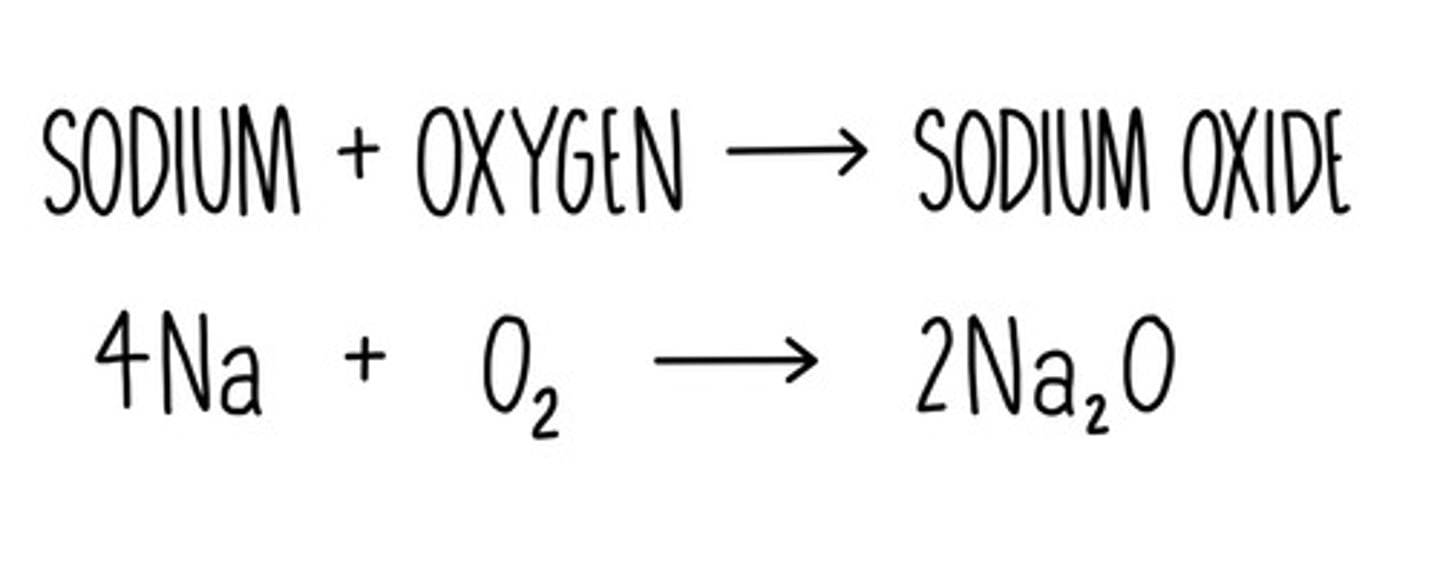
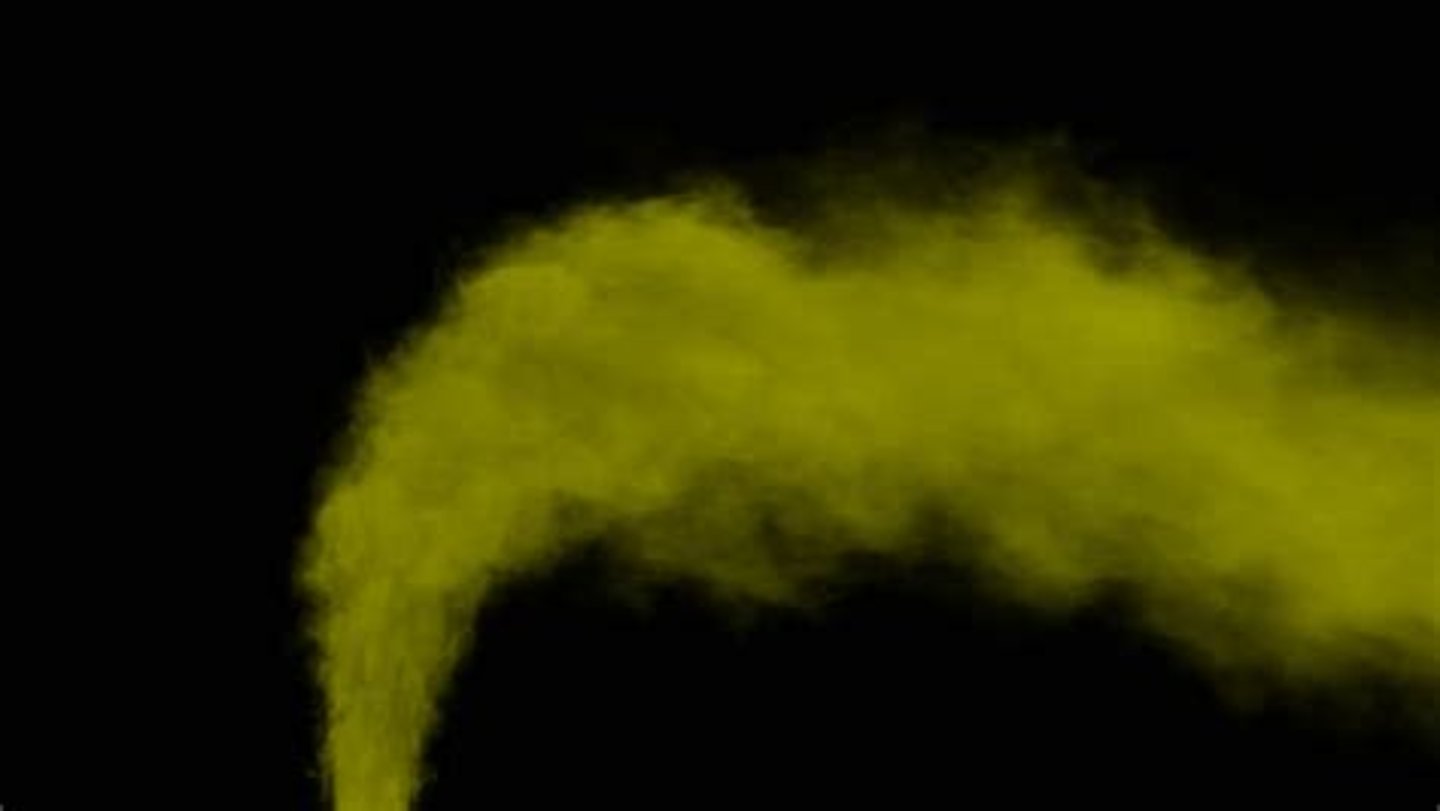
What is fluorine gas?
A very reactive poisonous yellow gas

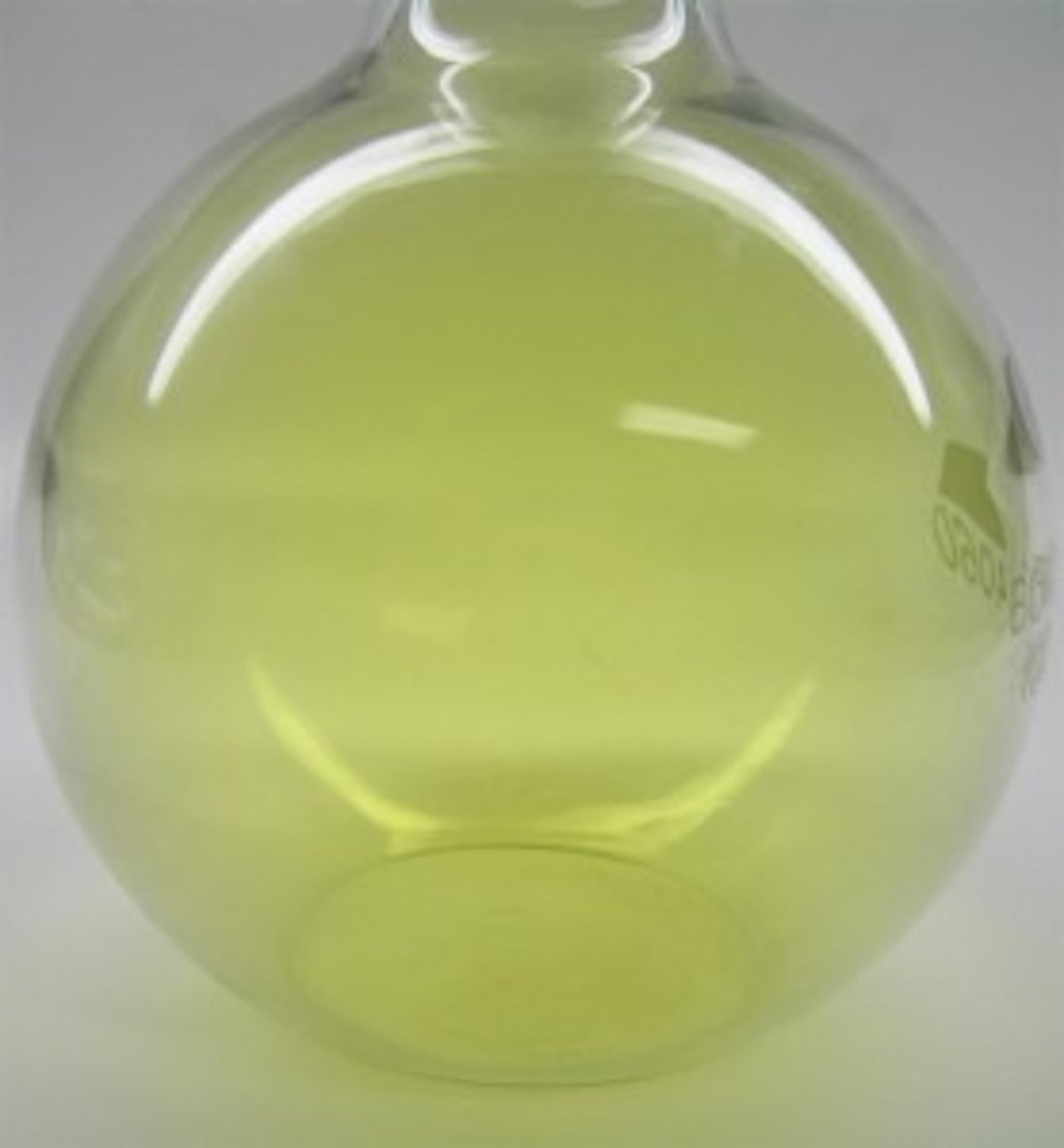
What is chlorine gas?
A fairly reactive poisonous dense green gas

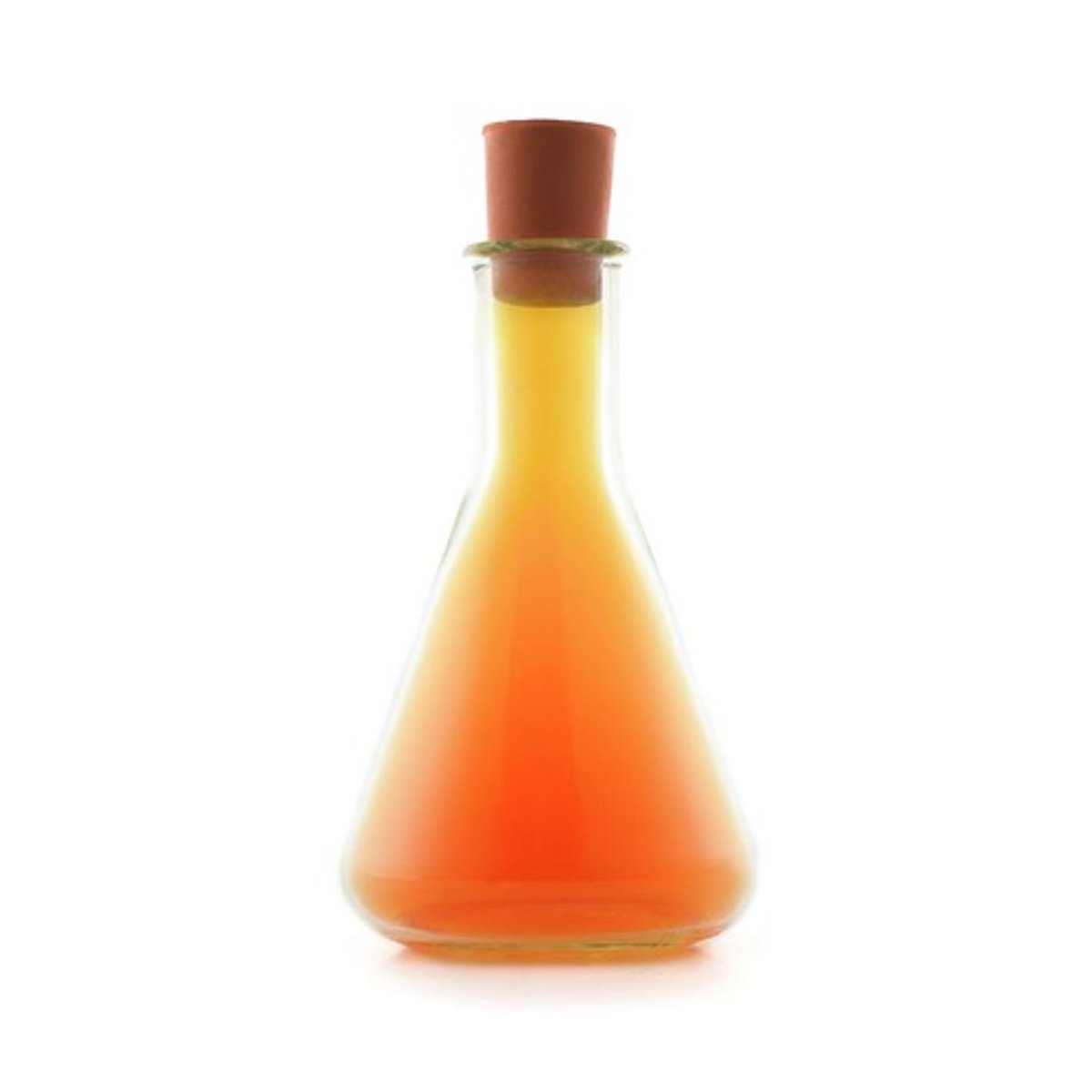
What is bromine gas?
A dense poisonous, red-brown volatile liquid

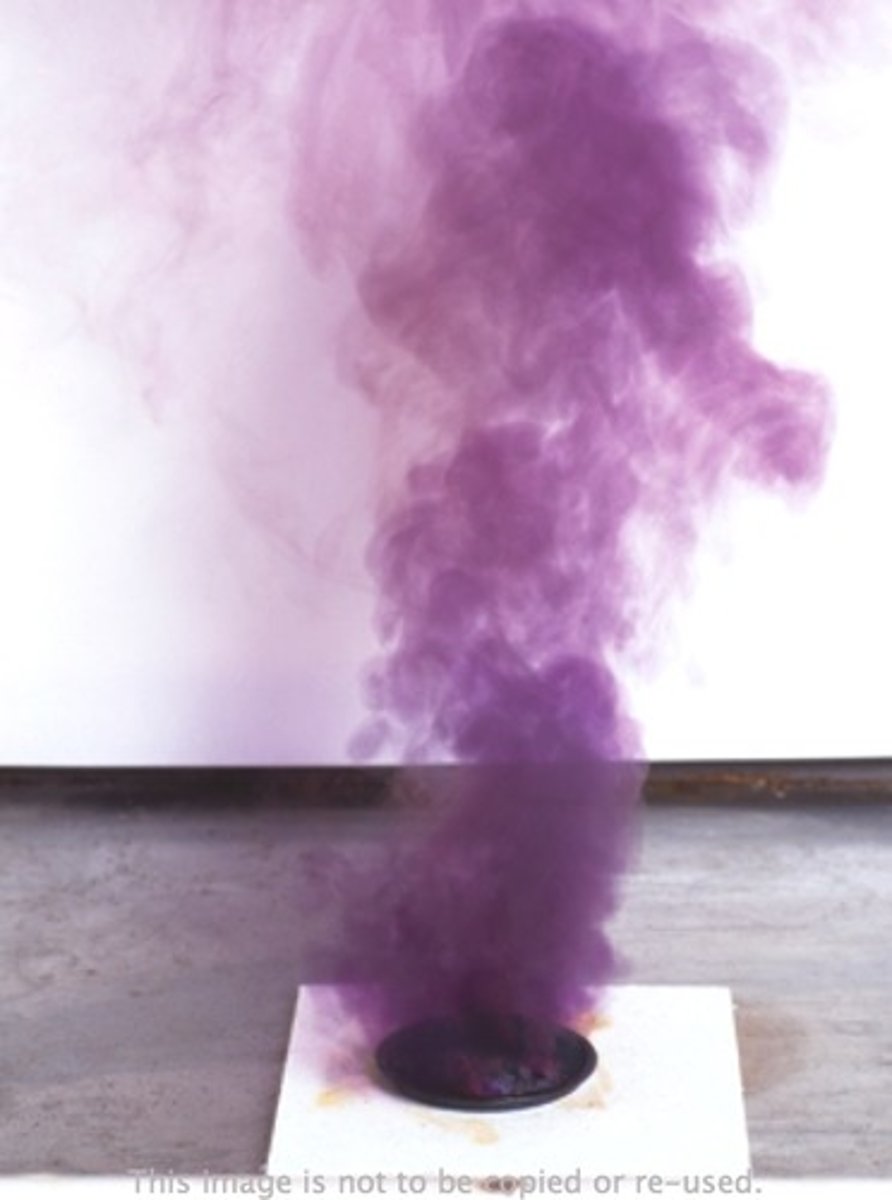
What is iodine gas?
A dark grey crystalline solid or purple vapour

In group 7, what happens if you go down the group?
1) Become less reactive (harder to gain an extra electron)
2) Have higher melting and boiling point
3) Higher relative atomic masses
What are the properties of noble gases (Group 0)?
The boiling point of the noble gases increase as you move down the group with increasing relative atomic mass
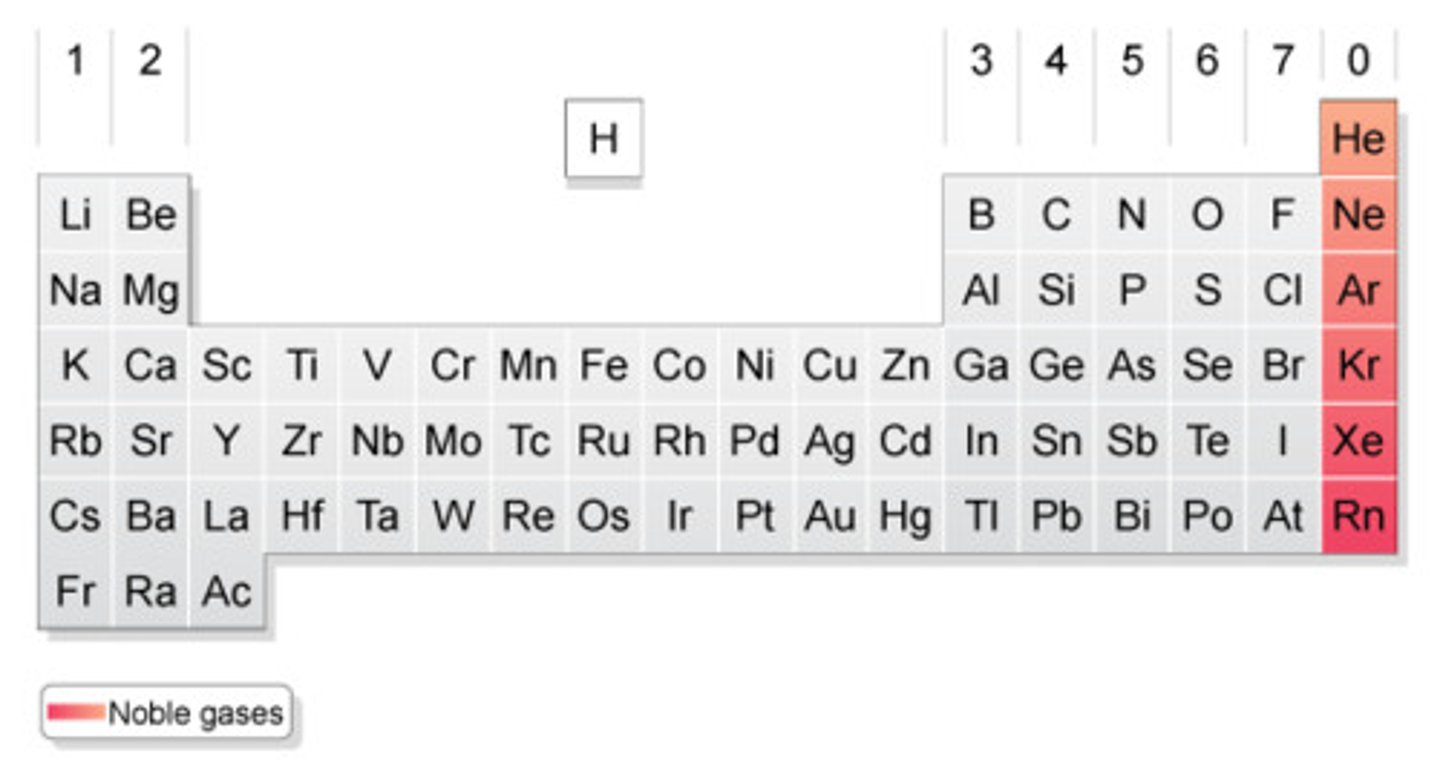
Why does the boiling point increase as you move down the group?
Increases the number of electrons in each atom leading to greater intermolecular forces between them which need to be overcome
Neon is a gas at 25°C. Predict what state helium is at this temperature.
Since helium has a lower boiling point than neon as it is further up the group, helium must also be at 25°C
Radon and krypton have boiling points of -62°C and -153°C respectively. Predict the boiling point of xenon.
Xenon comes in between radon and krypton in the group so you can predict that is boiling point would be halfway between their boiling points.
(-153) + (-62) = -215
-215 divided by 2 = -107.5 ~ -108°C